Pork tapeworm larvae that enter the body provoke a disease of the central nervous system - neurocysticercosis. Pathology of the central nervous system occurs due to cysticercosis of the brain - damage by tapeworm larvae. They enter the body mainly through food and manifest their existence in the human body only after a long time.
Neurocysticercosis is a dangerous helminthic infection with pork tapeworm.
What is neurocysticercosis - types
Neurocysticercosis is a helminth infection caused by pork tapeworm larvae that enter the gastrointestinal tract and from there spread throughout the body.
Gastric juice releases the larvae by dissolving the capsule shell. Along with the bloodstream, the tapeworm in 70% of cases enters the brain, thereby affecting the nervous system of adults or children. The first symptoms of central nervous system damage are epileptic seizures.
Pork tapeworm infestations, depending on the location of the parasites, are divided into six main types , which have different symptoms:
- Parenchymal - cysts are located deep in the brain tissue.
- Subarachnoid - characterized by not clearly expressed meningeal symptoms.
- Intraventricular – increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
- Spinal - a rare form, caused by an effect on the cervical and thoracic segments of the spinal cord.
- Asymptomatic - in 20% of cases, the disease is detected at autopsy, as a result of death from another disease.
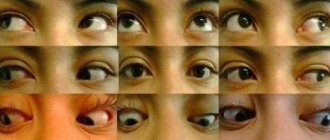
- Ocular neurocysticercosis is neurocysticercosis affecting the eyes. The malignant course of the disease cannot be treated with medication and requires surgical intervention.
Treatment directly depends on the degree of damage to the body and the location of the helminths.
Causes of neurocysticercosis
The most common cause of all helminth infestations is failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Since the causative agent of neurocysticercosis in humans is a pork/bovine tapeworm (tapeworm), the original host of which is a pig, infection is possible from this type of meat.
The infection is transmitted in case of insufficient heat treatment of pork when eating it. An adult with larvae can enter the stomach; with symptoms of vomiting or regurgitation, autoinoculation occurs (self-infection).
Preventive measures and prognosis
The main rule for preventing such a disease is strict adherence to personal hygiene and sanitary standards. Food products must undergo heat treatment before consumption. Before sale, meat undergoes the necessary sanitary control; before consumption, it must be completely boiled or fried. You should not eat unwashed fruits and vegetables; after visiting the street, you must wash your hands with soap.
Neurocysticercosis is a very dangerous disease that has asymptomatic development and a latent course for many years. Therefore, it is impossible to make an accurate prognosis of the disease. It depends on factors such as the time of diagnosis, the degree and extent of infection. One of the most severe consequences is blockage of the 4th ventricle of the brain, which inevitably leads to hydrocephalus. If medical intervention occurs late, death is possible.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of the pathology is expressed mainly in the form of symptoms of irritation. Symptoms of loss of neuronal function appear to a minor extent:
- shallow paresis (difficulty in motor activity or partial paralysis);
- sensitivity disorders;
- minor speech impairments.
The degree of loss of neuronal function is determined by the number of affected nerve cells; this pathological process is reversible.
The process of functional inhibition is a protective reaction of the body, which thus protects reversibly damaged neurons from complete death.
Treatment in this case is aimed at restoring the function of neurons and eliminating the inhibition process. It should be noted that symptoms of loss of neuronal function appear when the pathological process reaches significant development.
Neurocysticercosis is characterized by mental disorders. At the initial stages of the disease, such disorders manifest themselves as neurotic conditions. In case of severe infestation, depressive states, hallucinations, and delusions develop.
In some cases, cerebral edema develops, which manifests itself:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness.
If helminths are localized in the ventricular cavity, the following symptoms appear:
- attacks of severe headache;
- forced head position;
- breathing problems;
- heart failure;
- confusion.
The reason for this symptomatology is irritation of the bottom of the fourth ventricle.
If the parasites are localized in the lateral ventricles, the symptoms of neurocysticercosis resemble those of a tumor of the frontal part of the brain.
Neurocysticercosis of the base of the brain is characterized by the following clinical picture - signs of basal meningitis, headache attacks, vomiting, optic nerve disorders and shallow paralysis.
Neurocysticercosis has a long course with periodic improvement and exacerbations. There is no quick and spontaneous recovery.
Symptoms and manifestations of cysticercosis
- the appearance of asymptomatic forms of muscles and nodules in tissues;
- manifestation of frequent headaches and increased blood pressure;
- gagging, nausea;
- seizures;
- the occurrence of hallucinations;
- visual impairment, risk of blindness;
- increased eye pressure;
- heart pain;
- allergy;
- the occurrence of diarrhea, flatulence and painful abdominal cramps.
When the disease affects the brain, patients often complain of increased blood pressure and epileptiform seizures. The affected ventricular system may have acute symptoms consisting of intense headaches that worsen with the slightest movement. In addition, the pain is complemented by vomiting.
Cysticercosis of the eye often leads to the patient being unable to adequately perceive and evaluate objects, and the eyes constantly watering. Cysticercosis of the eye can affect either a separate area or the entire organ of vision. As patients note, they feel not only deterioration in vision, but also constant pain with a feeling of pressure on the eyes. Worms primarily occupy the vitreous body and the anterior chamber of the eye. Cysticercosis of the eye often results in blindness.
Any form of the disease does not have favorable stages and is very often characterized by mental disorders. Neurocysticercosis and its symptoms are a severe and difficult to tolerate disease, the most advanced form of which is cysticercosis of the brain.
Classification
Neurocysticercosis is classified according to the method of infection:
- endogenous – infection occurs through direct contact with an infected person, most often during vomiting;
- exogenous – the parasite enters the body as a result of poor hygiene.
The disease is also classified according to the location of the helminths:
- ventricular cysticercosis;
- cysticercosis of the base of the brain;
- cysticercosis of the cerebral hemispheres.
In case of massive infection, when the larvae are localized in several parts of the brain, mixed neurocysticercosis is diagnosed. The most dangerous is the mixed form of the disease, in which case the symptoms manifest themselves acutely, are severe and the prognosis is unfavorable. The most typical symptoms of the pathology are epileptic seizures, hallucinations, and mental disorders.
Definition of cysticercosis
Cysticercosis of the brain is considered a common but serious disease that quickly affects vital organs and is difficult to treat.
The disease often causes many pathologies of a neurological nature, and is sometimes fatal. Cysticercosis in humans is caused by cysticerci and finns, which choose the human body as an intermediate host. Pathogen larvae can have different shapes, changing from oval to spindle-shaped. The cysticercus looks like an oval formation with a head on which there are 4 suckers and a two-row crown of hooks. The outer shell of the larva gradually becomes denser, filling with salt deposits, which still allows the larva to remain viable.
Causes and routes of infection
As a rule, parasite eggs enter the stomach with food intake, through the fecal-oral route, or self-infection can occur (reverse peristalsis occurs). Migrating throughout the body, the larvae that emerge from eggs in the stomach form cysts in the soft tissues. In the brain, the larvae are localized in the soft membranes, superficial parts of the cortex and ventricles of the brain. If the parasite dies, its body remains in the brain and the development of the inflammatory process continues.
Causes of the disease
The causative agent of neurocysticercosis in humans is the pork tapeworm (tapeworm), or more precisely, its larval stage.
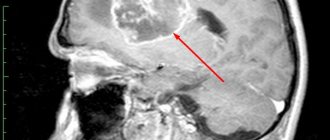
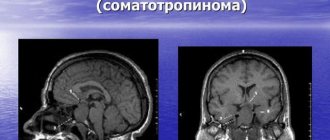
For a given worm, a person can be both an intermediate and a final host. Infection occurs by the entry of parasite eggs into the stomach, where the larvae are released and migrate through the circulatory system. MRI image of a brain affected by a parasite
The development of neurocysticercosis itself occurs when the larvae penetrate the brain, where they encapsulate, forming cysticerci. They can remain in this form for up to 30 years. Often hundreds and sometimes thousands of helminths are present in the brain at the same time. But there are also isolated specimens. The photo shows the results of an MRI of an infected human brain, where the white dots are cysticerci of parasites. They are located in the soft membranes of the brain - parenchyma (the size of these cysts is up to 2 cm), on the surface of the cortex, in the basal cisterns, and freely float in the cavities of the ventricles (the size of cysts is more than 5 cm). After the death of the worm, inflammatory processes persist at the site of its localization in the subarachnoid space, eventually becoming chronic.
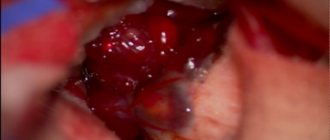
Pork tapeworm, a many times enlarged photo of which is presented here, has a toxic effect on brain tissue and membranes. This causes swelling of the brain. In addition, there is an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid secretion, which leads to hydrocephalus. All this is accompanied by impaired circulation, attacks of acute intracranial hypertension and reactive leptomeningitis.
Diagnosis of neurocysticercosis
Symptoms of neurocysticercosis in humans are characteristic of many diseases, which greatly complicates the correct diagnosis.
Due to the fact that tapeworms are the larval form of parasites, the disease is characterized by an increase in eosinophils in the blood .
A serological study is also carried out ; in adults and children, the readings of protein and lymphocytes are elevated, and glucose readings are decreased.
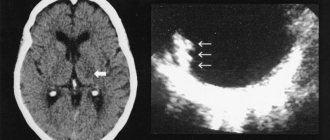
The doctor can visualize the patient’s neurological abnormalities and prescribe an X-ray of the skull. The x-ray image clearly shows the location of the calcified parasites.
Computed tomography reveals calcifications, nodules, ring-shaped edematous areas and cysts. If ocular neurocysticercosis is suspected, a fundus examination is performed.
Therapy
Treatment of neurocysticercosis involves the use of a number of measures and medications.
Doctors may prescribe:
- Medicines.
- Anthelmintic medications.
- Application of ventricular shunts.
- Removal of lesions through surgery (spinal neurocysticercosis and ocular neurocysticercosis).
It all depends on the form of the disease.
If the invasion is asymptomatic, the use of drugs, as a rule, is not the best method for therapy, since, by dying and disintegrating, cysticerci can only worsen the condition of the infected patient.
In the fight against the disease caused by the larval form of pork tapeworm, the following groups of medications are used:
- anthelmintics (Praziquantel, Cestox, Azinox, Albendazole, Sanoxal, Nemozol);
- steroids (Dexamethasone);
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen)
- anticonvulsants (Depakine).
However, in each specific case, therapy is selected individually by the doctor. Experts take into account a number of factors:
- Locations of lesions.
- Viability of parasites.
- Number of larvae.
- Patient's immune resistance.
The main thing in therapy is literacy and timeliness of its implementation. You cannot self-medicate or use folk remedies with such a serious diagnosis. All appointments must be made by an experienced specialist. He completely and completely controls the course of treatment. Otherwise, an infected person may harm himself and worsen an already difficult situation.
Parenchymal neurocysticercosis
This form of the disease can be detected at different stages of its development:
- When vesicular cysts form, this is the initial stage.
- During the formation of colloid cysts, this is the stage when the immune system begins to actively fight cysticerci, the cyst is filled with turbid liquid, its walls become denser, and parasitic activity decreases.
- With the formation of granulomas and calcifications, this is the stage at which the cyst turns into a dense calcified nodule.
To eliminate vesicular cysts, different drugs are used, depending on their number:
- One tumor – use of Prizaquantel for three days.
- From two to a hundred cysts - use Albendazole and hormones for seven days if adverse reactions occur.
- Over 100 tumors - use Albendazole for a week in large dosages and additionally hormonal agents.
Colloid cysts can be eliminated using the following medications:
- one cyst – no need for therapy;
- from two to one hundred tumors - Albendazone and steroids are prescribed;
- more than 100 tumors - no antiparasitic drugs are required, only hormonal agents and diuretics, for example, Mannitol.
Elimination of granulomas and calcifications is not required, and only occasionally steroids may be prescribed.
Extraparenchymal
Damage to the subarachnoid space requires the following therapeutic measures:
- If cystic (subarachnoid) cysts are detected, a course of Albendazole lasting 1 month, as well as large dosages of steroids, is prescribed.
- The development of angiitis or arachnoiditis requires the use of hormonal drugs in large doses, but antihelminthic drugs are not needed.
- Hydrocephalus is eliminated by applying a ventricular shunt. And there is no need for drug treatment.
Neurocysticercosis symptoms
In humans, manifestations of neurocysticercosis appear at least 1 year after infection. In this case, the symptoms pass in waves or worsen or decrease.
The ocular form of the infection involves blurred vision, chronic conjunctivitis, and confusion of the eyelid and eyeball.
Adults often suffer from epileptic seizures and neurological disorders. In some cases, treatment may not be appropriate.
Main symptoms:
- dizziness;
- violation of movement coordination;
- blurred vision, possible retinal detachment;
- epileptic seizures;
- syndrome of increased intracranial pressure;
- partial loss of sensation in the limbs;
- involuntary movements of the fingers;
- linguistic deviations in speech and many others.
Neurocysticercosis in a child symptoms
Children have similar symptoms to neurocysticercosis. Drug treatment is not always effective, and in some cases surgery is required.
In 17% of children, intraventricular single cysts are found. Other symptoms of neurocysticercosis completely coincide with the course of infection in an adult.
distinctive is the speed of development of the disease; in children the process occurs faster. Due to the fact that the child’s body has an unformed immune system, parasites affect it more intensely.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Therapy for this type of helminthic disease is carried out in two directions - medication and surgery. The choice of method will depend on the form of the disease.
Drug treatment of neurocysticercosis involves the use of antiparasitic drugs, such as:
- Azinox;
- Cestox;
- Nemozol;
- Paraziquantel;
- Albendazole;
- Sanoxal.
The action of these drugs is aimed at destroying parasites. After the helminths die, decay products are formed, and toxic substances begin to enter the bloodstream, which poison the body.
Article on the topic: Ointment for fungus between toes
As a result, the patient’s condition worsens, severe weakness, high fever, nausea appear, various allergies and inflammations occur, convulsive seizures intensify, and in some cases, cerebral edema may develop.
In order to protect a person from these dangerous complications, the following drugs are prescribed in combination with antiparasitic medications:
- hormones - Dexamethasone;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen, Diclofenac;
- anticonvulsants - Depakine.
Very important! Self-medication for this type of helminthic infestation is strictly prohibited! The drugs should be selected by a parasitologist or infectious disease specialist. The dosage and duration of the therapeutic course are calculated individually for each particular case.
Surgical intervention is required when the disease has a malignant course and in the ocular form of neurocysticercosis.
The malignant course of the disease is accompanied by a rapid increase in intracranial pressure, multiple cystic formations, and edema of the brain. To eliminate dropsy and lower pressure, bypass surgery of the ventricles of the brain is performed. The cysts are removed.
In case of damage to the organs of vision, surgical manipulations should be carried out before starting the use of medications, because when the cysts disintegrate, which occurs during the use of medications, inflammation will occur, and this can lead to irreversible loss of vision.
Diagnostic principles
Clinical manifestations of neurocysticercosis are nonspecific (that is, they can also occur in other diseases), so additional research methods are required to make a diagnosis.
Since cysticerci are the larval form of the helminth, the disease causes an increase in the content of eosinophils in the blood. Doctors know that the presence of parasitic worms in the body always provokes a similar reaction on the part of eosinophils.
When examining the cerebrospinal fluid, an increase in protein content, a decrease in glucose, an increase in the content of lymphocytes are detected, and eosinophils are found.
Serological diagnostic methods are of particular value. The complement fixation reaction is most often used; its informative value is 83-90% in the study of cerebrospinal fluid. Both false positive and false negative results are possible.
Neuroimaging methods can confirm the diagnosis of neurocysticercosis. X-rays of the skull reveal intracerebral calcified cysticerci, as well as signs of increased intracranial pressure. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reveals calcifications, granulomas, lesions with swelling in the form of a ring or a node when contrast is administered, multiple nodular lesions, and cysts. Of course, these changes do not have 100% specificity for neurocysticercosis, but taking into account clinical symptoms, eosinophilia, serological tests with similar changes on CT or MRI in most cases allows us to correctly establish the diagnosis.
If ocular cysticercosis is suspected, examination of the fundus may be informative. Sometimes you can even see free-floating cysticerci in the anterior chamber of the eye or in the vitreous humor.
How does a worm infection occur?
Any person who does not follow basic hygiene rules can contract pork tapeworm. Most often, infection occurs after an unsuccessful picnic in a dirty and unprepared place or after eating poorly cooked steak, chops, etc. Cysticercosis can await its future owner in unwashed vegetables, herbs, and fruits. This is especially true for meat, which must be processed not only with water, but also with temperature.
- carefully select meat for future cooking, giving preference only to proven products that have certain seals from the sanitary and epidemiological station;
- Thoroughly wash vegetables and herbs that may have become infected along with the fertilizer.
In addition, a person can become infected from a person. The process is called taeniasis (presence of tapeworm in the intestines). This can happen if a person becomes involved in the formation of worm eggs, that is, he turns out to be the primary carrier and instigator of the life of the parasite. With taeniasis, frequent vomiting is observed, with which the larvae enter the oral cavity and come out. The larvae, swallowed again, penetrate the gastrointestinal tract, provoking the onset of cysticercosis.
Cysticercosis of the brain, the symptoms of which are significant and unpleasant, is the most serious form of the disease. In addition to frequent headaches and attacks, patients constantly feel nausea, which cannot be eliminated by vomiting. Many of the symptoms occur due to disturbances in the distribution of cerebrospinal fluid, resulting in increased intracranial pressure.
A person may feel weakening and lethargy in the muscles, difficulty speaking, be in long-term depression, see hallucinations accompanied by mental seizures, and possible memory loss.
The worm can live in the brain for 15-18 years, which happens quite often. For parasitism, they choose the superficial layers of the cortex, ventricles, and meninges. Sometimes the number of parasites is more than one thousand, and the symptoms of the disease are similar to a brain tumor, meningitis, or epilepsy. If the larvae have infected the ventricles and spread throughout the brain, then it is extremely difficult to talk about a favorable prognosis.
Treatment of neurocysticercosis
Treatment of neurocysticercosis in children or adults should be based on the results of the examination: the location and number of parasites, the phase of ontogenesis and the individual characteristics of the body.
If taeniasis is detected, an infectious disease doctor prescribes anthelmintic therapy. The following drugs are used: Albendazole, Praziquantel, Niclosamide, etc.
The death of the parasite, through treatment, involves its decomposition in the body, resulting in the release of toxins that provoke severe allergic reactions and increased symptoms, such as seizures. To avoid adverse reactions, the patient is prescribed anticonvulsants and corticosteroid hormones.
There are cases of complications, the development of appendicitis, blockage of the bile duct or pancreas, which require surgery.
Treatment of neurocysticercosis with folk remedies
As a rule, treatment with folk remedies is intended to either improve the medicinal effect of drugs or eliminate remnants of worms. In any case, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Traditional medicine methods include the consumption of spicy and hot vegetables, such as garlic, hot peppers, onions, horseradish , etc.
Prevention
By following the simplest rules of hygiene, you can avoid contracting this deadly disease. You can only eat pork that has been thoroughly heat-treated, and you can only buy meat from trusted sellers with a sanitary and epidemiological inspection seal. Fruits, vegetables, and herbs must be washed before consumption. When in nature, you should not use water from standing reservoirs. Patients with taeniasis must be treated in a hospital, since it can infect both others (by the fecal-oral route) and themselves (by vomiting).
Drugs for neurocysticercosis
The form of treatment depends entirely on the location of the helminth infection and the quantitative presence of pork tapeworm in the human body. Antihelminthic therapy includes the following measures:
- Antiparasitic drugs: Praziquantel, dosage 50 mg/kg per day, divided into 3 doses. Course up to 30 days.
- Hormonal drugs: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone.
- Anti-inflammatory: Ibufen, Nimesil.
- Anticonvulsants: Napoton, Neurol, Benzonal.
The ocular or malignant form of the disease requires surgical intervention.
About the life cycle and development of the disease
Having learned what cysticercosis is, it is necessary to take a closer look at the life characteristics of the causative agents of the disease. The source of infection can be any sick person who defecates larval eggs. The adult larva of this tapeworm is distinguished by an extremely small head with a very long and jointed body. Thanks to suction cups and hooks, the worm connects to the human body.
Research shows that, in general, one parasite can lay about 600 million eggs, which are deposited in feces on the ground or plants. To develop, parasites need an intermediate host. Initially, eggs penetrate into the stomach of any animal, from which a larva then appears, penetrating into the blood of the selected victim.
The cause of the disease is the entry of parasite eggs into the gastrointestinal tract. The life cycle of the parasite is divided into 3 stages:
- egg;
- larva;
- adult.
Often the intermediate host is a pig or a person who has ingested a pork tapeworm egg. In the gastrointestinal tract, under the influence of gastric juice, the shell of the eggs disintegrates, and they, migrating through the intestinal wall, settle in the soft tissues of the muscles and the brain. Some larvae penetrate the brain and its membranes, causing symptoms of a central nervous system infection.
The adult helminth lives in the intestinal area without manifesting itself in any way. An infected person releases many parasite eggs into the environment along with feces. They can land on household items, clothing and food, which become sources of infection for healthy people. Self-infection also occurs very often.
After entering the brain, the embryos take the form of larvae. The larva looks like a capsule measuring 10 mm with liquid inside. Cysts can be either several pieces or several hundred. At the site of their localization, a focus of inflammation is formed, and subsequently a fibrous capsule, which clearly demarcates the brain tissue from the larva.
After a long time (more than a year), the parasites may die, and the remaining capsules undergo calcification, i.e., cysts with calcium deposits form. Thus, inflammation continues and becomes chronic.
In the brain, cysts are localized on the surface of the cerebral cortex, at the base of the brain, in the soft callosum, and inside the ventricles. In addition to causing inflammation, they also interfere with the natural circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, irritate and put pressure on brain tissue.
Pathogenesis
Neurocysticercosis, first of all, has a negative effect on the nervous system. As a result, the tissues and membranes surrounding the brain become inflamed. The disease is accompanied by:
- cerebral edema;
- hydrocephalus.
It is important! Parasites have a complex negative effect on the body, which consists of mechanical damage to tissues and intoxication with waste products.
Complications
Intracranial hypertension accompanying echinococcosis causes compression of the optic tract and leads to atrophy of the optic nerves with a decrease in visual acuity. The course of epilepsy in cerebral echinococcosis, resistant to anticonvulsant therapy, is often complicated by the development of status epilepticus.
Seizures that follow each other continuously are life-threatening because they provoke a malfunction of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. In the absence of timely diagnosis and adequate treatment of cerebral echinococcosis, an enlarging cyst causes displacement of brain structures. Increasing hypertension causes compression of the brain with dysfunction of vital nerve centers and subsequent death. A rare complication is rupture of the echinococcal bladder with contamination of surrounding tissues.
General symptoms of neurocysticercosis
Visible symptoms are minimal until the period when the larvae begin to die and cause inflammation and swelling. Symptoms similar to epileptiform seizures, mental disorders and focal neurological manifestations begin. If cysts affect the ventricles of the brain, obstructive hydrocephalus develops. When the cysts rupture, their contents enter the cerebrospinal fluid. Subacute eosinophilic meningitis develops. Half of the cases are fatal.
Why is cysticercosis of the brain dangerous?
Cysticercosis is a helminthic disease of the central nervous system from the group of cestodes, which occurs due to the spread of pork tapeworm larvae throughout the body. They can be found in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, spinal cord, bones, and internal organs.
But the most common sites of injury are the brain, eyes and muscles. Once in the brain, the parasite settles there for a long period of time - from 5 to 30 years, but the symptoms of cerebral cysticercosis may not appear for a long period of time.
Therapeutic measures
To prescribe effective treatment for neurocysticercosis, it is important not only to evaluate all the symptoms, but also to obtain accurate information about the number of larvae, their viability and location, as well as the resistance of the patient’s immune system to helminths. Treatment is selected individually for each clinical case and is carried out comprehensively:
- medications are prescribed to eliminate the symptoms of the disease;
- anthelmintic therapy is carried out;
- if necessary, lesions are removed surgically;
- ventricular shunts are applied.
Therapy for parenchymal neurocysticercosis
- For a single lesion, treatment is carried out with Albendazole at a dosage of 100 mg per kilogram of weight. The duration of therapy is three days.
- If the degree of infection is moderate, treatment is carried out with Praziquantel in a similar dosage. The duration of therapy is seven days. If side effects occur, steroids are prescribed as a concomitant drug.
- In case of severe infection (when the number of larvae is more than one hundred), Albendazole is prescribed at a dosage of 15 mg per kilogram of weight (this is the daily dosage). The course of therapy is a week. In parallel, treatment with steroids is carried out.
If colloid cysts are found, treatment is carried out as follows:
- if the affected areas are single, treatment with anthelmintic drugs is not carried out;
- for moderate infection, treatment is carried out with Albendazole for one week at a dosage of 15 mg per kilogram of weight;
- in case of severe infection, steroids are prescribed in significant dosages in combination with osmodiuretics.
Therapy for extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis
- If cystic cysts are detected, Albendazole is prescribed at a dosage of 15 mg per kilogram of weight, while the patient takes steroids in parallel. The course of therapy is one month.
- If a patient develops arachnoiditis or angiitis, the doctor prescribes steroids in large dosages. The course of therapy is long and supervised by a specialist. With this diagnosis, there is no need to prescribe special antiparasitic drugs.
- For hydrocephalus, no medications are prescribed; a ventricular shunt is applied.
Therapy for ventricular neurocysticercosis
- Ventricular cysts are removed surgically. As for anthelmintic drugs, they are prescribed at the discretion of the specialist.
- For ependymitis, anthelmintic medications are not prescribed. If the pathology is accompanied by hydrocephalus, a ventricular shunt is required and steroids are prescribed in parallel in high dosages.
Sources
- https://fitohome.ru/bolezni/parazity/nejrocisticerkoz-u-cheloveka-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
- https://parazit.expert/vidy/soliter/svinoj/cisticerkoz/nejrocisticerkoz
- https://InfoParazit.ru/ploskie-chervi/drugie/nejrotsistitserkoz.html
- https://otravleniehelp.ru/parazity/chto-takoe-neyrotsistitserkoz-simptomy-lechenie.html
- https://doctor-neurologist.ru/nejrocisticerkoz-prichiny-simptomy-principy-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya
[collapse]