Causes of paralysis
The decisive factors for the occurrence of a stroke in the right cerebral hemisphere may be the same reasons that are characteristic of a stroke in the left hemisphere.
The following factors can trigger a cerebral stroke:
- Drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Excess body weight;
- Increased blood cholesterol levels;
- Sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia);
- Taking combined oral contraceptives;
- Excessive physical and emotional overload;
- Chronic kidney and cardiovascular diseases.
In addition, no less significant factors in the development of right-sided cerebral catastrophe are congenital or acquired cerebral aneurysms, as well as traumatic brain injuries.
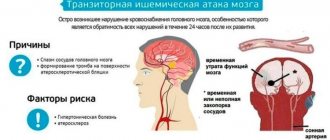
Stroke is the death of brain cells due to thrombosis or bleeding in the brain. The degree of paralysis after a stroke is determined by the location of the damage and the size of the damaged brain tissue. The speed of providing assistance to the victim immediately after a stroke is also important.
The nervous system, which is partially destroyed due to a stroke, is closely connected to the entire body and is responsible for the functioning of muscles, joints and organs. One hemisphere of the brain controls the motor functions of the opposite side of the body, and when cells in one hemisphere die, partial or complete paralysis can occur.
A stroke is damage to the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. These vessels can be both superficial and deep, and their rupture or blockage can lead to necrosis of certain areas of the brain. If small capillaries are damaged, a micro-stroke occurs; if large arteries are damaged, necrosis can be extensive, affecting almost all areas of the hemisphere.
To protect yourself and your loved ones from serious consequences due to late treatment at the clinic, remember the first signs of a stroke:
- General: disturbances of consciousness, headache and dizziness, nausea, visual and hearing disturbances, impaired coordination of movements.
- Symptoms of a stroke on the left side: partial or complete paralysis of the right side of the body and face, speech disorders (in a mild degree, a person expresses himself in fragmentary sentences-nouns, in a severe case, he cannot speak clearly, he mumbles), mental disorders, disturbances in the logic of thinking.
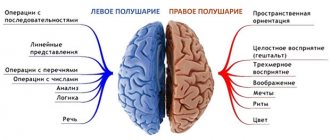
What functions is the left hemisphere of the brain responsible for?
In both men and women, the left hemisphere of the brain is responsible for speech abilities, vision, reading, and memory. This part of the brain also controls logic and analytical thinking. If a large number of cells die in this area, then the likelihood that a person will experience psycho-emotional dysfunction will increase. The patient's vision may sharply decline, memory will deteriorate, and he will suffer from attacks of aggression and stress.
Experts warn that recovering from such a cerebral hemorrhage is extremely difficult (especially in old age), and in order to somehow recover, you will need not only drug treatment, but also consultation with a neurologist.
Distinctive features
In a right-sided stroke, a loss of functional manifestations of the organs on the left side of the body occurs: there may be a lack of response to external stimuli in the left arm or leg, and there may be no hearing in the left ear. The most important thing that characterizes a right-sided ischemic stroke is a distortion of the patient’s psychophysical state, in which anagosia occurs (lack of reaction to what is happening around).
Damage to the right part of the brain has characteristics in old age: against the background of atherosclerotic encephalopathy, disturbances in cognitive processes appear - thinking slows down, memory and attention decrease, volitional apathy, and a decrease in intellectual and emotional manifestations are observed. An elderly person needs time to sense an impending disaster and call for help. The destruction of the volitional sphere is especially dangerous, since the recovery period requires precisely the efforts of the will in exercise therapy classes.
Types of paralysis
A characteristic complication of a stroke is paralysis - complete or partial. Paralysis of the right side is observed when the left hemisphere is damaged, and a noticeable loss of strength and decreased muscle tone are clearly expressed.
Paralysis on the right side has good prospects for the future, but there are a number of significant problems:
- Loss of control over your own body, hence complete helplessness, a feeling of dependence, and increased stress.
- Hardening of muscle mass, worsening joint immobility;
- Prolonged immobility. The result is the formation of bedsores, the formation of blood clots, and the development of pneumonia. Preventive measures - you need to turn the patient over after 3-4 hours, monitor the condition of the skin, and ventilate the room more often. Limitation of motor activity after a stroke with complete paralysis of only the right side has serious consequences for the patient and requires long-term persistent recovery. Here you will need the help of others so that rehabilitation measures are carried out systematically. It is important to remember the special danger of paralysis in this area: if the right side is paralyzed, the parts of the brain responsible for the functioning of the heart and lungs are damaged, therefore, paralysis can lead to the death of the patient at any time.
The degree of consequences of paralysis will always depend on the size of the organic lesion, as well as its location.
If the lesion is localized in the internal capsule of the left hemisphere side of the brain (the region of the posterior thigh), a person may develop in the acute period such a form of paralysis as right-sided hemiplegia (complete paralysis).
In this case, there will be no movement in the upper and lower limbs on the right side. This form is associated with loss of all types of sensitivity or hemihypestension and impaired visual function, manifested in the form of bilateral blindness in half the visual field - hemianopsia.
- Pronounced right-sided paralysis of the body.
- Speech dysfunction.
- Asthenic-depressive state.
From the moment the source of the stroke is removed from the capsule itself, there will be a decrease in motor disorders: some parts of the limbs will be affected by paresis. A similar condition predominates in a person’s right arm or leg. When the focus of the disease is located in the white matter, in this case, a violation of the distal parts of the lower and upper extremities occurs.

Paralysis can manifest itself in different ways, depending on the location of the lesion. Paralysis after a stroke is classified depending on the number of limbs affected, the level of motor neuron damage and other factors.
When a person's limbs fail, the paralysis is named based on how many limbs are affected.
- Monoplegia - one limb is affected on the right or left side.
- Paraplegia is damage to two limbs of the same type, for example, only the legs or only the arms.
- Triplegia – damage to three limbs.
- Tetraplegia – four limbs are affected.
Depending on the location of the brain damage, there are two types of paralysis:
- central (spastic) – occurs due to cell death or inflammation in the corticospinal tract, and motor functions are affected;
- peripheral (sluggish) - called in the case of disturbances in the peripheral motor neuron, and at the same time reflexes and sensitivity disappear in the affected parts of the body, muscle hypotonia may be observed.
The general classification of paralysis consists of only two classes:
- central paralysis, also divided into cerebral and spinal, is characterized by general or partial damage to a person’s motor functions;
- peripheral (flaccid, atrophic) paralysis is characterized by loss of sensitivity and reflexes in the affected parts of the body in combination with muscle hypotonia.
The massive degree of damage to motor motor neuron connections, brain pathways and brain tissue (superior capsule, white matter or cortex) leads to the development of paralysis of one of the limbs on the right side of the body or to the manifestation of progressive right-sided hemiparesis - damage to the arms and legs.
Types of stroke
Experts distinguish three types of stroke, which have different signs and symptoms. It is very important to recognize in time what type of lesion is observed in a person, since the set of resuscitation measures that are provided to the patient before he is transported to the hospital depends on this.
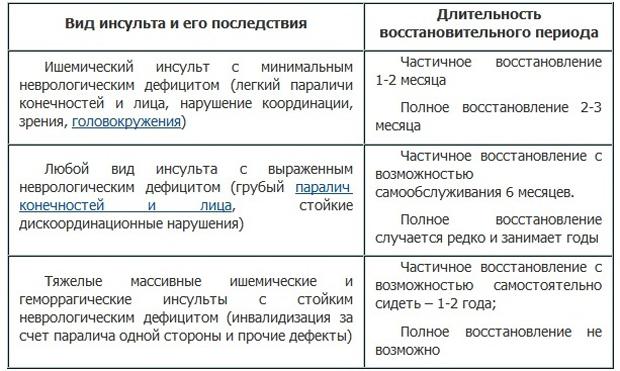
Types of stroke and its consequences
Hemorrhagic left-sided stroke
When a hemorrhagic lesion of the brain occurs, a blood vessel ruptures, resulting in blood entering the cerebral hemisphere. Symptoms for this type of pathology develop rapidly - from a few minutes to 1-2 hours. Despite the left-sided localization of the process, the patient shows signs of pathological effects on the right side. This is due to the fact that during apoplexy the nerve endings connecting both hemispheres are damaged. The prognosis for a left-sided hemorrhagic stroke can be favorable only if assistance is provided to the patient within 15-20 minutes after the onset of the attack. In other situations, the probability of disability will be more than 88%.
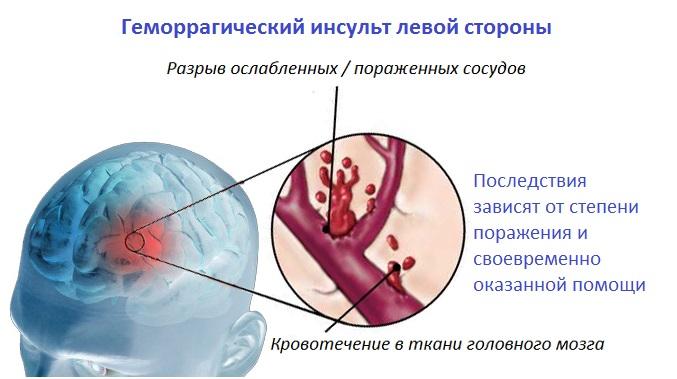
Hemorrhagic stroke of the left side
A hemorrhagic stroke on the left side can be distinguished by the following features:
- violation of orientation in space;
- instant memory loss (a person suddenly forgets the names of people around him, where he is, etc.);
- paralysis of the facial muscles on the left side, causing impaired facial expressions;
- sudden loss of self-care skills.
The patient may not feel his body, he cannot dress himself, he confuses the names of objects and the names of people. After an attack, such patients often suffer from depressive disorders, complete or partial amnesia, and behavioral changes.
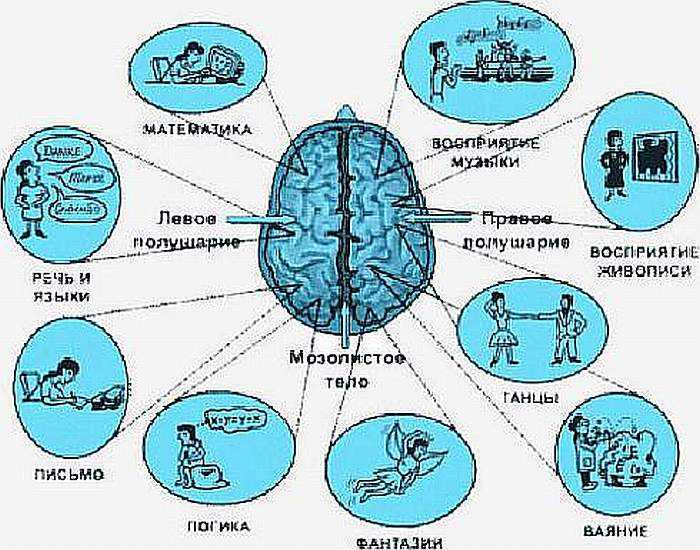
Functions of the left and right hemispheres of the brain
Important! With a left-sided lesion of the hemorrhagic type, there is no speech impairment, or the changes in the first hours are weakly expressed. This is a distinctive sign of pathology compared to right-sided localization.
Ischemic stroke of the left side
With cerebral ischemia, a blockage of a blood vessel occurs, causing slow blood flow and poor circulation. At this moment, brain cells experience acute hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and a lack of nutrients. After a few hours, the process of cell death begins. From the onset of the pathology to the attack, it usually takes from 3 to 6 hours. If the disease is diagnosed during this period, the prognosis for future life will be quite favorable, since the most important task of stroke therapy is the elimination of negative consequences and the prevention of possible complications.
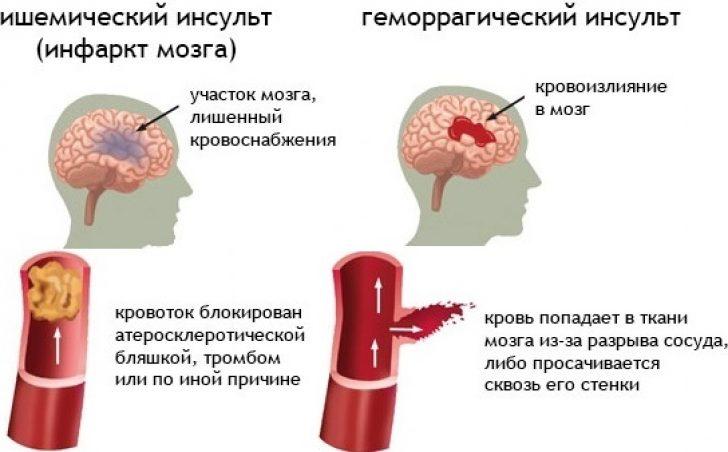
Hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke
An ischemic stroke always begins with an ischemic attack, which can last from 10-15 minutes to 2 hours (in rare cases, up to 10-12 hours). After this, the attack itself occurs, the duration of which in some situations can reach 24 hours.
Note! In very rare cases (less than 3-5%), the patient may experience a massive stroke in which both hemispheres are affected. There is almost no chance of a favorable prognosis for this clinical picture: more than 80% of patients die before doctors arrive or during surgery.
Children's cerebral infarction: features and prospects
Over the past few years, stroke has become significantly “younger” - the disease is increasingly occurring in young people. A teenager, and even a child, can get a cerebral infarction; the reason lies in individual health characteristics. The risk of stroke increases if you have congenital heart defects, inherited blood diseases, or problems with the endocrine system. The symptoms have a clear localization:
- Loss of sensation on the left side of the face;
- Trembling hands, legs, cramps;
- Problems with speaking – difficulty pronouncing certain sounds;
- Loss of coordination.
If a cerebral stroke is diagnosed promptly and accurately, treatment and subsequent rehabilitation lead to a full recovery and restoration of brain activity in full.
Signs
With a heart attack in the right hemisphere of the brain, the following are observed:
- complete loss of control over one’s actions (possible loss of consciousness);
- nausea, dizziness, severe right-sided headache;
- breathing problems - shortness of breath, respiratory rhythm disturbance;
- external signs: change in facial expression, immobility of the left side of the body. The hemorrhagic form of stroke has similar symptoms, but in a more pronounced form. It is possible to understand that what happened is an ischemic stroke on the right side by some specific features of the patient’s condition. If there is partial immobility or paralysis of the left side of the body, it means that the central part of the brain is affected on the right side. When the area of the parietal part of the right side of the brain is affected, many problems arise with the sense of touch, a violation of sensitive factors is noted: there is no sensation of ambient temperature, the person stops responding to pain, and loses the ability to navigate in space and time. Right-sided strokes are especially hard for left-handed people because their speech center is located on the right side.
Left hemisphere stroke has a rather characteristic, vivid clinical picture:
- Language and speech abnormalities are the first, most striking and obvious sign of this type of stroke: slurred pronunciation, failure to understand the speech of other people, incoherent expression of the patient in fragmentary phrases, words or a sequence of sounds, impaired articulation. It should be taken into account that for left-handers this symptomatology has a polar feature: speech impairment for them will be observed when the other, right hemisphere is damaged.
- There is a loss of verbal and speech memory, the recall of necessary words and speech patterns is impaired, and reading and writing become impossible.
- Paralysis of the right side of the body after a stroke: facial nerve, arms, legs. It is observed that it is impossible to perform active motor movements in the absence of atrophy of muscle fibers that are in a characteristic state of hypertonicity.
- Reflexive, spontaneous movements of paralyzed limbs are observed - synkinesis: extension for the leg and flexion for the arm.
- A psychological sign can be considered a person’s depression and isolation, since the disease significantly limits his communication with others.
The patient’s external appearance is quite typical: the right arm bent at the elbow and pressed to the body with the hand clenched into a fist, the leg bent at the knee joint with the foot turned inward, a drooping corner of the mouth and a sagging lower eyelid on the right side of the face.
Symptoms
A major stroke has the following symptoms:
General cerebral, nonspecific
Consciousness is impaired: the patient is stunned, his reaction is slow. Drowsiness, lethargy. Often the desire to sleep is suddenly replaced by excitement. Headache, nausea and vomiting. Dizziness. The patient is lost in space.
Focal, specific to the left hemisphere
- paralysis or flaccid paresis of the right side of the body
- impaired sensitivity on the right: the entire side may become numb;
- cramps on the right.
If the left hemisphere is dominant, speech is disrupted.
Signs and symptoms
The occurrence of right-sided paralysis is facilitated by a stroke suffered by a person, the lesion of which is determined in the left hemisphere region of the brain. It is characterized by partial or complete paralysis of half the human body, accompanied by impaired sensitivity and changes in muscle tone.
With this disease, a person is diagnosed with:
- Motor aphasia (there is a decrease in the active activity of the speech function).
- Violation of logical thinking.
- Depression.
- Vomiting reflex.
- Impaired consciousness.
- The appearance of an acute headache.
- Severe dizziness.
One of the most visible and understandable symptoms of paralysis is the loss of reflexes, lack of sensation in the arms or legs. The patient may not feel the limbs. In addition, paralysis may have the following symptoms:
- the appearance of trembling;
- arms or legs cannot perform specified movements, such as holding a 90° angle for 10 seconds;
- no pain;
- slurred speech;
- feeling of lethargy in the muscles;
- one or more limbs go numb.
The death of cells in the right hemisphere of the brain can lead to paralysis of the left side of the body. The precentral gyrus is a region of the cortex that is responsible for motor activity. It is violations in its integrity that lead to problems with the limbs, including paralysis of the left side.
According to statistics, paralysis of the left side of the body is fraught with longer treatment than paralysis of the right side. In this case, the patient does not feel his left limbs, cannot assess their size and perform simple movements. In addition, vision in the left eye may fail and problems with auditory perception may occur. This is due to the fact that in the right hemisphere there are many centers responsible for various functions of the body.
This type of paralysis occurs more often than left-sided, but is also easier to tolerate by patients. Treatment of such paralysis takes less time, and doctors give more favorable prognoses. This is because the right side of the body contains fewer vital organs (especially the heart, which is located on the left side of the chest).
Most often, paralysis of the right side is accompanied by problems with speech and facial expressions - this symptom allows doctors to quickly make a diagnosis. Timely treatment will allow you to get rid of paralysis within six months, but these periods vary for each case individually. Rehabilitation depends on the size of the affected area.
You can learn more about the atypical first signs of stroke in women from our article.
Consequences of left-sided stroke in people of different ages
When the left hemisphere of the brain is damaged, the patient develops serious complications that significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life and his emotional state. After suffering a left-sided blow, the patient experiences the following disorders:
- Lack of mobility of the limbs on the right.
- Distortion of the facial muscles from the right side to the left.
- Hemiparesis (critical muscle weakness on one side of the body).
- Aphasia sensory or motor. In the first case, the patient can speak, but does not understand either his own speech or the speech of the speaker. With motor aphasia, the patient cannot speak, but understands everything that is said to him.
- Amnesia. Moreover, both long-term and short-term memory can be impaired.
- Loss of ability to write, read and think logically.
Important:
the patient’s recovery rate during the rehabilitation period depends on the degree of damage and age group.
Treatment of paralysis of the left side of the body after a stroke
Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, due to their different natures, have radically different therapeutic methods.
For ischemic stroke, treatment is chosen that involves eliminating the causes of blockage of blood vessels. Ischemic stroke is treated with neuroprotective therapy drugs, thrombolytic agents, and also with drugs that can counteract the formation of blood clots in the bloodstream. All foci of ischemia formation are exposed to therapeutic effects.
With a hemorrhagic stroke, under the influence of high pressure in the brain, hemorrhage occurs - the walls of the blood vessels cannot withstand the pressure of the blood flow, they burst, soaking the brain tissue. The deep nature of the lesion requires rapid intensive care. However, the catastrophic consequences of vascular rupture increase rapidly, and death cannot be avoided.
Treatment of strokes consists of a specific set of measures, accompanied by qualified assistance. This method is called basic. It is in no way related to the nature of the stroke itself and usually begins at the prehospital stage. In order to clarify the status of cerebral stroke, this therapy should be supplemented with medications and differentiated treatment.
The combination of basic and differentiated types of therapies constitutes a complex that provides the necessary system in the field of treatment of cerebral strokes.
The rehabilitation period can begin as early as seven days after the attack. It includes:
- Therapeutic physical culture.
- Revitalizing massage.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Kinesitherapy techniques.
- Surgical intervention.
- Drug treatment.
To the question “does paralysis after a stroke go away or remain forever?” It’s impossible to answer exactly. Of course, modern treatment methods allow many patients to recover within 6-12 months, but with severe brain damage, paralysis can become permanent.
Just as the brain is connected to the periphery, the periphery influences the hemispheres. Therefore, scientists have long developed a method for treating paralysis by influencing damaged brain cells using the following methods:
- massages;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy;
- various methods of traditional medicine.
Taking medications also in combination with other rehabilitation methods can speed up the healing process. It is very important for the patient to give up bad habits, eat right and receive good psychological support from family and friends.
The patient is placed in a hospital, where he is constantly monitored by medical workers. As soon as the condition stabilizes and begins to improve, the patient is sent home or to special sanatoriums for treatment.
Drug therapy is prescribed for each case individually. At the very beginning of rehabilitation, medications can be administered through injections and droppers, and then in the form of tablets.
Such drugs can be hemostatics, neurostimulants, neuroprotectors, medications that improve the nutrition of nerve tissues and the conduction of impulses. Doctors also prescribe vitamin B1 injections. To normalize blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
Diet food
After a stroke, a paralyzed patient needs to monitor his diet. First of all, you need to give up alcohol and smoking.
To avoid blood thickening, you need to exclude potato dishes from your diet - they contain starch, which promotes thickening. You should definitely avoid eating foods that are too fatty. Prohibited use:
- fatty meat;
- cheeses;
- sweets;
- butter and products that contain it;
- margarine.
The fats that the body usually gets from such foods can be replenished by eating fish.
You can protect yourself from pressure surges by giving up coffee and tea, replacing them with compotes and freshly squeezed juices.
A huge number of fruits that nature provides can be used to treat paralysis using traditional methods. Let's consider several options.
- Grind the peas into powder, take 1 tsp. 3 times a day before meals. Pea flour helps improve nutrition of cerebral cortex cells.
- Brew an infusion of equal proportions of valerian roots, oregano herbs, mistletoe and yarrow. Patients with paralysis after a stroke are recommended to drink about 3 teaspoons per day, divided into 3 doses, each before meals.
- Infuse 100 grams of sage in 200 ml of water for at least 8 hours. Take 1 tsp after meals. You can drink it with milk or compote.
- 1 tsp Brew dry peony roots in 3 cups of boiling water. Leave and strain. Take 1 tbsp. l. three times a day shortly before meals.
- Prepare an infusion of young walnuts using kerosene. Take 10 fruits and grind in a meat grinder. Pour the resulting mixture with three glasses of purified kerosene. It is necessary to insist for at least 1.5 months, or in a dark, cool place for about 2 weeks. The tincture is filtered using gauze.
If a patient wants to be treated with traditional methods, it is best to check the most suitable ones with a doctor - only a doctor can give practical advice based on the patient’s age, the degree of brain damage and the dynamics of treatment.
Massage
The main purpose of massages for paralysis is to develop muscles and improve blood circulation. The latter is very useful, as the blood is saturated with oxygen and the formation of blood clots is prevented. It is advisable to attend massages every day and combine them with rubbing and compresses.
When performing massages, you can use creams that contain medicinal plants.
The massage must be performed by a qualified specialist, and it is best to entrust this procedure to professionals in rehabilitation sanatoriums. Medical workers in such institutions have long been dealing with paralysis and know the main ways to influence the brain through massaging the limbs.
It is very important that the victim receive medical assistance as soon as possible, because the longer the cause of the stroke remains untreated, the larger the area of brain tissue necrosis and the more severe the consequences.
With a mild ischemic stroke, the patient may experience partially reversible speech dysfunction, paresis of the muscles on the right side of the body, dyslexia and dysgraphia, loss of adequate perception of reality, memory, understanding of spoken speech, and severe depression. In more severe cases (with an extensive hemorrhagic stroke, for example), the above disorders may remain irreversible and even worsen.
According to medical statistics, left-sided stroke occurs more often than right-sided stroke (up to 57% of cases), but it is more easily tolerated by patients. Treatment of the consequences of a stroke should begin immediately upon the patient’s arrival at the hospital. After identifying the lesion, doctors surgically try to eliminate the cause of the stroke (they remove the blood clot that has blocked the vessel during ischemia or, on the contrary, during hemorrhage - they inject a coagulant to close the gap in the vessel wall, drain the hematoma to avoid compression).
In the first days after a critical illness, drug therapy includes the administration of decongestants and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as drugs that stimulate cerebral circulation. Then the possibilities of physiotherapy (from electrophoresis to mud therapy), therapeutic exercises, speech therapy, defectology and psychotherapy are connected.
Rapidly developing local or global brain damage may have different mechanisms of occurrence with hardly distinguishable symptoms, but completely different treatment methods.
| Ischemic |
|
| Hemorrhagic |
|
Ischemic strokes are much more common, but, like hemorrhagic strokes, they are deadly. Treatment of stroke in the acute period and its consequences during the rehabilitation period depends only on its type.
The resulting paralysis of the right side after a stroke, in the absence of medical prohibitions, begins to be treated as early as possible: recovery during the rehabilitation period can begin 5-7 days after the attack. The basis of treatment is various correction of motor disorders:
- Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy), which is a set of therapeutic gymnastic exercises without intense loads.
- Revitalizing massage and manual therapy.
- Therapeutic physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, etc.), orthopedic auxiliary methods, “mirror” therapy.
- Kinesitherapy techniques associated with loads on the muscles of the right side of the body altered by the disease.
- Acupuncture methods of physical influence on certain points on the body surface (reflexotherapy, acupuncture).
- Surgical and medicinal treatment of orthopedic problems resulting from the development of paralysis.
In addition, the complex of treatment methods includes sessions with a speech therapist, necessary for the full or partial restoration of speech functions, as well as communication with a psychologist in order to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the brain and socialize the patient after suffering a stroke.
Features of treatment
Treatment of left-sided stroke at home is strictly prohibited. Any brain damage requires urgent medical intervention. The patient should be treated only in a hospital. And the sooner the patient enters there, the greater the chance of restoring lost functions.
Drug therapy
With the help of drug therapy, only ischemic stroke or hemorrhagic stroke is treated, provided there is a small hemorrhage in the brain. In general, therapy is aimed at maintaining all important and basic functions of the body. The patient is prescribed drugs from the following groups:
- Thrombolytics. They work to dissolve blood clots.
- Anticoagulants. Prevents the formation of new blood clots. But they are not prescribed for hemorrhagic stroke, so as not to provoke additional hemorrhage.
- Hypotonics to normalize blood pressure.
- Neuroprotectors. Drugs that improve brain function and nutrition, as well as prevent the death of living neurons.
- Drugs to stop bleeding in hemorrhagic stroke.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is performed in case of hemorrhagic stroke. Here it is very important to remove the resulting hematoma, which will put pressure on the brain tissue and cause swelling. In this case, the patient may not only be paralyzed, he may fall into a coma. The operation is performed in the neurosurgery department. The possibility of performing surgical intervention is determined by such parameters as the availability of the necessary equipment and specialists of the required level in the clinic.
First aid for a stroke before the ambulance arrives
- Call an ambulance, and you should clearly explain everything that happened to the person. The patient requires the help of a neurologist, so the team that should come for the patient depends on how the dispatcher understands what happened to the person.
- The victim's head should be raised 30 degrees from the level of the body; you can place clothes or a blanket under the head.
- It is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room and loosen clothing that restricts breathing - belts, belts, collars. If vomiting occurs, place the patient on his side, after which you should help him clean his mouth or rinse it, if he is able to do so.
- Measure blood pressure and record the result.
The speed of providing first aid for a stroke determines not just the duration and complexity of further rehabilitation of the victim, but even a person’s life. It is very important to recognize the signs of a stroke as early as possible and provide adequate pre-hospital and then medical care in a hospital setting - medication or surgery.
Consequences and recovery after a stroke on the left side
With a stroke of the brain on the right side, the consequences that develop in patients are closely related to the type of brain catastrophe.
The most dangerous form of cerebral catastrophe is a right-sided hemorrhagic stroke of the brain. Right-sided hemorrhagic lesions of brain tissue are characterized by severe and aggressive symptoms. On the eve of the disaster itself, a person may be bothered by symptoms such as dizziness, hypertension, shortness of breath, and pain in the heart.
With a hemorrhagic stroke on the right side, the consequences are severe. They are expressed in partial or complete disability, cerebral edema, even cerebral coma.