The first stroke is behind me. Stress, fear of dying, becoming disabled or a vegetable has receded. Everything turned out well, the first signs of a stroke were recognized in a timely manner, the ambulance arrived on time, hospitalization took place in the shortest possible time, the examination made it possible to recognize the type of stroke and carry out competent and adequate treatment, rehabilitation took place in a specialized center, there were almost no residual effects, and there were almost no disturbances in motor activity. In general, life was good.
Few people think that the reason that led to the first brain attack remains, and if you do not change your lifestyle towards health, the likelihood that the disease will recur will not decrease, but increase.
Statistics on recurrent strokes say that relapse occurs in the first year after recovery from the previous one. Survival rates are not encouraging, with only a 30% chance of staying alive. Therefore, having passed the sad consequences of the first apoplexy, you should think about how to avoid a second stroke.
Why does a recurrent stroke occur?
At high risk are older people and patients who are irresponsible about their health. Recurrent stroke is most often diagnosed in people who do not follow a diet and drink alcoholic beverages.
Repeated stroke often occurs due to the following causes:
- Decreased patient mobility.
- Increase in body weight.
- Slowing down metabolism in the body.
- A sharp change in the patient’s character: increased irritability and temper.
- The patient has increased meteosensitivity.
- Sleep problems.
- The predominance of foods containing animal fats in the diet.

If the emotional atmosphere in the family is unfavorable, the prognosis is disappointing. In this case, the risk of a recurrent stroke increases many times.
Pathogenesis
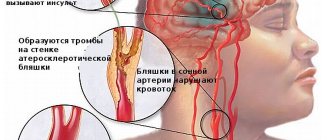
In the development of secondary ischemic stroke, the main role is played by vascular lesions in the area:
- extracranial – atherosclerosis of the main arteries (usually the carotid) before they enter the cranial cavity (40% of cases);
- brain – intracerebral small arteries (35%);
- cardiac - formation of an air or fat embolus in the left ventricle and subsequent blockage of the middle cerebral artery (15 - 20%).
Vascular lesions leading to cessation of blood flow are represented by:
- blockage of the lumen of the vessel with an embolus;
- thickening of the wall due to the deposition of cholesterol plaques on it.
In the first minutes and hours, rapid necrotization of neurons occurs, caused by a pathological chain: -> blockage of the artery -> cessation of blood flow -> hypoxia and oxidation of brain tissue -> disturbance of the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates -> inhibition of the production of neurotransmitters and a decrease in their quantity in the synaptic cleft -> formation of infarction foci. Foci form within 5-8 minutes. In the first hour and a half, the hypoxia zone covers 50%, in the next 6 hours – 80%. Secondary cerebral edema develops over 3 to 5 days, while the neurons of the affected area become necrotic and the process partially stops. After this period, neurological symptoms come to the fore.
The severity of a recurrent stroke, compared to the primary one, is determined by:
- the area of the previously existing affected area;
- possible transition from ischemic to hemorrhagic;
- late onset or lack of positive dynamics.
What can trigger a recurrent hemorrhagic stroke? Rupture of cerebral arteries and hemorrhage in the brain, leading to compression of the trunk, disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and venous blood.
For reference. Ischemic foci are formed, neurons become necrotic. Over time, a cyst forms at the site of the hemorrhage.
Is there a high chance of another strike?
According to many experts, the likelihood of a second stroke in people over 45 years of age is 15 times higher than in younger patients. It increases sharply if the patient has diabetes mellitus or atherosclerosis. Indeed, with atherosclerosis, the lumen of blood vessels sharply narrows. Therefore, the patient needs to follow a special diet. In some cases, the doctor prescribes medications to the patient to lower blood cholesterol levels. It is worth remembering that the probability of a second stroke within 12 months after the initial stroke is approximately 15%.
Prognosis for acute cerebellar circulatory disorders
The main centers of the cerebellum control the coordination of movements. The ability to maintain body balance, muscle tone, maintain a certain posture, and navigate in space depends on them.
These disorders come to the fore with ischemia of the cerebellar zone. Infringement of this structure during cerebral edema manifests itself during the first three days simultaneously with the stem structures. And since more important centers for life are located there, the patient falls into a coma with fatal consequences.
The importance of proper nutrition
The patient needs to follow a daily routine and eat right. After the first stroke, the patient should avoid the following foods:
- Liver.
- Confectionery.
- Hot spices.
- Sausages.
In order to reduce the likelihood of a recurrent stroke, you need to include vegetables, seaweed, fruits, and low-fat fermented milk products in your daily menu.
What other recommendations should you follow?
Many patients would like to know the answer to the question: how to avoid another stroke? First of all, the patient needs to spend a lot of time in the fresh air and do therapeutic exercises. Heavy sports activities are unacceptable in his condition. It is recommended to perform physical exercises under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor. It is recommended to measure your blood pressure daily. It must be remembered that it is impossible to sharply reduce blood pressure. You must take medications strictly as prescribed by your doctor. You can also use folk remedies:
- 10 grams of celandine are poured into 200 ml of boiling water.
- It is recommended to leave the product for 2 hours.
- After this time, the resulting mixture must be filtered.
- You need to drink 10 ml of the product 3 times a day.
Celandine is a poisonous plant, so the indicated dosage should not be exceeded. The duration of treatment varies from 14 days to two months.
Medications to prevent recurrent stroke
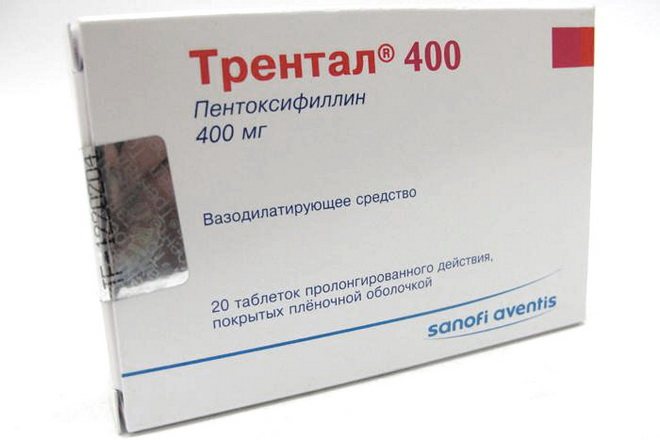
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor. For the treatment of chronic cerebral vascular ischemia, medications such as Trental and Cavinton are usually prescribed. These medications help prevent the development of thrombosis.
Many experts recommend taking aspirin to reduce the likelihood of another stroke. But if the patient has chronic diseases of the digestive organs, you should stop using this medication.
Spa treatment
As is known, repeated stroke causes serious consequences. Therefore, relatives must take care of the patient. A stroke survivor needs positive emotions. He needs to avoid stress; the patient is indicated for treatment in a rehabilitation center. It is best to undergo a therapeutic course in cardiological sanatoriums. A trip to another country is disastrous for the patient, so priority should be given to Russian medical institutions.
Treatment options
The consequences of a stroke can only be eliminated in a hospital setting under the close supervision of medical staff. The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Anticoagulants (Warfarin, Apixaban) - prevent blood from thickening and help facilitate its passage through the vessels. Prescribed with extreme caution if there is a threat of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Antihypertensive drugs – stabilize blood pressure.
- Nootropics – promote rapid restoration of cerebral circulation.
- B vitamins – normalize the conductivity of nerve impulses and promote the activation of neural connections in the limbs.
- Diuretics – remove excess fluid from the body, preventing the development of cerebral edema.
The list of medications can be supplemented taking into account the patient’s health condition.
After the acute phase of the stroke has passed, the rehabilitation stage begins, in which the main factors are:
- Therapeutic exercise is aimed at restoring muscle tone and strengthening them. It is prescribed by a specialist and performed under his strict supervision.
- Physiotherapy - helps restore activity in affected areas of the body by enhancing the conduction of nerve impulses.
- Diet – the patient’s diet should consist of protein foods and carbohydrates. Cholesterol should be limited. It is important to eat small portions, but often, which will reduce the load on the digestive tract and normalize metabolic processes.
- Active recreation and positive emotions - it has been proven that the care of loved ones and a good mood help to rehabilitate faster.
Physical therapy is one of the ways to treat recurrent stroke Please note! The sooner medical assistance was provided and comprehensive treatment was started, the greater the chances of a full recovery. If treatment is not started within 3 days after the stroke, there is a high probability of death in the next few months.
Symptoms of secondary stroke
Repeated ischemic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Feeling of numbness in the limbs or face.
- Severe headaches.
- Speech impairment.
- Facial asymmetry.
- Paleness of the skin.
There are other signs of an ischemic stroke: the patient's vision may suddenly deteriorate and he or she may have difficulty pronouncing words. Repeated ischemic stroke is often preceded by attacks of angina.
The main signs of hemorrhagic stroke should be noted:
- Cramps.
- Sudden increase in blood pressure.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Breathing problems.
In most cases, the signs of a recurrent stroke are similar to those of a primary stroke. Therefore, the patient’s relatives should quickly seek medical help.
Consequences
The prognosis of a recurrent stroke depends on the extent of the lesion, residual effects after the first event, timely medical intervention, competent support during the rehabilitation period, and the patient’s mood.
The consequences of a second stroke are much more significant than after the first attack:
- persistent hemiparesis or paralysis that confines the patient to bed;
- severe speech disorders;
- significant visual and hearing defects;
- violation of mnestic functions;
- emotional-volitional disorder;
- loss of self-care skills;
- inability to lead a normal lifestyle.
For reference. All this leads to disability, dependence on others, which causes depressive moods, often with suicidal thoughts.
A little about the complications of recurrent stroke
Are the consequences of a recurrent stroke different from the complications that arise from a primary stroke? As a rule, the prognosis is unfavorable: after a second stroke, a person often loses control over his senses. Secondary strokes have a negative impact on the patient’s mental activity. Approximately 80% of patients who have a second stroke become disabled. They experience serious changes in the structure of the cerebral cortex. Some patients fall into a coma after a second stroke.
The future of the patient after the third blow
The prognosis after a third stroke is usually dismal. A person develops serious health problems. A patient who has had two strokes is unlikely to be able to return to normal life. The patient's musculoskeletal system functions deteriorate, sclerosis develops, he becomes nervous and irritable.
The third stroke becomes a difficult ordeal for the patient and his relatives. In some cases, a person cannot swallow food, so he needs artificial tube feeding at home.
After the third stroke, conversational function and memory deteriorate significantly. The patient may develop complete paralysis. Therefore, if a person has already had two strokes, he needs to carefully monitor his health.
What can be done for prevention?
Doctors focus their attention precisely on the stage of preventive treatment and thereby fight to reduce the number of recurrent strokes.
The only effective cure for the disease is the patient’s vigilance towards his health. This is the only way to control risk factors for recurrent stroke.
Specialists carry out a number of activities designed to prevent the occurrence and development of diseases such as:
- atherosclerosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- thrombosis.
To avoid a recurrent stroke, doctors prescribe pharmacological drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid (antiplatelet treatment). Medicines are selected individually based on tolerability:
- Thrombo-ass;
- Cardiomagnyl;
- Aspirin-cardio.
However, the patient himself is able to reduce the risks by giving up smoking and drinking, and bringing his weight back to normal. By adhering to a diet (reducing salt and fat intake), a routine and doing simple physical exercises, a person is able to provide adequate resistance to the impending disease.
It will not be amiss if the patient pays due attention to his blood pressure and gets into the habit of taking daily measurements using a tonometer. Along with this, it is necessary to monitor the health of the heart muscle by periodically visiting a doctor.
Specialists can prescribe antihypertensive therapy, the purpose of which is to stabilize high blood pressure. The following drugs are used for this:
- diuretics;
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors.
Other preventive methods are also used:
- carotid endarterectomy;
- Doppler ultrasound examination.
These techniques are used to improve the patency of the circulatory system.
A repeated stroke is very dangerous to human health. Poor blood circulation in the brain can occur due to improper treatment or incomplete treatment. Medical studies have found that recurrent cerebral hemorrhage occurs in 30% of patients who have had a stroke. When a recurrent stroke is diagnosed, the consequences are usually very serious. The danger of such a relapse is that it can occur within a year after the first incident. There is a very high risk of death. The likelihood of having another stroke depends on many factors. It is quite difficult to make any forecast.
Risk groups and causes of recurrent stroke
A recurrent stroke may damage brain tissue, or it may be a more complex form characterized by rupture of intracerebral vessels.
There are groups of people who are prone to having another stroke.
At-risk groups:
- people who had their first hemorrhage over the age of 45;
- patients who neglect specialist advice. This applies to the use of alcoholic beverages, nicotine, and drugs;
- those who have not completed the full course of treatment and recovery;
- those who do not adhere to the recommended diet;
- who are characterized by frequent stress and overwork;
- in the absence of moral support from loved ones.
In this case, it is necessary to pay great attention to prevention and full compliance with all doctor’s recommendations.
Recurrence of cerebral hemorrhage occurs in a similar way to the first case. At the same time, the patient’s health is not in the best condition, and the body is even more susceptible to all deviations from the norm.
In this case, prognosis of the patient's condition is almost impossible.
The reasons that can provoke a recurrent stroke are as follows:
- A forced lifestyle, which will be characterized by limited movement. This is due to the onset of paralysis.
- Gaining excess weight.
- Deterioration of metabolic processes that can provoke an increase in cholesterol in the body.
- The patient becomes very irritable and demanding. Typically, these factors contribute to increased blood pressure.
These are common causes that can cause cerebral circulatory problems.
But there are also reasons that are called individual:
- consumption of alcohol, nicotine;
- lack of normal rest and sleep;
- eating large amounts of fatty and sweet foods;
- individual patient dependence on changing weather conditions;
- bad ecology.
A recurrent stroke can occur not only in patients at risk. This can be influenced by the individual characteristics of the patient and external factors. No specialist will make a forecast in advance.
Signs and first aid for a second stroke
There are certain signs by which you can determine the presence of a second ischemic stroke.
The person will experience:
- within 3-5 days the patient will feel numbness in the head, where the hair grows, on the forehead, cheeks, arms or legs;
- the patient will experience pale skin;
- in the morning he will complain of headaches;
- severe general weakness;
- a darkening effect will appear in the eyes, vision will deteriorate significantly;
- speech will be impaired, the person will begin to pronounce words poorly;
- blood pressure becomes below normal;
- the patient may lose consciousness.
If an ischemic stroke recurs, a heart attack or angina may be diagnosed.
If a stroke occurs due to a rupture of a vessel, it is called hemorrhagic: it can be triggered by increased pressure or greater physical activity.
Symptoms will be expressed as follows:
- the face will become red;
- significant increase in pressure;
- manifestation of seizures;
- if the patient loses consciousness, breathing will be difficult;
- upon examination, it can be revealed that the pupils have become different sizes;
- urination becomes uncontrollable.
In this case, urgent medical attention is needed. But you can provide first aid yourself.
While waiting for a doctor you need to:
- Place the patient horizontally and tilt his head to the side. This will prevent him from choking.
- If the patient has a blood pressure pill, you can try to help him take it.
- Ease your breathing if possible.
- If possible, the patient can be offered Aspirin or Glycine forte.
- Try to prevent the person from losing consciousness and control his breathing.
- Apply a cold compress to your head.
Correctly provided first aid can significantly influence the further success of treatment and can contribute to a good prognosis for improvement of the condition.
Health care
Treatment for a second stroke will be the same as for the first case. The doctor selects medications and prescribes dosage. This is done on an individual basis. Hospitalization necessarily occurs.
Main methods of treatment:
- The patient must be admitted to the intensive care unit.
- Depending on the type of stroke, you need to raise your head, put something under your knees, and apply a cold compress to your head.
- To reduce pressure, droppers or intramuscular injections with medications are used.
- To reduce swelling of the brain, magnesium sulfate is prescribed.
- To stop bleeding, use Vikasol, Aminocaproic acid or Etamsylate.
- To widen the arteries, Papaverine, No-shpa, Eufillin are suitable.
- To reduce blood density, Reopoliglucin is prescribed. It will help prevent blood clots from forming.
- You can bring the vessels into working condition with the help of Vinpocetine, Cavinton.
- The activity of brain tissue can be improved by using Cerebrolysin and Cortexin.
After discharge, the patient is still registered with a neurologist and continues treatment at home. How the rehabilitation course will proceed is decided by the doctor who carried out the treatment.
Following all the doctor’s recommendations will help you avoid another stroke. He will advise you on the right diet. Usually a second stroke involves a disability group, but it can also be working. But in any case it will be easy work.
A person who has had even one stroke should always monitor their blood pressure and take medications if necessary. But they must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. It can cause complications that lead to complete immobilization or death. The forecast is always made individually.
The normal functioning of all systems and organs depends on the work of the brain centers. If certain structures of the central nervous system malfunction, this immediately affects a person’s well-being. Over the past 10 years, the number of patients admitted to medical institutions with a diagnosis of “recurrent stroke” has increased. This is due to many factors, ranging from an unfavorable environmental situation to inattention to health.
In most cases, the primary attack of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke can be successfully overcome. If you go to the hospital within six hours from the moment the first symptoms appear, the consequences of this pathology will not bother the patient for a long time. Strict adherence to all doctor’s recommendations and maintaining a healthy lifestyle is the main prevention of recurrence of transient ischemic attack.
Recovery after the second attack
Recovery after another vascular accident occurs within a year: during this period, the patient gradually returns to self-care skills, cognitive and motor functions. The completeness of recovery is different for all patients and depends on many factors.
To restore motor function, physical therapy is prescribed. Sessions begin immediately after the patient’s condition has stabilized. Passive gymnastics, as well as breathing exercises and massage are recommended for paralyzed patients. The return of speech skills will be faster with classes with a speech therapist. To restore cognitive functions, nootropic drugs are prescribed.
A secondary stroke leads to the death of a colossal number of neurons, so a complete restoration of all body functions is unlikely.
Important! The recovery process takes a long time and requires strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, taking medications, performing physical therapy exercises, and maintaining a positive attitude for the patient and his loved ones.
Diet as medicine
To prevent a recurrent ischemic stroke, the consequences of which may simply be irreparable, it is necessary to take as many measures as possible to keep the vessels clean. If the vessels are not cluttered with cholesterol and plaques, the risk of a recurrence of an attack is reduced. To do this, you just need to exclude junk food from your diet. Prohibited foods include everything sweet, fatty, fried, and floury. It is undesirable to consume eggs and liver in unlimited quantities. It is better to abstain from smoking and alcohol altogether, filling the body with vitamins and microelements contained in supplements.
To prevent the manifestation of the disease from recurring, it is advisable to include pomegranate or kiwi in your diet every day. Nutritionists note the benefits of sprouted wheat sprouts and citrus fruits, which can cleanse the body of cholesterol while cleansing the blood. No less useful are fresh homemade juices, to which a small amount of olive or flaxseed oil has been added.
Knowing the causes of a recurrent stroke, you can start consuming inexpensive preventive medications. The simplest and most useful medicine may be Aspirin, which is recommended to be taken a quarter of a tablet daily. The only thing that people suffering from ulcers or other stomach problems should know is that eating citrus fruits and taking Aspirin should be avoided when taking Cavinton as a medicine.
Further treatment
After successful resuscitation measures, the patient is transferred to the neurological department, where treatment is continued with the aim of:
- improve microcirculation of brain vessels;
- prevent neuronal hypoxia;
- reduce A/D;
- reduce cholesterol levels;
- reduce thrombosis;
- stabilize the nervous and mental state;
- prevent constipation.
For hemorrhagic stroke, medications are prescribed to stop bleeding. Vasodilators and anticoagulants (thrombolytics) are prohibited.
When the patient’s condition stabilizes, he is transferred to home treatment, where he continues to take medications and undergoes a course of long-term rehabilitation.
Another vascular accident can lead to dangerous health consequences:
- memory loss;
- blurred vision or complete blindness;
- loss of speech skills;
- decreased cognitive abilities, dementia;
- irreversible changes in the brain;
- problems with bowel movements;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- partial or complete paralysis.
After a relapse, patients experience uncontrollable mood swings, experience deep depression, fall into apathy, and lose appetite. The patient needs continuous care from medical staff and relatives.
Resuscitation measures
A specialized ambulance team carries out all necessary measures at home and on the way to the clinic. Transportation should be as gentle as possible. The patient is placed in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. Diagnostics are carried out to determine the area and level of the lesion, possible consequences and choice of treatment tactics. They do a blood test for cholesterol, sugar, prothrombin, and a general urine test. Neurological status is assessed using the US and Scandinavian stroke scales. Instrumental types of research are carried out - CT, MRI, EEG, EchoEG, ECG, EchoCG.
In the first hours of repeated ischemic stroke, try:
- restore the hemodynamics of damaged arteries - antispasmodics, nicotinic acid, saline solutions;
- reduce thrombosis by administering thrombolytics;
- protect neurons - neuroprotectors;
- prevent cerebral edema - dehydration.
Resuscitation measures for secondary hemorrhagic type include:
- stopping bleeding - hemostatic agents;
- prevention of compression of the brain stem by hematoma - removal of the tumor. Conservative treatment is indicated only for minor hemorrhages.