Causes of a cold nerve
Most often, people call this phenomenon “a cold nerve”, as it is associated with the onset of a cold. In fact, this is close to the truth: most often, nerve pain appears after a person is blown by a cold wind or freezes in the cold.
But this does not always happen; in some cases, neuritis can occur not only because you were exposed to a draft. Sometimes, such nerve symptoms occur as a result of a serious middle ear disease or injury to the temporal bone. Often, neuritis of the facial nerve occurs in people with a brain tumor, as well as when infected with borreliosis and polio.
If you have an inflamed nerve, it is recommended that you first see a doctor to confirm the diagnosis. A specialist will be able to tell you what is best to do in case of nerve inflammation, and what treatment will be optimal in your case.
A cold nerve may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- shooting nature of pain;
- aching pain in the jaw area;
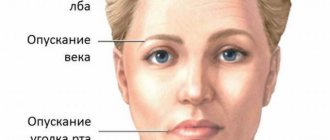
- increased sensitivity in the eyelid, forehead or eye area;
- increasing pain when teeth come into contact with cold water or food.
The inflammatory process that begins in the nerve of the tooth begins when pathogenic bacteria enter the pulp. In this case, inflammation of the nerve is accompanied by sharp, throbbing pain that must be treated urgently. In some cases, there is an increase in temperature and other very unpleasant symptoms. The main thing in this case is not to wait, but to begin urgent treatment.
If the dental nerve is actually cold, then it is better not to ignore the symptoms. In this case, you will need professional dental treatment, otherwise the consequences may be unpredictable. If proper treatment is not provided, the disease can become purulent and, as a consequence, tissue necrosis. In this case, the nerve begins to die. Ultimately, the pain will go away, even if you do nothing, but the inflammatory focus will spread to nearby tissues.
How can you get a cold on the facial nerve?
The anatomical location of the facial nerve is quite confusing. It passes through the facial canal of the temporal bone and exits into the auditory canal. At this point it intersects with the intermediate nerve.
It is quite easy to get colds in the maxillofacial area. However, this disease is similar in symptoms to others. It is important not to self-medicate, but to consult a specialist in time.
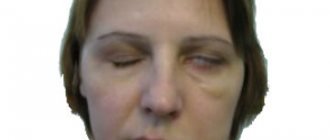
The nervous system is complex. The skin and muscles are equipped with nerves that intersect with each other. When viruses damage the facial muscles of the face, neuritis or neuropathy of the facial nerve develops. Neuritis is inflammation of a nerve. Neuropathy is a disease that causes unilateral paralysis of the facial muscles.
Physiotherapy
If the facial nerve is cold, then it is recommended to do special gymnastics. Trying to treat inflammation with gymnastics, you will encounter unpleasant sensations, since you will have to “work” with parts of your face that are almost paralyzed in half. So, how to treat a nerve with gymnastics:
- raise your eyebrows as high as you can. Try holding them in this position for a while, then lower them. Repeat several times;
- frown, bringing your eyebrows as close as possible to the bridge of your nose. Relax your muscles and tighten them again;
- try to puff out your cheeks and bulge your eyes. Press your hands on your cheeks on both sides, while holding the air in your mouth as hard as you can. “Spit out” the air forcefully;
- close your eyes tightly and immediately open your eyes as wide as possible;
- try to imitate a whistle by stretching your lips with a tube. Exhale slowly through the straw. Relax your lips;
- clench your teeth tightly and show a “grin” by parting your lips. To be convincing, you can even growl;
- push the lower jaw forward, move it to the side where the affected nerve is located. Press your jaw with your fingers and return it to its original position.
Treatment of the nerve with such exercises must be repeated 10-15 times. Don’t be lazy, perform the complex two or three times a day until a positive result appears.
Symptoms and manifestations of dental hypothermia
The symptoms of hypothermia directly depend on the depth of cold exposure in the specified location.
Under the layer of enamel and dentin there is the central part of the tooth, which is filled with pulp - it, in turn, consists of blood vessels and nerves, forming a spherical “tangle”. If hypothermia has not reached it (i.e. hypothermia is only superficial and short-lived), then a person can only feel an unpleasant sensation in the oral area, slight numbness localized in the dentition.
If low temperatures begin to directly affect the pulp, then a characteristic symptom complex with all its negative manifestations is formed.
Hypothermia of the tooth is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Aching pain in the jaw area. It does not disappear over time and intensifies with chewing activity;
- Painful “shots”
. Occurs upon any contact with cold or too hot food, and is expressed in an instant increase in pain until unbearable; - Increased sensitivity of neighboring locations. The patient may feel discomfort in the forehead, eyelids, eyes, nearby skin, sometimes the pain even radiates to the neck;
- Slight increase in temperature
. Diagnosed in the late stages of development of the post-reactive stage of the pathology, it is usually associated with a secondary bacterial infection that has penetrated into the localization due to a decrease in local immunity and a long-term absence of any therapy with pulpitis extending beyond the boundaries of the root and the formation of a purulent sac with swelling.
Treatment with folk remedies
A pinched facial nerve can be treated with folk remedies for internal and external use. Often, such nerve treatment includes the use of various medicinal herbs, alcohol-containing preparations and bee products. So, you can treat it in the following ways:
- You can treat a nerve paralyzed by the disease using a tincture of a complex composition. To create it, it is recommended to take one pharmaceutical bottle of alcoholic tinctures of hawthorn, peony, calendula and motherwort. All tinctures should be mixed in one glass. Pour half a bottle of Corvalol into the mixture and add three tablespoons of honey, dissolved in a water bath. Drink the resulting composition one teaspoon before bed. The duration of treatment is three months. For treatment to be successful, it is necessary to take a break of two months and repeat the course again. In severe cases, the course of treatment should be carried out at least three times;
- You can treat nerve inflammation using traditional methods using rose tea. Brew dark red rose petals in a simple teapot and drink as simple tea at any time of the day. This remedy is extremely effective for neurasthenic tendencies and has a calming effect. Duration of treatment – three weeks;
- Treatment of neuritis is carried out using goat's milk. It should be heated, add a tablespoon of acacia honey and a small, bead-sized seed of mumiyo. This remedy must be drunk every day before bed. It will be great if you combine taking this remedy with rubbing fir oil into the numb part of your face. The duration of treatment is 21 days, then we take a break of two weeks and repeat the course;
- grind fresh wormwood, brew it in a small amount of boiling water so that a green thick paste comes out. Add a teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil to the wormwood “puree”, mix and apply to the sore spot. At the same time, you can take a decoction of wormwood orally, which is prepared as follows: an incomplete handful of crushed wormwood is poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water and infused for 30 minutes. Take the medicine before meals, one tablespoon up to 5 times a day. You can soften the bitter taste of the infusion by adding a little honey to it;
- if during neuritis of the facial nerve there is severe pain, then flaxseeds will help get rid of them. Place a handful of flax seeds into a cloth bag and place in a steamer over boiling water on a wire rack. Apply the steamed seeds to the sore spot, having previously wrapped them in polyethylene and a warm scarf.
Treatment of a cold nerve will be especially effective if you follow all the recommendations of a neurologist. It is imperative to see a doctor throughout the course of treatment to avoid complications. At the same time, do not forget to protect yourself from hypothermia and drafts.
Pain in the jaw area is not a disease as such. And when we say that our jaw is “blown out,” we primarily mean inflammation of the facial nerve.
Why the jaw near the ear may hurt, depending on the location of the pain
The jaw may hurt near the ear on the right or left; it is usually painful for patients to chew and speak; sometimes the pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Pain can occur only when pressed or at rest, be burning or aching.
There are many combinations of pain syndromes, and each indicates a specific lesion.
Therefore, doctors first conduct a detailed survey of the patient, and after that they prescribe additional clinical and laboratory tests - MRI, radiography, general blood test.
If discomfort and pain appear in the area of the ear, cheekbone and jaw, you need to determine which doctor you should consult. A disease that causes pain in the jaw area can be treated by an otolaryngologist, surgeon or dentist:
- The treatment of pain caused by a disease of the soft tissues of the face is carried out by a surgeon.
- If pain occurs due to inflammation of the lymph nodes, ears, sinuses, larynx or tonsils, or infectious diseases, you should consult an otolaryngologist.
- If pain in the jaw near the ear, which manifests itself when chewing, is caused by an inflammatory process in the gums or teeth, a dentist will help get rid of the pathology.
- Maxillofacial surgeons and dental surgeons specialize in the treatment of diseases of the temporomandibular joint, dentofacial apparatus, phlegmons and abscesses.
- Painful symptoms in the facial area can be caused by diseases of the peripheral nervous system. To identify inflammation or pathology of nerve fibers, you should consult a neurologist.
It is difficult to independently determine what caused the pain syndrome. You should make an appointment with a therapist, who will examine the clinical picture and redirect the patient to the right doctor.
If your jaw hurts suddenly and very severely, you must immediately call an ambulance. Such symptoms may indicate a dislocation or even a fracture.
Pain localized in the upper jaw can be caused by sinusitis. The disease develops against the background of injuries to the skull and nose, prolonged hypothermia, pulpitis and periodontitis. Sinusitis can be identified by the following signs: nasal congestion (usually one nostril), thick mucus or pus discharge when blowing the nose, a nasal voice, elevated body temperature.
The area of maximum pain sensitivity is usually located near the nose, but in advanced cases the pain can spread to the entire face.
Sometimes the disease affects the paranasal sinuses on both sides, but most often it is unilateral.
We invite you to read: Minimum period for wearing braces in adults
If the patient's jaw hurts only near the ear on the left, and it does not hurt him to chew on the right side, it means that inflammation develops in the sinuses located on the left.
Pain in both the upper and lower jaw occurs for the following reasons:
- Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the jaw. It develops as a result of unprofessional treatment of sinusitis, tooth extraction, implant installation, or sinus lift. The disease is accompanied by an increase in temperature, the pain may radiate slightly to the left or right lower jaw.
- Gingivitis is an inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the gums. This disease is characterized by aching pain and bleeding gums. Additional symptoms include a slight increase in temperature and the appearance of bad breath.
- Alveolitis is inflammation of the tooth socket after tooth extraction. The zone of pain innervation is small, the temperature is increased.
- Submandibular abscess, phlegmon.
Pain in the jaw that occurs when chewing and is accompanied by discomfort near the ear may indicate the following problems:
- Carotidynia. The syndrome can develop due to dissection of the temporal artery and soft tissue tumors that irritate the nerve endings located next to the carotid artery. The pain is paroxysmal, the most intense pain is expressed in the upper jaw, radiating to the ear, neck and oral cavity. When you press on the side of the neck and the area under the Adam's apple, a sharp sharp pain occurs.
- Neuralgia of the ear node. It can develop as a result of a previous sore throat, sinusitis and hypothermia. The disease can be recognized by a burning, paroxysmal pain that originates in the temple area, passes through the ear and spreads all the way to the lower jaw and chin area. The jaw hurts the most when pressed under the ear; there is practically no pain inside the oral cavity. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are clicking in the ear and increased salivation.
- Erythroothalgia syndrome. It can occur as a result of cervical spondylosis, functional disorders of the temporomandibular joint and damage to the thalamus. The syndrome causes severe pain in the ear on the left or right side, and the jaw ache is weaker. Often the pain syndrome affects the back of the head and frontal area.
Pain in the jaw near the ear can occur due to dental, surgical and neurological reasons. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the provoking factor, the location and nature of the pain, and accompanying symptoms.
Aching pain in the cheekbones and jaw may appear after dental procedures. Often the cause of pain is poor-quality wisdom tooth removal, caries treatment, or advanced carious processes and prosthetics themselves.
Jaw pain of this origin is usually accompanied by swelling and inflammation at the operation site.
If it does not go away within a few days from the moment of intervention, you should contact a more qualified dentist to eliminate the medical error.
An exception that does not require treatment is aching jaw pain on the left and right, caused by wearing braces to correct the bite. This pain causes constant pressure on the jaw bones; it is normal and can be eliminated with the help of painkillers.
Pain caused by dental diseases and pathologies is usually pulsating in nature and intensifies closer to night. Due to dental pathologies, the cheek may become very swollen. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to get rid of the source of pain.
Pain during ARVI
The main complication of respiratory diseases is the spread of infection throughout the body. The inflammatory process, as a complication of acute respiratory viral infection, can begin in any part of the body - lungs, intestines, knees, side, mouth. This is why your cheekbones and jaw can hurt when you have a runny nose or a common cold.
If maximum pain is observed between the maxillary and mandibular arches, the reason most often lies in the fact that the joint sac has become inflamed due to the influx of bacteria and viruses. With this pathology, the jaw hurts near the ear and not during chewing, but constantly.
When the ear is inflamed, the cheekbone near the ear may hurt. Usually the ear hurts more intensely, and the pain only radiates to the jaw. Such inflammation is often accompanied by general malaise and an increase in temperature to 37.5–38 °C. Otolaryngologists specialize in treating people with complications of respiratory diseases.
- Soft tissue bruise. Even a mild bruise of soft tissues without affecting the bones is accompanied by an acute pain attack, swelling and hematoma. To exclude the possibility of a fracture, which may not be palpable due to the swelling of the cheek, it is necessary to take an x-ray. The consequences of such an injury should be treated if the symptoms do not disappear within several days.
- Dislocation. Dislocation can occur not only due to a blow, but also due to a sharp opening of the mouth. With severe dislocation, even simple chewing and swallowing movements are difficult. After the surgeon visually determines the dislocation, he will take a control photo to rule out a fracture, and then reduce it. Dislocations are characteristic only of the lower jaw, which is why the pain manifests itself from below.
- Fracture. When a fracture occurs, unbearable pain occurs around the injury site, spreading to the entire face. The victim requires immediate medical attention in a medical facility.
Jaw dislocation
Tumors
The ear and jaw on one side may hurt when a bone tumor forms, both benign and cancerous.
Before specific symptoms appear, numbness in the muscles, mild swelling, swelling and discomfort in the joints are observed.
If there is a tumor under the same ear in the area of which the jaw aches, there is a high probability of developing atheroma - a benign neoplasm. Atheroma can be cured.
Problem Definition
1. Inflammation of the jaw joint.
Jaw pain in the ear area is a characteristic sign of inflammation of the temporomandibular joint.
In this case it is observed:
- Aching pain, crunching in the ear area while chewing, opening the mouth or closing the jaws.
- Constant change in pain intensity from mild discomfort to acute sensations.
2. Dental diseases.
Pain in the jaw, which is accompanied by pain in the teeth, is a symptom of diseases such as pulpitis, caries, osteomyelitis, periodontitis, dental trauma, and gum inflammation.
- The pain is pulsating.
- Intensifies when chewing hard food.
- With osteomyelitis, facial swelling may occur and body temperature may increase.
3. Neuralgia.
If the facial, laryngeal nerve or ear node is damaged, intense pain is observed in the upper, lower jaw, and area near the ear.
- The pain intensifies with jaw movements.
- Heavy salivation may occur.
- Noises and clicking sounds appear in the ear.
With arteritis, pain can affect both the chin area and the area of the upper lip, nose, reaching the corners of the eyes.
5. Other pathologies.
Pain in the upper jaw may indicate sinusitis or inflammation of the parotid salivary glands. Discomfort under the lower jaw may indicate inflammation of the lymph nodes, pharyngitis or sore throat.
If the cause of pain is a problem with bone tissue
Pain emanating from the bone and joint structures of the jaw can spread to the ear area.
Bone fractures
During accidents and other types of incidents, head injuries can occur, which cause fractures of the facial bones of the skull and jaw.
The most common injury accompanied by jaw pain is a jaw fracture. It occurs due to the great force of the blow applied to the face, which is why pain is felt in the jaw in the ear area.
This type of fracture can be identified by symptoms:
- hematoma at the fracture site;
- pain when trying to open your mouth and chewing;
- swelling of the tissues; with a severe fracture, severe swelling is possible, spreading to the face;
- With complex fractures, bones are displaced and the soft tissues of the oral cavity are damaged.
This disease is characterized by damage to the bone tissue of the jaw. It occurs under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the bone through the root canals of diseased teeth. This disease is considered a consequence of neglected dental problems and not timely treatment of pulpitis.
In addition to pain in the jaw and ear, symptoms include:
- increased body temperature, feeling of chills;
- swelling of facial tissues and the appearance of its asymmetry;
- lymph nodes increase in size.
This disease is very dangerous and requires qualified treatment.
Bone fractures
First aid
If the attack happened in the evening, at night or on a weekend, or you currently do not have the opportunity to visit a doctor, then you should take the following measures:
- Drink painkillers (“Nurofen”, “Efferalgan”, “Analgin”).
- Provide complete rest for the temporomandibular joint. Do not open your mouth wide, chew hard food or chewing gum.
- If your teeth hurt, you need to rinse your mouth with a soda solution:
- Soda 1 tsp.
- Water 1 tbsp.
...or herbal infusions (sage, chamomile):
- Herb of choice 1 tbsp. l.
- Water 1 tbsp.
- If your ear hurts, apply a warm compress (provided your body temperature is normal). A compress of vodka and honey helps a lot.
Treatment of tooth hypothermia
If a tooth becomes too cold, it is imperative to visit a dentist. If this is temporarily not possible, then at least start adequate therapy, but do not leave the problem to chance, due to the fairly rapid formation of a number of complications.
First aid procedures for dental hypothermia include:
- Immediately stop contact with cold. It is necessary not to open your mouth, if possible, get out of the cold into a warm, heated indoor room;
- In case of dental hypothermia, it is forbidden to warm the localization,
either with compresses or liquids, or with food, so that the restoration of the temperature regime is as natural as possible. In case of severe hypothermia, it is rational to apply a heat-insulating bandage through the chin made of layers of cotton wool and gauze to the jaw; - Using home remedies. In the reactive stage, after hypothermia, you can use a solution of 1 teaspoon of soda and salt, which is thoroughly mixed in 1 glass of water at room temperature, then rinse your mouth.
Medications
To prevent inflammation of the dental nerve from hypothermia, especially against the background of acute pain, it is rational to use special medications.
Similar articles
Groups of medications for tooth hypothermia:
In case of flux formation from hypothermia, which in our case is a complication of cold pulpitis, it is imperative to consult a dentist - we are talking about a direct secondary bacterial infection, so the treatment procedure, in addition to taking antibiotics (most often Amoxiclav, Levomycetin or Ciprofloxacin) includes microsurgery with an incision of a purulent formation and thorough cleaning of the cavity.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can be used for additional treatment of tooth hypothermia only in the absence of serious complications in the form of gumboil, periodontitis, periostitis and other pathologies, and it is imperative to consult a dentist.
Traditional medicine recipes:
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine complements general therapy and helps to recover faster. Let's look at the most popular and effective recipes.
To rub the sore area you will need:
- White acacia flowers 4 tbsp. l.
- Vodka or alcohol 1 tbsp.
Pour vodka or alcohol over white acacia flowers. Let it brew for a week. Rub the problem area twice a day for a month.
- 10% mummy solution a few drops
- Several cotton pads
Apply a small amount of 10% mummy solution to a cotton swab. Massage the sore area with light movements for five minutes.
Mumiyo is also recommended to be taken orally. For this you will need:
- Mumiyo 0.2 g
- Honey 1 tsp.
- Warm milk 1 tbsp.
Dissolve 0.2 g of the substance and a teaspoon of honey in a glass of warm milk. Drink a glass a day for two weeks.
For the compress you will need:
- Chamomile 3 tsp.
- Boiling water 1 cup
Steep chamomile flowers in a cup of boiled water. Let it brew for 15 minutes. Place it on your face and cover it with a woolen cloth. Apply compresses once a day.
To warm up you will need:
- Salt 1 tbsp.
- Cloth bag 1 pc.
Heat table salt in the microwave or in a frying pan. Place in a cloth bag and apply to the sore spot for a month.
What not to do if you have this disease
When a tooth is affected by a cold, no rinsing or painkillers help. They provide temporary relief, but then the pain returns. People often use special dental drops, but for colds they are practically useless, and in some cases they can be harmful. Self-treatment almost always leads to further progression of the disease.
It is forbidden to use antibiotics for this disease, since they are practically unable to help the inflamed nerve. Before going to the dentist, it is better not to use painkillers. They will prevent the doctor from making an accurate diagnosis.
Patients often try to use traditional recipes. But success in this case is possible only after consulting a dentist, who, after conducting an examination, can suggest which folk recipes will help eliminate the problem.
Patients should be aware that there are other restrictions for dental colds. For example, it is forbidden to use various warm compresses, as they can only increase the pain. The patient is recommended to simply bandage the cheek on the side of the damaged tooth with a wool scarf.
If it is not possible to see a doctor, then we must try to alleviate the patient’s condition using alternative medicine.
First, it is recommended to roll a ball of cotton wool (the size should be small), moisten it in medical alcohol or vodka, and then apply it to the affected area. Cotton wool should not get on the gum, as this may increase the pain due to its burn.
Another folk remedy that is very effective is often used - lard. It can be used fresh or salted. A small piece of the product is placed in the area of the diseased tooth. It is kept for ⅓ hours. The pain gradually goes away.
Some patients prefer to use a Chlorhexidine rinse. A few drops of the medicine are diluted in 200 ml of warm water. You can use the mixture to rinse your mouth 3 times a day.
For some people, the pain goes away after they chew a fresh sorrel leaf. Sometimes a clove of garlic cut in half, which is placed on the gum near the cold tooth, helps. The pain disappears in almost 5-6 seconds, but gum burns may occur. If you infuse chicory in 1 glass of boiling water for 10 hours, you can quickly relieve tooth pain with the resulting solution.
The following recipes can be used:
- Take 0.1 liters of alcohol and pour it into 25-30 g of birch buds. Insist for 8-12 days. To use against colds on teeth, cotton wool is soaked in the solution and applied to the patient’s tooth enamel.
- It is recommended to soak a cotton ball in clove oil and apply it to the gums. This recipe is used when there is no visible damage to the teeth.
- Make a decoction of pharmaceutical sage according to the instructions indicated on the box. The solution is cooled, but before use it is diluted with warm water. It is best to rinse your mouth with the resulting liquid every 30 minutes.
- Place 5 tsp in boiling water. willow bark, ground into powder. Before use, the solution is diluted with water. Rinse your mouth every 2 hours. Along with pain, willow will also relieve inflammation.
- Hydrogen peroxide diluted with water has proven itself well. They rinse their mouth with it. The pain goes away quickly.
- Some people use a paper equivalent of a cigarette, into which powder from the dried leaves of the cat's paw plant is poured instead of tobacco. There is no need to inhale the smoke, just blow it into the mouth. After 20-30 minutes the pain goes away.
A solution of baking soda in warm water is considered an effective remedy. For this, 1 tsp. The product is diluted in 200 ml of liquid. It is recommended to use this medicine for rinsing 4-5 times a day.
Prevention of dental colds is of great importance. The most common cause of this disease is the development of caries. Therefore, to prevent its occurrence, it is necessary to systematically examine the jaw in the dentist’s office, and urgently take action if symptoms of caries are detected.
It is necessary to choose the right clothes appropriate for the cool season, since you can get a cold on your tooth due to the temperature change when leaving the house.
Contents of the article: classList.toggle()»>expand
By the term “tooth hypothermia,” dentists usually mean local hypothermia of the dental nerves - an unpleasant condition accompanied by constant pain.
What are the causes and symptoms of this condition? What to do if a tooth hurts after hypothermia and how to treat it? How serious are the potential consequences of the pathology? You will read about this and much more in our article.
Gymnastics
A complex of therapeutic exercises will perfectly help you get back to normal. First, stretch the muscles of your neck and shoulder girdle. Sit down and completely relax your facial muscles. Then start doing the exercises.
- Frown your eyebrows, then raise them in surprise.
- Squint your eyes and make circular movements.
- Smile with your lips closed. Repeat, but this time exposing your teeth.
- Raise your lower lip and show your teeth. Repeat the same with the top one.
- Puff out your cheeks, then suck them in.
- Push your lips out into a tube.
How to treat the jaw joint?
Analgesics will help relieve acute pain in the jaw joints. However, taking them will not solve the problem once and for all. It is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the pathology, which becomes:
- Dislocation (we recommend reading: jaw dislocation: symptoms and treatment). Persistent displacement of the maxillary joint, in which the head of the articular process of the lower jaw extends beyond the physiological position. The specialist sets the jaw in place and applies a fixing bandage.
- Bruise, pain in the cheekbone. First aid is a cold compress, after which you should consult a traumatologist. The specialist prescribes an x-ray, which excludes a fracture, and applies a fixing bandage.
- Fracture. If your teeth hurt, your jaw hurts acutely, splinting and intermaxillary fixation are performed (see also: what to do if one of the front teeth hurts?). In the open form - osteosynthesis with titanium plates.
- Osteomyelitis. The affected tooth is removed, purulent foci are opened, and drug therapy is performed.
- TMJ dysfunction, pain in the jaw joint. Orthodontic treatment, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and prosthetics are used.
- Diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillitis, tonsillitis). Treatment using painkillers, antiviral, antiseptic drugs.
- Jaw jammed. What to do if your jaw is jammed? Treatment uses anti-inflammatory therapy, physiotherapy and acupuncture to relieve muscle tension.
- Swelling under the ear. Consultation with an otolaryngologist and dentist is necessary, who will determine therapeutic tactics.
- The upper jaw is blown out, the skin on the face hurts when pressed (we recommend reading: what to do if your facial nerve is blown out?). In the case when the dental nerve is cold, with neuralgia of the jaw, drug therapy, rubbing, compresses on the problem area, and complete rest are indicated.
- Piggy. Typically, a child's pain is caused by mumps. It is characterized by swelling in the dentofacial area, high fever, and dry mouth. Treatment is medication, complete isolation.
Prevention
To prevent a relapse of the disease, it is important to follow preventive measures.
- Avoid hypothermia and drafts.
- Treat viral diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid stress.
- Eat right and take vitamins.
- Toughen up.
- Do a light self-massage of your face.
Inflammation of the jaw is a serious disease that can have serious consequences. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment. Inflammation of the jaw is the cause of many complications, although it is not so common in dental practice.
The etiology of the disease is different, but often the cause of its appearance is infection. Treatment of the inflammatory process can take quite a long period of time, even with timely diagnosis.
What not to do if you have this disease
When a tooth is affected by a cold, no rinsing or painkillers help. They provide temporary relief, but then the pain returns. People often use special dental drops, but for colds they are practically useless, and in some cases they can be harmful. Self-treatment almost always leads to further progression of the disease.
It is forbidden to use antibiotics for this disease, since they are practically unable to help the inflamed nerve. Before going to the dentist, it is better not to use painkillers. They will prevent the doctor from making an accurate diagnosis.
Patients often try to use traditional recipes. But success in this case is possible only after consulting a dentist, who, after conducting an examination, can suggest which folk recipes will help eliminate the problem.
Patients should be aware that there are other restrictions for dental colds. For example, it is forbidden to use various warm compresses, as they can only increase the pain. The patient is recommended to simply bandage the cheek on the side of the damaged tooth with a wool scarf.
If it is not possible to see a doctor, then we must try to alleviate the patient’s condition using alternative medicine.
First, it is recommended to roll a ball of cotton wool (the size should be small), moisten it in medical alcohol or vodka, and then apply it to the affected area. Cotton wool should not get on the gum, as this may increase the pain due to its burn.
Another folk remedy that is very effective is often used - lard. It can be used fresh or salted. A small piece of the product is placed in the area of the diseased tooth. It is kept for ⅓ hours. The pain gradually goes away.
Some patients prefer to use a Chlorhexidine rinse. A few drops of the medicine are diluted in 200 ml of warm water. You can use the mixture to rinse your mouth 3 times a day.
For some people, the pain goes away after they chew a fresh sorrel leaf. Sometimes a clove of garlic cut in half, which is placed on the gum near the cold tooth, helps. The pain disappears in almost 5-6 seconds, but gum burns may occur. If you infuse chicory in 1 glass of boiling water for 10 hours, you can quickly relieve tooth pain with the resulting solution.
The following recipes can be used:
- Take 0.1 liters of alcohol and pour it into 25-30 g of birch buds. Insist for 8-12 days. To use against colds on teeth, cotton wool is soaked in the solution and applied to the patient’s tooth enamel.
- It is recommended to soak a cotton ball in clove oil and apply it to the gums. This recipe is used when there is no visible damage to the teeth.
- Make a decoction of pharmaceutical sage according to the instructions indicated on the box. The solution is cooled, but before use it is diluted with warm water. It is best to rinse your mouth with the resulting liquid every 30 minutes.
- Place 5 tsp in boiling water. willow bark, ground into powder. Before use, the solution is diluted with water. Rinse your mouth every 2 hours. Along with pain, willow will also relieve inflammation.
- Hydrogen peroxide diluted with water has proven itself well. They rinse their mouth with it. The pain goes away quickly.
- Some people use a paper equivalent of a cigarette, into which powder from the dried leaves of the cat's paw plant is poured instead of tobacco. There is no need to inhale the smoke, just blow it into the mouth. After 20-30 minutes the pain goes away.
A solution of baking soda in warm water is considered an effective remedy. For this, 1 tsp. The product is diluted in 200 ml of liquid. It is recommended to use this medicine for rinsing 4-5 times a day.
Prevention of dental colds is of great importance. The most common cause of this disease is the development of caries. Therefore, to prevent its occurrence, it is necessary to systematically examine the jaw in the dentist’s office, and urgently take action if symptoms of caries are detected.
It is necessary to choose the right clothes appropriate for the cool season, since you can get a cold on your tooth due to the temperature change when leaving the house.
What to do at home if you have a cold in your teeth?
Classification of the disease
The inflammatory process in the jaw can be classified into several types:
- Osteitis. In this case, the spongy substance in the bone tissue becomes inflamed. It does not last long and takes the form of periostitis.
- Periostitis . The inflammatory process is localized in the periosteal tissue of the jaw and is the result of a complication of periodontitis. Speaking about the clinical picture, the following symptoms can be identified:
- The gums around the diseased tooth begin to swell, it becomes hyperemic and swollen;
- strong painful sensations appear;
- it is possible to discharge purulent contents from the swollen gums.
If a purulent cavity occurs, fistulas may form to allow the pus to escape. In advanced situations, an intensification of the pathological process and purulent inflammation of bone tissue is possible.
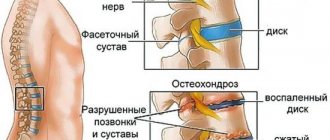
- Osteomyelitis. In this case, all layers of bone tissue are affected, and most often this is observed in the lower jaw.
The disease with neuritis is especially difficult, i.e. when the trigeminal nerve is also involved in the process. If inflammation of the jaw nerve occurs, the symptoms are expressed in excruciating pain, mainly on one side of the face.
There are also several forms of jaw inflammation:
- Acute course of the disease. Pain and inflammation are localized in one place. Symptoms of body intoxication appear quite sharply.
- In the subacute form, the patient feels a little better and may think that the disease has subsided, but this is not so. The inflammation still continues, it’s just that a fistula has formed and pus has broken through, so the pain has subsided somewhat.
- In the chronic form there are no special clinical symptoms, but during this period there is a great danger to the patient’s health, since untreated inflammatory foci can cause more serious complications.
It is very important to notice the disease in time and consult a doctor for help.
Types of disease
- Epidemic parotitis - in this case, intoxication of the body occurs due to viruses.
- Otitis – Otitis media leads to perforation of the eardrum, causing infection in the facial nerve.
- Hunt's syndrome - a herpetic rash occurs on the anterior part of the tongue and ear. Due to the penetration of microbes, the salivary glands become inflamed, resulting in compression of the facial nerve.
- Merkenson-Rosenthal syndrome is a rare type of neuritis that is hereditary.
Inflammation of the lower and upper jaw
So how does inflammation occur? There are several pathways through which infectious agents penetrate the bone marrow and bone. As a result, the periosteum becomes inflamed, swells, and periostitis develops.
Depending on the severity of periostitis, the following forms can be distinguished:
- The form is simple. Appears as a result of injuries, severe bruises and fractures.
- The form is fibrous. As fibrous tissue grows, the layers of the periosteum thicken.
- Ossifying form. In this case, the tissues also grow, and the formation of a chronic inflammatory process begins.
- The form is purulent. Purulent cavities form. The more there are, the more serious the danger to the body.
Moreover, when abscesses form, the process spreads to the entire bone and the development of limited osteomyelitis begins with the gradual capture of large areas of the jaw.
Upper jaw
Inflammation of the upper jaw is somewhat different from a similar process in the lower jaw. Especially in this case, the orbit, maxillary sinus, and middle ear are vulnerable.
Due to the fact that inflammation often develops covertly, the disease is diagnosed already in the later stages, and this is fraught with the development of various complications due to the release of large volumes of purulent masses.
These may include the following consequences:
- phlegmon;
- abscess;
- sepsis (blood poisoning);
- decreased mobility of facial veins, etc.
Also, involvement of the maxillary sinus in the pathological process can cause the development of sinusitis, sinusitis, etc.
To understand what this entails, let's look at its functions:
- forms nasal breathing;
- develops an individual timbre and sonority of the voice;
- participates in odor recognition.
In addition, the ciliated epithelium, located in the maxillary cavities, also performs a cleansing function, so inflammation in the right maxillary sinus, left, or on both sides is considered a fairly serious complication requiring medical intervention.
Lower jaw
As a result of the progression of purulent periostitis, inflammation of the lower jaw develops. A feature of this disease is that the pathological process can affect not only bones, but also soft tissues.
In frequent cases, the cause of the pathology is the odontogenic route of infection as a result of advanced carious processes in the teeth or untreated periodontitis. To learn more about inflammation of the lower or upper jaw, we suggest watching the video in this article.
If the cause of pain is joint problems
Disturbances in the functioning of the temporomandibular joint can cause pain spreading from the jaw to the ear. Patients describe their sensations as if their ear hurts when they move their jaw. Inflammatory processes occurring in the joint limit its normal motor ability.
Diseases such as arthritis and arthrosis affect joints; these degenerative phenomena destroy joint tissue, causing the patient a lot of inconvenience. The pain is more often described as aching, pressing. There is a feeling of a joint clicking when moving, a feeling of clinging. After sleep, stiffness in movements is felt. When pressing on the joint area, pain occurs.
Inflammation can occur due to hypothermia of the joint area; it is not uncommon for a person to be blown away. Along with the joint, other organs, such as the ear and nerves, can also become hypothermic. Hypothermia can cause problem teeth to ache.
Photos and videos in this article will demonstrate the nature of the origin of pain during degenerative processes in the joint.
There are several standard causes of pain in the jaw near the ear. They can appear separately or in combination. Sometimes one painful condition turns out to be a consequence of previous ailments: for example, untreated caries can precede inflammatory processes in the gums and contribute to nerve irritation.
Neuralgia is an inflammation of the nerve plexuses, which is the result of pathological processes in the surrounding tissues. Arthrosis is the thinning and degradation of the cartilage tissue of the jaw joint, requiring immediate measures to restore body functions.
- Neuralgia is often unilateral. Discomfort occurs after complex extraction of a chewing tooth. A painful impulse can be triggered by brushing teeth, pressing on a problem area, the onset of a cold, or hypothermia. Neuralgia develops as a result of prolonged irritation of peripheral nerve endings during long-term treatment of dental pathologies.
- Inflammation of the glossopharyngeal or trigeminal nerve often occurs as a result of demyelinating processes accompanying multiple sclerosis, Devic's opticomyelitis - in this case, neuralgia is considered secondary.
- Post-traumatic conditions with nerve pinching are possible.
- Hypothermia remains a common cause of nerve inflammation: you should take care of your face in the cold frosty wind, and washing your face with ice water is simply dangerous.
- Malocclusion can also cause neuralgia or arthrosis of the maxillary joint.
- Destructive processes and wear of cartilage tissue in the jaw joint, characteristic of arthrosis, can cause a lot of concern.
In parallel with pain during chewing and discomfort in the jaw near the ear, swelling or hyperemia of the skin may occur.
Impacts without displacement of the joints of the bones of the jaw apparatus or with minor subluxation, bruising of soft tissue areas lead to temporary painful sensations during chewing. Sometimes such conditions manifest themselves as aching pain in the ear.
Caries
Often the cause of pain of unclear localization is advanced caries of the upper molars.
It can develop in a tooth covered with an old, deformed crown; the damage is often invisible from the outside, but the destructive process inside the tooth has already started.
The pain “spreads” over an indefinite area, and it is difficult to determine its underlying cause. It becomes difficult to chew, the jaw in the ear area hurts.
This option is not excluded for young people. During teething, the dental crown damages the gums, creating significant discomfort. The pain can have different localization.
During this period, the formation of the correct bite occurs. If there is significant pain, the doctor may loosen the structure.
Osteomyelitis of the jaw
The disease is characterized by changes in bone tissue and manifests itself with a variety of symptoms, including pain in the ear area. Sometimes sharp bursts of pain resemble otitis media. But osteomyelitis most often develops in areas of the lower jaw; only 25% of diagnoses occur in the upper jaw. This is an extremely dangerous disease!
Carotidynia
This is one of the types of migraine, the nature of its occurrence is little studied. Paroxysmal pain covers the upper jaw, surrounds the ear, then spreads to the face and other parts of the head.
Oncology
Tumors of various kinds can also provoke pinched nerves and other inflammatory processes. Therefore, you should not ignore the rolling pains that radiate to the upper jaw or ear and subside for a while.
Often pathological processes develop asymmetrically. Therefore, pain can only appear on the left or right side. Aches in the joint, discomfort near the ear on one side are characteristic of all types of neuralgia.
- With arthrosis or primary dysfunction of the jaw joint, it is extremely rare that the destructive process involves both joints. The painful condition often occurs if a person constantly overloads one side.
- The root cause may be improper prosthetics or lack thereof: after removing a tooth, the patient is often in no hurry to see an orthopedic dentist to install crowns or an implant. But a gentle attitude towards one part of the jaw apparatus provokes an unbearable load on the delicate little other joint. Then a loud cracking sound occurs when you try to open your mouth wider, and the jaw next to the ear hurts only on the left or right.
- If caries develops, inflammatory processes cover the gum tissue, then the focus in 80% of all diagnosed cases is also located only on one side. The same manifestations are characteristic of the growth of the last - eighth - molars.
- Injuries and manifestations of osteomyelitis provoke disorders only on the right or left. And wearing braces can cause symmetrical pain.
Completely unexpected manifestations are possible:
- Pain in the jaw on the left may be a symptom of angina or a pre-infarction condition. Blood circulation is impaired, so vasospasm occurs.
- The right side reacts sharply to standard stimuli.
If the cause is injury, then the pain will be either on the injured side or on the opposite side - the patient can spare the injured part and put an extreme load on the healthy jaw.
If the jaw joint near the ear hurts, treatment requires first identifying the source of the pain. The problem is not always caused by diseases of the jaw.
Without an examination by a specialist, it is definitely impossible to answer why the jaw hurts near the ear.
We suggest you read: Crowns on teeth: types, how they are placed, how much it costs to install a dental crown in Moscow
The cause of the pathology can be various damage to soft and bone tissues, from correction of malocclusion with braces to a malignant tumor.
Among the common causes of pain in the jaw are:
- The need to wear braces or dentures. Correction of the bite, normal placement of teeth is accompanied by pain for some time.
- Wisdom tooth growth. Deviation from the accepted norm (for example, an incorrect angle relative to the jaw) causes damage to the soft tissues and the jaw itself. When chewing, the pain intensifies.
- Surgical intervention (removal of a cyst, the tooth itself) may cause pain for some time, but if it does not go away after complete healing of the wound, there is reason to assume the development of a new disease.
If pain in the jaw is not associated with bite adjustment or surgery, then it is recommended to visit the dentist as soon as possible.
- Arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint leads to stiffness and pain when opening the mouth. While chewing food, pain in the jaw is aggravated by noise in the left ear.
- Arthritis. Inflammation of the jaw joint is accompanied by severe pain and a crunching sound when chewing.
- Joint dysfunction. The pain manifests itself when trying to chew, tightly connecting the upper and lower jaws. The sensations are transmitted to the ear area and cheek area. As soon as you open your mouth wide, clicks are clearly audible.
- Gingivitis. Inflamed mucous membranes of the gums react sharply to attempts to chew rough food.
- Osteomyelitis. Pathogens are considered to be pathogenic microorganisms that have penetrated the bone tissue. As a result of their activity, a purulent process begins in the bone, which causes uncomfortable sensations in the form of pain in the ear on the left side. Because of this, during chewing, pain in the jaw increases noticeably.
Jaw injuries
If your jaw hurts near your ear on the left, and it hurts to chew, it may be the result of injuries. The severity of the damage determines the speed of disappearance of the symptom that prevents you from chewing calmly on one side. The mildest injury is considered to be a bruise. Acute pain and swelling leave the owner after just a few days.
A fracture is considered a fairly dangerous jaw injury. In addition to severe pain, hemorrhage under the skin and swelling, the patient experiences serious difficulty opening his mouth. As a result of a fracture of the upper jaw, hemorrhage may be observed in the orbital area, which leads the specialist to suspect a fracture of the base of the jaw.
ENT diseases
The jaw on the left near the ear may hurt so much that it hurts to chew as a result of advanced purulent processes or inflammation in the sinuses themselves. Among the ENT diseases that can cause pain when chewing on the left side, inflammation of the tonsils and tissues close to them is also noted.
Mumps or mumps is a viral inflammation of the parotid gland, making it painful, which is felt in the area of the upper and lower jaw, ear.
Additionally, the patient's temperature rises, weakness, and swelling on one side are observed. The disease often occurs in childhood.
Caries of the jaw, which is caused by the movement of infection along with blood from the affected tooth to the jaw. This phenomenon usually results from injury. In addition to painful sensations in the jaw, which tend to intensify during chewing, a person observes other changes in his body:
- high temperature, capable of reaching 40 degrees;
- swelling under the skin;
- asymmetry, distortion of the face due to severe swelling;
- examination of the oral cavity makes it easy to identify the “culprit”, which necessarily has pulpitis or a significant carious defect;
- inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Causes of pathology
Maxillofacial inflammation can occur for many reasons. They can be divided into several groups, which will be presented in the table below.
Next, the inflammatory process spreads to the periosteal tissue, and then affects all layers of the bone. In this case, there is also a great danger of infection (usually anaerobic bacteria, streptococci, staphylococci) entering the lymph nodes with subsequent infection
- untreated caries;
- pulpitis;
- flux;
- periodontitis, etc.
First, the bone itself may be affected, and then the teeth. Most often, this route of transmission occurs against a background of weakened immunity.
- purulent otitis;
- angina;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- tuberculosis;
- mastoiditis;
- scarlet fever;
- diphtheria, etc.
- hit;
- severe bruise;
- fracture;
- chewing solid food;
- gunshot wound, etc.
Causes of jaw inflammation
There are also several predisposing factors that can trigger the development of an inflammatory process in the jaw:
- poor nutrition, stress and overwork, leading to a weakening of the body’s defenses;
- hypothermia;
- the presence of carious teeth (the more there are, the higher the risk of developing the disease);
- the presence of acute or relapse of chronic inflammatory foci, etc.
What symptoms accompany the inflammatory process?
The clinical picture depends on how severe the inflammatory process is and how the severity of its course is assessed.
Speaking about the general group of symptoms, we can highlight the following signs:
- symptoms of intoxication of the body appear (body temperature rises, the patient feels weak, apathetic, his sleep is disturbed and his appetite disappears);
- around the inflamed area there is hyperemia of the skin, as well as swelling and pain when pressed;
- with strong compression of the upper and lower jaw, you can hear a crunch;
- due to possible displacement of the jaw bones, distortion of facial shape occurs;
- severe pain occurs when eating or talking;
- after sleep, it is difficult for the patient to open his mouth;
- Dizziness, headaches, and decreased sound acuity may occur;
- pain occurs with irradiation to the back of the head, ear, temple.
Attention: the chronic course of the disease occurs with less severe symptoms. The pain is characterized by less severe and sharp pain that occurs during sleep or in the morning. Pain increases when eating or talking. If the inflammatory process occurs in a purulent form, a dense formation is formed, in the place of which the skin becomes stretched with a bright red tint.
If inflammation of the maxillofacial nerve occurs, the clinical picture may be supplemented by the following symptoms:
- cyclical acute excruciating pain that occurs in attacks, especially when chewing food, talking, while washing, etc.
- the face may turn red at the time of pain, drooling or lacrimation may occur;
- There may also be pain in the tooth if the second or third branch of the innervation of the trigeminal nerve is affected.
Any warning symptoms should not be ignored by a specialist. Only a doctor can adequately assess the extent of the lesion, its cause and prescribe treatment.
A few facts worth noting
To understand the disease in more detail, we offer you several important points:
- The pathology most often occurs in an acute form.
- In the case of dental origin of the inflammatory process, the affected gum will turn red, become swollen and painful. When purulent masses penetrate into the gum area, it may recede and loosen the tooth.
- If the inflammation is localized in the premolars and molars, the lip, wings of the nose and the bottom may swell.
- With a palatal purulent lesion, swelling of the lymph nodes in the submandibular region will be noticeable. Such inflammation is often provoked by carious processes in the roots of molars and premolars, and incisors. It can spread to the area of the pharynx, tongue and the entire oral mucosa, and with an increase in the volume of purulent exudate, any meal or attempt to speak can be very painful. When the tissue thins and the thin film breaks through, purulent masses enter the oral cavity, and then can reach the gastrointestinal tract, and this is fraught with other serious complications.
- Odontogenic inflammation of the maxillary sinus can affect the area of the eyes and eyelids, and swelling can spread to the cheekbones, temples and cheeks. Swelling of the eyelids leads to narrowing of the palpebral fissures.
- The inflammatory process in the parotid region often provokes damage to the salivary glands.
Attention: The abundance of purulent exudate is a fundamental factor in the appearance of intoxication of the body, as well as in the occurrence of phlegmon, and then an abscess. These conditions threaten not only the patient’s health, but also his life.
Neuritis of the facial nerve in a child
The causes of damage to the facial nerve in a child can be as many as in an adult: hypothermia;
- inflammation of the middle ear;
- damage to the facial nerve itself.
A reliable symptom of the development of the disease is the skewing of the mouth in the healthy direction when trying to bare teeth. Treatment of the disease in younger patients depends on its etiology, but usually recovery occurs within 2-3 weeks. In some cases (when the cause is a serious illness), more time is required.
During therapy for fever, antipyretics are prescribed. In the acute phase of neuritis, anti-inflammatory and vasoactive medications are also prescribed. During the remission phase, exercises may be prescribed, which the child performs first with a doctor and then with a parent.