05.10.2016 MDM therapy is a new effective method
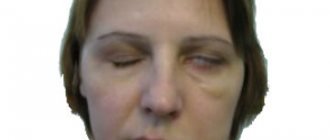
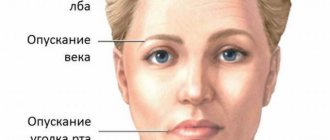
Neuritis of the facial nerve is damage to the root or trunk of the facial nerve at various levels. Depending on the area where the nerve is affected, certain symptoms of the disease appear. But the first place is always taken by the characteristic distortion of the face, which occurs due to paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles. If neuritis is left untreated, it can lead to persistent facial asymmetry and the development of contracture of the facial muscles.
Does exercise therapy help with Bell's palsy?
Exercise therapy is one of the most effective means of rehabilitation of patients with damage to the facial nerve.
Special gymnastics leads to the following positive changes:
- improving blood flow in affected tissues;
- reducing tension in healthy muscles and toning the affected ones;
- increased flow of oxygen and nutrients to affected tissues;
- reduction of inflammatory processes;
- returning the patient to his previous motor abilities.
All the positive effects of exercise therapy can be achieved only with regular exercises , which must be carried out in accordance with all the rules and taking into account the characteristics of a particular patient.
If you treat gymnastics without due attention, it will not give the desired effect, or it will be greatly delayed.
Recommendations for implementation
Before starting self-study, you must consult with a physical therapy instructor.
It is necessary to conduct classes only in front of a mirror in a sitting position. This is necessary to relieve excess tension in the body and fully control the process of performing each movement and track progress.
To prevent gymnastics from making your face asymmetrical, watch the duration of each movement : healthy muscles should perform fewer repetitions. To avoid unnecessary effort, you can sometimes cover the healthy side of your face with your palm.
Make sure that only those muscles for which it is designed participate in the exercise. If you tense your lips or tongue, your eyebrows should not wrinkle.
Don't try to do a lot of effort right away . Increase the load gradually so that the body does not receive additional stress.
Exercise for the shoulder girdle
Start the complex with a little self-massage. To do this, lightly rub your shoulders and neck so that you feel a surge of warmth in this area.
Then move on to the exercises:
The last two exercises help relieve tension from the muscles, so you need to repeat them a comfortable number of times and without much effort.
The entire complex must be repeated daily for 3-4 weeks . Then you need to track your progress and seek advice from a specialist who will help you adjust the complex depending on the results achieved.
Special facial gymnastics
Before facial gymnastics, it is also necessary to do self-massage. To do this, lightly stroking the entire surface of the face, starting from the lower part: chin, cheeks, nose, eyes and forehead, is sufficient. In this case, all movements should be performed from the center to the edge of the face.
For a massage, 2-3 minutes are enough, after which you can proceed to perform exercises, each of which must be repeated 5-10 times:
Move your nose, lips and other facial muscles so that the imaginary mosquito flies away. Repeat the exercise for 5-10 seconds, then take a short break;
Before starting a gymnastics course, take a photo of your face . After 4 weeks of daily implementation of the complex, take a second photo.
After this, it is advisable to visit your doctor or exercise therapy instructor to receive recommendations and advice on further changes to the complex.
Gymnastics for neuritis of the facial nerve, video instructions:
Therapeutic exercise to restore the articulatory apparatus
Sequencing:
- open your mouth and press your tongue as hard as you can against your right cheek, then against your left;
- open your jaw slightly, stick out your tongue a little and try to turn it sideways so that the right edge touches the upper jaw, and the left edge touches the lower jaw. Then turn your tongue the other way;
- Open your jaw and try to make a circular movement with your tongue so that it touches the front surface of your teeth. In this case, the lips must be kept closed. Start with 10 circles in each direction and gradually increase the number of repetitions to 50;
- try to touch your nose with your tongue, then your chin.
- pronounce the sound “prrrrr” with a long vibrating r for 5-10 seconds. Then take a break.
Repeat all exercises 5-10 times, unless special recommendations are indicated. The course should last at least 3-4 weeks.
Contraindications and precautions
Despite all the benefits, therapeutic exercises have a number of contraindications:
Most of the conditions described are not an absolute contraindication to gymnastics. As soon as the unpleasant symptoms pass, you can begin to perform exercises.
In addition, it is worth noting that neuritis of the facial nerve has two main periods: acute and recovery .
The first lasts about 2 weeks, and during this time you should not do gymnastic exercises. After 2 weeks, you need to consult with your doctor, and if he gives the go-ahead, you can proceed to perform a set of exercises.
When you first start exercising, follow these tips:
- Do not try to make movements until you feel pain, because this can worsen your health and delay progress even further.
- If you feel tired during an exercise, rest a little longer between repetitions.
- Try to do a gymnastic complex in the first half of the day. If you move it to the evening, it can overexcite the nervous system, which will impair sleep and the process of restoration of affected tissues. Sometimes late exercise can lead to morning swelling.
Social and forensic psychiatric significance
Only in isolated cases (persistent remission after treatment) can the patient be allowed to return to his previous professional activity. During a forensic psychiatric examination (see) of the patient, insanity is established in almost all cases (see). Only with treated P. p. with a stable remission lasting at least 3 years can the patient be declared sane.
Bibliography:
Venereal diseases, ed. O. K. Shaposhnikova, p. 174, M., 1980; Gordova T. N. Clinic and course of progressive paralysis treated with malaria, M., 1959, bibliogr.; Gurevich M. O. Pathological features of progressive paralysis in connection with clinical data and treatment of malaria, in the book: Psychiat. hospital on the path to reconstruction, ed. I. N. Koganovich, p. 179, M.-L., 1934; Miniovich P. A. Malarial therapy of neurolesia and other diseases of the nervous system, Rostov n/D., 1934; R o-zenblum A. S. On the relationship of febrile illnesses to psychoses, Works of doctors Odessa. mountains hospitals, in 2, p. 73, Odessa, 1876; Bruetsch WL Neurosyphilitic conditions, Amer. handb. psy-chiat., ed. by S. Arieti, v. 2, p. 1003, NY, 1959, bibliogr.; Gerstmann J. Die Malariabehandlung der progressiven Paralyse, Wien, 1928; Handbuch Geisteskrankheiten, hrsg. v. O. Bumke, Bd 8, T. 4, S. 147, 315, B., 1930, Bibliogr.; W a g-ner-Jauregg J. Fieber- und Infektionstherapie, Wien ua, 1936; Weitbrecht HJ Psychiatrie im Grundriss, S. 216, B. - NY, 1973.
D. S. Ozeretskovsky.
Advantages and disadvantages of treatment
Advantages:
- the patient avoids the unpleasant consequences of neuritis, such as synkinesis and contracture;
- when performing gymnastics, the recovery process occurs much faster;
- Getting the first progress from doing the exercises, the patient begins to feel more confident and his emotional state improves.
Flaws:
- the need to maintain discipline and do exercises every day in full;
- Unfortunately, you won’t be able to get an immediate effect. To achieve noticeable results, you will have to spend at least a month on classes.
Therapeutic exercises give good results for neuritis of the facial nerve. Most importantly, do not forget to consult with your doctor and exercise therapy instructor before you begin the exercises.
Strictly adhere to all the rules and advice when performing the treatment complex , and take a photo of your face before starting the course to easily track all changes.
Facial nerve damage is a fairly common diagnosis. The disease can affect a person at any age; it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible and begin to follow the recommendations.
How long does paralysis last?
If the cause of the disease is hypothermia, then in 95–99% of cases patients recover completely. If the patient is simultaneously diagnosed with a stroke or HIV, then full recovery will not occur.
Bell's palsy is treated in hospital. The patient needs hormones, neuroprotectors and other medications, physiotherapy and facial massage, as well as special physical therapy. Improvement, according to doctors, with inpatient treatment occurs on average after 7-10 days, recovery - after 14 days.
— At home, it is not always possible to receive proper treatment, and then a cosmetic facial defect may remain for life: the facial muscles on the affected side atrophy, the skin hangs, the eye does not close when you close your eyes and during sleep. And even plastic surgeons won’t help here,” explained Mikhail Moiseev.
However, the best treatment is prevention. At the very least, don’t rush to put your warm jacket away in the closet.
As Life previously reported, hypothermia also triggers sexually transmitted diseases.
Introduction to the topic
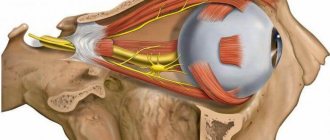
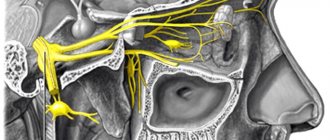
Weakening of the muscles of one half of the face, the inability to control facial expressions, and perform chewing movements - all these are manifestations of neuropathy of the facial nerve. The nerve ending from the brain exits into the narrow ear canal, so any swelling or compression due to damage to the jaw can lead to unpleasant consequences.
The causes of the disease can be infectious diseases, bruises and damage to the temporal lobe, otitis media, viral diseases, and blood circulation disorders.
You can cope with the symptoms and prevent the consequences of such lesions with the help of exercise therapy of the facial nerve. A set of exercises is prescribed by the doctor, based on the area of the lesion and the reasons for the manifestation of such a symptom.
diagnostics
There is no specific test for Bell's palsy. Your doctor will look at your face and ask you to move your facial muscles by closing your eyes, raising your eyebrow, showing your teeth, and frowning, among other movements.
Other conditions such as stroke, infections, Lyme disease, and tumors can also cause facial muscle weakness, mimicking Bell's palsy. If you are not sure why you have symptoms, your doctor may recommend other tests, including:
- Electromyography (EMG). This test can confirm the presence of nerve damage and determine its severity. EMG measures the electrical activity of a muscle in response to stimulation and the pattern and speed of electrical impulses along the nerve.
Scanning images. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan may be needed to rule out other possible sources of pressure on the facial nerve, such as a tumor or skull fracture.
The benefits of exercise therapy for damage to the facial nerve
It is worth starting physical therapy for paresis of the facial nerve from the first days of illness in order to avoid paralysis and exacerbation of physical conditions.
Exercise therapy treatment consists of three stages:
- the basic stage lasts up to 10 days, includes positional therapy;
- main – up to 3 months;
- residual – can last a lifetime.
In addition to performing gymnastics and physical exercises for neuritis, for inflammation you need to follow the recommendations:
- sleeping on the affected side;
- chewing food on both sides;
- sitting with your head tilted towards the affected area for 5 minutes several times a day (3-4 times), supporting your cheek with the back of your hand;
- tying the scarf so that the muscles on the unaffected side are pulled towards the affected side.
Exercises during the remainder of the period
The final period of therapy begins 4 months after the onset of the disease and lasts 2-3 months until the symptoms of neuritis disappear. At this point, the patient has practically restored the motor activity of the facial muscles, there is practically no asymmetry observed, however, he should continue exercise therapy to consolidate the result.
During this period, the main emphasis is on physical therapy. The patient should continue to perform the basic exercises daily, but the intensity and frequency can be reduced. The decision to stop gymnastics is made by the attending physician.
Set of exercises
Exercise therapy in the early period for neuritis of the facial nerve is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the healthy side and stimulating the muscles on the affected side.
In the basic period, it is shown to tense and relax healthy muscles, work with facial tendons responsible for laughter, smiling, develop articulation, pronouncing the sounds [p], [b], [v], [f], [m], [o], [ y].
You can also combine consonants and vowels:
| A | ABOUT | U | AND | Y | |
| B | BA-BA, AB-AB | BO-BO, OB-OB | BU-BU, UB-UB | BI-BI, IB-IB | WOULD-WOULD, YB-YB |
| P | PA-PA, AP-AP | PO-PO, OP-OP | PU-PU, UP-UP | PEE-PEE, IP-IP | PY-PY, YP-YP |
| IN | VA-WA, AB-AV | VO-VO, OV-OV | VU-VU, UV-UV | VI-VI, IV-IV | YOU-YOU, YV-YV |
| F | FA-FA, AF-AF | FO-FO, OF-OF | FU-FU, UV-UV | FI-FI, IF-IF | FY-FY, YF-YF |
| M | MA-MA, AM-AM | MO-MO, OM-OM | MU-MU, UM-UM | MI-MI, IM-IM | WE-WE, YM-YM |
The main stage of treatment of facial nerve paresis using exercise therapy consists of performing the following exercises:
- Frown and move your eyebrows up and down.
- With your eyes closed, perform circular movements with your eyeballs (holding the eyelid of the affected eye).
- Smile with a closed mouth.
- A smile with the mouth wide open, showing teeth.
- Squint and open your eyes wide.
- To frown.
- Exhale air with your head down, making “snorting” (vibrating) movements with your lips.
- Flare your nostrils.
- Perform movements as if whistling.
- Lift your upper lip up and lower your lower lip, exposing your teeth.
- Blow on a lit candle or match.
- Puff out your cheeks.
- Pull in your cheeks.
- Drive air from one part of the mouth to another.
- Puff out your cheeks and release air.
- Move the corners of your mouth down.
- Stick out your tongue.
- Roll your tongue into a tube.
- Move your tongue sticking out in different directions, left and right and back and forth.
- Make the mouth a tube or a “duck”.
- Follow with your eyes objects or a finger that moves in a circle in different directions.
- Place the upper part of the lips over the lower part.
- Move your tongue over your teeth and gums with your mouth closed.
Therapeutic exercises for neuritis of the facial nerve.
LH is carried out individually or in a small group method while sitting on a chair in front of a mirror.
The set of exercises for neuritis of the facial nerve is divided into three parts:
1). Exercises for the shoulder girdle while sitting on a chair are included to improve blood circulation in the head and neck area. (For example, move your arm to the side and look at it; place your hands on your shoulders - rotate your arms clockwise and counterclockwise; raise and lower the upper shoulder girdle, and so on).
2). Special exercises are exercises for facial muscles: mouth, cheeks, eyebrows, eyes within the symmetry of the face, that is, during therapeutic exercises we try to prevent the face from skewing in the healthy direction. To do this, we intuitively hold the muscles on the healthy side with our hand, making sure that they do not work at full strength (in other words, the muscles on the healthy side of the face “play giveaway”), and on the sore side we tighten the muscles, achieving normal, full-fledged symmetrical movement. That is, we help “correct” the face with our hands.
3). We definitely include exercises for the articulatory apparatus with the pronunciation of sounds and words. We combine five vowel sounds (a, o, u, i, y) with various consonant sounds, but the obligatory ones are b-p, v-f, m, since these are the sounds that help to maximally use the facial muscles. It is important not just to pronounce sounds, but to train the articulatory apparatus, so we achieve expressive lips for each sound.
| A | ABOUT | U | AND | Y | |
| B | BA-BA, AB-AB | BO-BO, OB-OB | BU-BU, UB-UB | BI-BI, IB-IB | WOULD-WOULD, YB-YB |
| P | PA-PA, AP-AP | PO-PO, OP-OP | PU-PU, UP-UP | PEE-PEE, IP-IP | PY-PY, YP-YP |
| IN | VA-WA, AB-AV | VO-VO, OV-OV | VU-VU, UV-UV | VI-VI, IV-IV | YOU-YOU, YV-YV |
| F | FA-FA, AF-AF | FO-FO, OF-OF | FU-FU, UV-UV | FI-FI, IF-IF | FY-FY, YF-YF |
| M | MA-MA, AM-AM | MO-MO, OM-OM | MU-MU, UM-UM | MI-MI, IM-IM | WE-WE, YM-YM |
In addition, it is necessary to practice pronouncing words syllable by syllable. For example, milk, hut, thekla, beet, doll, snail, audience, bagels, air, drum(s), stick(s), grandmothers, cone, cat, kidney, barrel, boy, barefoot, beads, shoes, toys, raisin, cuckoo, grandma, folder, mother, slippers, puma, etc.
Then, when the condition improves, we include reading children's fairy tales in front of the mirror in order to control the symmetry of the face while reading and the expressive position of the lips when pronouncing sounds.
Clinical picture
P. p. is a serious disease of the whole organism, and its most striking manifestations are disturbances in mental activity. The main syndrome is progressive total dementia (see): the intellect suffers severely, disorders of judgment appear early, criticism and especially self-criticism disappear. There is no awareness of the disease, memory sharply decreases, and confabulations occur (see Confabulosis). Manifestations of dementia intensify due to the often observed euphoria (see Psychoorganic syndrome). Neurol. the symptoms consist of speech disorders, primarily in violation of articulation - dysarthria (see). Speech becomes unclear, slurred, especially when pronouncing long words, the patient skips or rearranges syllables, and does not pronounce the endings of words. Handwriting becomes uneven, individual letters and syllables drop out of words. The timbre of the voice changes, it becomes dull. The patient's face is expressionless and mask-like, because the innervation of the facial muscles is disrupted, and blepharoptosis occurs (see Ptosis). Tendon reflexes are often increased and uneven, except in cases of taboparalysis (see). Due to sphincter disorders, patients cannot retain urine and feces. As a result of vasomotor and trophic disorders, swelling, brittle bones, muscle atrophy, and bedsores appear.
Based on psychopathol. manifestations, four stages of the disease are distinguished: latent (from infection with syphilis to manifestations of P. p.), the stage of initial manifestations, the stage of full development of the disease and the stage of marasmus (see). In the latent stage, headaches, dizziness, fainting may occur, and in some cases characteristic changes in the cerebrospinal fluid are observed (see). The stage of initial manifestations is characterized by increased fatigue, irritability, and weakness. Patients complain of loss of strength and decreased performance, although they can still perform their usual work to some extent. Previously, such conditions, due to their external resemblance to neurotic symptoms, were incorrectly called preparalytic neurasthenia. In some cases, at the stage of initial manifestations, depressive and delusional disorders are observed - anxious depression with hypochondriacal statements, anxious-agitated depression, delusional ideas of jealousy, persecution, poisoning; as the symptoms of dementia increase, these endoform disorders disappear. Memory loss is detected very early. Certain actions indicate a violation of criticism. The sphere of desires is upset, patients become gluttonous and erotic. The increase in these disorders indicates the transition of the disease to the stage of full development, the edges manifest themselves in different wedges. forms. The expansive, or classic, form (previously widespread) is more common in men. It is characterized by the presence of manic excitement with the manifestation of anger, grandiose delusions of grandeur (see Delirium). The dementia form is characterized by increasing dementia against the background of inactive euphoria. In the depressive form, a depressed mood develops, often with anxiety and a desire for suicide (see Depressive syndromes), and absurd hypochondriacal delusions of nihilistic content are often observed. The circular form, first described by S.S. Korsakov, occurs with alternating states of excitement and depression. The hallucinatory-paranoid form is characterized by the development of paranoid syndrome (see) with predominantly auditory hallucinations and delusions of persecution. In the catatonic form, a stuporous state occurs (see) with phenomena of mutism and negativism (see Catatonic syndrome). In the stage of insanity, conscious activity ceases, speech disappears, patients make inarticulate sounds, and cannot stand or move. At this stage they die from an intercurrent disease.
Along the way, a particularly malignant agitated form is distinguished (galloping paralysis) with sharp motor excitation and disturbance of consciousness of the amentive type and the so-called. stationary paralysis, in which there is a slow course with a gradual decrease in intelligence and lethargy.
Atypical forms of P. p. are youthful and senile P. p., as well as Lissauer’s palsy and taboparalysis (see). Juvenile P. p. develops on the basis of congenital syphilis; usually begins at the age of 10-15 years. Sometimes it is preceded by signs of congenital syphilis, in other cases it occurs in children who were previously considered healthy. Most often occurs in the form of dementia; Local symptoms are often observed, for example, optic nerve atrophy. Senile P. p. occurs over the age of 60 years and is characterized, first of all, by a long latent stage (up to 40 years). Wedge, the picture resembles senile dementia (see) with severe memory disorders; sometimes the disease occurs like Korsakov's syndrome (see).
Lissauer's palsy and taboparalysis are characterized by a relatively slow progression of dementia. With Lissauer's palsy, there is a tendency to local damage to the brain, mainly the parietal lobes, with the development of aphasia (see), agnosia (see), apraxia (see), apoplectiform and epileptiform seizures. Taboparalysis is a combination of symptoms of P. p. and tabes dorsalis (see), and spinal disorders precede the development of symptoms of P. p., usually its demented form.