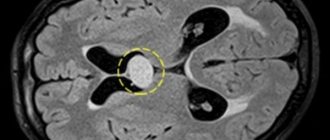
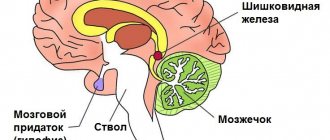
A subependymal cyst is a benign brain formation and develops from the ependyma (tissue lining the inside of the brain ventricles).
In the vast majority of cases, a subependymal cyst of the brain does not affect the child’s health.
Characteristics
It is necessary to differentiate two concepts: pseudocysts and true cystic formations.
| View | Characteristic |
| Pseudocysts | Rather, they refer to intrauterine developmental defects. They do not have an epithelial lining. They are localized under the ependyma of the lateral ventricles of the cerebral hemispheres in the region of the lateral angles of the anterior horns and bodies of the lateral ventricles, as well as in the border region between the head of the caudate nucleus and the optic thalamus. |
| True (arachnoid, retrocerebellar, cerebrospinal fluid) | They have an epithelial lining. As a rule, their appearance is associated with hemorrhages, trauma and other external causes. |
For this reason, a subependymal cyst in a newborn child would be more correctly called a pseudocyst.
Features of the pathology:
- The cavity is filled with serous fluid without signs of infection. There are no signs of hemorrhage.
- More often it occurs in the ependymal tissues of one ventricle, less often in two.
- The wall is formed by a layer of glial cells (the structure is thin-walled because there is no internal lining).
- It has no tendency to grow because it fills with liquid extremely slowly.
- It has a round shape, small size and clear and even contours.
Infants with such a pathology require clinical monitoring by a neurologist (periodically monitored by ultrasound, MRI/CT). No treatment required.
The pathogenesis is based on intrauterine disruption of the normal development of ependyma in the fetus (cell hyperplasia, slowdown in their differentiation). Various external influences lead to disruption of normal cerebral circulation in the fetus, which leads to hypoxia/ischemia and necrosis of areas of the ependyma. This serves as a predisposing factor in the development of pseudocysts.
Education may include:
- endophytic location - in the wall of the ventricles of the brain in place of the underdeveloped ependyma;
- exophytic location - on top of the ependyma with prolapse directly into the lumen of the ventricles.
Consequences of a subependymal cyst in a newborn baby
The most common complications that arise during pregnancy and during negative labor include a subependymal cyst in a newborn child.
More than 10-12% of children whose pregnancy occurred with pathologies were born with this cystic formation.
Concept
All cysts have a similar structure - they are cavities in which fluid is located - and can form in different parts of the body.
A subependymal cyst forms in the brain under the influence of one or more unfavorable factors.
Small cystic formations do not cause significant negative consequences and
resolve on their own over time , but large cysts that are poorly located require increased medical supervision.
What are the consequences of cephalohematoma in newborns? Find out about this from our article.
Reasons for appearance
A cyst is formed under the influence of the following factors:
- Hypoxia. It develops under the influence of various negative influences, including anemia, diseases of the lungs, heart, kidneys, smoking, diabetes, infections, placental abruption.
- Birth injuries. If a child suffers head injury during childbirth, the risk of developing cystic formations increases. This can occur with narrow birth canals, large fetal head sizes, deformities of the pelvic area, and rapid labor.
- Toxicosis. Severe toxicosis at the beginning of pregnancy negatively affects the development of the fetus.
- Deficiency of vitamins and microelements. Develops with insufficient maternal diet and starvation.
- Anemia. With this disease, the concentration of hemoglobin, responsible for the delivery of oxygen, decreases. With anemia, the fetus develops hypoxia, it lags behind in development and is vulnerable to various infectious diseases.
- Hemolytic disease. A discrepancy between the Rhesus of mother and child leads to the fact that the immune system begins to attack the fetus. The child's hemoglobin disintegrates under the influence of antibodies, and multiple organ lesions develop. This disease can lead to fetal death.
- Excess or lack of amniotic fluid. Polyhydramnios increases the risk of pathologies of the brain and gastrointestinal tract of the fetus. Also, if there is too much water, it can break prematurely and the baby will suffer. If there is a lack of amniotic fluid, the fetus is not sufficiently protected from external mechanical influences and pressure from internal organs.
- Multiple pregnancy. If a woman carries more than one fetus, there is a chance that the children will be born with low birth weight. During pregnancy and childbirth, complications during multiple pregnancy are also greater than during normal pregnancy.
- Infections. Any infectious diseases, from diphtheria to a common cold, can have a negative impact, since the fetus is extremely vulnerable to the effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
Localization and symptoms
Cystic formations form in areas of tissue necrosis , preventing the spread of the lesion, and occur in both the left and right lobes of the brain.
Most often they form in the area of the ventricles: cavities in the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The symptoms observed with a cyst are closely related to its location, size and growth rate. Different areas of the brain perform specific functions, and when tissue is compressed, the work of these areas is disrupted.
- The occipital region is responsible for vision, so the child experiences symptoms associated with impaired visual perception: diplopia, myopia, blindness.
- The temporal region controls auditory perception: hearing may deteriorate or disappear completely.
- The cerebellum affects coordination of movements: problems may arise when holding the head, sitting, holding toys, and walking.
- The pituitary gland produces hormones, including growth hormone, which is extremely important for the development of the baby. Developmental delays occur, and in rare cases dwarfism develops if the child has genes that affect this. In this case, a cyst in the pituitary gland becomes a provoking factor.
- Damage to the frontal lobe is characterized by disturbances in motor functions and disruptions in the stages of speech formation: the late appearance of humming and babbling.
Common symptoms include :
- sleep problems;
- high level of anxiety;
- reluctance to drink milk from the breast;
- weight does not gain or even falls;
- pathological muscle tone;
- continuous or very frequent screaming for no reason;
- tremor in the limbs, excessive movements;
- severe regurgitation;
- periodic loss of consciousness, up to a coma;
- pathologies of the fontanel: it may pulsate, look swollen, tense;
- epileptic seizures.
In the absence of therapy, symptoms will continue to progress, and focal lesions will become more acute as the child grows.
Forecast and consequences
If a cystic formation prone to growth is not detected in time, it will begin to increase in diameter and gradually compress nearby tissues.
Focal symptoms will begin to progress: for example, a growing cyst in the occipital zone initially manifests itself only in some visual disturbances, but as it grows, the child begins to go blind.
Cystic formations also lead to increased intracranial pressure, characterized by the appearance of symptoms such as:
- intense headache;
- feeling of tightness in the head;
- apathy;
- weakness;
- pronounced degree of fatigue;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diplopia;
- fainting.
If the cyst is large and there is no treatment for a long time, this can lead to disruption of the formation of the skull bones (the fontanel does not ossify), divergence of cranial sutures, which leads to retardation in physical and mental development, and in severe cases can result in death.
Cysts can also cause a stroke.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the size of the cyst, the timing of its detection, and the degree of growth intensity. Small cysts that do not increase in diameter do not lead to significant negative consequences .
And, accordingly, large cysts that are prone to growth pose a threat to the health and life of the child, and even after timely surgical intervention, disturbances may remain.
Read about the causes and treatment of hydrocele in children here.
Types and forms
Treatment, risks and symptoms depend on the characteristics of the cystic formation.
Based on size, cysts are divided into:
- Small (less than 3 centimeters). Usually they do not pose a significant threat to the child, resolve on their own and rarely require treatment: it is enough to only periodically monitor it during routine examinations.
- Large ones. The larger the cyst, the more risks it carries for the child. Large cysts require treatment, including surgery.
According to trends in educational growth, education can be divided into:
- Increasing. If the cyst grows rapidly, surgery and other serious measures may be required, since as the cyst grows, it compresses the brain tissue and impairs its functioning.
- Not increasing. If the cyst is small and does not increase in size, the prognosis is favorable.
By the number of chambers in the cyst:
- Single-chamber. Less dangerous and better treatable.
- Multi-chamber. They are more difficult to diagnose due to symptoms that are inherent in other pathologies. Worse to treat.
In addition to the subependymal cyst, there are other types of cystic formations in newborns:
- Arachnoid cyst. Appears due to injuries, infectious lesions, is prone to rapid growth and requires urgent treatment.
- Choroid plexus cyst. Occurs during intrauterine development under the influence of herpes. In most cases it disappears on its own.
How to recognize craniosynostosis in children? Find out the answer right now.
Diagnostics
Subependymal cysts are detected using ultrasound (neurosonography).
This diagnostic procedure is accurate, completely safe and does not cause any discomfort to the child.
ultrasound is used for children under one year of age whose fontanelles have not yet ossified. Routine neurosonography is performed when the child is one month old, but if the pregnancy was accompanied by pathologies and the birth was difficult, it may be performed earlier.
MRI and CT are indicated as additional diagnostic methods, which provide more accurate information regarding the characteristics and location of the cyst.
But these procedures are used no more than twice a year: infants are vulnerable to radiation.
Principles of treatment
The basis of treatment is working with the cause that provoked the occurrence of cystic formation: hypoxia and its consequences are eliminated.
Treatment of the disease takes place in several stages:
- The first minutes of birth. In case of hypoxia that occurs during labor, immediate initiation of resuscitation measures is required to reduce the risk of cyst formation. When resuscitating newborns, fluid is removed from the oropharynx, trachea and nasopharynx, artificial respiration is performed, and devices for respiratory support can be used: an oxygen tent, oxygen masks, nasal cannulas.
- The first three days. During this period, the newborn’s condition is monitored by a neurologist, who prescribes medications, a massage course and physiotherapy, which help eliminate oxygen starvation and improve the child’s condition. The following medications can be prescribed to children: injections of vitamin B12, Cortexin, Diacarb, Asparkam.
- Childhood. Drugs are prescribed that improve metabolic processes in the brain, promote the formation of skills, and increase cognitive activity - nootropics, for example Pantogam. Vitamin therapy is also indicated.
If the cyst is actively growing and is large, surgical treatment is indicated : fluid is removed from the cyst using an endoscope. In severe cases, open brain surgery may be required.
Dr. Komarovsky, a famous pediatrician, claims that cystic formations identified during neurosonography in infants do not pose any danger and do not require treatment.
Prevention
To avoid the development of a subependymal cyst , it is necessary to exclude causes that can cause hypoxia and other disorders.
- The diet of a pregnant woman should be varied and include a sufficient amount of nutrients;
- It is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- treat any infectious diseases in a timely manner and under the supervision of a doctor;
- avoid exposure to toxic substances.
If these recommendations are taken into account, the likelihood of developing a subependymal cyst will be significantly reduced, and the fetus will develop harmoniously and without complications.
Recommendations for the treatment of strabismus in children can be found on our website.
Dr. Komarovsky about a brain cyst in this video:
We kindly ask you not to self-medicate. Make an appointment with a doctor!
Source: https://pediatrio.ru/k/kista/subependimalnaya-u-novorozhdennogo-rebenka.html
Treatment
A subependymal brain cyst in a newborn that is small in size cannot be treated and does not in any way affect the life and development of the child.
Indications for surgical treatment
Surgery to remove a cyst is required in the following cases:
- fast growth;
- serious disturbances in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (development of hydrocephalus);
- suspicion of a malignant tumor (in this case we are not talking about the degeneration of a subependymal cyst, but about the presence of other formations that were not correctly interpreted);
- significant increase in intracranial pressure;
- convulsive syndrome that cannot be controlled with medication;
- suspicion of hemorrhage.
Typical signs of hydrocephalus:
- increase in head volume in a short period of time;
- pulsation and bulging of the fontanelles;
- divergence of the skull bones, which leads to visible deformation of the head;
- lag in psychological development as a consequence of ischemia of brain tissue under constant fluid pressure.
Preparing for surgery
Preparation for surgery includes the following studies:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- coagulogram;
- blood chemistry;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- Ultrasound;
- CT/MRI.
How to treat a pseudocyst of the brain of the head
Treatment of pseudocysts in children is not required.
Usually education occurs independently during the first year of life. The development of the child: his mental, emotional and physical state is not affected. To be on the safe side, a neurologist may prescribe Actovegin or a similar drug that improves blood circulation in the brain. But if during the first year the cystic formation remains unchanged, intracranial pressure has increased, medicinal, if indicated, manual therapy will be required.
Massage for pseudocyst is prescribed to improve the neuro-reflex and musculoskeletal system. It is carried out exclusively by a specialist. There are contraindications.
What to do if the pseudocyst has not resolved
In this case, the diagnosis of pseudocyst was made incorrectly.
Errors are rare, but they do occur. After determining the exact diagnosis, the doctor determines the symptoms of the formation and determines what consequences the disease led to. The likelihood of affecting the development of the child, the occurrence of convulsions and seizures is minimal, but if the cystic cavity exceeds the permissible size, anticonvulsant drugs are prescribed.
The main task of the specialist is to determine the causes of formation. Therapy is mainly directed against the catalysts of deviations and combating the symptoms of the disease. The course of treatment is aimed at improving blood circulation and metabolism. Homeopathy can be beneficial, but it is prescribed with extreme caution.
Folk remedies for cerebral pseudocysts
Folk remedies in treating a child should be used with extreme caution. Most medicinal plants provoke allergic reactions, so you should consult your doctor before use.

Baths and decoctions help relieve symptoms if the formation has reached its maximum size. Herbal baths relieve muscle tension and are a good relaxing and sedative. A decoction of hawthorn, which has an excellent taste, will help your child.
St. John's wort, which helps adults with similar problems, cannot be prescribed! For a child, grass is a strong poison. Before using any method of alternative treatment, it is better to consult a doctor!
A brain cyst is a terrible diagnosis for people who have just become parents. A cyst in the brain is a volumetric formation inside an organ, which is a spherical cavity filled with fluid, which is localized at the site of dead nerve tissue.
Pathology can occur in any area of the organ, be single or multiple. It should also be noted that a cyst is not a tumor-like formation!
Possible consequences
Consequences arise in the event of complications (rupture, suppuration, hydrocephalus) or after surgery:
- Delayed mental and physical development (speech delay, memory impairment). It does not appear immediately, but as the child grows by the age of 2-3 years. This complication is caused by prolonged compression of brain tissue and irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex. Manifests itself in varying degrees (if mild, disturbances will not interfere with normal life activities).
- Epileptic seizures. They arise as a result of reflex injury to brain tissue (disruption of nerve conduction in a separate area of the brain). Status epilepticus occurs rarely.
- Bleeding with the formation of hematomas in the ventricular cavity or in the substance of the brain. A serious complication, which in some cases requires repeated surgery and removal. Total hemorrhage (stroke) occurs rarely in children.
- Brain swelling. Occurs when the brain's aqueduct is damaged. In this case, the cerebrospinal fluid-carrying ducts may become blocked, and hydrocephalus occurs, but as a secondary phenomenon. The complication requires immediate treatment, since if the medulla oblongata is damaged, respiratory or cardiac arrest may occur.
- Accompanying infection with the occurrence of abscesses, encephalitis or meningitis. In this case, a mandatory course of antibiotics in the postoperative period is indicated.
- Focal symptoms (loss of visual fields, hearing impairment, loss of sensitivity). Manifestations will depend on the specific area that was traumatized during surgery.
Complications are relatively rare.
Diagnostics
Monitoring the course of pregnancy in women and preventing various pathologies in the fetus, including subependymal tumors, receives great attention from medical staff. During the entire period of intrauterine formation of the baby, an ultrasound examination is performed at least three times , during which the structure of the brain is assessed.
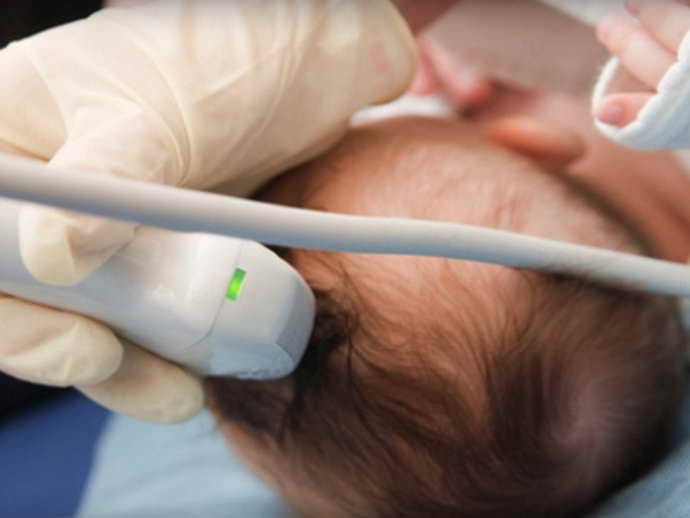
Modern diagnostic methods help diagnose subependymal cysts after the birth of a newborn:
- An ultrasound of the brain is performed through the large fontanelle - it is carried out quickly, painlessly, and allows you to identify the presence of a cyst and its location;
- neurosonography - examination of the conductivity of nerve impulses in brain structures;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging - detects even small subepindymal tumors in newborns;
- electroencephalography – diagnosis of foci of epireadiness.