Passive-aggressive personality disorder is one of the fairly common mental illnesses, characterized by isolation and depressing indifference of the patient to the reality around him. It is quite easy to recognize a person with such a disorder, and, what is especially important, even the closest people should not try to treat it on their own. Only a specialist can help the patient return to normal life.
Features of manifestation
You can suspect the presence of a passive-aggressive behavior pattern based on the following signs:
- A person does not know how to say “no”. He may even agree for the sake of appearance, shake his head, but immediately forget about the promise or deliberately ignore the request. Finding an excuse is not a problem for him.
- The aggressor procrastinates and sabotages the process. Such people will never ask for help and will not admit their own incompetence or unwillingness to do something. They will agree, will delay until the last minute and will let everyone down.
- The aggressor will under no circumstances agree to a direct showdown, but will demonstrate in every way the cruelty and inhumanity of the partner’s actions. In relationships, such people often say “of course, do as you want, you don’t care about me anyway,” but they will never say what they expect and want.
- In moments of quarrels and crisis situations, the partner withdraws into himself and remains silent. Passive aggressors never start screaming or explode. But they can ignore the offenders for weeks, and no one knows what thoughts will visit the person at that moment. Many passive aggressors also exhibit self-aggression and risky behavior.
- Manipulation based on feelings of guilt and pity. The abuser can't ask for help, but he will do his best to get you to offer it. The simplest method is to remind you of some diagnosis or similar story from the past that ended in tears.
- The aggressor wants to appear kind, sweet and pleasant, but combined with suppressed anger, this causes him to do nasty things behind people's backs. If he is jealous or suffers from a sense of injustice, he can file an anonymous denunciation against the “offender,” start a rumor, or ruin his reputation in other ways.
- Shifting responsibility to other people, fate and the universe. Passive aggression is childish, infantile behavior. A person who uses this model is afraid to take responsibility for his own life. Instead, he blames others: they gave him the wrong advice, didn’t guess about his desires, and generally ruined his whole life, didn’t let him finish his studies or get a job, etc.
- Passive-aggressive people prefer to complain, criticize, be sarcastic, use irony, and use sarcasm. They can be rude and cynical in their expressions, but they call it reality and the harsh truth, a statement of facts.
Childhood insults and games of silence gradually bring the partner to a breakdown. Even the calmest and most reasonable person will get tired of fighting against a closed door and sooner or later lose his balance. Then he descends to screams, and the passive-aggressive partner is content with this reaction. After all, this is exactly what he subconsciously sought.
Correction of passive-aggressive behavior
The fight against passive-aggressive personality disorder begins with psychotherapy. In some cases, the use of antidepressants is indicated, they are especially relevant in case of overly pronounced melancholic behavior of the individual, or suicidal threat. It should be noted that by threatening suicide, a person can also manipulate relatives or a psychotherapist. This reaction should be interpreted as an expression of anger, and not depression over the loss of love from family. Therefore, the psychotherapist should guide the person to more adequately express angry reactions.
Behavior with hidden aggression lacks assertiveness. Passivity in expressing aggression (if present) appears due to a person’s acceptance of the role of a victim (and everyone owes him, as if he is weak) or a manipulator (and everyone owes him, as if he is strong). The psychotherapist has an important task to formulate a new attitude in behavior - assertiveness - the ability of an individual to make decisions independently, to be able to say “no”, not to depend on external conditions, assessments and influences, to bear responsibility for decisions and behavior made. In the new role of an assertive person, the principles of passive-aggressive behavior are replaced by adequate communication with the message: “I don’t owe the other person anything, and the other person doesn’t owe me anything, we are each other’s partners.”
Treating passive-aggressive disorders is difficult because the patient lacks the motivation to do so. It is very difficult to establish the right relationship between therapist and patient to achieve a therapeutic effect. If the doctor gives in to hidden manipulators, the treatment will fail. If the patient's demands are denied, the psychotherapeutic contact may be lost. To effectively work with such patients, a highly qualified specialist is required.
Of all the psychological approaches, cognitive behavioral is the most effective. During therapy with techniques of this approach, the patient becomes aware of the social consequences of his passive-aggressive behavior.
Group and individual work is carried out to train coping (coping behavior), social skills are developed. If the client has taken a defensive, oppositional position, the therapist can also use this. For the desired result of therapy, it is necessary to give instructions opposite to what he wants to achieve.
Tips for communicating with such people:
- in working relationships, it is necessary to clearly monitor the actions of a passive-aggressive colleague;
- do not rely on such people for important tasks;
- there is no need to get involved in their games of manipulation;
- in a family, sometimes it is necessary to involve a qualified specialist in case of severe symptoms;
- avoid performing a responsible task together;
- it is necessary to firmly convey a different, alternative point of view;
- remain calm during confrontation so that the person sees that it is not so easy to infuriate others.
, Comments to the post Passive-aggressive behavior are disabled
Passive-aggressive behavior
Passive-aggressive behavior is actions that express anger, but look to the person himself as unintentional mistakes. Usually passive-aggressive behavior is people who, due to their beliefs or upbringing, cannot express anger at another person or refuse him something. .
An example of passive-aggressive behavior: a parent asks a child to clean the floors, but the child does not want to do it. He can’t refuse, so he washes the floors, but it’s so bad that the parent has to wash them. In this case, the purpose of this behavior is to ensure that the parents no longer ask the child to clean the floors. In addition, the child may already be angry about something for his parents, so it gives him special pleasure to watch the parent get angry and wash the floors himself.
One more example. The girl is angry with her boyfriend because he does not propose marriage to her, but she cannot express her anger, because she believes that the girl should not impose herself. She can make a mess at home, knowing that the guy really values order, or be late all the time, knowing how important punctuality is to him.
If a passive-aggressive person refuses, expresses anger, or takes revenge on purpose, he will feel a strong sense of guilt because he believes that doing so is wrong. However, if he does something bad not intentionally, but accidentally, then they rarely get angry at him in return, because it is not his fault. When there is a ban on the expression of negative emotions, they still manifest themselves in behavior in one way or another: either in irritated intonation or in the form of passive-aggressive behavior.
What are passive-aggressive behaviors? One of the most common passive-aggressive behaviors is to forget something important to another person, such as buying something that the other person cannot eat without, or forgetting papers that are important to that person. Constantly being 20-40 minutes late, with which a person is simply completely unable to do anything, is also an example of passive aggression.
The unconscious goal of passive aggression is to get back at another person for something, most often for one's inability to say “no” when that person asks for something. The passive-aggressive person first agrees to do something unpleasant for himself, unable to refuse, and then takes revenge and watches how the other person is upset or angry, and receives unconscious satisfaction from the fact that he is punished.
The second goal is to get away with revenge yourself. If we commit actions that cause anger in other people, then we are punished for this in the form of their dissatisfaction, reciprocal anger, or refusal of some action we need. Passive-aggressive behavior is usually not viewed by others as intentional, and therefore results in avoidance of immediate retribution, although the relationship gradually deteriorates as the other person still becomes angry at such actions and begins to avoid communication.
If you are communicating with a passive-aggressive person and cannot stop communicating with him, then I advise you to ensure that the second goal of such behavior is not realized. When something in another person's behavior angers you, express your irritation and insist that the behavior stop; say that it doesn’t matter to you whether the person does this accidentally or on purpose.
You cannot force another person to act differently, but you can help them understand the purpose of such actions. Most often, in this case, a person will stop doing this if his relationship with you is important to him and if he has reason to think that such actions will affect your communication.
Find and reveal the reasons for passive-aggressive actions, for example, say: “It seems to me that you didn’t want to do this for me, but you didn’t tell me no, and now you forgot this and thus took revenge on me.” Usually unconscious manipulations cannot be carried out further if the person begins to understand that he is taking revenge. This awareness can happen if you repeatedly connect something that may have upset the person and something that he “accidentally” did.
Passive-aggressive behavior (or passive aggression) is a behavior in which expressions of anger are suppressed. Passive resistance to the negative remarks of the opponent is expressed, in which, meanwhile, it is possible to achieve the goals set by the person using this behavior.
The main feature of a passive aggressor is the suppression of anger. He has a lot of resentment, anger, aggression, but he does not know how and is afraid to express negative emotions. Such people never say directly what they want, what they don’t want, what doesn’t suit them and what they are not happy with. Instead, they subtly avoid the conflict, torment you with omissions, and wait for you to guess what they are offended by. For the time being, such a character may seem like a good partner: he doesn’t swear, he doesn’t yell, he agrees with you in everything – he’s a real godsend! But the secret always becomes clear, and the relationship turns into a nightmare. However, a passive-aggressive relative (especially an older one), colleague or girlfriend is also a gift. But why are we all about others - maybe some of these points are about you?
1. They don't say no
To say directly, to your face, that he doesn’t like something, that he doesn’t want to and won’t do it, oh no, a passive aggressor will never dare to do that. He nods his head, agrees with everything, but doesn’t do it. He will “forget” about the deadline, “will not have time” to reserve a table in a restaurant that he really simply did not want to go to, or even break his leg on the way - just so as not to go to the theater with you.
2. They sabotage
If at work a passive aggressive person is given a task that he does not like or in which he feels incompetent, he does not admit it directly, but sabotages and delays until the last moment. Instead of honestly saying, “I’m having problems with this project and I need help,” they indulge in procrastination and demonstrate maximum inefficiency as best they can - in the hope that everything will somehow solve itself and the task will be passed on to someone else.
3. They avoid direct confrontation.
Even when feeling hurt to the core, a passive aggressor will not say it directly, but will send confused messages that should show you how soulless and cruel you are. If such a person is your loved one, then you constantly hear from him something like: “Of course, of course, do as you see fit, why should you worry about how I feel...”
4. They suppress anger
In their picture of the world, any disagreement, dissatisfaction, anger or resentment is better to be swept under the rug, rather than brought out. More than anything else, these people are afraid of open conflict. This often happens to those who were scolded from childhood for any manifestations of feelings, as well as to those who grew up in a very emotionally unstable family, where mother and father constantly swore, and even attacked each other with their fists. Such a child grows up with the feeling that anger is a terrible uncontrollable force, that it is ugly and unbearably shameful, so emotions must be restrained and suppressed. It seems to him that if he gives negative experiences even a little freedom, a monster will burst out - all the anger and hatred that he has been accumulating for years will pour out and burn all living things around.
5. They won't admit how they really feel.
It is clear that, believing in such a terrible power of negative emotions, the passive aggressor does not want to show them - it is better to hide them than to destroy a good relationship (or rather than appear angry). In a couple, the passive aggressor will never be the first to say that something is wrong. If you ask him what happened and why he is unhappy, he answers: “Nothing,” “Everything is fine,” “I’m great.” But his voice from a mile away demonstrates that everything is not at all okay or great. You are trying to figure it out, have a heart-to-heart talk, but it didn’t work out: it’s as silent as in a tank.
6. They play the silent game
When angry, such a partner does not explode, but withdraws and goes into all-round defense. A passive aggressor can remain silent for hours, days, weeks. Doesn't answer your questions, refuses dialogue. This is a way of punishment: this is how you will understand that you did something wrong, that you offended him in some way. What exactly? Where did you make a fatal mistake? What was your incorrigible guilt? Look what you want - everyone can do it! Oh no, in this club of sophisticated torture they will not tell you or explain anything to you - guess for yourself. Suffer, think, remember every word. Punished? What, would it be better if they beat you? No, you can't wait!
7. They provoke you to anger.
And avoiding open adult dialogue, and playing the silent game, and the favorite “Do as you know, you don’t care anyway...” - all this sooner or later brings you to the point of white heat, and you start yelling. Yep, gotcha! This is exactly what the passive-aggressive interlocutor wanted from you (most likely, unconsciously - at least something to justify him). He himself is afraid to express anger, so he transfers this honorable function to you: now he can rightfully consider you bad, angry, unrestrained... Actually, he thought so. Well, of course, he didn’t expect anything else from you. He, of course, hoped that you were not like everyone else, but how could he, naive, dream of such a miracle... In general, having provoked you into a fit of hellish rage, he will go through your self-esteem in full, and for himself he will get another confirmation: anger is a terrible, uncontrollable element, it must be restrained by all means, but building relationships with people openly and sincerely is impossible, it’s dangerous.
8. They manipulate
Passive aggressors constantly press their two favorite buttons: pity and guilt. Saying directly what they want is about as unrealistic for them as saying “no.” And if they need something, they follow complex, roundabout paths. Instead of simply asking you to help carry a heavy box, such a relative or neighbor will remember all his medical diagnoses, make heavy groans and whine that the last time under such circumstances he had a strangulated hernia, a heart attack and hemorrhoids.
9. They do bad things behind your back
They try very hard to show themselves as sweet, kind and want people to like them. But unexpressed anger, anger and envy do not disappear anywhere, but accumulate inside. When they envy someone's success or feel unfairly treated, instead of direct confrontation they choose secret methods of revenge - spreading a nasty rumor about someone, sending an anonymous denunciation to their boss. Yes, these harmless dandelions can ruin your reputation.
10. They pass the buck
As is easy to see, passive aggression is a very infantile, immature behavior. A passive aggressor does not feel like he is the master of his fate; he constantly blames life, circumstances, and other people for everything. Suddenly you find yourself to blame for all your loved one's misfortunes. Everything counts: you were not attentive enough and did not show sympathy, you did not guess why he was offended, you gave him unsuccessful advice, because of which everything went wrong, and simply the fact that he connected his life with you (or that you were born to him, if suddenly it was one of your parents) ruined this life completely.
Passive-aggressive personality disorder is a condition in which people express anger and negative feelings covertly through their actions instead of directly taking out aggression on others. It is characterized by a tendency towards obstructionism, constant procrastination, stubbornness, feigned forgetfulness and deliberate inefficiency in all matters. People with a passive-aggressive personality type constantly complain about everything, are in a depressed state, actively express their pessimistic attitude and are unyielding in everything. Very often they try to realize themselves in dependent relationships, finding satisfaction in resisting all the partner’s attempts to achieve adequate productivity, productive independent work, equal returns in household chores, etc.
General information about the disease
Social conflicts and communication difficulties can occur in any person. They do not indicate any personality deviations. But in some cases these manifestations become pathological. Passive-aggressive personality disorder is characterized by the following features:
- a person tends to think in a negative way, he is pessimistic, gloomy, set up for failure;
- there is a belief that people around him are negatively opposed to him;
- the patient denies his own role in certain circumstances where he is guilty, tends to refer only to external factors;
- he has a fear of disapproval of his own words and actions from society;
- the patient is convinced that his personal freedom is being limited, and often considers himself offended and insulted.
To assert themselves, people with passive-aggressive personality disorder tend to assert their rights through irritation and aggression. At the same time, they may not express their dissatisfaction for a long time, hiding it from others.
Clinical picture
Passive-aggressive individuals usually cannot stand up for themselves and speak directly about their wants and needs[1]. At the same time, they are constantly irritated, dissatisfied and disappointed with something or someone [1]. Patients constantly look for shortcomings in leaders or people to whom they are subordinate, while they make no attempts to free themselves from their dependent position[1].
Communicative behavior in patients is of a hostile-subordinate nature[1].
This personality disorder very often leads to work maladjustment; a longitudinal study showed that only less than half of patients retain a job or work from home[1].
| This section is not completed. You will help the project by correcting and expanding it. |
Causes of the disorder
Experts believe that a negative example of such behavior in parents becomes a serious risk factor in the development of passive-aggressive disorder in a child. Other reasons may be:
- chronic stress arising from conflicts in the family and at work;
- the emergence of transference and identifications. A person can identify with an aggressive person due to strong emotions, transferring to himself the character traits of a complete stranger;
- upbringing with authoritarianism, total control, overprotection.
Passive aggression is provoked by constant demands from parents to contain emotions. As a result of this, a person is unable to express them and can translate feelings into aggression towards other people. Very often, outwardly pleasant and reserved people, brought up in this way, are internally overstrained, filled with the desire to restore a certain justice to them alone.
The human psyche includes two main components: sexuality and aggressiveness. The latter is the driving force through which the desired is achieved. The leading emotion associated with it is anger.
Although many consider anger a negative manifestation, it is thanks to this quality that people survive. When aggression is suppressed and contained, negative energy accumulates inside. This is very dangerous for mental health.
The ability to suppress anger develops in childhood. A small defenseless child cannot be on equal terms with his parents: defeat them with actions or defend himself verbally. Children are forced to obey and restrain themselves.

The suppression of anger is an unfinished reaction of the body. All emotions are divided into a spectrum of hormones to which the body reacts. Anger is expressed by clenched fists, jaws, hypertension, tachycardia. This is not controlled by the brain, but appears at the level of instincts. If there is a physical or verbal threat, then reflexes are triggered involuntarily and irrevocably.
Children physically experience all emotions, but cannot often express them due to parental prohibitions. Therefore, gradually the child learns to suppress anger using two methods of reaction:
- Constantly silent and patient. When a child is tired of keeping everything to himself, he experiences an uncontrollable attack of aggression.
- Does not notice his own anger, which forms a certain behavior. The child is always dissatisfied, creates conflicts, blames everyone, and is constantly indignant.
Thus, passive aggressive behavior comes to us from childhood. Over the years, the disorder becomes an integral part of the character. Therefore, people do not even notice that they have such a mental disorder, especially if they do not know exactly how the disorder manifests itself.
Causes
Most often, passive-aggressive disorder develops in children who observe similar behavior from their parents and adopt this behavior pattern.
A child’s tendency toward opposition also contributes to frustration if the child manages to “involve” adults in the game and evoke the expected emotions in them.
Other factors:
- conflicts based on episodes of disobedience, coercion and subordination;
- conflicts over the manifestation of autonomy and independence with the accompanying reluctance to provoke aggression in parents and people replacing them;
- transfer of aggression.
Overprotective and authoritarian behavior of parents creates favorable conditions for the development of passive-aggressive disorder.
The child is forced to hide and suppress his emotions and “please” the stereotypes that are inherent in his parents.
For example, a mother forbids her daughter to scream and vigorously show her joy, arguing that “a girl should behave with restraint.”
If the family regularly uses sanctions and punishments for offenses or actions that are displeasing to adults, the child will also suppress his own emotions and hide his irritation in order to avoid unpleasant consequences.
But at the same time, hidden aggression remains, and if it is impossible to express it openly, the baby reacts through “passive manifestation.”
A potentially dangerous period is the so-called “three-year-old crisis.” For the first time, the child manifests himself as an independent person, tries to get rid of obsessive guardianship and acts in spite of adults.
If during this period parents suppress the personality, the person will “get stuck” at the stage of crisis thinking and negativism.
Symptoms of Passive-Aggressive Personality Disorder
Passive-aggressive disorder is easy to recognize in everyday life. It manifests itself in the following acts of behavior:
- frequent complaints about loved ones, friends, colleagues;
- writing reviews in the book of complaints and suggestions in the absence of objective reasons;
- drawing up reports to superiors, which highlight the guilt of employees, because of which the patient considers himself to be a victim.
People with this disorder are characterized by the appearance of automatic thoughts and ideas that are negative in nature. Patients always choose the path of least resistance and move away from their colleagues around them. They negatively interpret any events in life and extend negativism to all their behavior.

They follow the path of minimal resistance - they put things off until later, do them poorly, with a long delay. In any difficulties, a person expresses his dissatisfaction with his boss and other people in power. As a rule, outbursts of anger occur rarely. Most often, dissatisfaction manifests itself passively. People sabotage activities and subtly persuade others to do the same.
The predominant emotions in a person with passive-aggressive personality disorder are anger and irritation. They arise from a constant feeling of being undervalued. At the same time, the person himself cannot achieve professional and personal goals, which confirms his feelings. Patients do not understand that their attitudes lead to this. They do not feel responsible for personal failures.
- Passive-aggressive behavior is a way to express negative feelings in an indirect way.
- The pattern of negative attitudes and passive resistance emerges during adolescence and manifests itself in different contexts. You may notice four or more points in it.
- Passive resistance to performing routine professional tasks.
- Complaints about misunderstanding and lack of acceptance by others.
- Sullenness and quarrelsomeness.
- Criticism and contempt of authorities without reason.
- Showing envy and resentment towards those who are more fortunate.
- Exaggerated and constant complaints about failures.
- It does not appear only during depression and dysthymic disorder.
- Alternating between hostile defiance and repentance.
- Sullen and irritable mood and negative outlook.
Consequences
A person with passive-aggressive disorder does not feel like he is the master of fate, cannot control circumstances and act based on constructive considerations.
He is always pessimistic .
As a result of infantile behavior and a “blaming position,” a person cannot achieve success in the professional and personal spheres. It is difficult for him to establish contacts, and other people, as a rule, try to avoid close communication with a passive aggressor.
Distress , which is an integral companion of the disorder, negatively affects the emotional and physical health of a person (through the mechanism of psychosomatics). There is a high probability of developing concomitant mental disorders.
If, against the background of the disorder, a person is experiencing a crisis in all areas of life, the patient may experience suicidal thoughts and corresponding attempts.
Possible complications
The main negative consequence of passive-aggressive disorder is social maladjustment. People around the patient, due to constant negativism, attempts at sabotage and denial of responsibility, begin to move away from communicating with him. This confirms his confidence in his own thoughts and leads to increased symptoms.
Depressive patterns occur in 50-60% of patients. They tend to constantly progress and significantly worsen the prognosis. Alcoholism and drug addiction develop against the background of a negative perception of the world around us. Patients use them to avoid reality. The ability to hide behind an imaginary euphoria allows them to break out of the vicious circle, at least for a while.
Psychosomatic disorders are characterized by the occurrence of symptoms of diseases of internal organs against the background of psychological disorders. Patients with passive-aggressive behavior complain of discomfort, chest pain, frequent headaches, dizziness, and sensory disturbances in the extremities.
Symptoms and signs of the disorder
Passive-aggressive personality disorder has a number of characteristics. Five of them are enough to diagnose a disorder of this type:
- Red tape in various areas of activity - performing work, tasks, assignments, promises, obligations to relatives and friends. A person constantly postpones the moment of solving a problem - he finds a real explanation for why he does not begin to act actively, delays execution, and does not complete what he started. This creates difficulties for both the person with the disorder and those around them.
- Without sufficient grounds, they often protest against demands or requests made on them, considering them unreasonable and devoid of common sense. We are convinced that people who put forward such demands do not understand the situation and do not realize their uselessness and meaninglessness.
- Individuals with passive-aggressive disorder are moody, gloomy, and irritable. They get into arguments and give arguments in situations where they are asked to do something they don’t want to do. Argumentation comes down to the desire to prove that this is not necessary. The desire of others to force them to make some effort, to be active, spoils their mood, offends them, and changes their attitude towards those who are trying to force them to act. They perceive this as violence, as an unnecessary activity that infringes on their rights, as someone’s whim.
- They reject useful advice related to eliminating errors and improving the productivity of their work and enter into discussions. They may try to logically justify the inconsistency of these “teachings,” use transference, and project their shortcomings onto others, especially those who criticize them. They focus on events and facts from the past, trying to show that these people behaved incompetently and unprofessionally, and therefore have no moral right to lecture them or make any demands.
- Without sufficient grounds, they criticize and discredit those who occupy a more authoritative position.
- If they are not interested in work, then partly consciously, and partly unconsciously, they do the work so slowly that the employees working nearby become irritated and lose patience. They often make mistakes in their work, do it in the wrong way, and perform the task incorrectly. They ensure that others do this work in the future.
- They sabotage the attempts and efforts of others to do something in the production cycle at work, at home. A link in this chain of work is not performed or is done with serious errors.
- Fails to perform duties that are part of the work cycle. They avoid work, citing forgetfulness and absent-mindedness.
- They have the inner conviction that they did better than others assessed their performance. They believe that others are extremely biased, make excessive demands, find fault with little things, unimportant details, and do not see the main thing.
These signs manifest the inclusion of a “childish” model of behavior, resistance, protest. But this is not expressed directly, since a person with PPD feels inner weakness, inferiority, and fear of showing inadequacy. They strive to dominate indirectly, using manipulation: they emphasize a sense of justice, point out the weaknesses of those who have a higher status, try to attract other people to their side, and unite them around themselves.
Diagnostics
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) classifies passive-aggressive disorder as “other specific personality disorders” (F60.8). To be diagnosed, a person must have at least 5 of the following symptoms:
- constantly postponing work until later;
- gloominess, gloominess and irritability that arise when asked to do something;
- taking on obligations, but not fulfilling them due to “forgetfulness”;
- useful advice from others that can increase work productivity causes dissatisfaction and indignation;
- people in power are criticized, and their success is explained by a trivial coincidence of circumstances;
- disagreement with the assessment of one’s own work, despite its objectively low quality;
- performing tasks slowly or deliberately introducing inaccuracies in them. This refers to work that a person does not want to do.
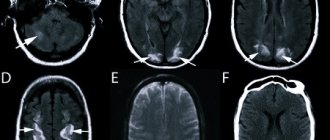
All patients with personality changes are advised to consult a neurologist. An examination by a specialist makes it possible to exclude organic causes of disorders, for example, tumor pathology, the consequences of cerebral ischemia, and others. To do this, the patient undergoes an EEG (electroencephalography), computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
When making a diagnosis, differential diagnosis is carried out with other personality disorders, primarily with borderline and hysterical. The main difference is the lack of drama and entertainment, as well as the passive nature of aggression towards people.
Concept
In passive-aggressive disorder, a person has an attitude toward hidden obstruction and passive resistance to any influence (direction).
Behind this attitude lies suppressed aggression that has not received external expression, which leads to disruption of the adaptation process and personality distress.
Reviews about the treatment of passive-aggressive personality disorder in Moscow
Treatment of the disease is difficult, since the patient does not consider his behavior to be the cause of social maladaptation, which reduces adherence to treatment. Many patients perceive visiting doctors as their own humiliation. At the same time, they retain internal hostility towards specialists.
The main method of treating passive-aggressive personality disorder in Moscow at the psychiatric department of Dr. Isaev’s clinic is psychotherapy. Various areas of psychotherapeutic assistance are used here. The work begins with individual sessions, when the psychotherapist helps the patient understand the pathological nature of his thinking and attitude to the surrounding reality.
Regular meetings with a psychologist and psychiatrist are helpful. Working with attitudes allows you to change many of the patient’s values and foundations and return his thinking to a positive direction. After individual sessions, group psychotherapy is indicated to consolidate the results of treatment. It lasts from one year or more.
During sessions with a doctor, the patient becomes aware of the negative consequences of his behavior. Working on the nature of thinking and creating new mechanisms for responding to stress eliminates the pathological symptoms of a personality disorder. The most effective are social skills training and group work through dangerous moments.
Medications are rarely used for passive-aggressive personality disorder. Antidepressants (Fluoxetine and other serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are used for severe depression, which independently worsens the patient’s social and professional adaptation. In addition to them, doctors can prescribe adaptogens that increase the overall tone of the body.

We guarantee our patients complete anonymity and preservation of personal data. We believe that disseminating information about visiting a doctor or calling a psychiatrist at home can significantly complicate the life of a sick person. Patients who are grateful to us often leave feedback about their impressions after completing a course of therapy. We store all responses, because they help make decisions about treatment for those patients who want to do it, but cannot for various reasons.
Prevention of the disorder
Prevention of passive-aggressive personality disorders is based on general recommendations that are recommended for all parents and loved ones to follow:
- Provide the patient with a positive emotional atmosphere, acceptance of the child at all stages of growing up.
- Avoid overprotection and authoritarianism in decision making. Infantilism and other characteristic signs of a personality disorder develop due to the child’s inability to independently solve emerging difficulties and make choices in everyday affairs.
- Avoid stressful situations. Children often experience stress: when studying at school, adapting among their peers. Parents should support the child and help him make the right decisions without exerting psychological pressure.
The development of passive-aggressive behavior is facilitated by bad habits - drinking alcohol and taking drugs. Teenagers and adults are advised to completely exclude them from their lives.
Questions and answers
The prognosis for this diagnosis is favorable. Timely initiation of psychotherapy and regular visits to a psychologist can eliminate the symptoms of pathology and reduce social maladjustment.
Once the mental state has stabilized, the person is advised to continue attending group or individual psychotherapy sessions. This is due to the fact that complete recovery is impossible, and manifestations of the disease may return due to stress, difficulties at work or in personal life.
Solution
To correct thinking and behavior, a passive aggressor needs to undergo treatment with a psychotherapist. During therapy, the doctor teaches the patient to believe in himself and overcome frustration. It is also important to learn to identify irritation, and then, without violating social boundaries, correctly express your dissatisfaction.
During treatment, strict rules must be followed. To overcome moments of passive-aggressive behavior, the method of discouraging is used. The psychotherapist offers the patient a change in requirements. This allows the client to break out of the usual pattern of behavior.
It is important that a patient with a passive-aggressive character type understands the negative consequences of his actions and gets rid of a number of attitudes that make him insecure. An equally effective method of treatment is conducting socio-psychological training.
Where does passive aggression come from?
This is not an innate trait, but a newly acquired trait. Most often, passive-aggressive behavior begins in childhood. There are several ways:
1) Parents often quarreled, shouted, and fought in front of the child, and the expression of anger became “dirty” and defiled for him.
2) Mom and dad forbade the child to show dissatisfaction, swear, yell, cry. “Don’t you dare talk to your elders like that!” He was taught that it was impossible to be offended, that anger was a trait of bad boys and girls, and that no one would love a “mean” person.
3) The parents themselves were passive-aggressive people, and instilled this example of behavior in their child.
As a result, the child is unable, unwilling, ashamed or afraid to express negative emotions. Over time, he finds other ways to get out of unpleasant situations.
Many people today are unaware of their tendency towards passive-aggressive behavior.
After all, over the years, these traits become an integral part of the personality, and if you look at your character under a microscope, it is quite difficult to recognize them.
Passive aggression is a behavior in which a person expresses his negative emotions in a socially acceptable form, in other words, anger is suppressed. A person may refuse to perform any action; pessimism and absolute inaction prevail in him. In moderate manifestations, this phenomenon is normally tolerated by both the person himself and his environment.
But ICD-10 also notes that there is a passive-aggressive personality disorder. That is, the constant suppression of anger and aggression can result in a pathological condition. Negative emotions must find a way out so that a person can free himself from psychological dirt.
Interestingly, this personality characteristic manifests itself differently in men and women. Hidden aggression in men is manifested by the following behavior:
In women, passive aggression is the spread of rumors and gossip; they do not strive to take responsibility for their own behavior. Representatives of the fair sex with a passive-aggressive personality type want to live the way they want, and do not tolerate various restrictions and subordination. If they show inactivity, they justify it as forgetfulness.
People with this type of aggression tend to:
- afraid of responsibility;
- experience fear of a situation of dependence;
- try to find the culprit of the current problematic situation in order to blame him for your failures;
- quarrel with people around you so as not to let them get close to you;
- switch from a hostile attitude to remorse for your actions and thoughts;
- look gloomy;
- do not say “no” even in critical situations;
- avoid visual contact with the interlocutor;
- ignore appeals to them, fulfillment of one’s own promises;
- dissatisfaction, sarcasm, contempt, irony and grumbling.
Some psychologists disagree with the idea that there is a special type of person with this behavior. They note that many people with these qualities grew up in conditions of disharmonious upbringing, irrational attitudes given to them in childhood by their parents or other adults.
Let's take a closer look at what features of upbringing lead to the development of passive aggression.