Diagnostics
Diagnostics is a mandatory step before starting treatment. The following diagnostic methods have proven themselves to be the most effective and accurate:
- Doppler ultrasound;
- rheoencephalography;
- magnetic resonance angiography;
- echoencephalography;
- neurosonography;
- electroencephalography;
- CT scan;
- positron emission tomography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
The presented diagnostic options are used in specific cases. One or two studies are enough to make a diagnosis. The most modern, but difficult to access methods include Doppler ultrasound (USD). This option combines ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. With its help, the speed of blood movement in the brain is established, narrowing, blockage, and atherosclerotic plaques are diagnosed.
Rheoencephalography (REG) is similar to enphephalography. With its help, blood circulation and vascular tone and their filling with blood are assessed. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is quite informative in diagnosing even the smallest areas of the brain. The indication is suspicion of thrombosis, micro-stroke, vascular disorders of the neck and head.
Echoencephalography (EchoEg) is an ultrasound diagnostic method that is performed using an oscilloscope. It shows information about the performance of all areas of the brain, its level of activity, and the state of the blood ducts.
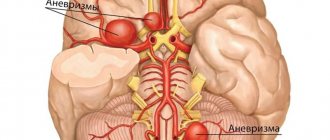
Neurosonography (NSG) is the safest method that is suitable even for children. It can determine the presence of aneurysms, determine the condition of brain tissue, and neoplasms.
Electroencephalography (EEG) records electrical impulses from the brain. Through this, the circulatory system is examined. It is also used to examine the brain for sleep disorders and suspected mental disorders.
Using computed tomography (CT), a layer-by-layer examination occurs. Therefore, the effectiveness of this method is difficult to overestimate. With its help, the state of each part of the brain, including its blood supply, is determined. It occurs with the help of X-rays.
No less informative is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It also allows you to take layer-by-layer images, but at the same time it acts using radio waves.
Positron emission tomography (PET) is the most modern diagnostic method. This study is carried out with radiopharmaceuticals. This allows you to create a three-dimensional image of processes in the brain.
Treatment of an aneurysm involves surgery. This is necessary in order to eliminate the likelihood of rupture of the affected vessel, as well as to avoid thrombus formation. It is also possible to use medications. In each case, their set may vary. The list of possible ones includes Nimodipine, Fosphentoin, Captropril, Prochlorperazine, Morphine, but its use is quite rare, only if very severe headaches are diagnosed.
Symptoms and signs of cerebral vascular stenosis
Cerebral artery stenosis often develops in stages, that is, the disease occurs in a chronic form. The pathological process is characterized by a diffuse form of damage to brain cells, therefore clinical manifestations are only general in the brain.
In total, there are 3 stages of progression of stenosis, but in some sources there is a zero stage, in which the disease proceeds latently. Since symptoms are completely absent at the onset of the pathology, this presents difficulties for timely diagnosis.
Clinical manifestations depending on the stage:
- The symptoms already clearly indicate pathological changes in the brain, but the suffering person, as a rule, does not pay attention to them. Headaches are present, but the patient cannot indicate the exact location; more often it is diffuse and paroxysmal. The pain is similar to a migraine and goes away on its own within 30–60 minutes (not relieved by analgesics). There are attacks of dizziness (spontaneously) during which it is difficult to maintain coordination; the symptom goes away after forced rest. The patient's general condition is similar to severe fatigue, but relatives note that the emotional background has changed dramatically - mood swings, irritability. The patient explains this by insomnia - a sign of stage 1, a person cannot sleep for a long time or often wakes up, after which he feels exhausted in the morning;
- Clinical manifestations of stenosis are increasing, and obvious impairments in the intellectual sphere (thinking, logic) are noted. The patient rapidly loses the skill of retaining information (short-term memory), and the behavior resembles a deviant form (inappropriate emotions arise in a certain situation, for example, laughing at grief). Headaches increase in intensity and are accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring a feeling of relief. Spontaneous fainting and convulsive attacks occur (can be combined with epileptic seizures). Coordination of movements is severely impaired, the person cannot control his body (tremor, “shaky” gait, spontaneous inappropriate movements). Dysfunction of the urinary system is noted (innervation is impaired);
- The brain contains extensive multifocal areas of necrosis. There is no chance of restoring full functionality of the central nervous system; rehabilitation helps partially and is mainly aimed at improving the quality of life. A sick person has no emotions, the world around him is not interesting. The brain does not control many physiological processes, which is why enuresis and involuntary bowel movements occur. The patient does not recognize relatives; there is total amnesia, which is irreversible.
Each patient is individual and the symptoms may manifest themselves in a completely different chronology, but at the same time all of them have signs of vascular dementia.
The progression of stenosis inevitably leads to an acute condition - cerebral stroke. An abrupt cessation of blood supply to the brain is manifested by sudden symptoms that rapidly increase - headache, dizziness, vomiting, fatigue, tachycardia.
In addition to general cerebral manifestations, stroke is also characterized by additional symptoms - focal. Manifestations will depend on the location of the stenosis, that is, depending on which artery the spasm occurred in, a certain area of the brain will suffer (paralysis or paresthesia of one part of the body, blindness in one eye).
Symptoms of narrowing
When a vessel is blocked by a thrombus and plaques, an acute cerebrovascular accident occurs - an ischemic stroke. The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by headaches for a long time. Through narrowed vessels, an insufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients reaches the brain. In a chronic course, vasoconstriction develops slowly, and the complex of symptoms expands.
There are 3 stages of the disease:
- At the first stage, there are no symptoms at all or mild headaches appear, which are attributed to overwork.
- During the second stage, the general condition worsens. The patient gets tired quickly. Emotional lability (mood instability) appears. As a result, quarrels arise with other people. The intensity of headaches increases over time, and attacks become more frequent. A changed gait occurs - it becomes shuffling or mincing.
- At stage 3, all symptoms of narrowing of arteries and veins are even more pronounced. Insufficient nutrition of the brain affects intellectual abilities. Memory decreases and concentration deteriorates. The first signs of dementia appear. Coordination of movements is impaired, so patients try to move slowly. And even with an unsteady gait, a person stumbles, losing his balance. Such signs are a serious reason to consult a doctor!
Since the symptoms appear gradually, the patient does not attach due importance to them, triggering the disease. But those who consult a doctor in a timely manner stop the progression without leading the problem to a stroke, heart attack or dementia.
Causes of vascular stenosis
Stenosis of the cerebral arteries does not occur spontaneously; the pathology is always preceded by concomitant diseases and, as a rule, in a chronic form.
Among the main diseases that provoke stenosis, there are various vascular pathologies and degenerative changes in the musculoskeletal system:
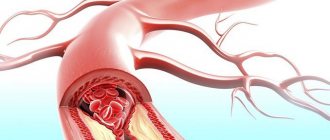
- Atherosclerotic damage to blood vessels - with high cholesterol in the blood, salts begin to accumulate on the walls or in the thickness of the vessel, which gradually layer and thicken. Thus, a cholesterol plaque is formed, which leads to structural disorders and micro-tears. Cholesterol compaction narrows the lumen inside the artery and affects hemodynamics;
- Hypertension - normally the muscular layer of blood vessels is in good shape, but with atherosclerotic changes or the influence of other negative factors, a compensatory mechanism is triggered. Signals are sent from the brain to restore blood flow, and since stenosis as a result of plaque growth is dangerous due to rupture of the vessel, a forced increase in tone occurs. The internal lining of the artery becomes denser, but this leads to a loss of elasticity and, as a result, the brain tissue begins to receive even less nutrients and oxygen (weak cerebral nutrition);
- Osteochondrosis – degenerative changes lead to deformation of all structures of the spine. Compression of the vertebral arteries in the cervical spine provokes mechanical stenosis, thus the brain does not receive enough blood to maintain its functionality.
In addition to concomitant pathologies, there are also risk factors that influence the occurrence of structural changes in the vascular bed:
- Bad habits (alcohol, tobacco);
- Unbalanced diet (frequent diets) or consumption of large amounts of fat;
- Frequent stress;
- Excessive consumption of caffeinated drinks;
- Hormonal surge in the juvenile period;
- Hereditary pathologies.
Structural changes in blood vessels inevitably occur after the decline of reproductive function, both in women and men.
Who needs vascular strengthening?
Veins, arteries and capillaries in the brain become weaker with age
The likelihood of rupture under the influence of mechanical factors increases. Let's consider categories of citizens who need special attention to their blood vessels
Athletes - increased blood pressure occurs with increased stress on the body. With increased blood pressure on the vessels, their walls must be strong enough.
Patients whose lifestyle is not active enough. When a person moves, more intense blood circulation is ensured. This reduces the likelihood of blood clots. When patients do not move enough, blood flow slows down, swelling in the tissues and thrombosis appear.
Frequent stressful situations provoke the production of large amounts of hormones that contribute to the narrowing of the lumen of arteries and veins; insufficiently strong walls can be damaged. Patients with poor heredity or who consume too much alcohol and tobacco.
Consequences of cerebral vascular stenosis
As a result of vasoconstriction, the brain cannot compensate for the insufficient blood supply to the tissues for a long time. The destruction of nerve tissue occurs gradually, and individual neurons die, but the process is diffuse (scattered). Therefore, brain atrophy manifests itself only over the years, in the form of memory impairment and various cognitive processes.
Untimely treatment threatens the development of emergency conditions in which there is a high risk of death. Arterial blockage or rupture are considered the most dangerous complications of secondary stenosis.
Diagnostics
Determining the localization of stenosis and the cause of the pathological narrowing is possible only by visualizing the cerebral vessels. If atherosclerosis is suspected, the level of cholesterol in the blood must be determined.
A diagnostic test is selected by a neurologist depending on the severity of clinical manifestations. Each study has a number of contraindications, so the procedure is prescribed after collecting anamnesis and necessary samples.
Diagnostic methods:
- MRI or CT;
- Doppler ultrasound of head and neck vessels;
- Angiography followed by head x-ray;
- EEG (assessment of brain activity).
After examination and identification of the primary pathology, the neurologist, together with a therapist or cardiologist, selects the most effective therapy.
How to treat vascular stenosis
Initial forms of stenosis can be successfully treated using conservative methods. Medications are prescribed to eliminate the main cause of stenosis (concomitant disease), as well as to maintain metabolic processes in the brain.
Various physiotherapy and exercise therapy help improve cerebral circulation, so rehabilitation is carried out comprehensively. But the conservative treatment method does not always solve the problem; advanced cases or life-threatening conditions require neurosurgical surgery (bypass surgery, angioplasty).
Brain prevention
There is no need to know everything about blood vessels to understand that if blood does not flow to the brain, serious consequences are inevitable, so taking care of blood vessels should become an integral rule of everyday life.
The risk of getting sick increases with age, especially if you have a less than healthy lifestyle and physical inactivity.
Therefore, the older a person gets, the more carefully he should monitor his diet: give up fatty, fried, smoked and salty foods.
The basis of the diet should be fresh fruits and vegetables, seafood. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to the rapid appearance of cholesterol plaques, so in order to preserve blood vessels, you need to move. And it’s not at all necessary to torture yourself in the gym for this.
Daily walks in the fresh air for at least 30 minutes or light gymnastics are enough.
Prevention of stenosis, recommendations from doctors and traditional medicine methods
It is possible to maintain the healthy functioning of the central nervous system with the help of preventive measures aimed at strengthening blood vessels:
- Balanced diet;
- Elimination of stressful situations;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Physical activity;
- Self-massage techniques for the cervical-collar area;
- Regular medical examination.
In folk medicine, there are many recipes for maintaining vascular tone and reducing blood cholesterol. But before use, you should consult your doctor, since many herbs cause allergic reactions and are contraindicated for certain diseases.
Timely seeking medical help helps eliminate pathology at the initial stage and prevent degenerative changes in the central nervous system.