Spastic diplegia, also called Little's disease, is a common form of cerebral palsy, characterized by changes in muscle tone, impaired motor functions of the limbs and back. Sick children often exhibit decreased intellectual abilities, delayed development of speech and mental functions. Other typical manifestations: hearing loss, pseudobulbar syndrome. Patients require lifelong rehabilitation, medical supervision and often outside care. The prevalence of cerebral palsy is 2-3 children per 1 thousand newborns. The diplegic form of cerebral palsy is detected in 75% of cases.
Concept of spastic diplegia
According to the World Health Organization, spastic diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy in which there is a complete disruption of the functioning of the muscles of the limbs.
Doctor Nikonov
In my opinion , spastic diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy in which the functioning of the muscles of the neck, back and buttocks is impaired. The limbs do not move due to the fact that the back muscles do not relax and do not allow the muscles of the limbs to move. Watch a video on the topic:
Neurologists believe that moderate and mild spastic diplegia is caused by damage to both hemispheres of the brain, therefore movements in the upper and lower extremities are impaired.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion is based on what Professor Sergei Savelyev saw through an electron microscope. Changes in muscles (edema) began in utero before brain development.
Neurologists have a tentative opinion.
Professor Savelyev’s opinion is provable and clearly presented.
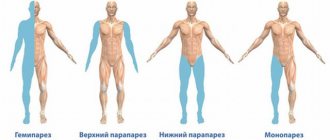
Neurologists believe that spastic diplegia is G 80.1. characterized by lower spastic paraparesis, or tetraparesis, which mainly affects the child’s legs. The expression of pathology can vary - from pronounced to mild awkwardness.
Neurologists believe that the cause of the disease in question is increased muscle tone in the arms or legs.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: increased muscle tone disappears by six months after the birth of the child. Since increased muscle tone is needed for the fetus to be in the fetal position. At exactly six months, not a single child has increased muscle tone.
Neurologists do not know about muscle swelling , so they answer about increased muscle tone based on assumption, not knowledge.
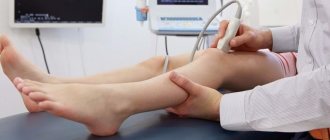
Due to the fact that the muscles of the neck, back and buttocks do not move, the arm is bent at the elbow joint and turned towards the body with a clenched fist. The lower limbs are in a semi-bent position and may cross when walking. Look at the picture below, which shows a typical posture for spastic diplegia:
Recommended video to watch:
The presented video is not educational. The video is the result of the work. Repeating procedure techniques without training from Dr. Nikonov may result in serious injury.
Characteristic
Cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) is one of the main causes of childhood disability. Cerebral palsy, which develops in childhood, is characterized by a chronic course, manifested by a disorder of body posture and motor dysfunction. Spastic diplegia is a pathology that is manifested by muscle spasms, which causes the following characteristics:
- The presence in the clinical picture of tonic reflexes (labyrinthine, cervical - symmetrical and asymmetrical). Tonic reflexes are clearly manifested when changing the position of the body.
- Synkinesia (reflexive uncontrolled cooperative movement of the second limb) at moments when the patient makes voluntary movements with one limb.
- Disruption of the interaction between antagonistic and synergistic muscles (cocontraction effect - simultaneous increase in the tone of flexor and extensor muscles).
- General revival of reflexes (the startle reflex effect, when the patient reacts to a sudden stimulus in a certain way - he shudders sharply, blinks, characteristic facial expressions appear on the face, pronation of the forearms is possible, clenching of the hands into fists).
The severity of the effects of muscle spasms varies. Secondary changes that occur against the background of spasticity affect muscles and joint-tendon structures and increase motor dysfunction. The resistance that occurs in a muscle in response to stretching is caused by factors:
- Tonic tension of reflex type.
- Fibrosis (intramuscular proliferation of connective tissue).
- Atrophy (reduction in volume and decrease in functionality) of muscle tissue.
- Contracture.
It is worth noting the features - disinhibition of spinal reflex reactions in response to stretching with the simultaneous preservation of elementary postural (reflexes aimed at maintaining a given body position in space) automatisms. Spastic diplegia is a pathology that is a form of cerebral palsy, which causes similarity in pathogenesis and clinical manifestations.
Causes and risk factors for the development of spastic diplegia
Since neurologists do not know , they presumably name many reasons. And if at least one of them coincides with your lifestyle or an event in your life during pregnancy, then neurologists are happy: they found the reason, blaming you for this event .
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: the mother is not to blame, the father is not to blame. Swelling in the muscles is not inherited, and the density of muscle fibers adjacent to each other depends on the information that both the mother and father passed on to the child. This is visible under an electron microscope in a fetus at 6 weeks.
I will list the reasons for the development of spastic diplegia according to neurologists:
- Heredity.
My opinion: there is no data to support this statement, since children with spastic diplegia have all their chromosomes intact.
Neurologists:
- Fetal ischemia or hypoxia. If the blood supply to the brain is disrupted and oxygen starvation, brain damage can occur.
My opinion: there is no evidence either on ultrasound or MRI. This is an assumption, i.e. essay on the topic of oxygen starvation of the brain.
Neurologists:
- Infectious lesions of the brain and musculoskeletal system. When a newborn is infected with an infection, serious diseases can develop, such as meningitis, encephalitis and others, due to which complications are noted, since the body is small and is not able to fight such lesions.
My opinion : not all children develop spastic diplegia after suffering from infectious diseases. This disease develops in those children who have suffered infectious diseases and already have swelling in muscle cells or between muscle fibers.
Neurologists:
- Toxic factor. Alcohol, smoking, taking strong medications, etc. may provoke the development of pathology.
My opinion : it has been proven that the body produces alcohol during meals. For this reason, people feel relaxed after eating. It is impossible to provoke pathology. It either exists (look through an electron microscope) or it doesn’t. The placenta will not allow harmful substances to pass through it - it is a natural filter.
Neurologists:
- Physical impact. Brain damage can occur due to radioactive, x-ray irradiation of a pregnant woman, as well as as a result of electromagnetic irradiation.
My opinion: learned biologists and physicists exclude the possibility of spastic diplegia arising from such physical influences, based on data from studies of children after the atomic explosion in Hiroshima. Neurologists send you for an ultrasound scan themselves.
Neurologists:
- Mechanical reasons. Brain damage can be caused by trauma and damage immediately after birth.
My opinion: A child with the most common form of cerebral palsy, spastic diplegia, could be born with difficulties, since muscle swelling was present in both the mother and the baby, who was born with the pathology. Watch a video on the topic of spastic diplegia:
Symptoms
- A child under one year old cannot hold his head or lift it independently.
- Doesn't turn over.
- Does not focus attention on bright objects.
- He doesn't sit down on his own.
- Doesn't crawl.
- Doesn't stand on legs.
- Doesn't use the affected hand.
In older children, the following symptoms are observed with spastic diplegia:
- Change from sudden movements to sluggish ones.
- Uncontrolled muscle contractions.
- Making unnecessary movements.
Common manifestations are delayed mental and speech development, dysarthria. Pathology of the cranial nerves is quite often observed: strabismus, atrophy of the optic nerves, hearing impairment, speech impairment, moderate decrease in intelligence.
Spasticity is the main symptom of paralysis.
By spasticity, neurologists understand a motor disorder that is one of the components of upper motor neuron syndrome and is characterized by an increase in tonic stretch reflexes (or muscle tone) in combination with an increase in tendon reflexes.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: spasticity is swelling in muscle cells and redistribution of muscle fiber nuclei and mitochondria.
Neurologists believe that an increase in muscle tone in spastic diplegia is due to an increase in the tonic stretch reflex. Spasticity is associated with a violation of a number of neurophysiological mechanisms, the decisive role in which is assigned to disruption of the differentiated regulation of alpha and gamma motor neurons, hyperexcitability of spinal alpha motor neurons, and a decrease in the activity of certain inhibitory mechanisms. Spastic diplegia has been called “pyramidal” since the 19th century, but it is now believed that increased muscle tone is associated with damage not to the pyramidal fibers, but to the fibers of the extrapyramidal system closely intertwined with them. The degree of muscle spasticity is most often determined using a modified 5-point Ashforth scale.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: there is no evidence of the influence of the pyramidal tracts of the brain on the formation of spastic diplegia. Neurologists have been treating this pathology with drugs that stimulate the pyramidal tracts for 100 years without any results!
There is no evidence of the influence of the extrapyramidal system of the brain on the formation of spastic diplegia.
Neurologists are still treating this disease without any results.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of spastic diplegia is made in about 60-75% of all cases of cerebral palsy. The main methods of instrumental diagnostics are MRI, ENMG (electroneuromyography - a comprehensive examination aimed at determining the nature and degree of patency of nerve impulses in muscle tissue). Pathology is more often detected in premature infants.
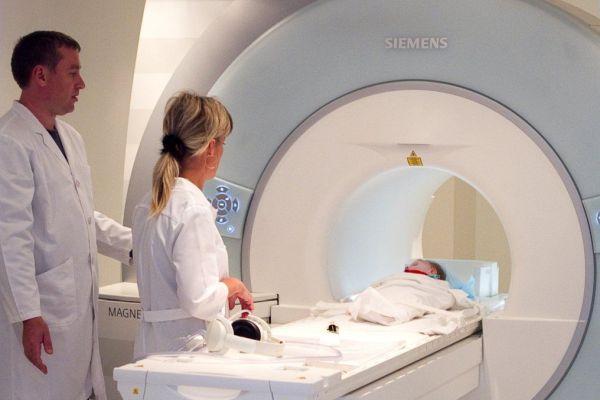
MRI reveals signs of hemorrhages localized in the ventricular system, as well as periventricular leukomalacia (damage to the white medulla near the ventricular system). The diagnosis can be made by a doctor of any specialization due to the pronounced visible disturbances in motor activity typical of cerebral palsy.
Treatment of spastic diplegia by neurologists
Neurologists: according to the World Health Organization, curing spastic pathology is impossible.
My opinion is presented in the video:
The goal of treatment by neurologists is to mitigate muscle damage and adapt the child to society. To achieve treatment goals, general physiotherapeutic rehabilitation procedures are used. This could be: regular massage to improve blood circulation in order to reduce muscle tone and prevent contractures.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: it is impossible to improve blood circulation. There is either blood circulation or there is not. If blood circulation deteriorates, there will be gangrene. An electron microscope shows the growth of additional arterial capillaries in the muscles where the nuclei have “fell off.” Therapeutic massage is not able to eliminate swelling from muscle cells.
Neurologists prescribe physical therapy, acupuncture, and swimming.
My opinion: for a child with spastic diplegia and his parents, all the recovery methods listed by neurologists are a game of daughter-mother. Until you eliminate the swelling from the muscle tissue, there will be no positive changes. Only exposure using the Nikonov method can eliminate swelling.
Neurologists like to prescribe vojta therapy, a technique for activating reflexes.
My opinion: you can activate reflexes only in those muscles of the child that are without swelling. Only the appearance of improvement is created due to non-swollen muscle groups at the time of application of the technique for a short period of time.
Neurologists prescribe wearing a power system consisting of support elements and elastic adjustable rods.
My opinion: it is impossible to teach a child to walk correctly if the muscles do not move correctly due to swelling.
Drug treatment includes the use of nootropics and homeopathic medicines. Treatment is prescribed in the presence of auxiliary lesions in the form of delayed intellectual and psychological development.
I don't prescribe medications.
Watch a video on the topic of spastic diplegia in children:
It is impossible in the article to describe every particular case of restoration and training of parents to restore their children. Therefore, I am providing you with links to my video channels, where you will find complete information:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcKEOLTWN3sy9QV5VK2axig
https://www.youtube.com/user/NikonovNikolay
They also suggest watching my video, which shows examples of complete recovery of children:
Me, my patient Bogdan and his happy parents:
Clinical signs of spastic diplegia
The incidence of this form of cerebral palsy is 50%.
of the musculoskeletal system include:
Bilateral damage to the extremities of a sick child, legs to a greater extent than arms, earlier formation of deformities and contractures, deformation of joints and spine. Muscle tone in the adductor muscles and hip extensors is greatly increased, the child’s legs are brought close to each other, often crossed. Additionally, symptoms of Babinsky, Rossolimo, etc. may appear. Walking in the case of the formation of contractures and deformities of the feet is difficult or impossible.
Disorders of mental and speech development , pathologies of the sensory organs:
Pseudobulbar syndrome, pathological changes in the cranial nerves, which entails atrophy of the optic discs, hearing impairment and strabismus. There is a delay in speech development. Speech development in children with spastic diplegia is delayed. Speech disorders are manifested by dysarthria and alalia. Hyperkinesis of the articulatory and respiratory muscles makes speech blurry and jerky. Children with this form of the disease have difficulty studying, quickly become exhausted, and are distracted. Memory is reduced.
Other pathologies: Convulsions are possible, but relatively rare.
The decrease in intelligence is moderate or completely absent.
Watch a new film about the Nikonov method:
Classification
According to the severity of clinical symptoms, spastic diplegia is classified into the following forms:
- Mild
- in the first half of the year the child develops normally, later spastic paresis is expressed in the area of the lower extremities, movements in the arms are not limited. The patient is able to move without aids. Mental and mental development is not affected. - Moderate severity
- severe spasticity in the legs makes the patient’s movement possible only with the use of improvised means (crutches, sticks). The cognitive sphere suffers slightly, social adaptation is possible. - Severe
- noticeable from the first days of life. There is pronounced tetraparesis with an accent in the legs. Patients cannot move independently. Social adaptation is impaired.