Hemiparesis is usually understood as a disease that is a consequence of damage to higher subcortical functions. As a result, a person experiences incomplete loss of sensation on a certain side of the body.
This may manifest as right-sided or left-sided hemiparesis. Also, a person often has an upper or lower localization of the disorder.
In any case, it is very important to take adequate measures in a timely manner to help avoid dangerous consequences.
Many people are interested in what is the difference between hemiparesis and hemiplegia. Thus, hemiparesis is usually understood as a decrease in strength in half of the body. In this case, hemiplegia is a complete lack of strength in half the body. In essence, this disorder is paralysis.
Pathogenesis of the disorder
Hemiparesis is a disease characterized by partial paralysis, which provokes weakening of muscle tissue on a certain side of the body. At the same time, the other side remains healthy.
This condition is a consequence of damage to the upper motor neurons, as well as their axons. In addition, there may be a disruption in the functioning of motor neurons. In most cases, this disease is of cerebral rather than spinal origin.
To determine the severity of the manifestations of the disease, you need to pay attention to the symptoms of focal damage to the cortex. To them
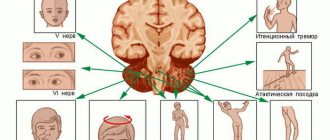
Wernicke-Mann gait in hemiparesis
include speech disorders, problems with making purposeful movements, and difficulties in perception. A person may also experience epileptic seizures, sensory disturbances, and cognitive disorders.
Individual brainstem lesions are characterized by a combination of ipsilateral lesions of the nerves located in the head with contralateral hemiparesis.
If a person has abnormalities in the structure of the body, the disease develops more rapidly.
In this case, the patient may experience postictal hemiparesis, which develops after a focal motor attack.
This disease is characterized by the presence of epileptic seizures, which affect the formation of a brain abscess or tumor.
Diagnostics
To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a number of tests and undergo some examination. Among the first, the doctor determines the signs of the disease using the Barre test. To do this, the leg damaged by paralysis is raised and then allowed to gradually lower, while the second is held in its original state.
The Mingazzini test is performed by stretching the paralyzed arm forward. The healthy limb remains in its place along the body. The Garkin test is carried out as follows - for this the patient needs to bend the forearm and raise the hand vertically, on which the fingers must be spaced as wide apart as possible; on the injured limb the finger moves slightly, squeezing slightly.
Causes
The cause of hemiparesis can be a huge number of congenital or acquired diseases. These usually include the following:
- stem tumor formations;
- intracerebral or epidural injuries;
- the appearance of subdural hydroma , which is of traumatic origin;
- cerebral stroke or infarction, acute ischemia;
- a hematoma in the brain , which is the result of carotid artery thrombosis that occurs in Todd's palsy;
- parenchymal hemorrhage;
- Farah's disease - characterized by the appearance of brain stones;
- hysteria;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hemiplegic migraine , which can be spontaneous or genetically determined;
- Brown-Sicard syndrome - is a spinal tumor that is localized in the cervical region;
- syphilitic gumma - is a soft tumor formation in tissues.
Hemiparesis in children in most cases is congenital. This is due to intrauterine abnormalities in brain development. Also, this disease can be caused by deviations during childbirth, which are accompanied by compression of nerve fibers. In children, in most cases, left-sided hemiparesis is observed.
Congenital and acquired disorder
In adults, an acquired form of the disease usually occurs.
Acquired hemiparesis can cause:
- stroke;
- tumor lesion of the brain;
- encephalitis;
- epilepsy;
- multiple sclerosis;
- diabetic brain damage;
- migraine;
- acute circulatory disorders in the brain.
In children, most often, hemiparesis is congenital and develops as a result of a malformation of the brain or trauma received during childbirth.
In this case, there is a left-sided form of the disease, which becomes visible several months after the birth of the baby. At an early stage of pathology, minor disturbances in the motor activity of the limbs may occur:
- asymmetrical movements;
- weak movements of the affected limbs;
- clenching the hand into a fist;
- poor support function on the affected side;
- spread hips in a lying position.
The doctor makes the final diagnosis at approximately 12-18 months. When the baby begins to move, the disturbances become more noticeable. In complex cases, the pathology is accompanied by impaired speech and mental abilities.
Clinical signs
The incidence of this form of cerebral palsy is 2%.
of the musculoskeletal system include:
Bilateral spasticity, expressed equally in both the upper and lower extremities (spastic quadriplegia or quadriparesis). Please note that there are forms when spasticity predominates only on the hands. With spastic tetraparesis, secondary complications develop early, such as contractures, deformities of the trunk and limbs. Pathological hand and foot reflexes are detected.
Disorders of mental and speech development , pathologies of the sensory organs:
In this case, severe cognitive impairment. Strabismus, optic nerve atrophy, hearing impairment, pseudobulbar syndrome and, as a result, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia. In children with double hemiplegia, speech is usually slurred, nasal and difficult to understand by others. Incorrect pronunciation of sounds is often noted. The pace of speech has changed. The child pronounces words and sounds both excessively loudly, quickly, and weakly, slowly. Thinking in the most complex form of cerebral palsy is slow, inert, and memory is weakened. Disinhibition, euphoria, and apathetic-abulic disorders are often observed.
Other pathologies: epilepsy, secondary microcephaly.
Decrease in intelligence : pronounced.
Left-sided and right-sided hemiparesis
Neurologists were able to establish a certain relationship between symptoms in a certain part of the body and the brain hemisphere in which the abnormal focus is present. This connection is inverse.
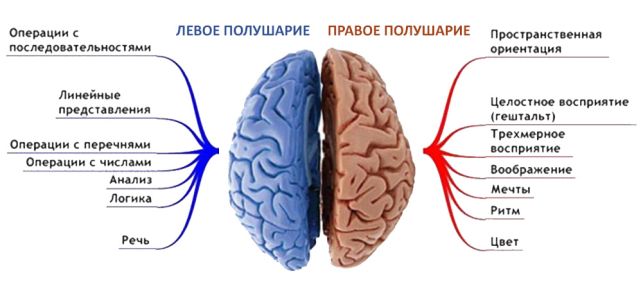
If a feeling of weakness is present in the right limbs, right-sided hemiparesis is diagnosed, but if the symptoms are localized on the left, left-sided hemiparesis is diagnosed.
Moreover, each hemisphere of the brain is responsible for performing certain functions of the body. So, if left-sided hemiparesis develops as a result of a traumatic injury or stroke, the person often experiences serious speech impairments.
It is the right-sided hemiparesis that is one of the most common complications of stroke, since circulatory disorders often occur in the left artery of the brain. These processes provoke loss of sensitivity and motor activity.
If a person has a left-sided form of the disorder, then the patient may experience mental disorders. This is due to the fact that in the right hemisphere of the brain there is a maximum number of nerve centers that are responsible for mental functions. It is important to note that the left-sided form of the disease is much less common.
Treatment
Therapy is always determined individually. Treatment tactics for spastic and other types of hemiparesis in adults and children directly depend on the provoking disease.
All available methods are used: medications, therapeutic exercises, massage, mechanotherapy, physiotherapy. It is the combination of these techniques that can lead to a positive result.
It is important to note that the treatment of tumors requires surgery followed by chemotherapy. If a patient is diagnosed with encephalitis or encephalomyelitis, therapy is prescribed based on the sensitivity and nature of the pathogen.
Therapeutic exercises are the main method of getting rid of hemiparesis and are recommended on an ongoing basis. Patient training is carried out by experienced instructors who, at the initial stages, monitor the correct execution of the exercises. You can do the following complex:
- Flexion and extension at the knee and hip joints while lying on your back.
- In the same position, you need to pull your foot towards you and away from you.
- The next exercise requires you to stretch the band between the supports. Afterwards, the affected leg is placed on it and the foot is made in a circular motion.
- Patients are recommended to rise on their toes and stand on their heels, while holding onto support. As you improve, you need to switch to walking in this position without support.
- As for the arms, patients are recommended to do flexion, extension and rotation in the wrist and shoulder joints.
- Another exercise is to clench and unclench your hand into a fist (use of an expander is allowed).
- With your hands behind your back, you need to connect them together.
Patients are also recommended mechanotherapy (gymnastics on special simulators), regular swimming and Nordic walking.
As for massage for hemiparesis, it helps improve metabolism and blood flow, normalize muscle tone and limb function. The procedure is carried out by a specialist, it begins with light circular movements, the intensity of which gradually increases. For hemiparesis, any type of massage is useful - general health, segmental, acupressure.
As for other methods, physiotherapy (electrical stimulation, paraffin wraps) and acupuncture have a good effect.
Treatment methods depending on the situation
The child has left-sided hemiparesis
For treatment to be effective, it is very important to eliminate the causes of the syndrome.
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate or reduce the symptoms of hemiparesis and restore normal motor activity.
The treatment method is chosen by the doctor taking into account the causes of the disease.
To completely cope with the pathology, you need to select complex therapy:
- If the cause lies in damage to the brain or spinal cord , surgery may be necessary. To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, the doctor can remove the tumor formation, hemorrhage, or abscess.
- In case of circulatory problems in the brain, medications are prescribed to improve this process. Usually there is a need to use nootropics and angioprotectors.
- In case of infectious lesions of the brain, there is a need to use antibacterial drugs.
- For botulism, the doctor administers a special anti-botulinum serum.
- For myasthenia gravis , medications are used that help improve neuromuscular conduction.
In mild cases, the doctor prescribes a special course of therapeutic exercises. In addition, the following means are used:
- swimming;
- massage;
- reflexology;
- hardening;
- Charcot's shower;
- fitball exercises;
- hippotherapy;
- dousing
In difficult cases, specialists select medications. After discharge from the hospital, therapy continues at home.
Once the diagnosis is determined, the specialist selects drug treatment methods. In this case, the use of medications should be accompanied by special physical exercises.
Since the development of hemiparesis is accompanied by damage to certain areas of the brain, an increase in muscle tone is often observed. To reduce it, the doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants - these are the drugs that reduce the severity of the symptoms of the pathology.
These medications are important not only for muscle relaxation. They also help prepare the patient for massage and therapeutic exercises. At the same time, it is necessary to treat associated disorders.
For this purpose, speech or vision correction can be carried out, and anticonvulsant treatment is carried out, the need for which appears in case of epilepsy. Many patients with this diagnosis need consultation with a psychologist.
Muscle relaxants are usually prescribed in long courses, which can last up to six months. This is due to the duration of the recovery period of the affected areas. Such drugs do not allow cells to recover, but they create favorable conditions for the rehabilitation of patients.
Quite often, therapy for this disease is carried out using the following medications:
- Mydocalm;
- Baclofen;
- Pantogam;
- Piracetam;
- Neuromidin.
In addition, effective therapy is impossible without the use of vitamin complexes. Vitamins B and E are especially useful.
If the affected area has not recovered within a year, treatment may be delayed. Courses of drug therapy are repeated from time to time. Along with this, the use of massage, therapeutic exercises and acupuncture is indicated.
Exercise therapy can be done in special rehabilitation centers. If this is not possible, you can do the exercises at home. However, this must be done systematically in order to achieve tangible results.
With this diagnosis, various types of massage are very useful. In addition, experts advise working out your abs, jumping on one leg, developing hand motor skills, and stretching the muscle tissue on the affected side.
Various sports play an important role in recovery - swimming, water gymnastics, and horse riding are especially useful.
Classification
Depending on the etiological factor, such a violation occurs:
- organic – characterized by persistent changes in the nervous system;
- functional - may suddenly disappear even without medical intervention.
Taking into account the location of the lesion, the following is distinguished:
- contralateral hemiplegia - manifests itself on the side opposite to the source of the lesion;
- homolateral form - the damage is on the same side as the affected limbs;
- double hemiplegia – the pathology involves the arms and legs on both sides at once. It is considered the most severe form of this disease;
- spinal form.
According to the course of action, the following is distinguished:
- cross hemiplegia - differs in that the paralytic lesion affects the arm (for example, on the left) and leg (on the right side);
- flaccid type – muscle tone of the upper and lower limbs is significantly reduced;
- central hemiplegia - in such situations, in addition to paralysis, muscle hypertonicity is present;
- spastic hemiplegia - the upper limb is affected to a greater extent than the lower.
Depending on the side of the lesion, the following can be diagnosed:
- bilateral hemiplegia;
- right-sided hemiplegia;
- left-sided hemiplegia.
Based on the level of damage, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- cortical – the cerebral cortex suffers;
- supracapsular – the damage is located near the internal capsule;
- cortical-subcortical;
- pyramidal-thalamic;
- capsular;
- alternating hemiplegia;
- alternating optical-pyramidal.
The pathological process has the following stages:
- diaschisal;
- progressive;
- regressing.
According to the etiological factor it is divided into:
- acquired – occurs most often;
- congenital – also called

childhood hemiplegia.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis is largely influenced by the stage and severity of the syndrome and the causes of its occurrence. In addition, good results can only be achieved if a person receives timely and adequate therapy.
Otherwise, there is a risk of developing dangerous complications. If not treated correctly, the patient may develop complete loss of muscle strength on the affected side.
Hemiparesis is a very serious disorder that can be congenital or acquired. To cope with this disease, you need to establish the causes of its occurrence and, based on this, select adequate therapy.
Prevention
Preventive measures that can be taken to prevent this condition are mostly general, including:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits (for a teenager);
- balanced diet;
- visiting a doctor for preventive examinations;
- moderate physical activity;
- avoiding injury;
- compliance with data by specialist physicians (for patients at risk).
If we talk about hemiplegia due to perinatal pathologies, then prevention is the timely elimination of health problems in children during their newborn period.