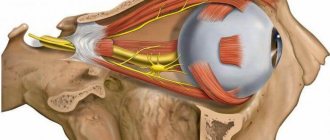
Structure and functions of the trigeminal nerve
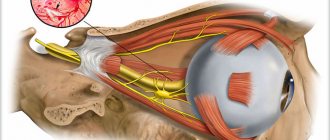
The trigeminal nerve, the largest element of the peripheral nervous system, originates in the nucleus located in the brain. In its different sections, cranial nerves originate, which have their own name and digital designation. Being a pair, the trigeminal nerve also belongs to one of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves, namely the fifth. It branches into its three leading branches:
- orbital nerve;
- maxillary nerve;
- mandibular nerve.
The orbital nerve, passing through the orbit, itself, in turn, is divided into the frontal, lacrimal and nasociliary nerves, which are responsible for the innervation of the upper third of the face, partly the eyes and the nasal cavity. Nerve fibers of the maxillary nerve innervate the temporal zones, lateral areas of the nose, upper lip and upper teeth with gums. The innervation of the lower part of the face, with the chin and lower teeth, goes to the mandibular nerve. In addition to providing sensitivity, the trigeminal nerve is responsible for motor functions, mainly for the movement of the masticatory muscles and facial expressions.
Surgical intervention
Conservative therapy does not always show good results. If the symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face do not go away, the doctor may decide to perform surgery. This may also occur in the presence of tumors in the affected area.
Microsurgical decompression is a method of radical surgical elimination of neuralgia. A small trepanation hole is made in the area behind the ear, through which the surgeon inserts instruments with a microscope. The intervention is performed exclusively under general anesthesia. Therefore, elderly patients (over 70 years of age) are at risk of cardiovascular complications.
A less radical method is percutaneous radiofrequency destruction. The procedure has many advantages. The specialist can easily influence small areas without damaging nearby sensory nerves. The patient's recovery occurs quite quickly. The risk of complications is minimized.
Within a week after surgery, a person can return to a full life. If radiofrequency destruction is performed correctly, its effect lasts for years. The patient forgets for a long time what the trigeminal nerve is. However, unfortunately, relapses cannot always be avoided.
If there are formations in the trigeminal nerve, stereotactic radiosurgery can be performed. This is a minimally invasive technique that allows you to penetrate tissue without much risk and destroy the tumor at the cellular level. In this case, vital structures are not damaged.
As a rule, patients with trigeminal nerve pathology are offered surgery after 3-4 months of unsuccessful conservative treatment. Surgical intervention may involve eliminating the cause or reducing the conduction of impulses along the branches of the nerve.
Operations that eliminate the cause of neuralgia:
- removal of tumors from the brain;
- microvascular decompression (removal or displacement of vessels that have dilated and put pressure on the nerve);
- expansion of the exit of the nerve from the skull (the operation is performed on the bones of the infraorbital canal without aggressive intervention).
Operations to reduce the conductivity of pain impulses:
- radiofrequency destruction (destruction of altered nerve roots);
- rhizotomy (dissection of fibers using electrocoagulation);
- balloon compression (compression of the trigeminal ganglion with subsequent death of fibers).
The choice of method will depend on many factors, but if the operation is chosen correctly, attacks of neuralgia will stop. The doctor must take into account the patient’s general condition, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the causes of the disease.
- Blockade of certain sections of the nerve. A similar procedure is prescribed in the presence of severe concomitant pathologies in old age. The blockade is carried out using novocaine or alcohol, providing an effect for about a year.
- Ganglion block. The doctor gains access to the base of the temporal bone, where the Gasserian node is located, through a puncture. Glycerol is injected into the ganglion (glycerol percutaneous rhizotomy).
- Transection of the trigeminal nerve root. This is a traumatic method, which is considered radical in the treatment of neuralgia. To implement it, extensive access to the cranial cavity is required, so trepanation is performed and burr holes are applied. At the moment, the operation is performed extremely rarely.
- Dissection of the bundles that lead to the sensory nucleus in the medulla oblongata. The operation is performed if the pain is localized in the projection of the Zelder zones or distributed according to the nuclear type.
- Decompression of the Gasserian node (Janetta operation). The operation is prescribed when a nerve is compressed by a vessel. The doctor separates the vessel and the ganglion, isolating it with a muscle flap or synthetic sponge. Such an intervention relieves the patient of pain for a short period of time, without depriving him of sensitivity or destroying nerve structures.
It must be remembered that most operations for neuralgia deprive the affected side of the face of sensitivity. This causes inconvenience in the future: you can bite your cheek and not feel pain from injury or damage to the tooth. Patients who have undergone such surgery are advised to visit the dentist regularly.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis
Any pathological process in this nerve affects sensitivity and motor functions. However, it is important to accurately establish the diagnosis - trigeminal neuritis: its symptoms and treatment should not be confused with neuralgia of the nerve, in which only its myelin sheath is affected. Neuritis turns out to be a more serious disease, since the nerve itself is involved in the inflammatory process. The most susceptible to inflammation are the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves.
- The decisive symptom for diagnosis is pain. Depending on which branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved in the painful process, toothache, pain in the brow ridges or temples, in the gums, lips and chin appear. The nature of the pain can be cutting, shooting, sharply piercing and causing torment to a person. The pain can be periodic, increasing gradually and sometimes releasing for short periods of time. It may be painful for the patient to bite his teeth; during an exacerbation of the attack, he breathes heavily or tries to hold his breath and is afraid to make an unnecessary movement.
- Loss of sensation is another sign of trigeminal neuritis. The patient complains of loss of taste, decreased sensitivity of the mucous membrane, and sometimes a complete feeling of numbness in the chin or gums.
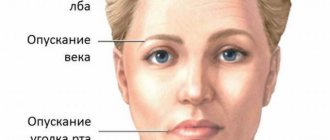
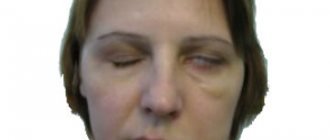
- Disturbances in the motor function of the nerve are manifested in difficult chewing movements, fine muscle tremors like tics, convulsions that make it difficult for the patient to swallow food, impaired facial expressions and even facial asymmetry.
Causes
The chronic course of an infectious disease can provoke the development of postherpetic neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve. In other cases, determining the cause of the development of trigeminal neuralgia is more difficult. It is customary to identify a main group of provoking factors, which include:
- pressure on the nerve during the development of a tumor, abnormal arrangement of blood vessels;
- hypothermia;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- helminthiasis;
- multiple sclerosis or cranial aneurysm;
- metabolic disease;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- severe form of allergic reactions.
Pathology can develop against the background of mental illness.
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis
Depending on the identified cause, the direction of treatment is chosen, aimed primarily at eliminating the factor that caused the disease: the tumor is removed, excess filling material is eliminated, efforts are directed to destroy the infection, if it was the root cause of the disease, factors associated with intoxication of the body are eliminated and allergies. At the same time, a number of measures are carried out aimed at relieving swelling of the nerve trunk. To combat inflammatory phenomena, the patient is prescribed non-steroidal drugs (ketanov), as well as B vitamins (neuromultivitis). Symptomatic treatment involves taking painkillers and anticonvulsants. Physiotherapy gives good results: novocaine electrophoresis, ultrasound, acupuncture, and later treatment at appropriate resorts with a dry, warm climate.
Prevention
Trigeminal neuritis is more difficult to treat with age. In order not to encounter this painful illness, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- this is mandatory monitoring of the condition of teeth and mucous membranes;
- hardening and maintaining immunity at the proper level;
- timely treatment of infectious and colds;
- avoiding stress;
- good nutrition, saturating the body with vitamins;
- prudent behavior: do not overcool, do not expose your wet head to drafts, do not walk in cold damp weather without a hat.
ethnoscience
There is an opinion that you can relieve pain from trigeminal neuralgia with the help of black radish juice. The same remedy is effective for sciatica and intercostal neuralgia. It is necessary to moisten a cotton swab with juice and gently rub it into the affected areas along the nerve.
Another effective remedy is fir oil. It not only relieves pain, but also helps restore the nerve in case of neuralgia. It is necessary to moisten a cotton wool with oil and rub along the length of the nerve. Since the oil is concentrated, do not use it vigorously, otherwise you may burn. You can repeat the procedure 6 times a day. The course of treatment is three days.
For neuralgia, fresh geranium leaves are applied to the affected areas for several hours. Repeat twice a day.
Treatment regimen for a cold trigeminal nerve:
- Warming your feet before bed.
- Take vitamin B tablets and a teaspoon of beebread twice a day.
- Apply Vietnamese “Star” to the affected areas twice a day.
- Drink hot tea with soothing herbs (motherwort, lemon balm, chamomile) at night.
- Sleeping in a hat with rabbit fur.
When pain affects teeth and gums, you can use chamomile infusion. Infuse a teaspoon of chamomile in a glass of boiling water for 10 minutes, then strain. You need to take the tincture into your mouth and rinse until it cools. You can repeat the procedure several times a day.
Tinctures
- Hop cones. Pour vodka (1:4) over the raw material, leave for 14 days, shake daily. Drink 10 drops twice a day after meals. Must be diluted with water. To normalize sleep and calm the nervous system, you can stuff your pillow with hop cones.
- Garlic oil. This product can be purchased at a pharmacy. In order not to lose essential oils, you need to make an alcohol tincture: add a teaspoon of oil to a glass of vodka and wipe the whiskey with the resulting mixture twice a day. Continue the course of treatment until the attacks disappear.
- Marshmallow root. To prepare the medicine, you need to add 4 teaspoons of the raw material to a glass of cooled boiled water. The product is left for a day, in the evening gauze is soaked in it and applied to the affected areas. The top of the gauze is covered with cellophane and a warm scarf. You need to keep the compress for 1-2 hours, then wrap your face with a scarf overnight. Usually the pain stops after a week of treatment.
- Duckweed. This remedy is suitable for relieving puffiness. To prepare duckweed tincture, you need to prepare it in the summer. Add a spoonful of raw materials to a glass of vodka and leave for a week in a dark place. The product is filtered several times. Take 20 drops mixed with 50 ml of water three times a day until complete recovery.
It must be remembered that any folk remedies can only be additional treatment measures. Since complications can be critical, a specialist should be consulted for each remedy used.
To forget forever about what the trigeminal nerve is, all methods are good. Traditional medicine recipes are also popular. Some of them really show high efficiency. However, it is important to discuss any method of therapy with your doctor to avoid complications.
For the treatment of neurological diseases, herbal remedies are widely used: burdock, aloe, lemon balm, geranium, yarrow, etc. Medicinal lotions and infusions for oral use can normalize the inflamed trigeminal nerve. Where to get raw materials for preparing products? Medicinal plants can be collected independently or purchased at a pharmacy in dried form.
A medicinal decoction based on mint, valerian and St. John's wort shows good results. The dried raw materials are mixed in equal proportions (150-200 g each). Pour two tablespoons of the resulting mixture into half a liter of water, bring to a boil and simmer for another 10 minutes. Then the product must be cooled and left for another 5 hours in a dark place. The finished medicine is filtered and taken a tablespoon three times a day for two weeks.
If symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve appear, treatment at home can be carried out using a decoction based on burdock and chamomile. The dry ingredients are mixed in equal proportions, 300 g of the mixture is poured with half a liter of water, brought to a boil and cooked for another 15 minutes. The finished medicine is infused for a day under a closed lid, then filtered. The infusion is drunk in small sips over the next day.
If you had to find out what the trigeminal nerve is and how its inflammation manifests itself, you should pay attention to aloe. This plant will help eliminate pain and speed up the process of regeneration of affected tissues. For therapy, aloe should be used that is no more than three years old. A teaspoon of plant juice should be consumed three times a day before meals. People who are prone to allergies will have to refuse such therapy.
If unpleasant symptoms appear, treatment of the trigeminal nerve at home can be carried out using birch sap. The drink has a unique composition, with its help you can cope with inflammation and strengthen the body's defenses. You should drink at least two glasses a day. Birch sap can also be used to wash your face.
A variety of medicinal lotions are widely used. Geranium will help to quickly relieve pain from inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. The cut plant is applied to the sore spot and secured with a gauze bandage. After a few hours, the lotion is removed and a new plant is applied.
Compresses made from marshmallow root are effective. A few roots are crushed and 200 ml of boiling water is poured. The product should sit for 24 hours. A piece of bandage or linen cloth is moistened in the finished product, wrung out and applied to the sore area. A warm towel is placed on top. The duration of the procedure is 30-40 minutes. This therapy can be carried out several times a day.