Alternative Treatments
Let's talk in more detail about these tools:
- prepare a tampon from grated beets and gauze, which is then placed in the auricle on the side where there is inflammation;
- add a steep decoction of aspen bark to the water and take a bath before bed for 15 minutes before bed;
- prepare an ointment based on any animal fat and a decoction of lilac buds, using the substances in the following quantity - per 100 g of fat from 30 to 50 g of infusion. Keep the resulting ointment strictly in the refrigerator;
- a boiled chicken egg will help relieve an attack of pain at the very beginning; to do this, you need to peel and cut the egg into two parts, and then apply them to the most painful areas of the face;
- Surprisingly, alternating cold and hot compresses, for which ice is used in some cases and hot water in others, perfectly relieve pain.
Types of inflammation
Since each part of the trigeminal nerve is divided into smaller branches that lead to all areas of the face, the nerve covers it as a whole. These branches are responsible for facial sensitivity.
The first branch is responsible for the eyebrow, eye, upper eyelid and forehead. The second - for the nose, cheek, lower eyelid and upper jaw, the third - for some masticatory muscles and the lower jaw.
There are two types of disease:
- type one (true): the most common, occurs due to impaired blood supply or compression of a nerve, and is independent. In this type, the pain is severe, periodic and piercing;
- type two (secondary): a symptom, often a complication of a previous disease, arising as a result of complications of other diseases. With neuralgia of this type, the pain is burning and constant, and can occur in any part of the face.
The most popular cases of neuralgia of the nerve process are only on one side of the face, however, there are cases of inflammation of two or three branches at once, sometimes on both facial sides. The pain is intense, attacks last for 5-15 seconds, often reaching several minutes.
Use of Diclofenac for intercostal neuralgia
With various types of neuralgia, the main symptom is pain. This disease is very dangerous, and only a specialist can diagnose it. Complex therapy necessarily includes Diclofenac for neuralgia - an effective remedy that can relieve pain of varying severity. It is prescribed for neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve, occipital nerve, intercostal neuralgia and other types of this disease.
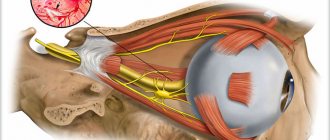
Where is the trigeminal nerve located?
This collection of neurons emerges from the pons. The trigeminal nerve is divided into 2 parts: the motor and sensory roots. Both components are directed forward, passing through the dura mater of the brain. During the transition, the sensitive root forms the trigeminal cavity, located on the temporal bone. Inside it is a ganglion, where the nerve is divided into the following parts:
- eye branches;
- mandibular branches;
- maxillary branches.
The motor root goes around the ganglion from the inside and in the area of the foramen ovale becomes part of the mandibular branch. The trigeminal facial nerve is mixed, so damage to the branches is accompanied by a reaction of the nervous and muscular systems. Damage or inflammation of the fibers can cause loss of sensitivity in some parts of the face, reduction or disappearance of the mandibular reflex.
Diagnostics
Human anatomy is such that it is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis based on symptoms. That is why it is sometimes quite difficult to diagnose by eye whether the trigeminal nerve hurts or whether it is due to another disease.
Any doctor, in order to find the cause and source of the disease, must conduct a correct diagnosis. When treating the trigeminal nerve, it consists of a conversation with the patient, examination and palpation of his face, and review of the hospital card.
Very often, an MRI or CT scan must be done to accurately determine the diagnosis. In Moscow, you can contact some treatment centers for electroneurography, electroneuromyography or electroencephalography procedures. Such instrumental research methods allow us to have a more accurate picture of the disease.
General information
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a common disease of the peripheral nervous system. It occurs in 30-50 people out of 100,000, most often affects women over 45 years of age and has a predominantly right-sided localization - in 70% of cases. Left pathology develops in 29% of patients, and bilateral pathology in 1%. Young people are susceptible to NTN in multiple sclerosis. The disease is characterized by attacks of acute, shooting pain, spreading along the innervation of one of the branches of the nerve (less often two at once).
The pathology has a chronic course and is characterized by frequent relapses. Synonyms for trigeminal neuralgia are trigeminal neuralgia, painful tic, Fothergill's disease.
The trigeminal nerve is a pair, located on both sides of the face. In form it is represented by three branches:
- upper (first) – ophthalmic, innervates the eyeball, forehead, lacrimal gland, eyebrow;
- middle (second) - maxillary provides sensitivity to the nose, cheekbones, cheeks, upper jaw, palate, temple;
- lower (third) - the mandibular is responsible for the innervation of the masticatory muscles, lower lip and jaw.
The trigeminal nerve is mixed in nature; it provides sensory and motor function. Along the path of passage, the branches are located in the canals and openings of the bone tissue, intertwined with blood vessels. Such proximity as a result of injury or the development of pathology leads to compression of the nerve roots. An inflammatory process occurs that disrupts the integrity of the fibers. The response to any irritation is severe pain.
There is a second type of disease - atypical trigeminal neuralgia. It is less common, but is difficult and poorly diagnosed. Its hallmark is constant aching pain.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
It is extremely difficult to cure this disease and even radical treatment methods do not always give a positive result. But proper therapy can relieve pain and significantly alleviate human suffering.
The main treatment methods for trigeminal neuralgia include:
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical treatment.
Medications
Various groups of drugs are used in drug treatment, including:
- Anticonvulsants
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants.
Finlepsin for trigeminal neuralgia is one of the most common anticonvulsants. The active ingredient of this drug is carbamazepine. This drug plays the role of an analgesic for idiopathic neuralgia or a disease that occurs against the background of multiple sclerosis.
The dose of Finlepsin (carbamazepine), with which patients can talk and chew painlessly, should remain unchanged for a month, after which it should be gradually reduced. Therapy with this drug can last until the patient notes the absence of attacks for six months.
Other drugs for trigeminal neuralgia:
- Gabapentin;
- Baclofen;
- Valproic acid;
- Lamotrigine;
- Pregabalin.
Each of these drugs has indications for use in trigeminal neuralgia. Sometimes these drugs do not help, so phenytoin is prescribed at a dose of 250 mg. The drug has a cardiodepressive effect, so it should be administered slowly.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic procedures include paraffin baths, the use of various types of currents, and acupuncture. To get rid of severe pain, doctors give the patient alcohol-novocaine blockades. This is enough for some time, but the blockades are less and less effective each time.
- The following methods are used:
- Acupuncture;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultrasound;
- Laser treatment;
- Electrophoresis with drugs.
Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
During surgical treatment, the doctor tries to eliminate the compression of the nerve trunk by the blood vessel. In other cases, the trigeminal nerve itself or its node is destroyed in order to relieve pain.
Surgical treatments for trigeminal neuralgia are often minimally invasive. In addition, the surgical method also includes the so-called. Radiosurgery is a bloodless intervention that does not require any incisions or stitches.
There are the following types of operations:
- Percutaneous surgery. Used in the early stages of the disease. Under local anesthesia, the trigeminal nerve is destroyed by exposing it to chemicals or radio waves.
- Nerve decompression. This operation is aimed at correcting the location of the arteries that compress the trigeminal nerve.
- Radiofrequency destruction of the nerve root. In this operation, only a certain part of the nerve is destroyed.
The type of operation is prescribed depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s disease.
A characteristic feature of all surgical methods is a more pronounced effect when performed early. Those. The earlier this or that operation is performed, the higher the likelihood of cure.
Carbamazepine (Carbamazepinum)
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
Trade names in Russia
Carbamazepine, Finlepsin, Tegretol, Zeptol
Release form
Tablets: 200 mg
NBN nomenclature
Blocker of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels [2].
Ministry of Health of Russia
- E23.2 Diabetes insipidus
- F10.3 Withdrawal state
- F30 Manic episode
- F31 Bipolar affective disorder
- G35 Multiple sclerosis
- G40 Epilepsy
- G40.1 Localized (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with simple partial seizures
- G40.2 Localized (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with complex partial seizures
- G40.3 Generalized idiopathic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes
- G50.0 Trigeminal neuralgia
- G52.1 Lesions of the glossopharyngeal nerve
- G63.2 Diabetic polyneuropathy (E10-E14+ with common fourth character .4)
- R35 Polyuria
- R52.9 Pain, unspecified
- R63.1 Polydipsia
FDA recommendations
- Partial seizures with complex symptoms
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal)
- Mixed seizures
- Trigeminal neuralgia pain
- Acute episode of mania/mixed mania
UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency guidelines
- Generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures
- Trigeminal neuralgia pain
- Prevention of manic-depressive psychosis in patients not responding to lithium treatment
Target symptoms
Convulsions
Unstable mood, especially mania
Pain
Mechanism of action and pharmacokinetics
- Initial dose: half-life 26-65 hours
- Repeated doses: half-life 12-17 hours
- The half-life of active metabolites is about 34 hours
- Eating does not affect absorption
Dosage and dose selection
- 400-1200 mg/day
- Children under 6 years: 10-20 mg/kg per day
Bipolar disorder, seizures (adults, children over 13): Start with 200 mg twice daily; increase every week by 200 mg/day in several doses; maximum for adults 1200 mg/day; maximum for children 13-15 years old – 1000 mg/day; some patients may require doses up to 1600 mg/day.
Trigeminal neuralgia pain: start with 100 mg twice daily; increase every week by 200 mg/day in divided doses.
- Best taken with food
- Slowly increasing the dose delays the onset of the therapeutic effect, but increases tolerance to sedative side effects
- If other sedatives are being taken, increase the dose slowly
- Over time, after several weeks of treatment, dose adjustment is required
How quickly does it work?
Response to acute mania may occur within a few weeks.
It may take several months for your mood to stabilize.
Cramps should stop after 2 weeks.
Expected Result
Disappearance of symptoms.
Treatment can be continued indefinitely to prevent mania or seizures.
If it doesn't work
(for bipolar disorder)
Increase the dose;
Switch to another drug or add another drug;
Connect psychotherapy;
Determine if there is a comorbid condition
How to stop taking it
Reduce the dose gradually. Abruptly stopping use increases the risk of bipolar disorder relapse. In epilepsy, abrupt cessation can trigger seizures [1].
Treatment combinations
- Lithium
- Valproic acid
- Atypical antipsychotics
- Lamotrigine
- Antidepressants (with caution, as there is a risk of mood destabilization) [1].
Cautions and contraindications
- You need to watch for bleeding, bruising, mouth ulcers, infections, and fever. Taking carbamazepine increases the risk of aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis by 5-8 times.
- Use cautiously with MAOIs.
- May cause exacerbation of angle-closure glaucoma.
- Reduces the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives.
- Restriction of fluid intake may be necessary due to the risk of interfering with antidiuretic hormone production.
- Cannot be used if the patient has a history of bone marrow suppression.
- Do not use if the patient is allergic to any tricyclic compounds.
Patients with liver disease
Use with caution [1].
Patients with heart disease
Use with caution [1].
Elderly patients
In older people, side effects are more pronounced.
Children and teenagers
- Approved for use in epilepsy.
- Children 6-12 years: initial dose 100 mg twice daily; increase every week by 100 mg/day in several doses; maximum dose 1000 mg/day; maintenance dose 400-800 mg/day.
- Children 5 years and younger: initial dose 10-20 mg/kg per day 2-3 times daily; increase every week if there is a need; maximum dose 35 mg/kg/day.
Pregnant
- In the first trimester, it increases the risk of fetal developmental abnormalities. If treatment continues, tests should be performed to identify pregnancy pathologies. To reduce the risk, you should start taking folic acid (1 mg/day) earlier than usual.
- For bipolar disorder, carbamazepine should be discontinued until pregnancy occurs. During pregnancy, atypical antipsychotics are preferred.
Breast-feeding
- It is recommended that you stop taking carbamazepine or stop breastfeeding.
Interaction with other substances
- Combination with lithium may increase the neurotoxic effect of lithium
- Combination with other anticonvulsants may affect thyroid function
- Carbamazepine reduces the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives
Tests during treatment
Before starting treatment: complete blood count, liver, kidney, and thyroid function tests.
During treatment: complete blood count every 2-4 weeks for the first 2 months, then every 3-6 months; checking the function of the liver, kidneys, and thyroid gland every 6-12 years.
During treatment, it is necessary to monitor the concentration of sodium in the blood due to the threat of hyponatremia.
Mechanism of side effects
The causes of side effects of carbamazepine are theoretically associated with excessive effects on voltage-gated sodium channels.
Major metabolites may cause side effects.
Side effects
- Sedation, dizziness, confusion, unsteadiness, headache.
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
- Leukopenia
- Rash
- Dangerous side effects: aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, purpura, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Parhon syndrome with hyponatremia.
- Weight gain: yes, but infrequently
- Sedation: yes, and may be significant and, for some patients, excessively strong
What to do about side effects
- Wait;
- Take in the evening to avoid sedation;
- To avoid irritation to the stomach, take with food;
- Switch to another drug [1].
Long term use
Reduces libido;
Monitoring the functioning of the liver, kidneys, and thyroid gland is required, as well as regular general blood tests and sodium level measurements.
Overdose
May be fatal; nausea, vomiting, involuntary movements, cardiac arrhythmias, difficulty breathing, sedation, coma.
Advantages
May help with treatment-resistant bipolar or psychotic disorder [1].
Weaknesses
Requires laboratory monitoring and control over many parameters.
Causes severe sedation.
Not suitable for pregnant women.
Expert advice
The highest risk of serious side effects is in the first months of treatment.
May be recommended in cases where patients do not respond to treatment with lithium and other mood stabilizers.
Footnotes
1. Stephen Stahl “Prescriber's Guide”, 6th edition, 2017
2. Neuroscience-Based Nomenclature (//www.nbn2.com/taskforce)
Source: //psyandneuro.ru/carbamazepine/
Video: Trigeminal nerve treatment at home with herbs
https://youtube.com/watch?v=qHsNibrNiJo
Popular recipes include:
- Ointment from 1 tbsp. dried lilac buds, ground to a powder, and 4 tbsp. lard. It is recommended to rub the thoroughly mixed composition into problem areas.
- Infusion of 1 tbsp. dried wormwood flowers, poured into a thermos with 300 cm³ of boiling water, must be used after 4 hours in the form of lotions or compresses.
- A chicken egg, boiled and cut in half, effectively relieves pain when applied to the inflamed area.
- A compress prepared from a mixture of 200 g of crushed horseradish roots and the same amount of black radish, 30 g of sea salt, 15 ml of table vinegar is recommended to be applied to the affected area and left until a strong burning sensation occurs.
- Herbal teas based on yarrow, chamomile, burdock or fireweed are intended to stimulate blood supply to affected nerve fibers. Two tablespoons of any herb are poured into 500 ml of boiling water and left overnight in a thermos. Then the entire volume must be drunk within 24 hours. Treatment of trigeminal neuritis at home also involves the use of these herbs.
- A tincture prepared from a pulp of a large clove of garlic and 200 cm³ of vodka, kept in a dark place for a week, provides a warming effect when rubbing problem areas. To reduce pain, it is recommended to use it several times a day.
- Vodka tincture of birch buds, infused for 14 days in a dark place, is also recommended for mixed type inflammation of the V pair of cranial nerves.
- Blue clay cakes mixed with table vinegar effectively relieve pain.
- A compress of equal proportions of black radish juice and honey is intended to reduce the inflammatory process.
Use traditional methods and be healthy!
Read more information in articles from the neurology category:
- Inflammation and neuritis of the facial nerve. How to treat them at home
- Disease - Morton's neuroma and its treatment at home
- How to get rid of leg cramps at home
- Home treatment for Parkinson's disease
- Treatment of the sciatic nerve (sciatica) with traditional methods at home
- Intercostal neuralgia: concept, symptoms and treatment at home
- Neuritis: folk remedies
- The concept of “hand tremor” and its treatment at home
- Proper treatment of stuttering in children and adults at home
- Self-treatment of neuralgia: symptoms and effective methods at home
- What is neurosis and how to treat it at home
- Epilepsy: causes, symptoms, first aid and treatment with folk remedies
- Effective treatment of multiple sclerosis with traditional methods
Traditional methods
There is an opinion that you can relieve pain from trigeminal neuralgia with the help of black radish juice. The same remedy is effective for sciatica and intercostal neuralgia. It is necessary to moisten a cotton swab with juice and gently rub it into the affected areas along the nerve.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what happens if you don’t insert extracted teeth
Another effective remedy is fir oil. It not only relieves pain, but also helps restore the nerve in case of neuralgia. It is necessary to moisten a cotton wool with oil and rub along the length of the nerve. Since the oil is concentrated, do not use it vigorously, otherwise you may burn. You can repeat the procedure 6 times a day. The course of treatment is three days.
For neuralgia, fresh geranium leaves are applied to the affected areas for several hours. Repeat twice a day.
Treatment regimen for a cold trigeminal nerve:
- Warming your feet before bed.
- Take vitamin B tablets and a teaspoon of beebread twice a day.
- Apply Vietnamese “Star” to the affected areas twice a day.
- Drink hot tea with soothing herbs (motherwort, lemon balm, chamomile) at night.
- Sleeping in a hat with rabbit fur.
When pain affects teeth and gums, you can use chamomile infusion. Infuse a teaspoon of chamomile in a glass of boiling water for 10 minutes, then strain. You need to take the tincture into your mouth and rinse until it cools. You can repeat the procedure several times a day.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Many patients complain of sudden and causeless pain, but also note the occurrence of neuralgia after stressful situations. Doctors are inclined to believe that the inflammation developed earlier - a stressful situation triggered the onset of pain.
The branches of the trigeminal nerve affect motor and sensory fibers, acute pain appears, spasms in the area of the masticatory muscles, all these symptoms indicate inflammation.
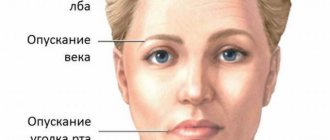
Symptoms of facial nerve damage are:
- acute piercing pain in one of the halves of the face, which has a through nature;
- distorted facial expressions due to skewed individual areas or in the area of one half of the face;
- headaches, chills, general weakness, muscle pain throughout the body;
- increased body temperature (hyperthermic reaction of the body);
- with severe pain – insomnia, fatigue and irritability;
- muscle twitching near the affected nerve;
- a small rash in the affected area of a certain part of the face.
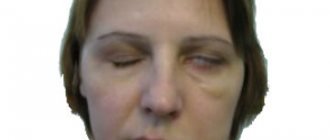
Severe shooting pain from the ear region to the midline of the head indicates the main manifestation of neuritis, after which a gross distortion of the face appears. Such changes may remain lifelong if the disease becomes protracted or progressive.
If the disease persists for a long time, paleness or redness of the skin, changes in the secretion of glands, greasy or dry skin, swelling of the face and even loss of eyelashes are possible.
Neuralgia pain is divided into two types:
- Typical pain is sharp and intense, periodic, and can fade and recur. With neuritis, the shooting, similar to a toothache, resembles an electric shock and lasts about 2-3 minutes. It affects only one part of the face and is localized depending on which part of the triple nerve is damaged. After paroxysmal pain, it is replaced by aching pain. Typical pain can be triggered by washing, brushing teeth, shaving, applying makeup - actions affecting one of the parts of the face. Pain appears during laughter, smiling and talking, most often occurring after exposure to low temperatures on one of the halves of the facial and ear areas.
- Atypical pain is constant with short breaks, covers most of the face, making it difficult for the patient to determine its source. It happens that a painful attack is accompanied by muscle spasm, then a painful tic occurs on the affected side of the face. Their sudden contraction looks like abnormal facial asymmetry and is accompanied by pain, and the victim cannot open his mouth until the attack ends. It is much more difficult to treat, since the pain torments the patient every hour, reaching its peak in 20 seconds, after which it continues for some time.
Carbamazepine: reviews from patients and doctors
I have friends who also took this drug. Usually they complain of severe drowsiness, which is the only way to knock them out. Some people cannot get out of bed at all. But more often than not, they simply started with high doses. As for the immediate effect, most often the drug helps with neuralgia. I knew of only one case when it didn’t help, but it turned out that the woman had facial pain, just like me, but if mine was even more or less treatable, then with her she didn’t want to react to anything, not even to lyrics .
Carbamazepine also works well as a mood stabilizer. But it will not relieve full-blown mania with psychosis, because there were precedents. Mild mood swings are fine, but something more serious is better treated with something else.
Soviet-trained doctors love carbamazepine and prescribe it left and right. More modern ones have switched to sedalite, but this is also not the safest drug. Other doctors, on the contrary, are afraid of carb and try with all their might not to prescribe it to you. But if you ask, they will write it out under your responsibility.
Prevention of inflammation: what to do to avoid problems
Preventive measures follow directly from the list of reasons:
- At a minimum, it is worth preventing exposure to harmful factors in the form of hypothermia, bruises, viral and other infections.
- If any of the previously listed diseases occurs, treatment measures must be taken immediately.
- You should also keep your cardiovascular system in working order - regular exercise (at least exercise in the morning), healthy sleep, and proper nutrition.
- In addition, a light facial massage (maybe with cream), which improves blood circulation, will bring additional benefits. Women can combine massage with beauty treatments.
Therapeutic massage of the facial area
So, one of the most effective ways to eliminate signs of inflammation is massage.
For a high-quality massage, no devices or means are needed (with the exception of warming bags). With its help, it is unlikely that it will be possible to completely cure inflammation at home, but it will completely relieve the symptoms of the acute phase.
The massage is intended to reduce tension in the facial muscles, as well as alleviate the general condition of the patient.
In addition to facial massage, a light massage of the whole body has an excellent effect.
It is recommended to use fir oil as a massage oil.
Additionally, special bags of buckwheat, which are pre-heated and applied to the location of the pain, will give an excellent effect.
You can also use honey (preferably with propolis) for massage. The massage is done until the skin becomes red, before going to bed. The next morning the pain should subside.
Symptoms, consequences
Symptoms play a decisive role in treatment, but their consequences are no less important. It is with them that you will have to actively fight if you delay the start of the main therapy or do it not quite correctly.
Symptoms
The main symptom of neuralgia is severe pain. It can manifest itself only in certain parts of the face, if the inflammation has affected one branch of the nerve endings, or over its entire area at once. Most often, pain appears abruptly, is very intense, lasts about 3 minutes, after which it fades slightly, turning into aching pain. A provoking factor can be any action during which there is physical contact of the face with any object, or the manifestation of emotions through facial movements using the facial muscles.
Sometimes the pain is atypical. It is characterized by its constancy and torments the patient almost always, occasionally interrupting. As a rule, such pain affects most or all branches of the trigeminal nerve. Often accompanied by muscle spasms, causing facial asymmetry.
Additional symptoms help ensure that the patient has inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Among them:
- Pain in the head and sometimes in the ears;
- Asymmetry and numbness of the face;
- Skin rashes;
- Weakness;
- Irritability;
- Tearing;
- Muscle spasms;
- Hearing impairment;
- Deterioration of vision, minor defects;
- Difficulty trying to move your jaw;
- Malfunction of taste receptors;
- Increase in body temperature to 37° C.
If the inflammation is secondary, then other manifestations corresponding to the underlying disease may be observed.
Consequences
If you treat the trigeminal nerve with folk remedies at home without consulting a doctor, do it incorrectly, or do not treat it at all, then there is a high probability of developing complications. They can be dangerous:
- Decreased immunity;
- Impaired functioning of the organs of hearing and vision;
- Weakening or paralysis of facial muscles;
- Long-term loss of coordination;
- Decreased sensitivity of the skin on the face;
- Mental pathologies, depression;
- Disturbances in the nervous system.
All these consequences can become chronic, and getting rid of them will be very difficult or even impossible. Therefore, you need to approach the issue of treatment as seriously as possible.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of neuralgia is severe pain, which is localized in the place where the inflammation occurred. Such localization is typical for the typical nature of the disease, but in the case of an atypical subtype of inflammation, the pain affects the entire face and in such a situation it is impossible to determine where exactly the lesion is located.
This pain is often confused with toothache. How to distinguish toothache from inflammation of the trigeminal nerve? A dentist can do this, and in most cases this is what happens, since a sick person first turns to dentistry.
As a rule, the dentist does not find the cause of the pain if the teeth are well-groomed. In the case where there is a problem of a dental nature (and this is often the case), the doctor takes measures to eliminate it and, while using painkillers, there may be some improvement in the patient’s condition, but not for long.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is dangerous to think that traditional medicine can help with such a dangerous disease.
The longer you wait to see a doctor, the more severe the consequences may be. At best, folk recipes are used only as a method of auxiliary therapy after consultation with a doctor. Here are some examples:
- Rub radish juice with lavender oil. A rub is prepared from these components in a ratio of 20:1, rubbed in the direction of the nerve. After rubbing, cover your face with a warm cloth for half an hour.
- Aloe juice is used internally. You will need to squeeze the juice from a plant that is at least three years old. Drink a teaspoon of aloe juice three times a day before meals.
Traditional treatment
Trigeminal neuralgia is very difficult to treat, which is why it is important to immediately prescribe the patient complex therapy, consisting of medications, physiotherapy, and folk remedies. If painful attacks follow each other throughout the day, then it is best to carry out treatment in hospitals, where most of the medications will be administered by injection
Use of medications
Treatment of nerve inflammation should be aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease and relieving pain. That is, it is always necessary to find out exactly what is associated with a pain attack in the face. The treatment regimen for trigeminal neuralgia most often consists of the use of the following groups of drugs:
Anticonvulsants. In most cases, a drug such as Carbamazepine is chosen; it reduces impulses in sensory nerve fibers. The medicine begins to act after about two days, under its influence the pain decreases and the intervals between attacks increase. The dosage is selected individually, treatment of neuralgia with Carbamazepine is carried out until exacerbations of the disease are recorded within six months. Anticonvulsants based on Oxcarbazepine, Clonazepam, and Gabapentin are also used. At the beginning of the development of the disease, a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is used; they are intended to relieve inflammation and reduce pain. Nimesil, Ketanov, Ibuprofen are prescribed.
Painkillers and antispasmodics are used to relieve pain. These are Trimecain, Baclofen, Baralgin. If the pain cannot be relieved when using analgesics, then a short course of narcotic drugs is used. Of course, with a doctor's prescription. Patients with trigeminal neuralgia are necessarily prescribed sedatives and antidepressants. Amitriptyline, Sodium hydroxybutyrate is used
The drugs must be prescribed by a doctor, since it is important to choose the right dosage and general course of their use. Vitamin therapy is important in the treatment of neuralgia
Most often, vitamins from group B, Rosolakrit and Neurobion complexes are prescribed. To speed up recovery and prevent relapses of the disease, it is recommended to take drugs that enhance the body’s overall resistance. These can be products based on echinacea, rose hips, ginseng, and royal jelly.
The patient is necessarily prescribed etiotropic therapy, that is, medications aimed at eliminating the main cause of nerve inflammation. It can be:
- Antiviral drugs if it is determined that the herpes virus is involved in the development of the disease. Laferon and Gerpevir are prescribed.
- In case of multiple sclerosis, it is necessary to use a course of medications that are involved in the restoration of the myelin sheath of the nerves.
- For atherosclerosis, drugs are prescribed that help dissolve cholesterol plaques - Rosuvalostatin, Atoris.
- When identifying a vascular aneurysm, it is necessary
Drug therapy is selected for each patient individually. In the process of taking medications, it is necessary to constantly evaluate their effectiveness in reducing the number of attacks and increasing the intervals between attacks. If necessary, the dose of essential medications is adjusted or replaced.
Physiotherapy
When performing physical procedures, pain is reduced and nutrition and blood supply to the affected area are increased, which helps restore nerves. For inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, in most cases the following is prescribed:
- UFO – ultraviolet irradiation of the face. This procedure helps relieve pain.
- UHF is used to improve microcirculation during the onset of atrophy of the masticatory muscles and to reduce pain.
- Electrophoresis with Platiphylline, Novocaine, Diphenhydramine helps relax muscles, thereby reducing pain. To improve nutrition of the myelin sheath of the nerve, B vitamins are administered using electrophoresis.
- Laser therapy inhibits the passage of nerve impulses through the fibers and relieves pain.
- Electric currents in pulse mode. This procedure has an analgesic effect and helps prolong the period of remission.
- Physiotherapy procedures are also selected for the patient individually, and they can be repeated periodically.
Finlepsin retard 200 mg n50 tab. – Evalar pharmacy
Pharmacy on PaveletskayaPharmacy on TverskayaPharmacy on OktyabrskayaPharmacy on NovoslobodskayaPharmacy on SmolenskayaPharmacy on SokolPharmacy on Aviamotornaya RUR 212.00 in stock: 1 pc.
Manufacturer: Teva
Anticonvulsant drug (dibenzazepine derivative).
It also has antidepressant, antipsychotic, antimanic and antidiuretic effects, has an analgesic effect in patients with Neuralgia Neuralgia (neuralgia; modern Greek νεῦρο - nerve, ancient Greek.
νεῦρον - tendon, fiber and ἄλγος - pain) - a type of sensitivity disorder, manifested by acute pain in the innervation zone (i.e. along the course) of the affected nerve, usually of a paroxysmal nature.
The most famous are neuralgia of the trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, and occipital nerves. .
The mechanism of action is associated with the blockade of voltage-dependent sodium channels, which leads to stabilization of the membrane of overexcited neurons, inhibition of the occurrence of serial neuronal discharges and a decrease in synaptic conduction of impulses. Prevents the re-formation of Na + -dependent action potentials in depolarized neurons.
Reduces the release of glutamate (an amino acid with excitatory neurotransmitter properties), increases the reduced threshold of convulsive readiness and, thus, reduces the risk of developing an epileptic attack.
Increases the transport of potassium ions, modulates voltage-dependent calcium channels, which may also contribute to the anticonvulsant effect of the drug.
Effective for focal (partial) epileptic seizures (simple and complex), accompanied or not accompanied by secondary generalization, for generalized tonic-clonic epileptic seizures, as well as for a combination of these types of seizures (usually ineffective for petit mal, absence seizures and myoclonic seizures).
In patients with epilepsy (especially children and adolescents), a positive effect on symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as a decrease in irritability and aggressiveness, was noted. The effect on cognitive function and psychomotor performance is dose dependent.
The onset of the anticonvulsant effect varies from several hours to several days (sometimes up to 1 month due to autoinduction of metabolism).
In case of essential and secondary neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve, in most cases it prevents the occurrence of painful attacks. Pain relief from trigeminal neuralgia is observed after 8-72 hours.
In alcohol withdrawal syndrome, it increases the threshold of convulsive readiness (which is usually reduced in this condition) and reduces the severity of the clinical manifestations of the syndrome (increased excitability, tremor, gait disturbances).
The antipsychotic (antimanic) effect develops after 7-10 days, which may be due to inhibition of the metabolism of dopamine and norepinephrine.
Active ingredients
Carbamazepine 200 mg.
Excipients
Methacrylate copolymers, triacetin, talc, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, highly dispersed silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate.
Pharmacological properties:
Suction
When taking the drug orally, carbamazepine is slowly but almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (food intake does not significantly affect the rate and extent of absorption).
After a single dose of 400 mg, Cmax is reached after 32 hours and averages about 2.5 μg/ml.
Distribution
C ss in plasma is achieved after 1-2 weeks of constant use (the rate of achievement depends on the individual characteristics of metabolism: autoinduction of liver enzyme systems, heteroinduction by other simultaneously used drugs, as well as on the patient’s condition, the dose of the drug and the duration of treatment).
There are significant interindividual differences in the value of equilibrium concentrations in the therapeutic range: in most patients these values range from 4 to 12 μg/ml (17-50 μmol/l).
Concentrations of carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide (a pharmacologically active metabolite) are approximately 30% of those of carbamazepine.
Plasma protein binding in children is 55-59%, in adults – 70-80%. Apparent Vd – 0.8-1.9 l/kg. In the cerebrospinal fluid and saliva, concentrations are created proportional to the amount of active substance not bound to proteins (20-30%). Penetrates the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk (the concentration is 25-60% of that in blood plasma).
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver, mainly along the epoxide pathway, with the formation of the main metabolites: active - carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide and inactive conjugate with glucuronic acid.
The main isoenzyme that ensures the biotransformation of carbamazepine into carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide is cytochrome P 450 isoenzyme 3A4.
As a result of these metabolic reactions, a low-active metabolite, 9-hydroxy-methyl-10-carbamoylacridan, is also formed. Can induce its own metabolism.
Removal
T1/2 after a single oral dose is 60-100 hours (on average about 70 hours); with prolonged use, T1/2 decreases due to autoinduction of liver enzyme systems. After a single oral dose, 72% of the dose taken is excreted in the urine and 28% in feces; while about 2% are excreted in the urine in the form of unchanged carbamazepine, about 1% - in the form of a 10,11-epoxide metabolite.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
There is no evidence that the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine changes in elderly patients.
Directions for use and dosage:
The tablets are taken orally during or after meals with a sufficient amount of liquid. If necessary, the tablets can be pre-dissolved in water or juice (while maintaining the ability for prolonged release of the active substance).
The therapeutic concentration of carbamazepine in blood plasma is 4-12 mcg/ml.
The average dose range is 400 -1200 mg/day, dosage frequency 1-2 times/day. The maximum daily dose is 1600 mg.
If you miss a regular dose of the drug, you should take the missed dose as soon as you notice it, and you should not take a double dose of the drug.
When used as an anticonvulsant, in cases where this is possible, Finlepsin retard should be prescribed as monotherapy. Treatment begins with a small daily dose, which is subsequently slowly increased until the optimal effect is achieved.
The addition of Finlepsin retard to already ongoing antiepileptic therapy should be carried out gradually, while the doses of the drugs used are not changed or, if necessary, adjusted.
For adults, the initial dose is 200-400 mg/day, then the dose is slowly increased until the optimal therapeutic effect is achieved. The average maintenance dose is 800-1200 mg/day. For children, the average maintenance dose is 10-20 mg/kg body weight per day.
Not recommended
- Bone marrow hematopoiesis disorders (anemia, leukopenia).
- AV block.
- Acute intermittent porphyria (including history).
- Simultaneous use with lithium preparations and MAO inhibitors.
- Children's age up to 6 years.
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug and tricyclic antidepressants.
The drug should be used with caution:
- For severe heart failure.
- If liver and/or kidney function is impaired.
- Elderly patients.
- Patients with chronic alcoholism (increased depression of the central nervous system, increased metabolism of carbamazepine).
- For dilution hyponatremia (ADH hypersecretion syndrome, hypopituitarism, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency).
- For prostatic hyperplasia.
- With increased intraocular pressure.
- When used simultaneously with sedative and hypnotic drugs.
Source: //asevalar.ru/catalog/lekarstvennye-sredstva/lekarstvennye-sredstva_13088.html
Massage
Using relaxation techniques can be an effective treatment for complementary trigeminal pain.
Massage is usually indicated for acute stages of the disease.
During attacks of pain, the affected tissues of the patient's face become tightened and hardened. Gentle massage and a heating pad can help relax and soften the tissue to a pliable level to relieve pain. Skull massage can help relieve pressure and restore the natural position of the bones in the head and neck area.
Once the acute pain has passed, acupressure techniques such as shiats can limit the spread of pain, while lymphatic drainage can relieve any fluid congestion that is increasing pressure on the affected nerve. A general relaxing massage to the rest of the body can also relieve stress.
Any pain around the head and neck requires caution and may indicate serious problems that require medical attention.
Tip 6: How to treat your eyes
A very healthy dish for the eyes is beef chop with fried carrots, because... the meat contains zinc, which increases visual acuity in the dark, and carrots support the normal functioning of the retina.
When you feel tired eyes, deteriorated vision, or work for a long time at a computer or with printed texts, corneal dystrophy occurs. For proper eye function, you need riboflavin, the source of which is mushrooms, vegetables, and dairy products.
Tea has an anti-inflammatory effect, which is ideal for eye irritation.
Inflammation of the eyes is best treated not with fresh tea, but with drunken tea. This is tea that was brewed in the evening and stood until the morning.
Under no circumstances should the drink be allowed to stagnate, because... after 2 days, bacteria actively begin to multiply in it, which will only harm the inflamed eye.
A cotton lotion soaked in warm tea leaves will help remove bags and circles under the eyes and eliminate the painful appearance. You should leave the compress for 10 minutes, and then apply the cream to the skin of the eyelids with gentle movements.
An infusion of chamomile tea will help relieve inflammation and prevent early wrinkles. To do this, make 2 bags from gauze, the size of the eye socket. Pour a small pinch of tea and chamomile petals into them. Heat boiling water and place the bags in it, leave for 10 minutes. Cool slightly and apply warm to both eyes.
For prevention, you should instill a few drops of drunk tea into both eyes.
Conjunctivitis, clogging of the mucous membrane, as well as inflammation of the eyelids are best treated with a cold infusion of a mixture of green and black teas with the addition of dry wine at the rate of 1 teaspoon of wine per glass of infusion.
If your eyes are watery, you can wash them with a weakly brewed tea drink. To do this, wash a container with a diameter suitable for the volume of the eye, for example, a shot glass, and pour boiling water over it. When the container has cooled down, rinse it again with clean distilled or spring water and place it in a shallow plate. Pour warm tea brewed with meniscus into a container to the brim. Dip your eye into the solution and blink several times. Repeat the procedure with the second eye, after washing the container.
It often happens that in windy weather dust or sand gets into the child's eyes. The white of the eye turns red, the eye becomes inflamed, and the baby experiences an unpleasant burning sensation. Especially if the child is small, and you cannot explain to him that you should not rub your eyes with your hands.
The method of washing children's eyes is quite simple; it is suitable for all ages, even infants. The child's eyes should be washed with weakly brewed warm tea or warm chamomile infusion. Under no circumstances should the solution be allowed to get from one eye to the other; in this way, the infection can spread to the healthy eye.
You will need to drop liquid into the inner corner of the eye with a pipette so that the solution and tear fluid flow out from the outer corner.
https://nashyzubki.ru/polezno/lechenie-trojnichnogo-nerva-v-domashnih-usloviyah.html
https://lechim-prosto.ru/lechenie-doma/polosti-rta/vospalenie
https://www.kakprosto.ru/kak-32033-kak-lechit-troynichnyy-nerv
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physical effects on skin receptors help their rapid recovery. They improve blood flow to the affected area, and the irritating effect helps to restore lost sensitivity.
Physiotherapy is prescribed during a period when there is no acute pain - for atypical neuralgia or during a period of typical remission.
Main methods of influence:
- Applications with paraffin - heated paraffin is applied to the affected area of the face. The procedure improves metabolism and nutrition in tissues.
- Bernard currents - the effect of diadynamic currents on the painful area. This method is also used in the acute period, due to its effect on the pain threshold. Prescribed only in complex treatment.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture) is a method of influencing pain points. Improvement often occurs from the first procedures.
Treatment with medications
Let's try to figure out what the most basic drugs are used in medical practice to treat trigeminal neuralgia. Let's divide medications into groups:
Anticonvulsants. These are remedies aimed at relieving cramps and spasms. In first place among such drugs is carbamazepine. The treatment regimen with this drug consists of gradually increasing the doses of the drug until the pain decreases as much as possible, after which the dose of carbamesipine is reduced.
Very important! Take the drug strictly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not exceed the norm, as the drug can lead to severe toxic poisoning of the kidneys and liver
Phenytoin and Convulex are often prescribed together with carbamesipine.
Drugs that relax muscles. These medications work well in combination with anticonvulsants.
- Baclofen, sodium hydroxybutyrate, is often prescribed.
- Finlepsin tablets have proven themselves well. Most often, 1-2 tablets are prescribed once a day, gradually increasing the dose to 3-6 tablets.
Antidepressants. A group of these drugs is used to relieve nervous tension and stress caused by pain during the disease process. This includes the drug amitriptyline and others.
- For vascular diseases, trental and agapurine are used.
- To relieve local pain symptoms, diclofenac, lidocaine and other anesthetic ointments are used.
- If the doctor suspects inflammation due to a viral disease, ceftriaxone and other antibiotics may be prescribed.
In particularly severe cases of the disease, surgical intervention is indicated. The surgeon’s actions are aimed at releasing the nerve ending from vascular pressure. Such operations are performed in cases of ineffectiveness of drug treatment.
Carbamazepine and alcohol
A very popular topic if you look at queries in search engines ???? In general, this drug is used to treat “squirrel”. The instructions say that it is “recommended to abstain” from drinking libations, which some will perceive as “ah, it is recommended, not prohibited, which means it’s possible!” But no. Carbamazepine is not prescribed for such a long time, so you can abstain. It does not reduce the concentration of the substance, but it hits the liver. And the carb also taps well on it. That is, there is a chance to knock out the liver, but do you need it? You can also catch some serious glitches and have a good vomit, which will damage your stomach and pancreas. And then it takes a long and tedious time to undergo treatment.
So we become teetotalers the moment we take carb! The liver will thank you.
Consequences
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is not fatal, but the consequences are very dangerous.
- Depression is developing rapidly.
- Constant pain causes mental disorders, there may be a need to avoid society, and social ties are broken.
- The patient loses weight because he cannot eat properly.
- The patient's immunity decreases.
Timely elimination of symptoms does not pose a health hazard, and remission, together with conservative treatment lasting several months, prepares the body for potential surgery.
Video: Fayyad Akhmedovich Farhat (Doctor of Medical Sciences, neurosurgeon of the highest qualification category) about a disease of the facial nerve.
Consequences and complications
The pathology does not have life-threatening consequences, but has a negative impact on the condition of the facial muscles. Weakening of innervation leads to decreased sensitivity, and then to paresis and paralysis of motor muscles. Partial atrophy of the masticatory muscles appears. Among possible complications, doctors note the development of depression, neurosis, and anxiety disorder. Without treatment, the likelihood of complications developing is 97%.
In order not to suffer from excruciating pain, you should follow preventive measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of neuralgia. Experts advise promptly treating caries, sinusitis, herpes and other infectious diseases.
How to relieve trigeminal nerve pain
- How to relieve trigeminal nerve pain
- How to treat the trigeminal nerve
- How to treat the trigeminal nerve
Irritants
If you experience occasional trigeminal pain, the first thing you can do is determine what is causing the pain. Keep track of when and under what circumstances you experience these pains. Strong winds and eating spicy foods are the most common irritants that cause trigeminal pain. Try to avoid any, even slight, draft in the room you are in. Stop eating hot and spicy foods; in some cases it may be necessary to avoid specific foods, most often coffee, citrus fruits, bananas, etc.
Trigeminal nerve pain forces a person to stop all physical activity. He is depressed and usually refuses to eat. However, you can use cold drinks to quell the pain. Try drinking them through a straw, this often helps reduce pain.
Consultation
Trigeminal nerve pain requires referral to medical specialists, in particular neurologists or neurosurgeons who are familiar with this kind of pain and have experience in treating it. You will undergo special diagnostics, such as an MRI, which will help determine the best way to further treatment.
Medications
To treat trigeminal nerve pain, doctors most often prescribe certain medications, usually antiepileptic drugs. These drugs help slow down the nervous system, dulling pain. These medications must be taken strictly according to the doctor's instructions, without exceeding the indicated dosages, otherwise serious complications may occur. The most effective drugs of this kind include: Carbamazepine, Oscarbazepine, Baclofen, etc. These drugs can cause a number of side effects, for example, nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, memory problems, allergic reactions, etc. If you experience them, try seeing your doctor to change your medication.
Healing procedures
Drug treatment may not produce the expected results, and the side effects from taking the drugs may be unbearable. In this case, doctors can prescribe you a number of treatments that help reduce pain or get rid of it completely. These include, for example, glycerin injection and radiofrequency nerve destruction. Such procedures are usually performed under anesthesia, but the patient goes home immediately after they are performed.
Side effects of carbamazepine
Besides the fact that you feel as if you had swallowed a bottle of vodka down your throat, there are other “fun things”. When, in severe pain, I started taking half a tablet at once, there were these helicopters... And, most importantly, my head was sober! I can think and talk, but I can’t stand up.
At first, the drug in any dosage will cause extreme drowsiness, so start taking it at night. Then it goes away. At high doses, you may experience glitches. Nausea - of course, sometimes even vomiting. Dry mouth, headache and even the inability to focus your eyes. You can read more in the instructions if you are interested in this. I didn’t find coma and death there and was upset ???? I've already seen this in many instructions. From all of the above, I had drowsiness, weakness and nausea.
But in general, you don’t need to expect any special side effects. If you gradually increase the dosage, then everything will be fine.