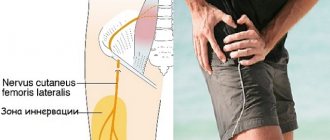
When a nerve is pinched in the hip joint (pelvic neuralgia), severe pain occurs, which is localized in the affected area and often radiates along the lower limb. This problem is of concern mainly after a traumatic injury or during pregnancy.
For pain, painkillers (often with novocaine), anti-inflammatory drugs (Movalis, Ibuprofen) and other medications are used to relieve general symptoms and restore nerve conduction.
How does pinching occur?
Pelvic neuralgia is a pathology caused by compression (compression), inflammation or pinched nerve. This nerve begins near the lumbosacral region, which explains the causes of pain in the back.
The pelvic nerve consists of the following fibers:
- ischial;
- femoral;
- obturator;
- upper and lower gluteals.
Pinching of the sciatic nerve occurs more often and the cause of this is mainly an inactive lifestyle or excess body weight.
Neuralgia of this type has no characteristic symptoms. In particular, when the innervation of the hip joint is disturbed, pain occurs in the lumbar region and radiates to the groin area. In such cases, patients look for a problem in diseases of the reproductive system, while the cause lies in a pinched nerve in the pelvis.
Prevention
A person who moves enough is unlikely to have such a problem even in old age. But for those who spend too much time without a break sitting at the computer, this is very possible. Especially if these people are slouching.
This is due to the fact that in a person with a stooped back, the organs begin to gradually move down and put pressure on each other. This is why pinching in the hip occurs in such a situation. So it's important to move daily. You shouldn’t do this a lot, the main thing here is regularity and methodicality.
Conclusion
If there is a sharp pain in the hip that does not go away, perhaps the problem is pinching. This is a problem that should not be ignored, and it will not work. It is advisable to deal with it as soon as possible to avoid complications.
Causes of neuralgia
Due to the nature of the fibers, pinching of the sciatic nerve in the hip joint leads to pathologies of the spine in the lower part:
- mechanical damage, fractures;
- tissue inflammation;
- tumors in the spine and hip joint;
- joint diseases (arthrosis, arthritis);
- systemic infections;
- blood flow disturbance.
Pinched nerves in this area are characteristic of spinal osteochondrosis, in which cartilage and bone tissue are destroyed, causing disc protrusion.
The risk group for developing neuralgia includes athletes and people who have suffered severe hypothermia. Increased loads on the hip region provoke inflammation of the piriformis muscle of the back, which compresses the sciatic nerve.
In some cases, the appearance of neuralgia is due to heredity. In some patients, the nerves in the pelvic area are in constant contact with bone tissue. This is due to a congenital abnormal arrangement of tissues or defects in this part of the skeleton.
Also, women often turn to doctors with a pinched nerve in the hip joint during pregnancy. The development of pathology in this case is associated with an increased load on the lower part of the body, which causes damage to the muscular and ligamentous apparatus.
Large or multiple pregnancies are considered the most dangerous in terms of the likelihood of neuralgia.
The possibility of pinching the hip nerve after surgical treatment of the joints cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the location of neuralgia of the hip joint, symptoms of inflammation appear in different parts of the body. This feature also determines the severity of the clinical picture.
In case of damage to the femoral nerve, which lies next to the psoas and iliacus muscles, neuralgia causes:
- intense, acute pain localized in the thigh and groin area;
- pain radiating to the lower back and ankle;
- decreased mobility of the ankle joint.
As inflammation progresses, atrophy of the hip nerve and quadriceps muscle develops. The latter is affected due to lack of innervation.
The obturator nerve runs from the lower back through the small pelvis, in the lower part of which it divides into two branches. When these nerve fibers are damaged, the following symptoms are of concern:
- pain syndrome localized on the inner side of the thigh and radiating to the groin area;
- muscle spasms that occur during movement;
- feeling of discomfort in the anal area.
The intensity of general symptoms when the nerve of the hip joint is pinched increases when the patient sits on a hard surface. At the same time, the person cannot move the affected limb to the side.
The most pronounced symptoms are neuralgia caused by pinching of the sciatic nerve in the hip area.
This is explained by the fact that these fibers run along the lower extremities, ending at the foot. With such lesions, the following phenomena are observed:
- burning pain extending from the lower back to the foot;
- decreased sensitivity of the buttocks and ankles;
- decreased mobility of the knee joint;
- limbs get tired quickly;
- change in gait (severe lameness);
- decreased mobility of the toes;
- increased sweating on the feet.
Due to the lack of innervation, over time, ulcers appear on the lower extremities, and the muscles of the thigh and lower leg atrophy. There may also be problems with urination. Mostly such symptoms appear on one side. In rare cases, there is impairment of motor function in both limbs.
The gluteal nerves (upper and lower) run between the muscles of the same name and end in the lower part of the hip joint. Such anatomical features leave their mark on the nature of the manifestation of neuralgia. When these fibers are damaged, pain is localized only in the buttocks and lower back. If the upper nerve becomes inflamed, it becomes impossible to bend the limb normally, and the lower nerve becomes impossible to move the thigh to the side.
Features of the nerve
The name of the obturator nerve in Latin is Nervus obturatorius. It originates in the plexus in the lower back. Has 3 branches:
- Muscular branch. Enters the obturator canal.
- Rear. Located between the major and short adductor muscles.
- Front. Continues the main trunk. It is located between the long and short adductor muscles and gives off to them and to the gracilis and pectineus muscles. These elements externally rotate the hip, adduct and determine the flexion. At the top of the thigh, the branch is made sensitive and supplies the skin.
Diagnostics
Pelvic neuralgia is relatively easy to diagnose. Hip neuritis is often identified by collecting information about the patient's symptoms and condition. In particular, the most characteristic symptoms occur when the sciatic nerve is pinched.
In addition to making a diagnosis, it is important to find out what triggered the neuralgia.
For this, the following examination methods are used:
- CT and MRI of the spine and hip joint;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound of the hip joint;
- electromyography, which helps evaluate nerve conduction.
If neuralgia of an infectious nature is suspected, general and biochemical blood tests are prescribed. If necessary, radiological examination is used to help identify tumors.
Diagnostic procedures
If a person feels nagging and sharp pain in the pelvis, radiating to the lower back and leg, an urgent need to consult a neurologist. During the initial examination, the doctor will listen to complaints, perform palpation, and try to find out the reason why the nerve is pinched. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is given a referral for the following diagnostic procedures:
- radiography;
- MRI or CT;
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- electromyography;
- blood and urine tests.
Return to contents
Treatment methods
Drug therapy
There are different approaches to how to effectively treat a pinched nerve in the hip joint. Treatment methods are selected taking into account the characteristics of the causative factor. Basically, for inflammation in this area, drug therapy is carried out with the aim of improving the patient's condition and suppressing general symptoms.
For such violations, the following are indicated:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. This group includes Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketonal. Anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain and eliminate swelling.
- Vasoactive agents. Nicotinic acid, Pentoxifylline and a number of other drugs accelerate blood microcirculation.
- Corticosteroids. "Hydrocortisone" and "Diprospan" are used in the form of injection solutions in cases where treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs has not produced results.
- Muscle relaxants. "Mydocalm" and "Baclofen" are prescribed for muscle spasms.
Due to the fact that for symptoms of inflammation of the nerve of the hip joint, treatment is prescribed depending on the causes of the disease and the localization of the pathological process. For neuralgia, anticonvulsants and antidepressants are often used. Drugs of these groups are used to restore sensitivity of the lower extremities.
As part of traditional therapy, reparants are used that stimulate the regeneration of damaged fibers. During pregnancy, pathology is treated with herbal medicines.
In extreme cases, drug treatment for a pinched nerve in the hip joint is supplemented with surgical intervention.
Physiotherapy
For neuralgia of the pelvic nerves, depending on the individual characteristics of a particular case, the following physiotherapeutic techniques are used:
- magnetic therapy;
- electro- and phonophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- UHF;
- exposure to dynamic currents;
- hydrogen sulfide and radon baths;
- paraffin applications.
When a nerve is pinched in the hip joint, treatment with massage and gymnastics is indicated.
Moreover, in some cases, physical therapy is enough to eliminate the symptoms of neuralgia and restore the patient’s condition. Exercise therapy for such disorders should be selected by a doctor. If the symptoms of the disease are mild, the following exercises can be performed to restore mobility of the lower extremities:
- Lying on your back, pull your legs to your chest and stay in this position for a few seconds.
- In a lying position, stretch your legs forward and make several rotational movements.
- In a standing position, lift one leg, bent at the knee, and perform several circular movements.
- Walk on your heels, toes, inner and outer sides of the foot, without bending the knee joint.
Massage for pinched pelvic nerves is performed according to doctor’s instructions. It is not recommended to carry out this procedure on your own.
Treatment at home
There are many methods for treating a pinched nerve in the hip joint at home. It is recommended to discuss each method with your doctor, as some of them can worsen the patient’s condition.
Treatment at home is carried out using:
- Luke. One head should be finely chopped and mixed with boiling milk. The mixture should be taken an hour before meals to eliminate pain.
- Burdock root mixed with Cahors. This composition must be heated for 5 minutes and then taken twice a day.
- Beeswax. It is used as a compress, which is applied to the problem area at night.
- Turpentine mixed with water. The bread crumb is moistened in this composition, which is then applied to the affected area, covered with cling film and kept for 15 minutes.
When a nerve is pinched in the hip region, baths with the addition of decoctions of pine shoots, oak bark, horse chestnut, calamus and chamomile help. Such procedures relieve pain.