Greetings, friends!
The lives of most modern people are filled with stress factors. Literally 40 years ago everything was completely different. People lived not so much carefree, but slowly and measuredly, they always knew what they would do in the evening. Their lives were often planned out years in advance. We live in a very dynamic world, every day we solve complex problems, we strive to find time for work, hobbies, entertainment, self-development and personal life.
To cope with all the tasks at hand, while maintaining physical and mental health, you need to have such an important quality as stress resistance. Today we will analyze in detail what it is, why it can decrease and how you can increase it with simple exercises.
Be cheerful
An active life position allows you not only to avoid failures, but also to maintain a kind of “immunity” against the onslaught of unfavorable events. Psychology provides advice that can be useful to people who are accustomed to taking responsibility for what is happening. To be cheerful means to try to notice favorable events in life, to be able to celebrate your own unique abilities and talents.
A person who knows how to rejoice will never in vain offend his interlocutor or hurt his loved ones. He won't get upset over trifles. Training your own will is quite difficult. To do this, you need to give up egoism to some extent and focus on completing the main task. Balance is achieved by working on yourself.
Resource state
A resource state is a state in which you felt good and comfortable at some point in time. This could be your trip abroad, it could be your visit to relatives or the purchase of some kind of animal. That is, everything is exactly what gave you joy and a feeling of happiness at that moment. Perhaps this is your receiving a cash bonus based on the results of your work, perhaps winning the lottery, etc. Everything here is very individual, and depends only on what exactly gives you a feeling of joy and happiness. Let's take an example of how this feeling comes to you while relaxing at sea.
Now you need to learn to mentally reproduce the situation when you are relaxing at sea. This way you get this resource back. The resource state that you had. The resource state has the property of giving you additional energy. If you have a lot of energy and your body’s protective functions are at a high level, then stress simply stops affecting you. The body becomes uninterested in experiencing stress!
Think about it: is a running rhinoceros stressed because he stepped on a couple of ants? Yes, he simply doesn’t notice them!
The task of the exercise is to be able to induce this resource state. Several times a day, when you have another break, you can close your eyes for a few minutes and imagine that you are at sea. You feel the sun, the beach, the warm water in which you swim. You feel good and comfortable. When you stay in this state for some time, you will feel a surge of strength and energy, which means stress will bother you less.
Achievements matter
How to develop stress resistance for a person who lacks self-confidence? He needs to try to concentrate as much as possible on his activities. It is best to find something for yourself that would captivate you and make you believe in the prospects available. Achievements are of great importance to an individual for the reason that in this way she gets used to celebrating existing victories. The fact is that low resistance to stress takes away a person’s emotional strength and makes him doubt his existing capabilities. Resistance to stress incredibly trains the will and helps cultivate tolerance.
Increasing stress resistance is due precisely to the fact that a person begins to believe more in his own prospects. When thinking about how to develop stress resistance, you should be very clearly aware of your own prospects. Developing stress resistance certainly changes the character of a person. No one can remain the same after coming out of a difficult situation. A person always becomes stronger by overcoming significant obstacles. Forming stress resistance is a long process that takes more than a single day. The more results a person strives to achieve, the more decisively she must act. Resistance to stress helps to increase the psychological resistance of the body and develop the habit of not giving in to difficulties.
How to develop stress resistance: 10 tips
Good endurance and the ability to control yourself are useful in any situation. In particular, stress-resistant employees move up the career ladder faster, and in some types of activities it is completely impossible to do without this trait. And in everyday life, calm and balanced people are usually more attractive to others.
Stress has a destructive effect on the human psyche, and with prolonged exposure it can cause serious harm even to physical health. This effect accumulates over the years, gradually worsening well-being, reducing immunity and weakening all body systems. Therefore, stress resistance is a quality necessary for everyone who wants to maintain mental and physical health for as long as possible.
The following recommendations will help you develop stress resistance:
- Monitor the quality and duration of your sleep. Poor quality sleep depletes the nervous system. In the modern world, many people sleep 5-6 hours a day, trying to save a couple of hours. This slowly but surely destroys the nervous system. Therefore, the first thing you need to do to increase stress resistance is to start monitoring the quality of your sleep and sleep at least 7 hours a day.
Talents and opportunities
Every person has certain abilities. You just need to be able to detect them in time and cultivate them in yourself. A person’s abilities are his individual characteristics, a gift from God that is given from above. A stress-resistant person is more attentive to his talents and does not let them go to waste. It is especially necessary to know your worth when you had a negative experience in childhood or adolescence. Cultivating stress resistance means that you must strive to realize your talents and abilities. High stress resistance appears in a person who is ready to work on himself every day and make certain efforts to achieve. Otherwise, you should not hope for quick results. With low dedication, stress takes over the entire personality and does not allow it to be itself.
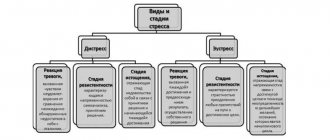
What is stress tolerance?
Stress resistance is a person’s ability to withstand stress and cope with any stress-generating factors, while maintaining calm and the ability to continue their activities at a normal pace. Individuals who have well developed this ability are usually not very emotional and are not prone to impulsive actions. However, this does not mean that “callous” people who do not experience strong emotions are resistant to stress.
Stress resistance makes it possible to remain calm even in critical situations. Thanks to this, a person can act as adequately and effectively as possible, without being distracted by emotions, but doing only what is required to solve the problems that arise. In everyday life, stress-resistant people also have an advantage, since they maintain a stable psycho-emotional state in any circumstances, do not get tired due to continuous stress and do not waste emotional energy.
Sense of responsibility
How to become stress-resistant if failures continue to haunt you? Is it worth fighting them? Of course, you shouldn’t give up, especially when the situation can still be improved somehow. When thinking about what stress resistance is, you need to be able to take responsibility. Unfortunately, not everyone is capable of this. At work, people must perform many tasks simultaneously. In order not to panic, you sometimes need to be able to calm yourself, persuade, and even redistribute responsibilities with colleagues. A sense of responsibility is the best protection against all sorts of worries. When a person acquires the habit of not blaming others for what happens to him, the process of spiritual growth begins.
Stress and stress resistance are concepts that essentially control a person’s life. Life cannot be lived ignoring difficulties. Only then does a person become truly strong when he knows how to cope with his own emotions. At work, you need to be as focused as possible on the activity at hand. Any advice from colleagues should be taken as some hint, help, and not as reproaches and suspicions.
Psychological training: Stress resistance. Prevention of crowding stress
Author: Averina Lina Valerievna, educational psychologist, Tula Regional Medical College, Tula
Description of material: psychological training program “Stress resistance.
Prevention of Crowding Stress" can be useful for educational psychologists in group correctional work with adolescents and adolescent students in a dormitory environment, as well as for dormitory teachers at secondary vocational education institutions. Psychological training “Stress resistance. Prevention of crowding stress” The purpose of the training: to increase the stress resistance of students living in a dormitory by gaining knowledge and developing skills to resist crowding stress in the dormitory microenvironment; Objectives: - develop resistance to stressful situations, - increase endurance and performance, - reveal hidden capabilities, - independently cope with stress thanks to various recovery techniques, - control your physical and emotional state, - improve your emotional state. Type of training: Personal development training, Educational training Contents: - psychotherapeutic effect; — learning effect, learning general effective techniques of social behavior; — armament with specific knowledge; Duration: 1 hour 1. Introduction
The trainer introduces himself to the seminar participants, introduces the topic of the training, and informs about the working hours.
2. Group rules
The group develops rules in accordance with which further work of the training seminar takes place.
Among the adopted rules there may be both generally accepted positions and points relating to the work of a specific group. 3. Exercise “Incomplete sentences” Purpose:
Clarification of the explicit and implicit rules operating in this group.
Content:
after accepting the group rules, participants are asked to write two ending options for each sentence: • In this group it is undesirable... • In this group it is dangerous... • From this group the one who will be excluded... • In this group it is possible... • In our group will receive encouragement that...
Discussion.
After the work, the participants answer the questions:
• To what extent are the current rules clear to the participants? • How wide is the range of unspoken norms? • Which ones are useful and which ones are burdensome? • What rules and regulations can cause discomfort and stress? • Should we jointly adopt additional rules in our group? 4. Game-acquaintance “Presentation and expectations” Purpose.
Acquaintance of participants with each other, development of partnerships.
Content.
The group is divided into pairs, each of which, having chosen a comfortable quiet place, conducts a mutual interview for 10 minutes (5+5).
Then the couples return to the circle and each introduces their partner. After the presentation, you can ask the person being presented if he wants to add anything to what was said and whether the story about him sounded correct. Next, the training participants voice their expectations about the upcoming training. Expectations are written down on a piece of Whatman paper and set aside until the end of the training. 5. Exercise “Me and Stress” Purpose
.
Helping participants understand and verbalize their ideas about stress and determine their attitude to this phenomenon. Identification of subjective difficulties currently experienced by group members and personal resources for coping with stressful situations. Content.
The trainer prepares A4 paper in advance (for the number of participants) and colored markers.
The training participants sit comfortably (in a circle or outside the circle). The facilitator warns them that this exercise is confidential, so during the exercise they should not ask each other any questions. Instructions from the trainer to the group. “Please draw a picture “Me and stress.” It can be made in any form - realistic, abstract, symbolic, artistic. Of greater importance is your degree of sincerity, that is, the desire to portray your thoughts, feelings, images that came to your mind immediately after you heard the topic. This drawing can become the key that throughout the training will help you recognize difficulties, find existing resources, and develop new successful stress management strategies. If necessary, you can use colored markers. You have every right not to show your drawing in the group if you want.” Participants draw for 4-5 minutes. Then the trainer begins to ask questions, which the participants answer independently (mentally), without writing down the answers on paper or saying them out loud. After each question, the trainer gives participants from 15 to 40 seconds to make changes and additions to the drawing. Questions a coach can ask
.
Look carefully at your drawing. 1. Does your drawing use color? See which colors (or which color) predominates in the drawing. What does this particular color mean to you? 2. Where do you picture yourself? Label yourself with the letter “I” in the picture. 3. How did you portray stress? In the form of a living creature, an abstract figure, a specific person? 4. See how much space your image takes up on the sheet and how much is stress. Why? 5. When depicting yourself and stress, did you use similar colors? Which? 6. Mentally divide the sheet in half with horizontal and vertical lines. Where did your figure end up? 7. Is there any barrier between you and stress in the picture? Maybe you are holding a saber, an umbrella or something else? If you feel the need, draw something else that can protect you from stress. 8. Do you have soil under your feet, what do you rely on? Or are you hanging in the air? Who can you rely on in life? If such people exist in your real life, but for some reason they are not in the picture, draw them. 9. What strengths would you note in dealing with a stressful situation? Try to find at least three positions in which you feel confident. What personal qualities help you achieve success? 10. What would you like to change or how would you like to improve your condition in a stressful situation? What personality traits and/or other factors are preventing you from improving it? 11. What other resources of yours do you see in this picture or would you like to add to it? Draw them please. Discussion.
After the participants answer the last question, the trainer asks them to form subgroups of 4-5 people.
As a rule, groups are created on the basis of the coincidence of any positions related to the perception of the concept of “Stress”, strategies and resources that appear in the drawings. In each formed group, those who wish can speak about their feelings, thoughts, etc., that arose during the drawing process. At the same time, others listen, complement, express their point of view, ask questions, but do not criticize. When talking about what helps and what hinders you from acting effectively in a situation of stress, you can speak both from your personal experience and based on observations of the behavior of people who know how to overcome stress. Each subgroup then formulates several main points about which they would like to change something in their reactions to stressors. All participants return to the circle. The trainer invites those who wish to speak about the work done or about their feelings. Representatives from subgroups read out their lists. The trainer explains to the participants what problems can be worked on during the training. 5. Mini-lecture “Crowding stress”
Using the brainstorming method, the group comes up with a definition of stress, after which the trainer introduces the students to information about this existing in psychological science.
Particular attention is paid to the problem of the causes and consequences of this type of stress and possible preventive measures. When considering the causes of stress, it is important for the trainer to bring group members to the realization that all of the listed causes of stress are only potential sources of negative impact on a person. It all depends on how the person himself perceives these reasons, whether he considers them stressors. Text of the lecture:
The concept of stress, like the concept itself, was developed and introduced into science by the Canadian physiologist Hans Selye, who drew attention to the fact that patients suffering from various diseases exhibit a number of common symptoms - loss of appetite, increased aggressiveness, insomnia, decreased motivation and etc.
For modern people, especially city dwellers, stress has become an everyday condition. A city dweller is, as a rule, a person who simultaneously belongs to a number of small and large social groups - he is a member of a family, an industrial or student team, a sports team, a friendly company, a public organization or a political party, etc. The norms of behavior and activities in these groups and associations are different, and moving from one group to another means for a person the need to quickly switch from one normative system to another, from one stereotypes of activity and behavior to others. Social conditions, information and intellectual overload, aggravation of interpersonal relationships cause mental fatigue and emotional stress in a modern city dweller. All of the above is especially relevant in the conditions of student dormitories: firstly, neighbors are not chosen, and secondly, crowding can develop - stress (English crowd - crowd) is a special term used to denote stress caused by a subjective feeling of lack of space, i.e. .e. the fact that there are more people around than we would like. There is such a concept - “interaction space”. During spatial interaction, so-called spatial contact occurs - direct awareness of the proximity of another person. The intensity of contact during communication is regulated by the distance between people and their direction. E. Hall (Hall E., 1966, 1970) - one of the first researchers in proxemics, proposed the following classification of communication distances: - intimate distance up to 45 cm - communication distance of only the closest people, all sensory channels are included in communication. It must be said that quite a wide variation in these boundaries can be expected in different cultures; - personal distance from 45 cm to 120 cm - the normal distance observed during daily communication between people; — social distance from 120 cm to 4 m. It is adhered to when communicating between strangers, at official receptions, in case of differences in status; — a public distance of more than 4 m is convenient when speaking in front of an audience. A person’s choice of distance is not conscious, but people always react if the actual distance does not correspond to their ideas about the norm. A person considers personal space to be his own, it is designated in a certain way, and the owner regulates the behavior of others in relation to this place - this can be a workplace or a space in the house (room, corner). In relation to a given place, more or less pronounced property relations appear. I. Kon writes that the need for personal space has changed over time. The life of a medieval person passed in full view of everyone. The dramas and comedies of family life, as well as weddings and funerals, took place openly with the participation of the entire community. In modern times, families begin to protect their everyday life from uninvited communication, acquire locks, door knockers, bells, and people make appointments in advance. At the same time, there is a desire for self-exposition, to express, emphasize one’s individuality, and decorate one’s home. That is why, at first glance, seemingly groundless conflicts often occur, the real reason for which is the violation of personal space. That is why it is necessary to remember the individuality of each person and the possible causes of misunderstanding in the microenvironment of a hostel, in a study group or in professional activities. After the groups have completed this task, the trainer suggests having a discussion. 6. Exercise “Throw away your problems” (Modification of exercise Newstrom, Scannel [1997]) Purpose.
Providing participants with the opportunity to receive feedback on their problem and exchange experiences.
Content.
The trainer invites the group members to write down on a piece of paper their problem that they would like to solve.
In order to remove possible resistance, the trainer can say, for example, that from the point of view of positive psychotherapy, a healthy person is not one who does not have problems, but one who has problems and tries to solve them. Sheets describing the problem are not signed; during the discussion, authorship cannot be disclosed. This is why the trainer asks participants to write legibly. After the participants have described their situations, the trainer invites them to crumple up their sheets of paper and throw them into a bag or bag. After this, the group is divided into subgroups of 4-5 people. Each participant approaches the leader and takes notes out of the bag. 5 minutes are allotted for discussing each problem. If one of the subgroup participants has guessed whose problem it is, he should not share his information or guesses with the participants. If a participant brings up his own problem, he should not admit his authorship. The discussion is carried out using the brainstorming method, that is, the task of each subgroup is to find as many possible solutions to the problem stated in the note. To increase the efficiency of this procedure, we propose choosing a secretary in each subgroup who would write down possible solutions and keep track of time. After the time is up, each subgroup reads out its “problems” and possible solutions. The trainer invites the rest of the group to add any suggestions and solutions. 7. Summing up. Target.
generalization of knowledge, skills and emotions acquired during the training.
Content.
Students sit in a circle and everyone is given the floor. Students share their impressions, give their assessment of new information, and note what new things they learned during the work. List of used literature: 1. Abolin L. M. On factors of resistance to stress // Mental stress in sports: Materials of the All-Union Symposium. - Perm, 1973. - pp. 67-69. 2. Andreeva A. D. et al. Mental health of children and adolescents in the context of psychological services / Ed. I. V. Dubrovina. - M., 1994. 3. Zharikov E.S. Psychological means of stress resistance. – M., 1990. 4. Nikiforov G.S., Filimonenko Yu.I., Polshin A.K. Psychological aspects of self-regulation of the state. – L., 1986 5. Selye G. Essays on the adaptation syndrome. – M., 1960.
We recommend watching:
Psychological games and exercises for preschoolers 4-7 years old Training for schoolchildren Unity training in 5th grade Training session on the dangers of drugs for schoolchildren
Similar articles:
Workshop on psychology of communication, 9th grade
Training on interaction with parents
Self confidence
Developing stress resistance is necessary for everyone who strives for a comfortable existence. Otherwise, constant worries will appear, the person will become irritable and absent-minded. Developing self-confidence begins with consciously thinking through your own prospects and additional actions. Stress resistance is a kind of skill that you need to strive to develop in yourself. Forming a positive attitude towards life is a special skill that not everyone has. In some cases, it is necessary not only to develop a different vision of the situation, but also to resort to objective treatment.

Working with thoughts
A person’s thoughts are what shapes his daily reality. Even if a person does not think about his feelings, they significantly influence his mood. Some people tend to succumb very quickly to any feelings and sensations. Such people often cry and often feel like victims of circumstances. Sometimes it seems to them that nothing depends on them. Weak people, as a rule, tend to shift their own responsibility onto the shoulders of others. Is it possible to overcome these manifestations with the help of stress resistance? There is no doubt about it!
Working with thoughts is about becoming aware of those beliefs that rush through your head in a stream every day. Monitoring your thoughts does not mean suppressing them. The body's resistance to stress is determined by how rarely a person gets sick. If you have a tendency toward depression, it means you have a lot of work to do on yourself. We need to try to develop a different attitude towards life, a more joyful and positive one. The stronger the mental organization, the better a person copes with everyday difficulties. It is necessary to develop an active attitude towards life constantly, without taking temporary breaks. Only in this case can we talk about developing high stress resistance.
Bodymaster.ru recommends Fitness Trainers:
To develop stress resistance, forget the phrases: “I don’t want to get fat”, “I want to stop being a skinny weakling”! Think affirmatively and measurably: “I want to lose 5 kilograms!”, “My goal is to compete in the spring!
Please note: the tone of this production is not helpless, but logical, positive and optimistic. It gives more potential! But although the new affirmation is positive, it does not relieve stress. A negative self-statement tends to reduce the level of mental stress by conveying that things cannot be changed; positive statements assert that the possibility exists and thus the pressure (stress) continues to weigh on the athlete's shoulders.

Tension gradually decreases in the application phase, when the athlete uses self-affirming thoughts and statements, first in low-stress situations, and then in gradually more anxious situations. Consequently, stress resistance increases.
The rehearsal phase as the development of stress resistance
Once new, stronger self-statements are formulated, the athlete rehearses them, repeating them daily. He “replays” the main statements in his head and classifies them as negative or positive.
Thanks to the inoculation method, you can use stress as a platform for new athletic achievements. For example, when you take stress as a basis: “I will never be able to bench press more than 100 kg!” and turn it into “I’m going to focus on the bench press for the next month!”
Application phase
Once you've developed positive statements about yourself, it's time to apply new strategies in more stressful situations.
Remember: stress management does not initially relieve stress! In fact, in a study conducted with competitive gymnasts, athletes performed better after training, although their anxiety levels were initially higher during competition than before developing stress tolerance.
Don't worry that stress doesn't magically go away. Cognitive anxiety—the mental stress you experience—will go away gradually over time. For an athlete, there is no better antidote to stress than the feeling of progress. Self-calming only provides temporary relief; you will be able to resist stress and become truly stress-resistant when you begin to train consistently and set clear goals.
Research on the effects of stress management on physical activity has generally been positive: sprinters ran faster, gymnasts performed elements more accurately, basketball and football players improved their throws and kicks. The difference is especially noticeable in free throws, which in themselves are a stressful part of the game.
Solving difficulties
A person’s life cannot always go smoothly and measuredly. Sometimes some unpredictable situations happen that turn everything upside down! The fact is that everyone has their own attitude to what is happening. Some people quickly forget about what happened, while others will constantly replay various unpleasant details in their heads. Solving emerging difficulties helps you develop a stable attitude towards life and become the master of your own existence.
Thus, stress resistance is strongly related to the internal resources of the individual. To increase stress resistance, you need to try to change your attitude towards life.
Post-traumatic stress in adults and children
Physiological mechanisms of stress
How does stress affect your periods?
Why insomnia?
The next point to analyze is insomnia.
It is well known that if a person does not recover during the night, that is, does not get enough sleep (and this is 7 or 8 hours of sleep), then he will not physically have enough strength to work through the whole day and function normally.
In this case, the body will simply begin to fail. In fact, this is fraught with the same psychosomatic diseases, when the body itself forcibly stops a person from certain activities. In other words, psychosomatics simply causes illness.
If year after year you have conflicts with the same person and the situation is not resolved, a simple psychosomatic illness begins, which, due to neurosis, forces you to go to the hospital or something even worse.
Therefore, sleep is a very important point that must be observed. You should always have enough energy for the day.