Received violation
: minor violation [*]
Reason
: Violation of clause 6.3.13 of the FSM Rules.
You can discuss the answer in the CC in the topic “Discussion of answers in the CC”, and not directly in the CC topic. Issued by
: Radomir.
Expires:
in 7 days.
Received violation
: minor violation [*]
Reason
: Violation of clause 6.3.13 of the FSM Rules.
You can discuss the answer in the CC in the topic “Discussion of answers in the CC”, and not directly in the CC topic. Issued by
: Radomir.
Expires:
in 7 days.
- Visiting a clinic, hospital, or emergency room. There, a certificate is issued with the diagnosis upon application, the nature of the injuries and the time of admission to the medical facility.
- With all the documents, go to the police to write a statement.
- Repeated examination with the participation of forensic doctors.
Trauma causes harm to health in the form of a sharp impairment of a person’s memory. After a severe head injury, the patient has no memory of what happened.
What happens during a concussion?
A concussion of brain tissue is a consequence of bruises, blows, and can even occur as a result of rapid movements.
For example, this can happen when falling. This is usually caused by fights, road accidents, injuries at home or in competitions. Medical professionals are not yet able to clearly answer what happens to our brain when it suffers from a head impact. The fact is that organic brain disorders cannot be detected if examined using computed tomography. Doctors suggest that a concussion causes problems with nerve cells in the brain of the head.
If a severe concussion occurs, blood vessels may rupture and certain areas of the brain may be injured. The main danger with this disorder is intracranial bleeding. The released blood permeates the structures of the organ and compresses it.
Another unfavorable process that injury can cause is swelling of brain tissue. It is especially difficult to survive those injuries that are complicated by swelling, shock, or affect the part of the brain that is responsible for blood pressure and breathing.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
To improve blood circulation in the brain tissue, the following are prescribed:
- medicinal electrophoresis with vasodilators;
- galvanization of the brain.
To increase the metabolism of nervous tissue, it is recommended:
- transcerebral UHF therapy;
- medicinal electrophoresis with drugs that improve metabolism;
- laser treatment;
- air baths.
In order to reduce high cerebrospinal fluid pressure, low-intensity decimeter therapy and therapeutic sodium chloride baths are prescribed.
To improve the rheological properties of blood, laser irradiation is performed.
Symptoms
A concussion in a person is manifested by loss of consciousness. This state can last from a few moments to a couple of minutes. Vomiting may occur. The main symptoms of the disorder are nausea and retrograde memory loss. At first after the blow, the patient cannot remember everything that happened to him. The amnesia does not last long, although its duration depends on the severity of the concussion.
American doctors have identified three degrees of concussion as a result of a blow:
- First. There is no amnesia and loss of consciousness, consciousness is confused.
- Second. There is no loss of consciousness, but consciousness is confused.
- Third. The man loses consciousness.
Physicians may understand and use different interpretations of “loss of consciousness for a short period.” In the domestic literature, the duration for this violation ranges from several moments to tens of minutes. A brain injury can mean that a person will not be able to recover for a long time, up to one hour.
When the patient does not regain consciousness after 6 hours, it is most likely that the brain tissue has been damaged. Experts say that in this case, diffuse brain damage occurs. These disorders occur with acceleration-deceleration injuries. As a result of this process, the axons of the white matter contained in the trunk and hemispheres are cut off or stretched. This process can be characterized as axonal diffuse damage.
When a person regains consciousness, he complains of headache, weakness, nausea, sweating, flushing of the face, and tinnitus. Concussion is characterized by autonomic symptoms and sleep disturbances. Pain may occur when moving the eyes, and sometimes the eyeballs may move around when reading.
Nystagmus and mild shell symptoms may also occur, which tend to disappear after a week.
What happens in the head during injury
Traumatic brain injury is physical damage to the bones of the skull, membranes, nerves and blood vessels. Violation of brain functions occurs due to vibration of nerve cells, and in the zone opposite to the impact. Changes in neurons at the molecular level lead to disruption of the functions of the brain region.
In an experiment on monkeys, it was established that at the moment of impact, similar rotational movements of the hemispheres occur in several planes. Twisting and tension of axonal processes occurs. At the moment of injury, the main force of damaging energy falls on the border of the hemispheres and the medulla oblongata. Due to the difference in pressure, microhemorrhages are formed inside the brain tissue due to damage to the cerebral capillaries.
Short term consequences
When assessing the severity of harm to health, a concussion is considered a special case of traumatic brain injury.
In order to most accurately determine the impact of injury on the victim’s health and make an expert assessment of it, it is necessary to take into account various factors in the course of this disease and its consequences.
And get the most accurate clinical and expert substantiation of the established fact of concussion.
Closed traumatic brain injuries (TBI) are divided into three categories:
- concussion (CHM);
- brain contusion without compression;
- brain contusion with compression.
Thus, a concussion is the mildest degree of TBI. Despite this fact, this injury is quite difficult to objectively diagnose, which greatly affects the correctness of the decisions of the forensic medical examination.
The condition of the victim, identical in symptoms, duration and severity of the disease, can be regarded by different experts as both a concussion and a brain contusion. It all depends on how they themselves assess this injury.
A concussion is caused by blunt head trauma and is a set of functional changes in the brain that are not irreversible.
Gradually, the body stops compensating for these changes, and they reappear with renewed vigor.
This phenomenon is often interpreted by experts as an independent pathology that is not a consequence of a concussion.
Thus, when determining the severity of damage to health, it should be taken into account that sometimes minor manifestations of symptoms of SHM do not correspond to the severity of post-traumatic changes.
When carrying out a forensic medical examination, it is necessary to take into account that it is very problematic to establish the facts of loss of consciousness and vomiting. These signs are proven only when they are seen by medical personnel or witnesses, and these facts are recorded in medical records. A much more significant symptom is considered to be traumatic amnesia.
When a forensic medical examination is carried out, the commission gets acquainted with the investigator's decision and other preliminary data, and then studies the case materials and medical documents, such as medical history, outpatient records, etc. If the victim is present at the examination, he is interviewed and the timing of the onset of clinical symptoms is analyzed.
At the end of all these preliminary stages, the information received is analyzed, on the basis of which the conclusions of the forensic medical commission are formulated. When drawing conclusions about the severity of the injury, the following are taken into account:
- how the injury was sustained and under what external circumstances;
- location of visible head injuries, their number, area occupied, etc.;
- how long each of the main symptoms lasted, and in what sequence they occurred;
- results of laboratory tests, x-rays and other tests;
- information about what the patient was sick with and what injuries he might have had at the time he received a concussion;
- how the symptoms of the disease manifested themselves after the victim underwent treatment;
- duration of stay in hospital and outpatient treatment;
- nature and duration of treatment;
- percentage of disability.
The main characteristic features for making a decision on the severity of harm caused to a person’s health are recognized as: a threat to life at the time the injury was received, as well as the duration of the period of incapacity and whether the ability to work was completely lost.
The severity of harm caused to health is described very precisely in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. There are three of them: light, medium and heavy. The main criterion in determining how serious harm was caused to a person’s health is how life-threatening the injuries were.
For all types of traumatic brain injuries, the types of grievous harm caused to health are divided into 2 groups: TBI that is life-threatening to the victim (for example, injuries that violate the integrity of the skull) and non-life-threatening, but causing grievous harm to health (paralysis, the onset of mental illness) .
Average severity of health damage occurs when health problems occur over a long period of time, and this period will be more than 21 days. In these cases, there may be less than 30% permanent disability caused by residual factors from the TBI.
In this case, the victim’s forced disability should not exceed 21 days, and the loss of working capacity should not exceed 5%.
When making a decision on a mild degree of harm to health, the fundamental indicator will be the short duration of temporary disability of the victim (usually less than 21 days).
It follows from regulatory medical acts that the estimated duration of health impairment with SHM ranges from 20 to 22 days, but it should still be taken into account that sometimes with a concussion there is a longer lasting health disorder caused by the development of various pathologies caused by receiving a cranial injury. brain injury.
From all of the above, we can conclude: when a person is diagnosed with a “concussion”, a forensic medical examination, as a rule, establishes that the victim suffered minor harm to health.
At the same time, there are more complex cases when a head injury caused various complications that affected the duration of treatment and the person’s health.
In this case, the examination may establish that the victim suffered a moderate injury.
When patients suffer a concussion, they may be susceptible to the following short-term problems:
- Headaches that can last up to two weeks. The intensity of such pain can only be reduced with the help of painkillers.
- Nausea and vomiting for no apparent reason.
- Dizziness, poor concentration, difficulty with brain function.
Such side effects tend to disappear after some time without treatment. But if after a concussion these signs are present for a long time, then you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination in order to clarify the diagnosis.
Inevitable consequences are more common in patients after a severe concussion. These are neuroses, psychoses, encephalopathy and post-concussion syndrome. The general clinical picture looks something like this:
- persistent changes in behavior and character;
- emotional instability from complete apathy to outbursts of causeless anger;
- often paranoid states with delusions and hallucinations;
- muscle spasms, convulsions, turning into an epileptic attack;
- general weakness and increased fatigue;
- nightmares or frequent insomnia;
- memory impairment, difficulty of perception and a significant decrease in mental activity.
Avoid head injuries at all costs. Often, all that is needed to continue living a full life is just to follow a couple of safety rules or avoid risk by anticipating the threat in advance. If an injury turns out to be unavoidable and you are diagnosed with a concussion, do not violate the gentle regime under any circumstances and methodically follow all treatment instructions.
VERIFIED This article has been reviewed by our experts, medical practitioners with years of experience. If you want to consult with the site’s specialists or ask your question, you can do this completely free of charge in the comments. And if you have a question that goes beyond the scope of this topic, use the button above. Great article 0
Brain contusion is harmful to health
Even light blows can lead to concussion; By this name doctors mean loss of consciousness.
caused by a sudden and strong mechanical impact on the head. Contusion is a relatively mild head injury and is usually not accompanied by significant and irreversible changes.
A brain contusion is a traumatic brain injury in which brain tissue is damaged and is characterized by the presence of a focus of necrosis of nervous tissue. Damage after injury can be unilateral or bilateral. The most common sites of damage are in the occipital, temporal and frontal lobes of the brain. A head injury and a brain injury are two different things. The first term implies a bruise of the skull when the brain substance itself is not damaged. In this case, irreversible (organic) and reversible (functional) structural changes occur in the spinal substance, and focal necrosis and hemorrhages occur in the membranes and vessels. What is considered to be a mild degree of injury in a road accident? Severe damage to brain tissue always accompanies spinal shock.
With a spinal cord contusion, spinal shock masks the true picture of the injury, and only after its resolution do persistent symptoms appear, which can be used to judge how seriously the spinal cord is damaged. It is characterized by a short loss of consciousness (sometimes it is completely preserved), and a satisfactory state afterwards. Within 7 days all complaints are resolved. No residual effects are observed. Closed craniocerebral injury occurs due to a rough impact on the skull (a blow to or against the head).
Intentional bruising of the skull with any blunt object is a criminal offense. The punishment for this bodily injury is determined by the relevant article of the Criminal Code.
Short term consequences
The consequences of a concussion can be varied and numerous. If these violations are repeated, they lead to consequences such as encephalopathy. It is often diagnosed in boxers due to the fact that head impacts are not uncommon for them.
Scientists believe that the first symptoms of encephalopathy are associated with the work of the lower extremities. At first, a person may limp, one leg may lag behind the other. But these are not the only symptoms, since a person may suffer from a balance disorder, and a stagger will be visible in his gait. Some patients may experience slow movements or even mental confusion.
Some people experience only mild symptoms after a concussion. But often people experience trembling in their hands and head, their psyche may change, for example, their vocabulary decreases, or their body movements become slower.
Regardless of how severe a traumatic brain injury a person has suffered, changes in character and physique are possible. Patients after injury may experience the following consequences:
- High sensitivity to infections or alcohol. At the same time, under the influence of one or the other, a person may feel strong mental agitation or may even experience mental disorders.
- Vasomotor disorders of a pronounced nature. Such disorders occur due to changes in the walls of blood vessels that affect tissue tone. In this case, a person feels a headache, which becomes stronger with physical activity and head movements. At the same time, dizziness may occur, blood may rush to the head, and then the face may become too pale. These symptoms may be accompanied by intense sweating, inability to concentrate and fatigue.
- Irritability.
- Excitability.
- Emotional outbursts.
- Aggression.
- Rage, after attacks of which the patient often apologizes for his behavior.
- Convulsions combined with seizures similar to epilepsy.
- The emergence of paranoia.
- Neuroses with anxiety, sleep disturbances and headaches.
Sometimes, after trauma, psychosis with poor perception of reality and hallucinations may appear. The patient may be delusional, and sometimes there is dementia. All this is combined with memory impairment, disorientation and poor thinking. But such cases are rare.
The most common complication for people who have suffered a concussion is post-concussion syndrome. This diagnosis can be made when a person who has suffered an injury complains of a headache, a feeling of fullness and splitting after a long time after the injury. Months or weeks may pass.
If strong painkillers are prescribed for this disease, they can cause addiction. And being treated by a psychotherapist is almost ineffective, although it rarely helps.
Thus, during a concussion, the nerve cells of this organ suffer. Concussion occurs as a result of falls, blows and other injuries, and entails consequences. These effects may be mild and will go away without treatment, but in some cases people need medical help.
Chemotherapy
Treatment of tumors with chemotherapy is a systemic method. This is due to the effect of medications on the entire body at once, which partly has a negative impact on health. Doctors prescribe the patient to take alkylating agents, antibiotics, synthetics, antimetabolites and some other drugs. Usually, only one drug is prescribed or a treatment plan is drawn up with alternate use of several. They can be given intravenously or taken in tablet form. A little less frequently, a liquor shunt is prescribed.
A course of treatment with chemotherapy usually consists of several cycles, with a long break between them to allow the body to recuperate. At this time, doctors evaluate how effective the effect on the tumor was and decide whether to continue therapy or review it. Removal of a brain tumor using chemical therapy is often complemented by radiation. This solution allows you to increase the effectiveness of treatment as a whole. But, like other methods of therapy, chemical therapy can cause complications.
Common consequences:
- reduction in the number of healthy blood cells;
- damage to the bone marrow;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- disruptions in the cardiovascular system and lungs;
- digestive system dysfunction;
- infertility or decreased likelihood of conception;
- increased vulnerability to infection;
- the appearance of fungal diseases;
- complete baldness;
- skin pigmentation;
- significant weight loss;
- development of other tumors.
Reviews
Oleksandr Kobets, 43 years old, Sevastopol.
The most common complication after a concussion is headaches and migraines, and often they cannot be completely cured. But this mostly concerns complications of injury. But I know several people who suffered head injuries several years ago, and there were no consequences. It is worth protecting children from head injuries, since such injuries are the most dangerous in childhood.
Marina Berdnikova, 25 years old, Pskov.
Recently, my heel hit a high threshold at work and fell. The floor is tiled, so I didn’t hit my head lightly. I didn’t even get up right away, I had to lie down for a while because something terrible was happening in my head. All day I was unsteady, dizzy and had a headache, but in the morning the pain subsided. And such mild pain tormented me for several more weeks, it didn’t seem like a migraine. Fortunately, everything has already passed and I feel fine. At first I was afraid that it might be a concussion and would have to be treated.
Evgenia Mukacheva, 30 years old, Minsk.
I recently had a concussion, this problem caused nausea, pain, dizziness, and generally made me feel worse. However, I did not stay in the hospital, but tried to lead my previous lifestyle. Once again, when I went to the supermarket, I had an attack similar to epilepsy, while I fell and hit my head.
In the morning I discovered a lump on my forehead, it was large, but soon almost all of it disappeared into the swelling above my eye. A bruise formed there, but the lump did not disappear. Then the doctor squeezed it out and put a bandage on it. At night a lot of blood leaked out of this bandage, and my skin was sewn up. But the lump has still not completely disappeared. It worries me very much, because I don’t know whether it will resolve on its own or whether it will have to be cut out.
Nikolay Starostenko, 28 years old, Orshansk.
Two days ago I fell when I slipped, but I felt pain in my leg and that’s all. An hour later my head started to hurt, and before going to bed I began to feel nauseous. In the morning I had no strength at all, I couldn’t do anything, I couldn’t eat because of the nausea, which by that time had not yet passed. The next day the temperature rose and remained at 37.7 all day. Today my temperature dropped and I felt a little better, I don’t know whether to see a doctor or not, I’ll probably go if it doesn’t go away at all.
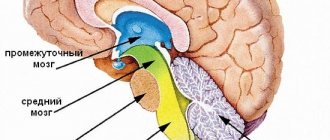
What is a traumatic brain injury?
This is a closed (CTBI) or open (depending on the classification) traumatic brain injury, damage to soft tissues, cerebral membranes, blood vessels and nerves of the brain. Most often, injuries are caused by mechanical impact and most are combined - they include several types of trauma (bruises, fractures, ruptures).
Traumatic brain injury is divided into two main types – open and closed.
- In the first option, there are ruptures of the skin and connective tissue, as well as a possible violation of the integrity of the skull. If an open injury is accompanied by involvement of the subdural membrane, then the injury is considered penetrating.
- With the closed type, there is no damage to the connective tissue aponeuroses of the head, although the skin may be cut.
Signs of bruise
Qualifying criteria include aggravating conditions of the crime. The corpus delicti necessarily takes into account the premeditation of the action, the number of participants and the motive.
The qualifying signs of causing grievous harm to health in accordance with Article 111, Part 2 and Part 3 include:
- An act against a person in the performance of official duties.
- A crime with special torment and bullying.
- If the actions were performed on a person in a helpless state.
- It was done with danger to society and carrying great destructive power.
- Performed for hire.
- Had antisocial motives.
- Committed by a group – refers to the category of particularly aggravating circumstances.
- Caused death by negligence.
According to this article, a crime that occurs without the above listed qualifying features is punishable by imprisonment for 8 years. In the presence of aggravating circumstances, the court provides for liability for up to 12 years.
According to the last point, when the act entailed death through negligence, two motives are regarded - intentionality of causing harm and subsequent death. For this offense, the offender faces up to 15 years in prison.
With regard to the qualifying characteristics under Article 112 “Intentionally causing harm to health of moderate severity”, the same circumstances are considered as for Art. 111. Exceptions include clauses on execution for hire, creating a public danger and causing death by negligence. A crime without qualifying characteristics is subject to liability - imprisonment for up to 3 years or forced correctional labor for up to 3 years.
In aggravating circumstances under Art. 112 according to part 2 is punishable by arrest for up to 5 years.
Important! In these cases, the assessment of the degree of responsibility is based more on the danger of the act than on medical criteria.
Depending on the severity of the injury, a brain contusion or compression may be diagnosed. Bruising is classified into mild, moderate and severe, each with its own symptoms.
- Mild form - loss of consciousness for up to 60 minutes, retrograde, congrade and anterograde amnesia. Drowsiness and lethargy. Single or repeated vomiting, arrhythmia of the heart and respiratory rhythm, increased blood pressure.
The injury is not life-threatening, symptoms disappear completely within 3 weeks and the patient recovers.
- The average form is an unconscious state for up to 4 hours. After returning to consciousness, the inhibited state remains for several days. Problems with orientation in time and space. Visual impairment and increased body temperature, psychomotor agitation. Severe headache and dizziness. Muscle hypotonia and paresis. Moderate bruises are often accompanied by subarachnoid hemorrhage and fractures of the cranial bones. Some symptoms may persist for up to 2 months, but the patient’s general condition improves. Some violations are irreversible.
- Severe form - loss of consciousness from several days to several weeks. Comatose state or psychomotor agitation with convulsions. Severe circulatory and respiratory disorders, including artificial ventilation, high blood pressure. A few days after the injury, paralysis of the limbs and loss of speech are possible. Recovery is long - from six months or longer.
Most changes are irreversible and the patient remains disabled. In 50% of cases it is fatal.
Restrictions from other species
Intentional harm of moderate and severe severity should be distinguished from beatings and torture:

Batterings are most often characterized by inflicting injuries of mild severity. A head injury that occurs as a result of numerous beatings is regarded as severe or moderate harm. Which automatically equates the act to Articles 111 and 112.
Surgical operations
The most common method of removing tumors is surgery. This solution involves creating a hole in the skull through which the tumor will be removed. This usually requires a fairly large trepanation, which makes access to the affected area easier, but increases the overall risk. Neurosurgical operations are allowed only in cases where the tumor has not yet begun to spread to nearby tissues.
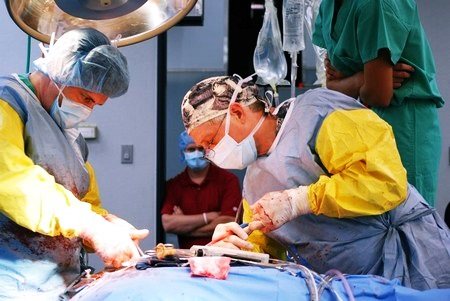
With such an intervention, removal can be complete or partial. Also, sometimes the operation is divided into two stages, as it can last several hours. In rare cases where there is no point in surgery, the patient may still undergo surgery to alleviate his condition.
Neurosurgical operations have a number of contraindications that must be taken into account by doctors. If they are not taken into account, the result may be disability or death.
Contraindications:
- severe decompensation of individual organs;
- spread of the tumor to several tissues;
- developing metastases throughout the brain;
- physical exhaustion of the patient's body.
Carrying out such operations involves serious risks. Even with the extensive experience of the doctor and the positive result of the entire procedure, there is still the possibility of complications developing. Some of them may not appear immediately, but months later, which worsens the situation.
Is it possible to determine the degree yourself based on the symptoms?
After receiving an injury, you should still seek help from a medical facility. Specialists will provide a reliable diagnosis and also provide qualified treatment. Determining the disease in case of a closed craniocerebral injury, and specifically a concussion, will help to accurately determine the severity of the harm to health.
You can do this, in fact, it’s not difficult. We turn to the same Order that we described above and look for a brain injury that matches the injury received by the victim. If there is one, we look at what degree of severity it is.
If not, the same Order contains an Appendix - “Table of percentages of permanent loss of general ability to work.” We are looking for trauma in it. Found - we look at the % of loss and correlate it with paragraphs 7.2 and 8.2 of the Order (moderate severity = from 10 to 30% inclusive, mild = up to 10%, the rest = severe).
Of course, this is just a rough definition. A forensic medical expert will tell you exactly - only his word will be authoritative.
Or, you can do it simpler: knowing your diagnosis, you can approximately determine the severity of the damage:
- A concussion or mild bruise is regarded as causing moderate harm to health - more details.
- For open craniocerebral injuries, only a severe degree is assigned - more details.
- Severe and moderate bruises, bleeding, cerebral hematomas, etc. are also severe.
- A concussion or mild bruise is regarded as causing moderate harm to health.
- For open craniocerebral injuries, only severe degree is assigned.
- Severe and moderate bruises, bleeding, cerebral hematomas, etc. are also severe.
Brain contusion - what does it mean for a person in the future?
The patient's prognosis depends greatly on the extent of the injury. Experts distinguish three degrees of severity of the patient’s condition.
It is often impossible to independently determine the prognosis and harm caused to health - even specialists require long-term observation and a lot of research. Intensive therapy, follow-up and proper management of the recovery period can significantly neutralize severe consequences and significantly reduce harm to health.
Observation by a specialist after an injury can last quite a long time.
Any traumatic brain injury, even mild, has negative consequences for human health. It is important that the consequences of a brain injury may not make themselves felt immediately, but only after some time. It should be noted that harm to health may not be immediately felt by the patient. Symptoms may occur after discharge from the hospital.
To the above-mentioned consequences, one must add postoperative complications, since brain contusion often requires surgical intervention. In general, the prognosis for the patient greatly depends on the severity of the traumatic impact, the speed of medical care and the professionalism of doctors. Managing the rehabilitation period is also important. Most often, purulent-inflammatory complications develop during the first 2 weeks after injury
How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice?
The sooner you contact a forensic expert, the easier it will be for specialists to establish the fact of harm. This can be done even before writing the application.
You can contact both specialized authorities - a forensic medical examination, and a hospital, having received a certificate from a traumatologist or neurologist.
If you write a statement about beating, then an examination will be ordered by law enforcement agencies.
What to do when contacting the police:
- How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice? Write a statement with a detailed description of the crime, the characters involved, the methods of inflicting pain and the locations of the blows.
- Examination by an expert in the direction of the police, followed by a conclusion on the severity level.
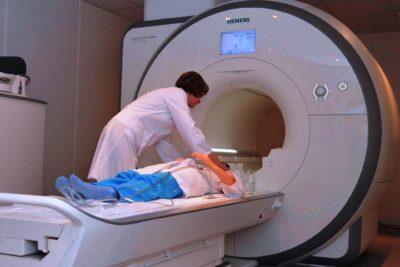
If you decide to identify harm yourself, then you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Visiting a clinic, hospital, or emergency room. There, a certificate is issued with the diagnosis upon application, the nature of the injuries and the time of admission to the medical facility.
- With all the documents, go to the police to write a statement.
- Repeated examination with the participation of forensic doctors.
The last point is not always fulfilled, since the investigation may only need documents from the hospital.
Important! Battery is a serious offense. Do not be afraid to seek help from law enforcement agencies; beatings can be repeated and lead to more serious consequences.
TBI is one of the most serious injuries. They are characterized not only by serious symptoms and a direct threat to life, but can also have long-term consequences. If they were received after a beating, there is no need to be afraid to contact the appropriate authorities. You should protect yourself in any lawful way, protecting your health.
{amp}gt;Concussions, how to find out the severity of harm to health yourself?
How to find out the degree of concussion yourself?
Immediately after a concussion, it is almost impossible to objectively assess the severity of harm to health on your own . But the 3 main signs you can look for for a moderate to severe concussion are as follows:
- The longer the loss of consciousness lasted (even in minutes), the more serious the injury.
- Severe nausea and vomiting.
- The patient does not remember how the injury occurred. And the more he doesn’t remember, the more severe the injury.
An accurate diagnosis can be made only after examination by a neurologist and a comprehensive outpatient examination. The effectiveness of treatment and how quickly and without consequences the patient will recover from injury will directly depend on this.