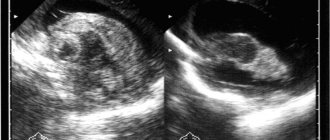
A cyst in the head of a newborn indicates abnormal fetal development. A benign tumor is detected during prenatal screening or after childbirth. According to statistics, more than 40% of children are susceptible to pathology. Using an ultrasound, a specialist identifies a cavity in the brain filled with fluid. It is not uncommon for children to be born with multicystic disease. With this condition, several small or large cysts form. Their position may change.
A benign tumor is detected during prenatal screening or after childbirth.
The disease in infants does not always require surgical treatment. There is a possibility that the brain tumor will resolve, but if complications develop, constant monitoring is necessary to reduce the risk of the cyst increasing in size.
Types of cystic formations
The brain is formed by an interweaving of nerve fibers and neurons and is penetrated by vessels of different sizes. Between the hemispheres there are natural cavities - the cerebral ventricles, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The brain is covered on top by three membranes:
- vascular - adjacent to the medulla, penetrates all convolutions and repeats their shape;
- arachnoid - connective tissue without blood vessels; cisterns filled with cerebrospinal fluid are formed between it and the choroid;
- hard shell - located under the cranial vault, it contains pain receptors.
A brain cyst can be located inside the medulla, then it is called cerebral. An arachnoid cyst forms above the choroid. They differ in the mechanism of formation:
- cerebral occurs at the site of death of areas of brain tissue;
- arachnoid - this is a consequence of the formation of duplication of the membrane, additional folds, adhesions that appear as a result of inflammation.
There are also special types of cysts:
- pineal body;
- choroid plexus;
- suprasellar cyst;
- colloidal;
- dermoid.
The last two types are congenital neoplasms.
Main types of disease
The main classification of this type of cyst is based on the principle of tumor localization. So, depending on the depth of location, two types are distinguished:
- a simple arachnoid cyst, which forms closer to the surface of the brain;
- retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst, which forms deep in the gray matter; At the site of the formation of such a cyst, gray matter cells die.
There are several localizations of this tumor in the brain:
- interhemispheric cyst - formed between the cerebral hemispheres;
- posterior fossa cyst;
- cyst of the frontal and parietal part;
- temporal lobe (right or left, symptoms are different);
- pineal gland cyst;
- cerebellar cyst (inside, on or near the cerebellum).
In addition, there is a gradation based on origin:
- Primary cyst - formed in the prenatal period; the cause of the appearance is usually an infection suffered by a pregnant woman;
- Secondary – formed as a result of external influence (trauma, infectious disease of the brain, complication after surgery, hemorrhage).
An arachnoid cyst can be simple or complex in composition. In a simple cyst, liquor fluid completely fills its cavity, but in a complex cyst there may be other cells inside, and the tumor itself can spread to adjacent tissues.
If the cyst increases in size, it is called progressive. If the cyst does not grow, it is considered frozen. Depending on the course of the disease, the doctor chooses the method of treating it.
Reasons for the formation of cysts
The causes of the formation of cystic cavities are associated with any adverse factors affecting the fetus. At an early stage, viral infectious diseases can lead to the penetration of the pathogen into the tissues of the embryo. The risk of such a complication is high for the herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus, because they are tropic to nerve tissues and are integrated into the DNA of neurocytes. But in most cases, it is not possible to determine the type of pathogen. The exception is severe damage to the fetus due to intrauterine infection.
The cause of a congenital cyst may be chronic intoxication of the mother. Most often this is observed with alcohol abuse, smoking, drug addiction and substance abuse. Abnormalities in brain formation can be caused by working in the production of hazardous substances.
Working in the paint industry, oil refineries, and gas stations negatively affects a woman's reproductive system and pregnancy. Toxic fumes accumulate in the body.
Congenital cysts can appear due to the following complications of pregnancy:
- fetoplacental insufficiency - the fetus does not receive enough nutrients, brain cells suffer, so in the presence of additional factors they die or form cysts;
- Rh conflict between mother and fetus - the condition is accompanied by an autoimmune reaction, which leads to damage to brain tissue and the deposition of toxic metabolic products in them;
- Fetal hypoxia – may be a consequence of placental insufficiency and causes damage to brain tissue.
Women who took medications with teratogenic effects for chronic severe diseases in the first trimester may also experience symptoms of a cyst in the child.
The cause of the pathology may be the bad habits of the mother
Post-traumatic cysts are distinguished separately. They are formed in children with a predisposition, small cavities, and abnormalities in the development of the meninges after a difficult birth. Predisposes to birth trauma:
- narrow pelvis in a pregnant woman;
- large fruit, large head volume;
- post-term pregnancy;
- anomalies of labor;
- rapid birth.
A hematoma must be distinguished from a brain cyst. This is also a cavity formation that forms after an injury and is filled with liquid or coagulated blood.
Preventive actions
An arachnoid cyst in a child is a preventable disease. You need to take care of this before the birth of the child, and even better - before pregnancy.
Future parents should try to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Fresh air, physical activity, a balanced diet, absence of bad habits - all this will contribute to the health of your family members for many years.
When your baby is born, all of these health fundamentals will need to be applied to him. A child of any age needs proper nutrition, physical education, walks, feasible exercise and, of course, positive communication with parents and loved ones.
A brain cyst in a newborn is a spherical formation, hollow inside and filled with fluid. Such a cavity is formed due to the death of nervous tissue in a certain area of the brain. The location of formation may vary, as well as the number of abnormal cavities.
How does a cyst manifest in a newborn?
The first signs of pathology are sometimes detected during the period of intrauterine development during a routine ultrasound of a pregnant woman. Small cavities of various locations appear in the brain, which can increase or remain unchanged. Their condition is monitored so that, if necessary, first aid can be provided to the newborn in the delivery room.
Symptoms of large cysts may become noticeable within a few days after birth. The child cannot complain of a headache or a feeling of fullness, hearing or vision impairment. Therefore, pay attention to changes in behavior or uncharacteristic signs:
- refusal to feed, loss of appetite;
- regurgitation or frequent vomiting;
- lethargy, weakness;
- restless behavior;
- a sharp cry for no apparent reason;
- convulsive syndromes;
- swallowing disorder.
It is difficult to identify motor disorders in newborns, their nervous system is immature, and movements of their arms and legs are chaotic. Therefore, signs of a cyst are detected during an examination by a neurologist by the appearance or extinction of various types of reflexes.
Sometimes the first symptom of a progressive cyst is the bulging or pulsation of a large fontanel. The volume of the skull is limited and cannot be stretched. The fontanelles are the only area with preserved connective tissue that can stretch. As the volume of the cyst increases, it puts pressure on other brain structures, which leads to bulging of the fontanel.
The consequence of brain cysts is occlusive hydrocephalus, when the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted.
Sometimes the cyst ruptures and the brain is compressed. In children, a persistent focus of pathological pulsation may form, leading to severe epilepsy.
At older ages, the consequences are associated with untimely initiation of therapy. Increased intracranial pressure does not allow normal development and leads to mental retardation, mental retardation.
True and false
There are two forms of porencephalic cyst - false and true.
True porencephaly can connect to the ventricles of the brain, while occasionally reaching the outer cortex of its hemisphere. Sometimes the cystic cavities do not connect to the ventricles. The size of the cavities can vary greatly, some of them can reach enormous sizes, filling half or more of the brain hemisphere. The inner surface of the cavity is usually smooth and covered with a layer similar to epindema. If the cavity communicates with the ventricles, the cyst contains spinal cord fluid; otherwise, the fluid has a yellow tint with a dominant amount of protein.
On the surface of the cystic cavity, using a microscope, you can observe areas that arise due to the incorrect structure of the cerebral cortex. In some cases, traces of local hemorrhages or microscopic anoxic necrosis can be found there.
Due to the influence of porencephaly, deformation of the lateral ventricles of the infant’s brain occurs. The cerebral convolutions may be directed inside the porencephaly or absent altogether, and instead of them there will be only a thin plate of medulla, which, when the cavity is opened, forms crater-like pits. The gyri located next to the cystic void change greatly and are characterized by incorrect orientation of the cell layers and a pronounced rarefaction of the ganglion cells. All such signs indicate the appearance of true porencephaly.
False porencephaly is a cyst located in the brain tissue, but unlike true porencephaly, it does not reach the cerebral cortex and does not connect to its ventricles. False cavities can be located only in one hemisphere or both at once; they are located mainly in the white matter. They connect with each other, but they can also be single. In this case, the convolutions of the brain are not deformed; scar tissue appears on the inner surface.
The most serious form of porencephaly is vesical brain. Both hemispheres, the basal ganglia and the trunk are involved in the formation of this disease. The name of the disease comes from its appearance - two huge bubbles on the head filled with liquid. Cystic disorders of the cerebellum are extremely rare.
The disease in the postnatal period (postpartum) in a baby is characterized by a delay in mental development, paralysis and paresis of the arms and legs, and occasionally epileptic seizures. There are signs of disruption of the extrapyramidal system. Also, in some cases, there may be incomplete development of the corpus callosum, loss of a small part of the brain matter, an asymmetrical shape of the skull with a pronounced bulging of the temporal lobe in the affected area, microcephaly and other defects in the development of human organs.
Diagnosis of porencephaly is complicated by the difficulty of differentiation - which particular form of the disease is present in the patient. It happens that cystic cavities, even in multiple forms, are expressed by focal symptoms, but without mental defects. The disease is diagnosed based on the clinical symptoms of organic brain damage and information obtained during a pneumoencephalographic examination.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis during pregnancy is carried out during a routine ultrasound of the fetus. If the doctor notices abnormalities in the structure of the brain, careful monitoring of the condition is necessary, and the issue of viability in the case of multiple developmental defects must be resolved. After birth, such children are under the supervision of neonatologists and pediatric neurologists.
If pathological symptoms or reflex disturbances appear, neurosonography is prescribed. This is an ultrasound of the brain, which is performed through an open fontanelle. A consultation and examination by an ophthalmologist and audiologist is necessary to determine the degree of visual and hearing impairment. The following diagnostic methods are used:
- audiometry - in most maternity hospitals, if equipment is available, it is carried out routinely three to four days after birth;
- ophthalmoscopy - examination of the eyeball, necessary for children who have suffered acute hypoxia or received a birth injury;
- measurement of intracranial pressure.
Auxiliary methods are CT and MRI of the brain. They allow you to accurately localize the cyst, clarify its size and some characteristics in order to determine the treatment method. In some cases, in order to better examine the cavity, it is necessary to inject a radiopaque substance into it. This allows you to differentiate a cyst from a tumor.
Signs of pathology - lethargy or sudden crying of the child
How is the treatment carried out?
Drug therapy is ineffective. It is possible to prescribe drugs that improve the flow of cerebral fluid, the transmission of nerve impulses and the metabolism of nervous tissue, and promote the resorption of the cyst. But surgical treatment may be required. Indications for surgery:
- cerebral edema;
- vomit;
- increase in head volume;
- bulging fontanel;
- an increase in the size of the ventricles of the brain;
- periventricular edema.
Surgery is performed by neurosurgeons. They can remove the accumulated volume of fluid from the cyst. But often, over time, cerebrospinal fluid refills and hydrocephalus develops. Therefore, in some cases, shunts are installed - special vessels that allow the discharge of cerebrospinal fluid. If a dermoid cyst is diagnosed, it needs to be treated as soon as possible due to the active growth of the tumor.
A brain cyst may not be diagnosed in time in a newborn, which leads to serious consequences. In an older child, the formation may be activated after a brain infection, head injury or serious illness.
Treatment of the pathology varies depending on the type and size of the cyst and can be medicinal and surgical.
A brain cyst is a formation of an indeterminate shape filled with fluid. It can form in any part of the brain, replacing dead nerve tissue.
Increasingly, this pathology is being detected in newborns, but not because it has become more common, but due to the improvement of diagnostic equipment.
Causes of cysts
A brain cyst itself indicates problems that occurred during intrauterine development and during childbirth, as well as some congenital pathologies.
- Injuries to the baby's head during childbirth
- Infection from the mother during childbirth (most often the cyst appears due to the herpes virus)
- Congenital pathologies of central nervous system development
- Insufficient cerebral circulation
The cyst itself is not a threat to the health and life of the baby.
But its growth and compression of nearby brain tissue is fraught with serious disturbances in the mental and physical development of the child.
Mechanism of formation and causes
There are several factors that can trigger the appearance of choroid plexus cysts in a fetus or infant.
In the fetus
As a result of the intensive development of cells and the brain, active accumulation of fluid occurs. Bubbles with cerebrospinal fluid in the vascular area sometimes indicate the mutation ability of the fetus, but in rare cases they are associated with mental disorders - Down or Edwards syndrome.
In newborns
But cysts discovered after birth indicate external negative influences. Plexuses are affected in the presence of inflammatory processes. Typically, under the influence of infection, a cyst forms in the villous tissue after 28 weeks. The reason for this is the pregnant herpes virus, ARVI, hypoxia due to insufficient blood flow, and birth injuries.
Types of brain cysts
The least dangerous is a choroid plexus cyst. It develops in babies during the perinatal period as a result of an infection received from the mother.
This type of cyst does not affect the overall development of the child and does not require special treatment. It is only important to rule out the infection that caused the formation in the brain and re-check the child’s brain using ultrasound.
An arachnoid cyst is located in any part of the brain, and there are usually several formations. Infants may develop meningitis due to meningitis shortly after birth. A further increase in its size is likely.
The subepindymal cyst is especially dangerous - it can progress very quickly, and therefore requires constant monitoring of its size using tomography. Always located in the ventricles of the brain.
Consequences
According to Dr. Komarovsky, the likelihood of complications developing due to a cyst in the brain in a newborn is negligible. A pediatrician known to many parents claims that choroid plexus cysts are a physiological norm. They disappear during pregnancy or with age without consequences for the child.
Candidate of Medical Sciences, mammologist-oncologist, surgeon
An arachnoid cyst is a benign neoplasm with liquid contents in the brain. It got its name from its location in the arachnoid membrane of the brain. There is a place in the brain where the membrane bifurcates, forming a small gap. Fluid can accumulate along this narrow fissure (closer to the posterior fossa or cerebellum).
The disease is more common in men than in women. Arachnoid cysts are diagnosed in approximately 3.5% of the world's population. With a small tumor size, it can occur completely without any symptoms and be diagnosed by chance, during an examination of the head for another reason.
Symptoms of a brain cyst: how does it manifest itself?
The growing cyst puts pressure on the tiny child's brain, causing strange behavior and disruption of the overall course of development.
- Excessive regurgitation after each feeding
- Impaired coordination of movements
- Slow psychomotor development
- Lagging behind normal height and weight
- Recurrent seizures
The final diagnosis is made after an ultrasound scan of the child’s brain. The use of modern equipment eliminates the negative impact on the baby’s brain and his body as a whole.
If the progressive nature of the pathology is detected, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed, which is repeated several times a year.
The rapid growth of a cyst in the brain poses a huge danger to the child due to tissue compression, increased pressure inside the skull and the subsequent manifestation of even more severe symptoms.
An increase in the intensity of seizures and even the development of a hemorrhagic stroke is likely.
Symptoms
Clinical signs depend on the location of the cystic formation in the child. If it is complicated, then various signs may appear, including threatening conditions.
A headache appears, and there is retardation in movements.
- Headache. The intensity of the symptom varies, but it usually appears after waking up. It is difficult to determine the presence of a headache in an unintelligent child. He changes in behavior, is capricious, sometimes cries for several hours.
- Deterioration of general condition. There is inhibition in movements, changes in sleep and wakefulness. Appetite worsens significantly, sometimes complete refusal of breast or formula occurs.
- Head enlargement. This sign indicates a large size of the cyst in the child, but it rarely appears. Along with a change in the shape of the skull, pulsation in the area of the fontanelle and its protrusion are detected.
- Impaired coordination. The symptom is a consequence of the growth of the capsule in the cerebellar region. Additionally, there is a visual disturbance due to compression of the optic nerve - double vision, floaters, blurry pictures.
There is a lack of coordination of movements.
- Deviations in sexual development. They occur during adolescence when a tumor forms in the pineal gland. A hormonal imbalance occurs, which leads to early maturation or significant delay.
- Epileptic seizures. Excessive electrical impulses are provoked by a cyst located deep in the membranes of the brain and its large furrows. Epilepsy is manifested by a convulsive state, rolling of the eyes, trembling of the eyelashes and loss of consciousness.
Treatment of brain cysts in newborns during the perinatal period - what treatment methods?
Treatment methods for brain cysts in young children directly depend on the reasons for the development of this formation.
If the cyst is not dynamic, that is, it does not invade new areas of the brain and does not increase in size, then treatment is not required, but only observation and control by a specialist. Treatment of brain cysts in children can be conservative or surgical.
With moderate progression of brain cysts in children, drug treatment is prescribed with drugs whose action is directed to the cause of the pathology. This includes drugs that improve blood circulation and blood supply to the brain.
If the cyst is caused by infections, then antibiotics and agents that fight viruses are prescribed. In case of reduced immunity and general tone of the child’s body, therapy also includes taking immunostimulants.
Surgical treatment is most often used for subenpindimal cysts and their rapid growth. Indeed, in this case, methods of conservative therapy are absolutely useless, and delaying the operation can lead to the most negative complications, including the death of the child.
Surgical intervention in the treatment of brain cysts in children, in turn, is divided into palliative and radical.
Palliative methods of cyst removal are bypass surgery and endoscopic method. In the first case, the contents of the cyst are eliminated using a shunt. The procedure is relatively less traumatic, but there is a risk of infection in the brain due to the long stay of the shunt in the brain tissue.
In addition, only the contents of the cyst are removed, and not the cyst itself, so relapse is likely. During the endoscopy procedure, fluid is pumped out from the cyst using a special device, an endoscope, through thin punctures. This method is the safest for the child.
A radical method of treating cysts is extremely rarely used in young children. The operation consists of opening the skull and completely removing the cyst, its walls and contents.
We discuss the treatment of mesadenitis in children here, let's talk about prevention.
Read about herpes type 6 in children, learn about treatment.