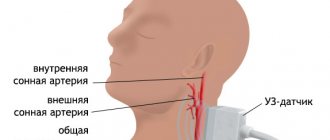
Positron emission tomography (PET) of the brain
is a new research method that allows, using special radiopharmaceuticals, to obtain information about the functional state of various parts of the brain. While MRI and CT are used to study the anatomical structure of brain tissue, PET is used to assess its functional activity, which is why it is called “functional tomography”. Thus, positron emission tomography is a qualitatively new diagnostic method, thanks to which it has become possible to diagnose diseases at the earliest stage of their development - before the appearance of morphological changes.
Brain PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
is the latest research method that allows, using special radiopharmaceuticals, to obtain information about the functional state of various parts of the brain. While MRI and CT are used to study the anatomical structure of brain tissue, PET is used to assess its functional activity, which is why it is called “functional tomography”. Thus, positron emission tomography is a qualitatively new diagnostic method, thanks to which it has become possible to diagnose diseases at the earliest stage of their development - before the appearance of morphological changes.
Indications and contraindications for PET/CT.
PET/CT is used in the presence of diseases such as:
- brain tumors of various types;
- stroke;
- dementia;
- epilepsy;
- multiple sclerosis;
- schizophrenia;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- cerebrovascular pathology;
- primary progressive aphasia;
- Pick's disease.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- decompensated and subdecompensated forms of diabetes mellitus;
- chronic diseases with exacerbations;
- general serious condition of the subject;
- inability to lie down and remain motionless for a long time.
Principle of positron emission tomography
The work is based on the ability of pathological and healthy tissues to absorb energy rays.
Using a tomograph, blood flow and absorption of oxygen and glucose by tissues are recorded. To do this, the patient is injected with a small amount of a radioactive compound that emits invisible rays. The technology registers them.
The computer processes the received information and converts it into graphic form. The brightness of the image depends on the amount of radioactive drug.
In malignant formations, the metabolism is higher, so this area will have more saturated colors.
PET/CT with glucose and methionine. What is the difference?
The principle of operation of a PET scanner is to construct a color image of the organs and anatomical structures of the patient’s body based on the data received from the radiopharmaceutical. The color of different tissue areas depends on the radiopharmaceuticals accumulated in them. Tumor foci in such images are marked in bright red, since they have accumulated the largest amount of radiopharmaceuticals.
Labeled glucose (fluorodeoxyglucose) is used as a radiopharmaceutical in 9 out of 10 cases. This choice is explained by the fact that for the intensive development of malignant tumors, sugar is vital, which they accumulate faster than normal tissues.
But the difference in the volume and rate of accumulation of radiolabeled glucose in the brain is not so significant. The thing is that accelerated absorption of glucose for the central nervous system is a physiological norm. There is certainly a difference, but it may not always be noticeable.
Therefore, another radiopharmaceutical, 11c-methionine, is currently used for brain research. This drug also effectively accumulates in malignant neoplasms, while healthy brain tissue practically does not absorb it. Years of research have shown that methionine PET/CT is a more accurate and informative method for diagnosing the brain than glucose PET/CT.
— Are there any contraindications?
— A relative contraindication is some severe somatic illness in a state of decompensation, when the patient himself will not be able to endure this study. The procedure is quite time-consuming - both preparation and execution. The patient stays at our center for at least two to three hours. The administered radiopharmaceutical itself does not have any effect on internal organs and their functions. However, there are restrictions for patients with diabetes: before starting the study, the glucose level should not be higher than eight millimoles per liter, because the drug administered is glucose-based.
After the administration of radiopharmaceuticals, the patient naturally becomes a source of radiation (this is necessary for the study), but for a very short period of time. The activity of the administered drug decreases very quickly. Within 24 hours, the patient becomes absolutely safe for others. Our method is contraindicated for pregnant women who plan to continue pregnancy. If a woman has already given birth and is breastfeeding, then performing our method is a relative contraindication. According to vital indications, it can be performed, but then for two days the woman will express milk and will not be able to use it to feed the child. In addition, after our research, it is not recommended to have close contact with infants under one year of age during the day - pick them up, rock them, cuddle them.
To quickly remove the drug from the body, you need to drink more water and it is advisable to do a cleansing enema.
— Do you need any preparation to take the test?
— The patient must come to us on an empty stomach—the fasting period must be at least six hours. On the eve of the study, the patient can have a light dinner. You can’t eat in the morning - just drink clean, still water as much as you like. Well, to make the CT part better, you can cleanse your intestines a little and follow a low-carbohydrate diet for three days.
—What do patients fear most?
— Some patients are afraid of radiation exposure.
— Is there a limit to the capabilities of PET diagnostics?
- Of course, this is the size of the tumor that needs to be found. It should be at least four to five millimeters. This is the limit of the method's resolution. On the CT scan we will see the formation itself, but we will not objectively determine the accumulation of the drug. You cannot expect PET scanners to detect a tumor at the level of one or two cells - they do not have such technical capabilities. Perhaps in the future, scientists and engineering minds will create scanners so sensitive that they will be able to record the oncological process at the level of one or two cells. But for now these are dreams!
Preparing for the study.
PET/CT examination is associated with the study of the metabolic process, so patients are advised to stop eating at least 6 hours before the appointment. And since the scan will take place with methionine (a radiolabeled amino acid), it is recommended to exclude this amino acid from entering naturally 24 hours before the appointed time. The diet consists of avoiding meat, eggs, fish, soy and all types of nuts.
It is also recommended to find suitable clothing for the examination, as you will need to remain still during the scan. The wardrobe should consist of soft and loose things that will allow you to completely relax and not feel discomfort.
Important! If there are relative contraindications, you should consult your doctor in advance to determine the possible benefits and harms of PET/CT diagnostics.
Modern tomographs used for PET studies
Manufacturer: Siemens
- Biograph mCT 16
Compact tomograph suitable for solving most clinical problems.
- Biograph mCT 20
A tomograph with higher accuracy while ensuring fast scanning and productivity.
- Biograph TruePoint
A diagnostic solution with high sensitivity and resolution of sensors allows you to find even small pathologies.
Manufacturer Philips
- Ingenuity TF PET/CT
A modern combined PET CT system, with a set of technologies that allows you to conduct specialized studies and obtain accurate data with a compressed scanning time.
- Gemini TF
The modern standard, due to the optimized parameters of the CT module, provides high quality images with low radiation exposure.
- GEMINI TF Big Bore
TF series version with wide tunnel aperture. The tomograph is as comfortable as possible for patient positioning and solves the difficulties associated with diagnosing overweight patients and fear of confined spaces.
How is it going?
The subject is injected intravenously with a solution containing labeled methionine 1 hour before the start of the procedure - this is exactly the amount of time the radiopharmaceutical needs for uniform distribution.
distribution throughout the body.
After this, the patient is positioned on the table of the tomograph, which will slowly move through an arch with a scanner receiving information from the radioisotope. The PET scanner and CT scan operate simultaneously, and the resulting data is combined by special software into a color 3D image.
Throughout the entire procedure, the patient is alone in the diagnostic room. Scanning duration is from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
How is the research conducted?
- You must arrive at the PET center at the time specified when registering for the study;
- please turn off mobile phones and maintain silence in the premises of the PET center (especially in the waiting room for patients);
- after you change clothes, you will be taken to the waiting room and asked to provide your passport to complete the necessary documentation;
- then you will be invited to the office for a conversation with the doctor performing the study, where you will provide medical documentation;
- after a conversation with the doctor, you will be taken to the waiting room for patients, where you need to take a comfortable position, close your eyes and relax as much as possible;
- At the time appointed by the doctor, you will be invited to the treatment room and a radiopharmaceutical – 11C-Methionine – will be administered. The drug is administered intravenously through a thin catheter - the procedure does not cause discomfort during administration and cannot cause the development of allergic reactions;
- the patient returns to the waiting room and continues to relax, sitting in a comfortable position with his eyes closed;
- 20–30 minutes after the introduction you will be invited for a scan, which lasts 25–30 minutes;
- scanning is performed in a supine position; during scanning you must lie still and not move (movements during scanning lead to the appearance of artifacts that make it difficult to evaluate the results of the study); The patient does not experience any sensations during scanning; the staff monitors the process and, if necessary, approaches the patient;
- for better relaxation, scanning is performed in a darkened room;
- After the scan is completed, the staff will escort you to the waiting room;
- After 15–20 minutes (the time required to reconstruct the diagnostic image), you will be informed about the completion of the examination and the approximate time for receiving the examination results.
Cost of the study.
Prices for PET/CT can vary significantly depending on the chosen medical center, the complexity of the diagnosis, the tomograph model used, and the experience of the medical staff. Thus, the cost of such a brain study in Russia is in the range of 25,000-85,000 rubles.
If you are a compulsory medical insurance card holder, you can undergo PET/CT completely free of charge. To do this, you just need to take a referral from your attending physician and make an appointment in advance at a radiomedicine center that practices duty-free diagnostics. It is worth considering that the queue for such an examination can last more than one month.
Indications for use
Reasons for diagnosis with positron emission tomography:
- Chronic headache, dizziness.
- Double vision or sudden darkening of the eyes, loss of visual fields.
- Loss of consciousness, somnolence.
- Convulsive syndrome: large and small seizures.
- A complex of vegetative symptoms: heart pain, sweating, loss of appetite, diarrhea and constipation, trembling in the limbs, cold fingers, a feeling of lack of air, abdominal pain of uncertain localization.
- Nausea and vomiting for no obvious reason.
Discounts
All discounts are confirmed by relevant documents. Discounts on all types cannot be combined. Discounts do not apply to contrast agent and additional services.
According to the MIBS standard, the results of a medical examination are formalized as a conclusion on paper with registration (recording) of the examination data and the issuance of images ON DISK. Registration (recording) of medical examination data on another medium (film, USB flash drive) or re-registration of medical examination data on a disk are independent medical services and are paid additionally at established prices (tariffs).
Make an appointment
Features of the procedure
This manipulation is completely painless and does not cause any discomfort or side effects. The only absolute contraindication is individual intolerance to any of the components of the radiopharmaceutical drug. In addition, the study is not prescribed to pregnant women, provided that preservation of the fetus is planned. If PE tomography is performed on a nursing mother, the child is transferred to artificial feeding.
When performing scanning, a dynamic mode, small doses of radiopharmaceuticals, and a short scanning time are usually used. This allows the results to be correctly interpreted and is also an additional benefit for the patient due to the maximum reduction in radiation exposure and the short duration of the procedure.
After an examination for several hours, during which the injected drug disintegrates and is eliminated from the body, the patient is in a diagnostic center. To accelerate the elimination of isotope decay products, it is recommended to consume large amounts of liquid at this time.
Also, according to some researchers, PET of the brain with methionine can be highly informative in determining areas of radiation, as well as in early assessment of the effect of radiation therapy. In addition, identifying areas of increased accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals within the tumor mass can improve the accuracy of the biopsy and can be used during its implementation. However, for now these are just assumptions, which require additional clinical trials to confirm.
Registration and inquiries by telephone in St. Petersburg in Balashikha
Preparation
10-12 hours before the procedure, it is recommended to exclude protein products of animal and plant origin from food: milk, meat, fish, legumes, etc. The evening before the test, a light dinner is acceptable.
Immediately before the procedure, you should not eat or drink sugary drinks. The use of still water is not limited. You can also drink tea and coffee without sugar. Possible restrictions in taking medications should be discussed with your doctor.
You need to have your passport, directions, data from previous studies along with disks with you. If the study is performed under compulsory medical insurance, a referral (form 057-u) and a protocol from the medical commission are issued. You also need to have SNILS and a compulsory medical insurance policy on hand.
Before scanning, you need to remove all objects containing metal (chains, earrings, other jewelry, belt).
When is it prescribed and what does this study show?
The main area of application of PET CT is the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms. The study may be prescribed if the oncologist needs:
- identify a tumor node at stage zero, that is, when it cannot be detected in any other way;
- clarify the nature of the pathology detected during CT scanning, ultrasound, x-ray, etc.;
- determine the presence and localization of metastases, including distant ones;
- evaluate the results of chemotherapy at the very beginning of the course of treatment;
- differentiate tumor relapse or progression from necrosis that developed as a result of radiation;
- solve other specific problems.
The most important advantage of this method in oncological diagnostics is the ability to determine absolutely all tumor foci, including the smallest metastases up to 1 mm in size, during one examination.
The second direction is the diagnosis of neurological diseases. Based on the examination results, neurologists can:
- assess the condition of the arteries supplying the brain and their role in cerebrovascular accidents;
- differentiate between malignant and benign brain tumors;
- establish the cause of dementia, including diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in the early stages;
- accurately identify foci of epilepsy, which is especially important when planning surgical intervention;
- obtain valuable diagnostic information for Parkinson's disease, Huttington's disease, degenerative diseases of the central nervous system (multiple sclerosis, etc.)
Cardiologists rarely resort to PET CT. In this case, the procedure allows:
- diagnose a temporary adaptive decrease in the volume of work of the heart muscle and differentiate it from heart failure;
- accurately determine areas of myocardial ischemia before surgery to restore impaired blood circulation (angioplasty, shunt installation);
- identify areas of post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
Types and modes of research
Depending on the diagnostic purposes, the following may be prescribed:
- full body scan;
- local brain scan;
- examination of the chest area.
Based on the type of radiopharmaceuticals (RP) used, PET is divided into:
- With 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose. Allows you to identify areas with different intensity of glucose accumulation. The cells of most cancers and other malignant tumors take up glucose most quickly. The more the drug accumulates in the tumor tissues, the brighter they glow in the images and the higher the degree of malignancy of the cancer cells.
- With choline, gallium-PSMA, PSMA-7. It is used in the diagnosis of prostate cancer, the tumors of which actively accumulate this substance. Choline is also sometimes used in liver and brain examinations.
- With methionine or tyrosine. Provides high quality images when visualizing gliomas (a type of brain tumor);
- With 13N-ammonium. Used to diagnose changes in the heart muscle.
- With FP-CIT and F-DOPA. Used for Parkinson's disease.
- With F18-FBB. Prescribed for Alzheimer's disease.
If it is necessary to obtain clearer CT images, the patient may need the injection of a contrast agent, and therefore PET/CT is also distinguished without contrast and with contrast.
Limitations, contraindications, complications
In addition to the contraindications common to any diagnostic methods associated with radiation exposure, positron emission tomography is not performed:
- in the first month after completion of chemotherapy;
- in the postoperative period;
- in the presence of severe inflammatory processes or during the height of an infectious disease.
In all of the above cases, the reliability of the results will be insufficient.
In addition, examination by this method is not indicated for patients during radiotherapy treatment and immediately after its completion. The recommended pause after a course of RT is 3 months.
If the prescription rules are followed, the examination does not cause any side effects, and the radiation dose is so small that, if indicated, it can be prescribed to children and nursing mothers. The only possible complication is individual intolerance to radiopharmaceuticals (extremely rare) or contrast agent (higher probability).
Preparation for PET diagnostics
Preparation for the study varies depending on the type of study and the patient’s health characteristics.
General recommendations boil down to limiting physical activity, stopping drinking alcohol and smoking 24 hours before, and stopping carbonated water and food 6 hours before the test.
These recommendations must be followed because intense physical activity, excess glucose, the presence of nicotine and alcohol in the blood lead to changes in the intensity of radiopharmaceutical accumulation, and gases and food make scanning of the abdominal organs difficult.
To increase the accuracy of diagnosis and reduce the risk of side effects from the administration of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, patients with diabetes mellitus take drugs that normalize the metabolism of sugars (trimetazidine, etc.) for 8–12 days before the examination. The day before the tomography, coffee is excluded from their diet and taking caffeine-containing medications is prohibited.
Before the choline PET/CT scan, a special diet is also prescribed, excluding protein-rich foods, B vitamins and some vegetables.
How the research is carried out
The patient is administered a radiopharmaceutical, most often intravenously, as well as a diuretic to accelerate the distribution of isotopes throughout the body. The radiopharmaceutical dose depends on the scope of the study and the patient’s weight.
After a certain period of time, during which the maximum accumulation of isotopes occurs in the parts of the body being studied, a scan is performed. In this case, the couch with the subject moves slowly inside or along the module with scanners. The whole process takes from half an hour to an hour or a little more.
After the procedure, it is recommended to consume large amounts of fluid to remove isotope decay products from the body, the lifespan of which is very short - from 2 to 22 hours. Thanks to this, no later than 24 hours later you can communicate with others, including pregnant women and children, without any restrictions.
Decoding the results
Data interpretation is carried out by radiologists with appropriate specialization. As a rule, it takes no more than an hour to evaluate the results and draw up a conclusion.