Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the best methods of in-depth non-invasive diagnostics. The procedure is carried out without any surgical intervention and allows you to make the most clear diagnosis, the cause of the disease and find suitable ways to solve it.
MRI diagnostician
Prokhorov Alexander Andreevich
Head of the department, Doctor of Medical Sciences.
It often happens that after a long day of work we simply get a headache. And this is normal, due to the stress and problems that have occurred throughout the day. But if you understand that the pain does not go away and becomes permanent, you need to do a tomography. And the sooner the better. The earlier you diagnose the problem, the greater the chance of treatment and a favorable outcome.
Advantages of radiography
This method is considered one of the most accurate and informative.
- The doctor gets the opportunity to examine in detail the state of the child’s internal organs and detect abnormalities that can cause serious illness.
- Such an examination is indispensable for fractures, injuries and bruises, since an external examination does not allow drawing conclusions about the extent and nature of the damage.
- Timely X-ray of the lungs makes it possible to avoid the development of serious diseases, including tuberculosis.
Harm of X-rays to the human body
Probably every person knows about the dangers of ionizing radiation, but how dangerous is a head x-ray for the human body?
According to the data, during an X-ray examination of the head, the patient receives about 0.12 mSv (millisieverts), which is up to four percent of the radiation that a person living in an area with normal background radiation can receive over the course of a year. It is worth noting that the same annual radiation dose, which is 3 mSv, can be obtained in just a few hours of exposure to the open summer midday sun.
It should be emphasized that most modern specialized clinics conduct X-ray examinations using digital X-ray machines, which differ from conventional ones in a lower level of radiation exposure and increased information content. In addition, they allow you to obtain images in digital form.
Despite the fact that the radiation dose during X-ray diagnostics of the head is very modest, experts do not recommend undergoing X-rays more than seven times a year, since in any case, X-rays can harm the body. X-ray examination is used only when indicated, and no specialist will recommend doing the procedure again.
Contraindications to X-ray examination:
- Pregnancy. X-ray irradiation is not recommended during pregnancy, and especially during the period when all the internal organs of the future person are intensively formed and developing, that is, in the first trimester.
- Excessive exposure to radiation. Despite the fact that the dose of radiation received when performing an X-ray of the head is insignificant, and is unlikely to lead to the occurrence and development of radiation sickness, there is still a risk.
Of course, in some situations, when there is a risk of loss of life due to a serious illness that can only be identified using an x-ray, this procedure will be performed as many times as necessary. In particular, in case of severe head injuries, when it is very important to conduct an examination and assess the situation, X-rays of the skull can be performed even on pregnant women. Naturally, in the process of carrying out this type of research, special lead pads are used to completely cover the pregnant woman’s abdomen.
On the frontal image, the doctor will be able to see:
Symptoms - reasons for an x-ray
X-rays have no age restrictions, but if we are talking about a child, you should agree to the procedure if the diagnosis cannot be made in any other way.
Reasons for performing an x-ray:
- Scoliosis;
- Suspicion of tachycardia or heart disease;
- Immunodeficiency (acquired or congenital);
- Bronchial asthma, if attacks occur frequently;
- Respiratory diseases – pneumonia and others;
- Manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Suspicions of abnormalities in the development of the gastrointestinal tract.
If necessary, use a contrast agent (for children this is gastrografin).
What the study can show
Brain X-ray is a non-invasive hardware diagnostic method, so no sensations arise during the examination. The result of the examination will show the consequences of brain injury or other pathological processes that caused clinical manifestations.
What can be seen in a brain image:
- Violation of bone integrity;
- Localization of the tumor or cyst;
- Hematomas;
- Congenital anomalies of the skull;
- Pathological thinning of the skull bones or deformation;
- Displacement of structures;
- Intracranial hypertension, cerebral edema.
The interpretation of the images is carried out by a radiologist; based on his conclusion, the attending physician makes a diagnosis and selects treatment tactics - conservative or surgical.
source
How is the examination carried out?
There is no need for special training, but there are general rules that parents should be aware of:
- The child is undressed to the waist;
- To ensure a clear picture, remove metal objects - buttons, hairpins, jewelry;
- Diagnosis can be carried out in a sitting, lying or standing position;
- The doctor will ask the child to hold his breath for a while or independently choose the appropriate time for the photo;
- Parts of the body that are not subject to examination are protected with a special lead apron.
Diagnostics are carried out in the most comfortable environment, in the presence of parents.
Where and how they do it
The answer to the question of where a child’s X-ray is taken is quite simple: in any medical center. If this is not a newborn baby, then no special equipment is needed to carry out the procedure. X-rays can also be performed in a regular clinic, if they have the necessary equipment. Today you can look on the website of almost any medical institution to see the availability of this or that device and what it is called.
Head examination
A head x-ray is quite simple:
- Before starting the examination, the patient must remove all metal objects, including jewelry.
- The head must be motionless during the procedure (special clamps are sometimes used for children).
- The patient remains motionless for several minutes, and the procedure is absolutely painless.
No special diet or drinking regimen is required before a head x-ray. Thus, in just a few minutes the doctor will be able to obtain a detailed picture of the condition of the brain, cranial bones and oral cavity.
Security measures
X-ray machines used today cause virtually no harm to the body. Parents should inquire in advance whether the medical institution is using a modern device. It is important to ensure that the protective apron covers the abdominal cavity and pelvic area.
To conduct pediatric radiography, it is better to contact a modern, proven clinic, experienced professionals.
If all rules and precautions are followed, the diagnosis will be as effective as possible and will take place without negative consequences for the child’s health.
What does a skull x-ray show and why is it prescribed?
A common misconception is that head x-rays are intended to examine the brain. In fact, this diagnostic method is more effective for studying the bones of the skull along with the teeth.
The doctor issues a referral for an X-ray of the skull if the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- tremor of the upper extremities;
- constant or recurrent headache;
- frequent dizziness;
- causeless nosebleeds;
- feeling of darkening in the eyes;
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- pain when chewing.
We recommend reading: Senade tablets for weight loss: composition, instructions for use, reviews - minus 5 kg easily
The purpose of the procedure is:
- establishing a primary diagnosis or checking an existing diagnosis;
- development of treatment tactics;
- determining the grounds for surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy;
- checking the effectiveness of the treatment.
“What does a skull x-ray show?” – people being examined often ask the doctor who ordered the x-ray this question.
A doctor of appropriate qualifications can determine from a high-quality image the presence of the following pathologies and diseases of the skull bones:
- cyst;
- osteoporosis of bone tissue;
- congenital anomalies of the structure and deformations of the skull;
- cerebral hernias and pituitary tumors;
- hematoma;
- osteosclerosis;
- osteomas (benign bone tumors), meningiomas (benign tumors of the soft membranes of the brain), malignant tumors, metastases;
- fractures and their consequences;
- signs of intracranial hypertension and hypotension;
- consequences of inflammatory processes in the brain.
Information content of X-rays in oncology
Neoplasms can form in any organs and tissues. Most often, the focal localization of oncology is located in the lungs, joints, bones, brain, pelvic organs and abdominal cavity. In order to identify pathology, a complex of various studies is used. The most informative among them is radiography. The procedure has a number of advantages, one of which is quick results.
However, it is possible to detect a tumor on an x-ray image only if certain conditions are met. First of all, this is the size of the neoplasm, which reaches 2 mm or more. Smaller tumors are much more difficult to identify.
In the photographs, the neoplasm is reflected as x-ray positive. But at the same time, tumor cells do not always reflect X-rays, as a result of which the formation is not detected even if it is quite large in size.
When examining an x-ray with pathology, you can notice a darkened spot
A tumor can only be identified if it is not covered by other tissues and organs and is located on the surface of the affected organ.
The X-ray examination technique helps to identify cartilaginous, epithelial, muscle and metastatic tissue lesions.
However, this type of study has a significant drawback - it does not allow us to determine the nature of the course of the disease. It is also not always possible to determine the benign quality of a tumor from images. Therefore, in addition to the main examination, a biopsy is prescribed.
If there are minor changes in the tissue structure on X-ray images, the doctor pays special attention to this. This may indicate the presence of a tumor.
Thus, we can conclude that x-ray examination allows one to determine the presence of a formation, but subject to certain conditions.
In order to clarify the diagnosis, other examination methods are prescribed: CT (MRI), ultrasound, blood tests. With a comprehensive examination, you can obtain accurate data and identify oncology even in the early stages of development.
To clarify the diagnosis, an MRI is performed
X-ray of the skull in Moscow
Take an X-ray of the skull using special equipment, get the necessary advice from a qualified doctor, undergo diagnostics - all these and other services are provided by a diagnostic specialist. The advantages of the clinic also include affordable prices. The price of a skull x-ray is from 1,700 rubles in one projection and from 2,300 rubles in two. The work of the center’s staff and quality treatment receive good reviews from visitors to the clinic.
You can make an appointment online, by phone or at the address: Davydkovskaya Street, 5. Do not delay treatment until later.
Methods of conducting X-ray examination
In modern medicine, two types of radiographic diagnostics are used, which are used based on the characteristics of pathological processes. Depending on the feasibility, the doctor prescribes a general examination or a targeted examination, although in some cases he may recommend one first and then the second for specifics.
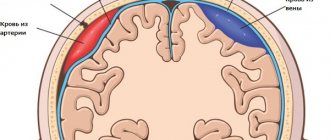
A plain radiograph is most often prescribed for head injuries. In this case, not only an X-ray of the brain is taken, but also of all the bones of the skull. The overview image will show, if available:
- congenital anomalies of the skull bones;
- fractures, displacements, cracks;
- hematomas caused by a blow or bruise;
- intracranial hypertension.
The review technique has this name because it is prescribed not to a specific area of the skull, but to its entire area in order to identify all possible disorders.
This technique is prescribed when there is a suspicion of the presence of a pathological process in any part of the skull. This significantly helps to narrow the search and thoroughly examine the required part of the bone tissue. The method is used to study the vessels of the brain, nasal, bones, orbits, jaws and other individual segments of the skull. When conducting a targeted radiograph, you can qualitatively track all possible changes in the examined area.
Sighting
X-ray of the sella turcica
- one of the methods for diagnosing the head
Prices
| Name | Price |
| X-ray of the entire skull in two projections | 2 300 ₽ |
| X-ray of the bones of the facial skeleton (1 projection) | 1 700 ₽ |
Prices Make an appointment
Craniography, or in other words, an X-ray of the skull, is prescribed to patients if it is necessary to examine the three groups of bones that make up the skull. All three bones are connected by a cranial suture in the form of a jagged line. Due to such a complex structure, diagnosing the skull is difficult, so an X-ray of the skull is prescribed in two projections (direct and lateral) or in one. It all depends on what kind of picture you need to take.
Indications for head examination and skull x-ray:
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Severe and constant headache.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Suspicion of neoplasms.
- Problems with the endocrine system.
- Asymmetry of the skull.