Spinal diseases can be caused by various reasons: injuries, degenerative changes, infections, tumors. Moreover, many diseases, especially in the initial stages of development, have similar symptoms. In medicine, professional diagnostics allows you to establish the correct diagnosis and draw up an effective treatment regimen. And its most important stage is an instrumental examination of the patient, which includes MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Types of instrumental methods of medical diagnostics
- The main instrumental methods for identifying pathologies of the musculoskeletal system are:
- Radiography . Allows you to identify changes in the position of bones, sizes and shapes of joint spaces, bone structure and find foci of destruction. Such a study of the spine allows us to determine disorders that are caused by osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, and spondylosis deformans.
- Computed tomography (CT). They are used to obtain images of bone tissue and soft structures in order to clarify the diagnosis. This research method allows you to obtain clear and contrasting photos of even the smallest joints. It is often used to identify pathological growths of bone tissue of the spine - osteophytes. To obtain a 3D reconstruction of the organ under study on a computer monitor, multislice spiral CT is used.
- Ultrasound scanning or sonography. With its help, the cervical and lumbar spine is examined if the presence of disc protrusions or intervertebral hernia is suspected, and the condition of the ligaments, tendons, joints, and muscle corset is diagnosed.
- Electromyography . It is carried out to identify lesions of the nerve roots due to intervertebral hernias. It allows you to distinguish this disease from peripheral neuropathy, determine its stage and the existing degree of damage. This study is also carried out if there is a need to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The most universal and safe method for examining the spine and joints. Allows you to obtain a clear image of the organ in the form of a series of longitudinal and transverse sections in order to accurately diagnose all pathological changes in bone and soft tissues (nerve structures, ligaments, muscles, blood vessels). MRI reveals degenerative changes and herniated intervertebral discs, spinal canal stenosis, hypertrophy of facet joints, etc.
Interpretation of magnetic resonance imaging results - localization of the process
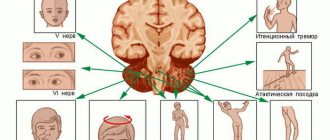
Having determined the pathological process, the doctor, based on his experience and knowledge, evaluates, first of all, its localization, which will allow us to talk about the importance of the affected structures, for example, a part of the brain: tumors of the base of the brain, as a rule, are much more life-threatening than those for the bark.
Size, shape and number of lesions
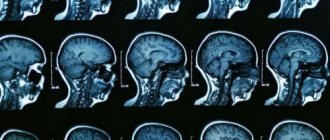
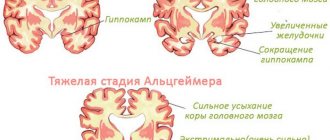
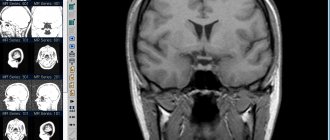
MRI image of a head with a tumor
Next, the size and shape of the pathological focus is assessed. If it is a tumor, then it is extremely important to know how large it is, as well as the number of tumors, if there is more than one. Also, the shape of the hearth is a very important indicator.
Again, the tumor can be tentatively characterized by its shape: clearly contrasting, with smooth edges, regular shaped neoplasia, most likely benign and in a capsule. However, only histological examination can give a final result on the prognosis of the course of the tumor. If there are multiple formations disseminated throughout the organ tissue, most likely they mean some kind of metastasis, be it tumor or infectious (tuberculous granulomas).
Hearth hue
Based on his knowledge of the pathological anatomy of diseases, the doctor can judge by the color and displayed structures of the lesion which particular pathological process is occurring in a particular organ. For example, a formation found in the liver can be either a tumor, including a metastasis, or a focus of echinococcosis or alveococcosis, a metastasis of tuberculosis, an abscess, etc. The focus of a change in the shade of gray in the brain tissue can be either a neoplasm or a softening of its tissue.
Indirect indicators of pathology
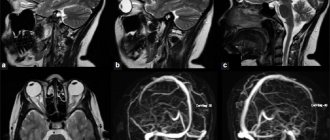
The indicators listed above relate directly to the specific outbreak found. However, some findings on tomograms can indirectly tell the doctor about the condition of the organ or system to which the patient’s complaints are directed. For example, a tomographic examination of the vessels of the head and neck can reveal the cause of cerebral ischemia or stroke.
Also, neurological symptoms can be caused by a violation of the outflow of blood through the vessels of the brain. Pathological processes can also be indirectly determined by changes in the position of organs and tissues relative to each other. For example, a tumor in the head of the pancreas can compress the common bile duct and cause obstructive jaundice syndrome. Or a brain tumor or obstruction of blood flow from the brain can increase intracranial pressure. This can lead to the so-called compression syndrome - a condition when the large opening of the skull (through which the brain passes - the transition of the spinal cord to the brain (oblongata)) compresses the centers of the medulla oblongata.
If a tomographic examination is performed repeatedly, the doctor evaluates the course of the disease over time. In this case, MRI interpretation is carried out taking into account previous examinations.
For example, if it is a tumor, then its growth or, conversely, regression is assessed. After a stroke, the presence, location and size of a brain cyst can be detected. With atherosclerosis of the subclavian or carotid arteries or their branches, the state of the brain can be assessed for softening of the nervous tissue.
The above suggests that the process of deciphering the results of magnetic resonance imaging requires a great understanding of the essence of the procedure itself.
What is MRI in medicine?
Modern MRI diagnostics – what is it? This research method is based on the use of the properties of a magnetic field .
The patient is irradiated with electromagnetic waves. In this case, the electromagnetic energy of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms is released, which is recorded using special sensors.
To obtain full and detailed images and thin sections of the diagnosed area, the results are subjected to computer processing. Next, a three-dimensional image of the organ is created, which can be examined on the monitor from different angles.
Hydrogen atoms are found in the greatest number in water molecules, so MRI clearly demonstrates the differences between different tissues of the body precisely in their water content.
This method is indispensable for diagnosing pathological processes that are characterized by an increase in fluid content in the affected areas (tumors, infections, foci of inflammation).
The technique is absolutely safe, as it does not create ionizing radiation.
Understanding how a magnetic resonance imaging machine works
In addition, to decipher tomograms, specialists are trained in the principles of magnetic resonance imaging. Tomography literally means “to draw segments,” in this case the human body. Magnetic resonance imaging means that the method is based on the resonance of the magnetic field created by the device with the position of the dipoles in the human body. Such dipoles are hydrogen atoms in organs and tissues, which are found in all organic molecules, as well as in water, that is, literally everywhere in our body.
The device determines the time during which hydrogen atoms, after the end of the magnet’s influence on them, take their original “habitual” position - spin time or relaxation time. Also, the receiving coil of the device (sensor) detects the magnetic resonance signal created by hydrogen atoms, being in a resonant state with each other and under the influence of a magnet. Thus, each pixel is given a certain shade of gray, which depends on the signal frequency and vector phase determined by the sensor.
This is important to understand, since a rough idea of the “density” of hydrogen atoms in tissues can be judged by properly assigning a tissue a certain shade of gray. For example, fabrics containing large amounts of water will have a longer relaxation time and therefore be darker.
Advantages of MRI in diagnosing spinal pathologies
Many instrumental diagnostic methods provide a limited amount of data that does not provide a complete clinical picture of the disease. Magnetic resonance imaging against their background has the following advantages:
- Obtaining a complete amount of information about the condition of the organ under study for the correct diagnosis and choice of treatment regimen.
- The safety of the procedure and the absence of any negative impact on the health of the subject allow the procedure to be repeated several times. And this is important when monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for spinal diseases.
- MRI makes it possible to diagnose twisted tissues and structures of all parts of the spine in a relatively narrow space, which is not possible with any other research method.
- In case of cancer, MRI helps to accurately localize the tumor and determine its size.
- By adding a contrast agent to the bloodstream, this diagnostic method allows you to track the process of blood circulation in small and large vessels and identify even the slightest deviations from the norm. This is especially important for patients who have had a stroke.
- An MRI machine makes it possible to take step-by-step photographs and create 3D projections. The doctor sees a picture of the patient’s tissue condition in real time.
- The method is suitable for patients with large body weight (110 kg and more) and has no age restrictions.
Research methodology
No special preparation is required for the patient before performing an MRI. The procedure can be performed at any time of the day; a referral for it is issued by the attending physician. You need to have with you an extract from your medical history, a referral and, if available, pictures from previous tomographs.
Before the session, you need to remove all jewelry, including the piercing. Women are not recommended to use decorative cosmetics, as some types, for example, mascara or eye shadow, may contain metallic particles.
The choice of clothing is also important. There should not be any metal parts on it. Many clinics offer patients to change into disposable pajamas before the procedure and undergo a preliminary examination using a hand-held metal detector to eliminate any errors. Since the MRI machine produces a certain amount of noise during operation, patients are allowed to use earplugs.
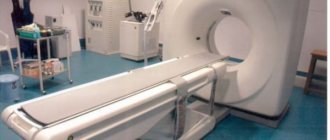
The patient undergoes the examination lying on his back in a tomograph tube. His limbs and head are fixed, since in order to obtain the clearest pictures the person must be motionless.
No strangers are allowed in the room while the MRI machine is operating. The doctor observes the patient through a special window and a video camera.
If necessary, the patient can give an alarm by pressing a button, or the diagnostician through the intercom.
The duration of the study is 30-60 minutes.