Sometimes neurologists diagnose cerebral ischemia, what is it? The disease affects an increasing number of people, especially the elderly. There is a threat not only to the patient’s vital activity, but also to his entire life. The sick person needs constant monitoring by a doctor and timely and effective treatment.
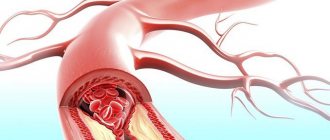
Ischemia is a serious disease. It causes oxygen starvation: the hematopoietic flow does not deliver the required amount of nutrients to the brain cells. This occurs due to the fact that the vessels through which blood flows are clogged with cholesterol particles and cannot transport blood at the proper level. Any tissue in the body suffers from a lack of oxygen, and the brain especially. About 20% of the blood circulating through human vessels passes through brain cells, although its entire mass makes up no more than 3% of body weight. Ischemia occurs in brain tissue that does not receive the required amount of oxygen.
Causes
The main cause of circulatory disorders in the arteries is various diseases, due to which there is loss of blood or a decrease in pressure in the arteries. These include: damage or compression of blood vessels (arteries) under the influence of tumor formations, frostbite, in which tissue nutrition is disrupted due to lack of blood circulation, and diseases caused by impaired blood supply to large and small vessels (thrombosis, atherosclerosis and other pathologies associated with diseases of the blood or blood vessels).
In clinical practice, ischemia in newborns most often manifests itself as a consequence of intrauterine pathologies or a consequence of birth trauma. It is caused by a circulatory disorder, in which the delivery of oxygen to the brain does not occur in full.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the development of cerebral ischemia in newborns are:
- age characteristics of the pregnant woman;
- pathology in the location of the placenta (previa);
- premature placental abruption;
- premature or late delivery;
- preemplaxia;
- vascular disorders in the placenta and impaired blood flow in the umbilical cord, provoking cardiovascular pathologies in the fetus;
- turbidity of amniotic fluid, indicating infection in the amniotic sac;
- multiple pregnancy, monozygotic or dizygotic genesis;
- diseases of a pregnant woman, occurring in acute or chronic form.
At the same time, simultaneous exposure to several factors greatly increases the risk of developing ischemia.
Classification and characteristics
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the degree of brain damage.
With grade 1 cerebral ischemia, signs of neurological changes are not clearly expressed and manifest themselves: pain and heaviness in the head, general weakness and a persistent feeling of fatigue, absent-mindedness and impaired concentration, memory impairment and insomnia, emotional instability.
The first degree of cerebral ischemia in newborns manifests itself:
- child's agitation or depressed state;
- sleep disturbance and reaction to weather changes;
- loss of appetite and frequent regurgitation;
- sluggish neonatal reflexes.
It is difficult to recognize the disease at this stage. Although it is at the 1st stage that cerebral ischemia is easily treated. Not only the current symptoms are relieved, but also the exacerbation of the condition is prevented.
Grade 2 cerebral ischemia is characterized by the manifestation of more pronounced symptoms and profound neurological pathology with dizziness, profound impairment of all types of memory, impaired motor coordination, and the formation of pathological reflexes (the result of focal brain lesions).
The main manifestations of ischemia in newborns at this stage of the disease are:
- convulsions and respiratory arrest (apnea);
- trembling and erratic movements;
- the skin becomes “marbled”;
- there are disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
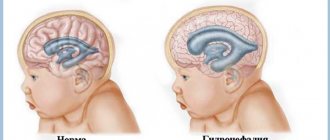
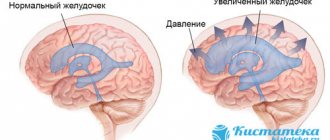
- hydrocephalic syndrome is expressed by rapid enlargement of the head and fontanelle, opening of the sagittal and other sutures of the skull on the head;
- manifestation of nystagmus, convergent strabismus;
- cardiac arrhythmia.
Grade 3 cerebral ischemia is characterized by extremely pronounced impairment of brain functions. There is a complete and permanent loss of ability to work, inability to self-care, and frequent fainting.
Symptoms of the third degree of cerebral ischemia in newborns are manifested by a coma (lack of consciousness and coordination), convulsive twitches and shudders.
The most dangerous outcome of this disease is the childhood form of cerebral palsy and falling illness (epilepsy). In principle, any ischemia (and cerebral ischemia in particular) is reversible. Timely treatment with restoration of blood circulation in the vessels will help restore tissues and organs to their original functions.
How to diagnose ischemia?
It is quite difficult to diagnose coronary artery disease, since the symptoms are very similar to some other cardiovascular diseases. This disease is identified based on observation of the patient, namely his complaints of poor health, as well as the results of a number of studies. It is not at all easy to identify signs of ischemia if the patient cannot determine the nature of his pain.
In the case when the patient comes without specific complaints of pain, ECG monitoring is performed, which can detect irregularities in the heartbeat rhythm. Coronary angiography is also performed, which can identify terosclerotic plaques that may be the cause of ischemia. The cause of concern about the presence of silent ischemia may be complaints of increased heartburn, increased shortness of breath, weakening of the left arm, changes in the number of heart beats per minute. An experienced specialist will immediately be interested in such signs that, at first glance, have nothing to do with the heart.
Symptoms and consequences of cerebral ischemia in children
Cerebral ischemia is a disease that develops due to a lack of oxygen in the brain, which is so necessary for its full functioning. This pathology can be either congenital or have an acquired, chronic form - the first is mostly diagnosed in newborns, while the second form is diagnosed in elderly patients.
Speaking about congenital cerebral ischemia in a newborn, the latter develops due to hypoxia during childbirth or during gestation. At the same time, the likelihood of developing oxygen starvation in a child develops and grows in proportion to the age of the woman in labor.
Thus, a young mother is less likely to develop cerebral ischemia in her fetus than those whose age has crossed the 30 -year mark.
Chronic cerebral ischemia
The chronic form mostly develops in older people - it is provoked by irreversible changes in brain tissue. Previously, we considered a similar issue about chronic cerebral ischemia.
This transformation of the pathology into its chronic course can be caused by diseases such as atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension , which affect the vessels of the brain, clogging them with blood clots and plaques and thereby cutting off the supply of oxygen to the brain.
Acute and chronic forms of the disease
Ischemic cerebral disease develops in two forms: acute and chronic. Severe hypoxia (the so-called oxygen starvation) causes acute ischemia. This degree of illness requires immediate treatment.
Otherwise, a transient ischemic attack occurs. Symptoms of this condition are paralysis of a part of the body, loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the body, blindness in one eye. They pass after a day or a little earlier.
The chronic form of the disease proceeds slowly, gradually, starting with some small and imperceptible moments. It all depends on the time of blockage of blood vessels. The faster this happens, the faster the disease develops. Most often, the cause of chronic ischemia is an acute form of the disease, for which timely treatment was not provided. The consequences of such a careless attitude to health have a sad result: in most cases, the result of the disease is ischemic stroke, which is the most common among all strokes (approximately 75%) and ranks next in mortality after cardiac ischemia. The second consequence of the chronic form of IBM may be an attack of myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
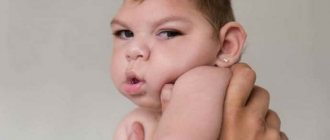
The fact that a child is developing cerebral ischemia can be clearly indicated by any deviation in its development, especially in the first week of life.
So, the following symptoms should be a reason for parents to visit a doctor:
- excessive, without apparent reason , nervous excitability of a child - this includes involuntary shuddering and trembling of the baby’s upper and lower extremities, lips and eyelids, restless sleep and crying for no particular reason;
- inhibition in the baby’s motor functions - for example, the child will have difficulty grasping and sucking the breast or pacifier, he has been diagnosed with swallowing problems;
- if the brain has a focal lesion , then the child may develop strabismus, and the symmetry of the face will be skewed;
- an increase in the size of the head, and especially the fontanel;
- convulsive clenching syndrome - in this case, the child will reflexively twitch his arms, legs and head, and some attacks may result in fainting;
Nutrition for IHD
Taking pills alone for cardiac ischemia, prescribed by a doctor, is not sufficient to obtain treatment results. It is also important to eat right to lower cholesterol and strengthen the heart. First of all, you need to limit your consumption of foods rich in saturated fats as much as possible. This is mainly food of animal origin - meat, eggs, milk, butter, sausages.
Cardiac ischemia is not a reason to completely abandon these products, but milk should be consumed exclusively low-fat, and meat should be lean, without fat. The best option in this case is turkey, veal, chicken and rabbit meat. All visible fat from meat must be removed when cooking. And when baking in the oven, place the meat on a wire rack to remove excess fat. When making scrambled eggs and omelettes, use no more than one egg per serving. To increase the volume of the dish, add only protein.
Fish, on the contrary, in case of cardiac ischemia, you should choose the fattest one, for example, mackerel. Fish oil contains many important components for cholesterol metabolism. And sea fish also contains a lot of iodine, which prevents the formation of sclerotic plaques. This component is also found in abundance in seaweed. The latter also dissolves blood clots, which are the cause of blood clots.
Unsaturated fats, on the contrary, are necessary for patients with cardiac ischemia. In the body they contribute to the production of the so-called. "good" cholesterol. These components are contained in vegetable oil, any oil - olive, sunflower, etc. Foods that contain a high content of dietary fiber reduce the amount of cholesterol. These are vegetables, bran bread, nuts, beans.
Berries are also very useful for cardiac ischemia, because they contain salicylic acid, which prevents the formation of blood clots. You need to eat bananas, peaches, dried apricots and other foods rich in potassium. You should avoid salty and too spicy foods, and do not drink a lot of liquid. It is better to eat in small portions up to five times a day. Limit yourself to vegetarian food a couple of times a week.
Degree of development of cerebral ischemia
In practice, doctors distinguish three stages of the disease:
- Cerebral ischemia degree 1:
- At this stage of the disease, its symptoms are very mild - usually the baby has headaches, the baby gets tired quickly and sleeps restlessly.
- At this stage, the child may have problems with vision and hearing - the baby reacts poorly to external sounds, the mother’s voice and light, and his mood may change sharply for no apparent reason.
- Cerebral ischemia grade 2:
- In this case, the pathology is characterized by more pronounced symptoms - such as weakness, dizziness and difficulties with the simplest movements.
- Problems with vision and hearing also arise in the child, seizures are more pronounced - the duration of the attack increases.
- At this stage, not only psychological difficulties are also noted, but emotional lability progresses.
- Cerebral ischemia grade 3
- At this stage there is organic damage to the brain - the child may often lose consciousness and the child cannot move his arms and legs and needs help with feeding and swallowing.
- At this stage, the child may develop so- called minor strokes or progress to a complete stroke - due to this, even dementia and the development of dementia in the child are possible.
- The quality of life sharply decreases - due to organic damage, there is a malfunction in the work of gnosis and praxis, which are responsible for normal orientation in space, the ability to recognize familiar objects and surroundings, and make complex motor movements of the body.
When to see a doctor
To increase the effectiveness of treatment of ischemia and not bring the disease to critical stages, you should consult a doctor immediately after the first symptoms of cardiac ischemia appear:
- At times you feel pain in the chest;
- Breathing can sometimes be difficult;
- You sometimes feel interruptions in the work of your heart;
- You find it difficult to endure even small physical activities like climbing stairs;
- You experience attacks of dizziness, shortness of breath, often feel tired, and sometimes faint;
- The heart sometimes seems to burst out of the chest for no apparent reason.
If the above symptoms occur in your case, then this is a serious reason to contact a cardiologist or therapist for comprehensive treatment.
Diagnosis of pathology
At the very beginning, to confirm or refute the diagnosis an external examination of the child is carried out, then the doctor will prescribe certain tests and hardware or instrumental examination.
So, external inspection:
- allows you to assess the general condition of blood vessels;
- the work of the heart and lungs can be heard;
- The level of the baby’s neurological condition is determined.
Duplex scanning of the head using ultrasound helps to assess the condition of the vascular system of the brain
Angiography also helps determine the general condition, the presence of narrowings and other pathological changes in the vessels - a contrast agent is injected into the child’s vascular system and then the entire blood flow system is scanned using X-rays.
In order to exclude other concomitant diseases and health disorders in the child, doctors prescribe an ECG , as well as blood sampling to conduct a general and biochemical blood test, as well as its composition for the presence of gases.
Symptoms of coronary artery disease
Only a doctor can determine the presence of any disease in a person. You should not diagnose yourself by referring to the words of a friend or neighbor, or to something you read somewhere. But there are symptoms that indicate that it is time to go to the doctor and get checked.
Symptoms of coronary artery disease consist of the following signs:
- Pressing sensation in the region of the heart.
- Burning, paroxysmal pain is felt in the chest.
- It’s hard to breathe, it seems like there’s not enough air.
- Weakness, nausea.
- Profuse sweating.
- Pain in the neck, left arm, between the shoulder blades, back.
- Changes in heart rate.
- Frequent nausea, shortness of breath, increased sweating.
Each of these symptoms should be the first signal that you need to see a cardiologist. Although the absence of signs is not a 100% guarantee of health. A third of patients with ischemia do not experience any of the symptoms. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a complete medical examination from time to time.
Treatment of cerebral ischemia in a newborn
Speaking about the treatment of the first degree of pathology, in this case the doctor prescribes both a course of medication and therapeutic massage - the main task at this stage is to restore normal blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain, thereby providing all the conditions for quick and effective recovery and recovery , normal brain function.
Regarding the treatment of 2nd and 3rd degree pathology - in this case, the doctor prescribes:
- A course of medications with vasodilating properties . They help improve blood flow and supply sufficient oxygen to the brain.
- Nooropic drugs are also prescribed - they effectively stimulate the child’s normal brain activity.
- As well as a course of taking avitamins - they help strengthen the baby’s body with diuretics.
Some experts note that when diagnosing the first degree of development of cerebral ischemia in a newborn, medications do not need to be used - the disease itself can be corrected with the help of a course of therapeutic massage.
And with the second and third degrees - definitely drug treatment , under the strict supervision of doctors.
If the case is critical and complex, the child is transferred under constant monitoring to the hospital, while prescribing a course of anticonvulsants , administering them using a dropper or intramuscular injections.
In the first stages of treatment, it is recommended that the child:
- relaxing and therapeutic massage;
- baths with soothing herbal mixtures;
- as well as limiting crowded and noisy places for a while, thereby limiting the baby from unnecessary stress and irritation of the nervous system.
The role of massage in the treatment of cerebral ischemia in newborns.
It is a professional, relaxing massage in the process of treating cerebral ischemia in the early stages that is an effective method that helps overcome the disease, speeding up recovery and enhancing the effect of medications. Thus, massage will allow you to relax the nervous system and relieve or significantly reduce an antispasmodic attack, having a beneficial effect on muscle function and the entire condition of the body.
So, during the first year it is recommended to conduct at least 4 sessions of therapeutic massage, with a break of 2-3 months .
Summarizing all of the above, we can definitely say that 90% of success in the treatment of cerebral ischemia in a child at the first stage of the pathology is ensured by massage.
And at stages 2 and 3 of the disease, it successfully complements drug treatment , since it promotes effective relaxation of a pinched and tense nervous system, improves muscle tone, increases blood flow and improves the general condition of the baby.
Treatment with folk remedies
ethnoscience
There are patients who prefer treatment with folk remedies. For this purpose, tinctures or decoctions of thyme herbs, sweet clover, borage flowers, and goat's rue seeds are used internally. Treatment is carried out in courses of 2-3 weeks. Many people believe that since folk remedies do not contain “chemicals,” they are safe to use. It's a delusion! All medicinal herbs have contraindications for use, as well as side effects in case of overdose.
Before starting treatment with folk remedies, in order not to harm your body, you must consult with your doctor.
Consequences and how dangerous the pathology is
When the diagnosis itself is made in a timely manner and treatment is prescribed, then, as the doctors themselves note, 5 of the patients have every chance of a successful, full recovery.
Other patients who have had this disease may experience in the future:
- frequent headaches and fatigue;
- poor memory;
- the likelihood of frequent attacks of convulsive spasms, especially at high body or environmental temperatures.
That is why children are not recommended to stay in the sun, live in hot climate zones, excessive stress, or great mental and physical stress.
If there is focal, atrophic damage to certain areas of the brain, the patient’s condition will be more serious.
The most common negative consequences of the pathology suffered are:
- frequent attacks of headaches and dizziness;
- sleep problems and increased excitability and irritability;
- the child’s inability to remember basic things and concentrate on one task, even the simplest action;
- frequent attacks of epilepsy;
- mental retardation;
- mental abnormalities
In the most advanced cases, a small patient may develop cerebral palsy of varying severity, ranging from partial dysfunction in the musculoskeletal system to complete immobility of the patient. We wrote in more detail about the causes of cerebral palsy in another article.
But the child grows, and his cells divide, and due to a correctly selected course of treatment, mild manifestations of the pathology disappear - the baby, as they say, outgrows his illness, and when the second and third degrees of pathology are diagnosed, the negative symptoms will weaken.
Severe consequences are determined not only by the diagnosis of one or another degree of development of cerebral ischemia, but also by the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Traditional methods of preventing coronary heart disease
To avoid the occurrence of cardiac ischemia in the future or slow down its development, following traditional folk recipes is extremely useful, along with traditional treatment.
Treatment of ischemia with rose hips and hawthorn
It is very useful to drink an infusion of hawthorn and rosehip in the treatment of cardiac ischemia. The fruits should be brewed like tea, steeped for 2 hours, and half a glass should be drunk 3-4 times a day.
Rose hips can also be used for baths. Pour 500 g of rose hips into 3 liters of boiling water and simmer the mixture over low heat for ten minutes. Then it is cooled and filtered, and added to the bath. Keep the water temperature at about 38 degrees; to get a good result, you will need to carry out at least 20 procedures.
Benefits of garlic
Cholesterol levels can be reduced by 15% by eating just three cloves of garlic per day. To prevent ischemia and treat atherosclerosis, you can prepare it as follows:
- Peel the medium-sized young garlic, crush it into a paste, put it in a jar;
- Pour a glass of sunflower oil over the garlic mass and place in the refrigerator;
- Every other day, squeeze about one tablespoon of lemon juice into a glass, add a teaspoon of prepared garlic oil and swallow the mixture.
Do this 3 times daily, half an hour before meals. After three months of the course, take a break, after which treatment of ischemia with garlic can be resumed.
Reviews about the disease cerebral ischemia
Anna. 36 years.
“Our baby was born prematurely, at 8 months, and was premature. He was cyanotic, and he was fed with a tube; he spent a month in intensive care on this method of feeding. Already on the third day, doctors diagnosed him with cerebral ischemia - we made a lot of efforts and they all gave a positive result.
Already at 3 months old, our Stas began to suckle on his own, at half a year he began to hesitate, but still hold his head, and he turned over on his own, took toys, but there was still no support on his legs. At the moment he is one year and 2 months old - he sits independently, moves with the help of a walker, but you know - he doesn’t walk, but seems to jump when moving.
All this time, we regularly treated the baby, attended massage , bathed him in a small bath and took medications such as Cortexin, Gliatilin, Encephabol, Cerebrolysin, Neuromidin . We quickly go to the clinic and register a disability due to developmental delay. But the issue of cerebral palsy is still a big question. This is what this pathology can lead to.”
Irina, 44 years old.
“Our son is now 2.4 years old, and doctors also diagnosed him with cerebral ischemia. The pathology began to manifest itself 10 days after birth - the most frightening things were the night cries and the fact that the child did not recognize anyone, increased excitability and anxiety, and refusal to breastfeed.
Then there were problems with the musculoskeletal system - the baby walked poorly, or rather, refused to stand on his feet and did not speak. Doctors prescribed Phenibut and Diacarb to Asparkam and they saved their child with them, and their last prescription was Cortexin - a drug that develops speech, but abroad, as I read from the Internet, it is not prescribed, since its effectiveness and how effective it is has not been proven. it is safe for the child.
We simply refused - now we practice therapeutic massage, swimming and educational games and see great progress in the treatment of pathology. And we’ll talk like that, without tablets and tablets.”
What is cerebral ischemia and how dangerous is it?
Article publication date: 08/07/2018
Article updated date: 02/28/2019
Author: Yulia Dmitrieva (Sych) – practicing cardiologist
Cerebral ischemia, or cerebral ischemia, is a pathological condition associated with oxygen starvation of nerve cells. It is a consequence of hypoxia - a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood below normal.
Its complication, in the form of severe ischemic encephalopathy, is the main cause of childhood disability and perinatal mortality.
Causes of the disease
Cerebral ischemia is not a diagnosis, but a syndrome that is part of various diseases. Absolutely anyone can suffer from this pathology: from a fetus in the womb and a baby to an elderly person.
Depending on age, the reasons for the development of pathology may be different.
In newborns this is:
- Chronic diseases of the mother, acute respiratory diseases during pregnancy.
- Alcoholism, smoking and drug addiction of the mother.
- Obstetric pathology: umbilical cord entanglement, weakness of labor, premature abruption of a normally located placenta, placenta previa, umbilical cord compression, premature birth, precipitate labor, post-term pregnancy, late gestosis.
- Mother's hyperthermia at the time of birth.
- Birth injury of the spine, especially the cervical spine.
- Postpartum pathology: sepsis, profuse bleeding.
- Developmental defects.
- Intrauterine pneumonia.
- Mother's age is under 20 and over 35 years.
In older children and adults:
- Congenital malformations.
- Chronic severe diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Neuroinfections.
- Chronic cardiovascular failure.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels and large arteries.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Anomalies of cerebral vessels (malformations, aneurysms).
- Systemic vasculitis.
- Amyloidosis.
- Blood diseases.
The pathogenesis of the development of cerebral ischemia in adults and newborns is similar, despite different causes.
The nerve cell does not have its own energy reserves, but receives them from the outside through the bloodstream. Any energy starvation (as a result of impaired blood flow or decreased saturation of blood with nutrients) leads to its degenerative damage, and in severe cases, to necrosis.
Degrees of development and their signs
The classification of ischemia is based on the severity of the syndrome of depression of cerebral functions. Infants have slightly different criteria than older children and adults.
This is due to the immaturity of the nervous system itself and the peculiarities of the neurological examination of newborns.
| Symptom | 1st degree | 2nd degree | 3rd degree |
| Onset of symptoms | First 7 days | First day | Immediately after birth |
| General state | Excitement, frequent crying, sometimes on the contrary drowsiness | Slow, frequent fainting | Profound cerebral depression |
| Muscle tone | Promoted | Weakened | Reduced or absent |
| Tendon reflexes | Promoted | Reduced | Reduced or absent |
| Newborn reflexes | Normal or slightly weakened | Reduced | Significantly reduced or absent |
| Breathing problems | Absent | Frequent episodes of sleep apnea | Frequent apneas, need for mechanical ventilation |
| Pathology of the cardiovascular system | Absent | Rhythm disturbance | Various rhythm disturbances, hypotension |
| Pathology of vision | Absent | Strabismus | Strabismus, nystagmus, uncoordinated eye movements |
| Convulsions | Absent | Possible clonic | Frequent, up to epistatus |
| Hydrocephalus | Absent | Possible transient | Progressive |
In adults and older children, total ischemia develops gradually, against the background of other diseases.
- Frequent headaches. In children, it may manifest itself as mood swings, constant crying;
- Insomnia;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Deterioration of memory, concentration, thinking;
- Initial coordination problems;
- Change in gait – becomes shuffling, mincing;
- Older people become intolerant of criticism;
- Character change;
- The appearance of pathological reflexes in the neonatal period is not in infancy.
- Unsteadiness of gait, poor coordination of movements;
- Weakness in the limbs;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Episodes of seizures are possible;
- Severe impairments of memory and attention;
- Emotional instability, apathy;
- Changes in personal qualities;
- Tearfulness is common;
- Patients gradually lose everyday and professional skills.
- Profound loss of coordination of movements;
- Spastic paresis and paralysis;
- Various disturbances of consciousness, up to coma;
- Significant difficulty, up to complete inability to navigate in space;
- Profound impairment of memory, thinking, even dementia;
- Difficulty speaking;
- Uncontrolled urination;
- Parkinson's syndrome.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods will also be different.
If the fetus has signs of hypoxia, then most likely there will be signs of cerebral ischemia in the infant.
Therefore, prenatal observation of the mother is aimed at early detection of the child’s hypoxic state and taking measures to correct it:
- Ultrasound of the fetus. The biophysical profile of the fetus and signs of intrauterine growth retardation are determined.
- Dopplerography. Blood flow in the placenta and umbilical vessels is examined. Signs of increased fetal vascular resistance are revealed.
- Cardiotocography. The change in fetal heart rate in response to uterine contractions is assessed.
Newborn
If there are signs of intrauterine hypoxia and/or asphyxia during childbirth, the presence of cerebral ischemia is not questioned.
But sometimes the clinical picture is not completely clear, or a more detailed examination is required to determine the degree of cerebral depression.
Then additional research methods are used:
- Neurosonography (NSG). The method is quite simple to implement and informative. Detects the presence of structural changes in the substance of the brain, as well as edema and swelling of the brain. It is NOT a leading method as it often produces false results, both positive and negative.
- Dopplerography of cerebral circulation. Detects various cerebral circulation disorders. For example, an increase in blood flow due to dilated arteries, a decrease in its speed in some branches.
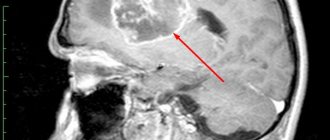
- CT, MRI. Detailed visualization of pathological changes.
- EEG. To determine the degree of neuronal damage, identify convulsive readiness of the brain, and select adequate anticonvulsant therapy.
- Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) according to indications.
- All laboratory tests: general clinical, biochemical blood parameters, coagulogram, blood electrolytes.
Older children and adults
First of all, complaints, medical history and neurological status are always assessed.
For accurate diagnosis, instrumental research methods are used:
- MRI or CT with angiography. Determination of the specific level of vessel occlusion, signs of other vascular disorders, as well as focal changes in the brain substance.
- Ultrasound Dopplerography (Doppler ultrasound) and duplex scanning of neck vessels. Based on their condition, one can indirectly judge the condition of the intracerebral vessels (the degree of damage by atherosclerotic plaques).
- Rheoencephalography. If it is not possible to perform more accurate studies.
- ECG, EchoCG. To identify cardiogenic causes of ischemia.
- EEG. Assessment of neuronal activity, seizure foci.
- General clinical and biochemical blood parameters.
- CSF analysis (to exclude neuroinfection).
Surgical intervention
Currently, the most common surgical treatment for coronary artery disease is coronary artery bypass grafting. The decision to carry it out is made when conservative methods do not bring results.
The essence of coronary artery bypass grafting is that bypass paths are created during the operation. Through them, blood will flow to the heart, bypassing the vessels, the lumen of which is narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques. The goal of treatment is to improve the patient's condition and reduce the number of exacerbations, the occurrence of which requires urgent hospitalization.
How does the treatment work?
It should be understood that it is impossible to completely restore damaged brain structures. Modern medicine can only stop the progression of pathology and help the brain partially compensate for impaired functions.
Treatment in the acute period is aimed at maintaining the vital functions of the body and depends on the stage of the disease:
- Ventilation In severe cases, independent breathing is impossible or significantly difficult.
- Treatment of seizures. They lead to an increase in the area of seizure activity in the brain, damaging previously untouched areas. Various anticonvulsants are used as therapy
- For severe spasms, muscle relaxants may be prescribed.
- Diuretics if there are signs of cerebral edema.
- Surgical treatment of hydrocephalus.
- Treatment of cardiovascular system disorders. Arrhythmias, pressure surges, low cardiac output aggravate the child's condition.
- Treatment of complications that develop in the acute period: pneumonia, bedsores.
Nootropics, neuroprotectors and drugs that improve cerebral circulation are used in combination and over long courses.
After stabilization of the condition, the next recovery period begins, which sometimes lasts a lifetime.
- Massage. For mild ischemia, the mother performs a relaxing massage on her own. In stages 2 and 3, massage is performed only by a specialist or under his supervision.
- Exercise therapy. An essential component of effective rehabilitation. Physical education is aimed at stimulating blood supply to the brain, developing paralytic limbs, and also at adapting the child to social life.
- Physiotherapy. The use of special devices, such as rollers, splints, to maintain spastic limbs in a physiological position.
- Classes with a speech therapist, various methods of psychological therapy and social adaptation.
For adults, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause:
- Neuroprotection. This may include taking statins, antiplatelet drugs, strict control of sugar and blood pressure.
- The use of surgical treatment methods (stenting, bypass surgery, thrombectomy, etc.), if it is possible to restore adequate blood supply to the brain.
- Special attention should be paid to psychological assistance for older people. Older people have a very hard time experiencing their own inadequacy and dependence on others. Therefore, it is important for relatives to pay attention to changes in the behavior and character of a loved one in time for timely diagnosis.
Fighting ischemia
The first stage of treatment for ischemia should be the organization of conditions for the patient so that the body can compensate for the damaged areas. That is, a new blood vessel must form to replace the old one. Moreover, its renewal must occur in such a way as to bypass the old vessels to the organ that has suffered from a lack of blood. The desired result is achieved using several methods:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- surgical intervention;
- use of medications.
If the patient is diagnosed with acute ischemia, then painkillers are urgently injected into his blood.
Ischemic disease is treated in several stages. Each of them is aimed at achieving a certain result, which as a whole will help overcome the disease. The following are steps to improve the condition:
- relieving vasospasm;
- expand arteries that have been damaged by atherosclerosis, strengthening their walls, and stopping the deposition of cholesterol plaques;
- removal of a blood clot that closes the lumen;
- blood viscosity decreases;
- conditions are created for the formation of a collateral network;
- carrying out procedures to protect the tissue of the damaged organ.
During treatment of ischemia, it is necessary to monitor that there are no surges in sugar, blood pressure, and that cholesterol in the body is not increased.
serdcezdorovo.ru
Possible complications
As a rule, cerebral ischemia in a newborn of grade 1 (mild) has no residual effects. It is characterized by functional disorders of the central nervous system. This degree is not always diagnosed and such symptoms go away on their own within a week.
Hypoxia is much more difficult for premature babies, in whom even a mild degree can lead to negative consequences in the form of persistent neurological disorders: mental and physical development delays and cerebral palsy develop.
Grade 2 (moderate severity) has vivid symptoms and is characterized by more significant damage to the nervous tissue. For the most part, the changes are irreversible. Without medical help, pathological changes in the brain increase. But with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, a favorable outcome is possible with minimal long-term consequences.
3rd degree (the most severe). Profound disorders of the central nervous system are not only irreversible, but also progressive. Hypoxia affects not only the brain, but also other organs. Multiple organ failure develops. The prognosis is unfavorable, more than half of children die. The surviving infant becomes disabled for the rest of his life.
In adults, cerebral ischemia has a progressive course, leading to the development of dementia and other psychosomatic disorders.