Medulloblastoma of the brain is a malignant neoplasm that originates from embryonic cells in the area of the posterior cranial fossa, where the midline of the cerebellum is located. Most often, this type of tumor is diagnosed in childhood; it is much less common in adults. Complex treatment involves surgical removal of medulloblastoma and administration of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
What's happened
Medulloblastoma has many names: neurospongioma, granuloblastoma, neurospongioblastoma, sarcomatous glioma, spheroblastoma, embryonal neurogliocytoma, isomorphic glioblastoma. All these terms mean the same disease – a cancerous tumor of the central nervous system.
The tumor is localized in the middle part of the cerebellum, on the so-called vermis. If the pathology begins to develop after 6 years, then the tumor forms under the tentorium of the cerebellum, rapidly affects the worm and grows throughout the entire cavity of the fourth ventricle of the brain.
A characteristic feature of the pathology is the rapid spread of metastases along the line of passage of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The rapid growth of the tumor impairs the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, resulting in increased pressure inside the skull and the formation of pronounced intracranial hypertension.
Carrying out histological analysis makes it possible to detect a large number of poorly differentiated, oval-shaped embryonic cells that have thin cytoplasm and a hyperchromic nucleus.
Classification
When prescribing treatment, the type and location of the tumor is taken into account. Several types of classifications are most often used.
Depending on location:
- A tumor in vermis (ventricular medulloblastoma) is found in 80% of cases.
- A tumor of both hemispheres is diagnosed in 20%, most common in children after 6 years of age.
According to histological structure:
- Classic medulloblastoma - consists of muscle tissue cells.
- Meduloblastoma with glial differentiation.
- Poorly differentiated - characterized by rapid growth and aggressiveness.
- Melanotic - consists of neuroepithelial cells, the structure of which is made of melanin.
- Desmoplastic - has a higher density, contains elements of connective tissue and a huge number of small vessels.
- Lipomatous - a structure of fat cells, has a favorable prognosis relative to other types.
- Anaplastic - characterized by the rapid spread of mutated cells.
Classification of metastases according to the Chang system
Metastasis and the extent of metastasis are determined according to Chang's classification:
- M0 - no metastases.
- M1 - abnormal cells are detected in small numbers in the spinal cord.
- M2 – tumor cells are found in the cerebellum, in the third and fourth ventricles of the brain.
- M3 - a cancer process with metastasis that affects the spinal cord.
- M4 – metastases are present in the extraneural area.
The doctor can talk about prognoses for the future, based on the type of tumor, size, stage of the lesion and prevalence.
Survival prognosis
Treatment for medulloblastoma largely depends on the stage at which the cancer was discovered. Patients are divided into two groups according to survival prognosis. The first includes patients at stage T1 or T2 M0. In this case, with total radical removal of the tumor, the success of treatment is assessed quite highly; 75% of patients will live 5 years or more. In the second group, patients with T3, T4, (grade 4/grade IV) and the presence of a metastatic process of different stages, with subtotal removal of the tumor, the survival prognosis will be moderate or poor. Only 35% of patients will live more than three years, subject to adequate comprehensive treatment.
The worst prognosis is for patients with relapses or if grade 4 medulloblastoma is diagnosed. In this case, most patients will not live more than one and a half years.
Causes
Scientists are still trying to figure out the etiology of meduloblastoma formation. However, to date only predisposing factors are known, the presence of which increases the risk of developing pathology, these include:
- Children's age from 5 to 10 years. In older people, the pathology is most often detected between 20 and 40 years of age.
- Male gender - judging by statistics, the male half of humanity suffers from the disease almost 3 times more often than the female half.
- The effects of radiation on the body, previous radiotherapy.
- Regular contact with carcinogenic substances.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- The presence of syndromes such as Turko, Gorlin, blue nevi, Rubinstein-Taybi.
The main danger of the disease is the rapid spread of metastases, which adversely affect the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to poor circulation. This often provokes the formation of complications that worsen an already unfavorable prognosis for the future.
Symptoms
The manifestation of the disease differs depending on the site of formation.
Localization of the tumor in the cerebellum:
- “Cerebellar gait” - when walking, the patient spreads his legs wider and swings his arms, which makes it possible to maintain balance.
- Unsteadiness when walking - the patient deviates from the straight route, now to the right, now to the left (drunk gait).
- Regular injuries - occur against the background of frequent falls of the patient, especially when turning.
- Deterioration of swallowing function.
- Uncontrolled movements of the eye pupils, and very fast (up to 300 movements per minute).
- Breathing disorders - occurs if the neoplasm has affected the brain stem.
- Deterioration of sensitivity in the legs and arms – with damage to the spinal cord. In more severe cases, paralysis occurs.
Damage to one hemisphere:
- Increased irritability.
- Cramps.
- Loss of orientation in the environment, in time.
- Excitement.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Severe headaches , especially in the morning.
In addition, the patient ceases to recognize loved ones and himself. From the very beginning of metastases, the patient's condition deteriorates significantly, which is a distinctive feature of medulloblastoma from other brain tumors.
Most often, primary lesions metastasize directly to the central nervous system. Less commonly, they can affect the lungs, liver, and bone structures; this happens in approximately 5% of cases.
Depending on the location of the metastatic lesion, additional symptoms occur. When the liver is affected, signs of jaundice and pain in the right hypochondrium appear. With secondary lesions in the lungs, pain appears in the chest area.
It should also be remembered that the course of the disease in adults is less aggressive than in children.
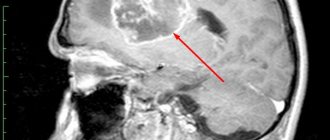
Pathological anatomy and localization of brain medulloblastoma
Morphologically, the tumor has the appearance of a nodular neoplasm of pink-gray color, isolated from healthy brain tissue. The histological structure of medulloblastoma is represented by dense undifferentiated cells that form regular or irregular rows resembling columns. Also, these tumors are characterized by the formation of rosette-shaped structures formed by pathogenic cells that have a ring-shaped arrangement. Moreover, their processes are localized in the center, forming a shape resembling a rosette.
Brain medulloblastoma cells are characterized by a high rate of division (mitotic activity). Cell nuclei are often dark, large and round, however, they can be oval or elongated, or large, containing little chromatin, with a clearly visible nucleolus.
The stroma of the neoplasm is penetrated by a small number of capillaries. Tumor growth is infiltrative, i.e. cells grow into adjacent brain tissue and its soft membranes. The formation of cysts or necrosis is not typical for this type of cancer.
Note. Medulloblastomas of the brain belong to a rare type of malignant neoplasms of the central nervous system, which are characterized by a metastatic process.
Metastatic cells separated from the tumor spread mainly through the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid into the tissues of the brain and spinal cord, as well as their membranes. Secondary lesions resemble small whitish nodules that grow. In rare cases, the metastatic process spreads beyond the central nervous system.
Localization of medulloblastoma: most often, the primary tumor forms in the midline of the cerebellum. This is the area at the bottom of the back of the brain, which is called the posterior cranial fossa. This location gives rise to characteristic clinical signs because the cerebellum is responsible for coordination, balance and movement.
Diagnostics
To clarify the disease, a number of diagnostic measures are required. First of all, the neurologist prescribes general urine and blood tests, as well as a biochemical blood test. The presence of pathological cells will affect the performance.
Tumor markers are determined in the blood; if a concentration disturbance is observed, the presence of a cancerous tumor can be suspected.
There is a need to perform a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid, but such a study gives accurate results. In 50% of cases with metastasis to the spinal cord, a negative result is obtained.
On this topic
- Neuro-oncology
How does a headache hurt with brain cancer?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 3, 2020
More accurate methods include neurosonography, but it is used only when diagnosing the disease in young children whose fontanel has not yet closed.
To identify pathology in adults, computed tomography is performed, which makes it possible to determine the location and size of the tumor.
To determine structural abnormalities of the brain and other tissues inside the skull, magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
The presence of metastases and their extent are detected using positron emission tomography.
Treatment
A puncture of cerebrospinal fluid is not always taken, since it is a surgical procedure. Any kind of brain surgery causes postoperative swelling, which significantly increases the risk of infection.
There are several types of surgical intervention, which are prescribed depending on the growth of the tumor process.
Stereotactic biopsy
This procedure is considered appropriate if removal of the tumor node is prohibited for some reason. Biomaterial is collected from at least 2 areas of the brain.
This method is very dangerous and is prescribed mainly to adult patients, since vital centers are located in the fourth ventricle and cerebellum.
Open biopsy
This procedure involves craniotomy. The result is a decrease in hydrocephalic syndrome.
Often, together with an open biopsy, shunts are installed, and additional actions are taken to improve the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Such actions are necessary in order to gain a certain period of time for radical surgery in the future.
Surgical therapy
Surgical removal of a tumor node can be complete or partial. Such treatment is carried out to reduce the size of the tumor, reduce the size of the tumor, and eliminate the consequences of neurological abnormalities.
Also during the procedure, biomaterial is collected for histological examination.
Radiotherapy
Radiosurgery and radiotherapy may be used. Irradiation is aimed at the site of removal of the formation 0.5-1.5 months after the operation. It is prescribed more often for adults; it is completely contraindicated for children under 3 years of age.
Chemotherapy
Treatment continues and combinations of Etoposide, Cyclophosphamide, and platinum derivatives are used.
Today, genetic biological drugs with antitumor effects based on cytomegalovirus and measles viruses are being developed. However, the results obtained are still contradictory.
Drug therapy
To reduce swelling, patients are prescribed diuretics and corticosteroids. The doctor determines the dose individually depending on the manifestation of symptoms, the degree of psychomotor impairment, the size of the tumor and the age of the patient.
If seizures are observed, anticonvulsant medications are prescribed. To eliminate pain, it is necessary to use analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe pain, drugs from the Carbamazipine group and its analogues, for example, Katodolon (Flupirtine), are used.
Fighting the tumor
Treatment of medulloblastoma is not such a difficult process in our 21st century. If no contraindications have been identified, then such a tumor is completely removed, preferably in its early stages. It is removed using microsurgery methods. During the operation, microsurgical techniques and intraoperative MRI navigation are used.
The later the tumor is discovered, the greater the consequences of surgery.
Depending on the development of the tumor, its growth and complications, the patient undergoes a set of measures:
- After successful surgery on the tumor and clean, metastatic-free organs, low-dose radiotherapy is prescribed. In cases where the tumor was not cut out at the root, part of it remained, and even with remnants of overgrown tissue, therapy is used in large doses;
- If the medulloblastoma has grown greatly, then its size is reduced by radiation therapy until it is operable;
- After surgery and radiation therapy, it is possible to resort to chemotherapy.