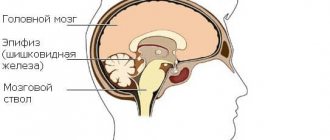
A brain lipoma is a neoplasm of adipose tissue. In the brain, proliferation is rare: 0.1-0.5% of all intracranial tumors. Lipoma is a benign neoplasm that has no tendency to transform into a malignant course.
In the brain, tumors occur where there are deposits of fatty tissue. The neoplasm is located in the sagittal sulcus, in the falx (a section of the dura mater that is embedded in the interhemispheric fissure), around the cerebellum, thalamus, next to the pituitary gland and around the corpus callosum.
Less commonly, a lipoma is located next to the third ventricle of the brain and near the frontal cortex. Despite the destructive localization, due to the slow growth and non-aggressiveness of the tumor, the clinical picture is poor and rarely causes exacerbations.
Due to its secretive course, patients rarely seek help from a doctor. The tumor is diagnosed accidentally: during routine or preventive examinations.
Etiology of the disease
It is almost impossible to establish the exact causes of cancer. Lipoma is no exception. The sources of its occurrence include general factors, namely:
- Hereditary predisposition. Therefore, people whose family has previously been diagnosed with a tumor need to pay special attention to their health;
- Radiation. Of course, this does not include minimal emissions from household appliances or medical equipment. But accidents at factories, which cause increased levels of radiation, may well contribute to the development of oncology;
- The effect of hazardous substances on the body. These could be: chemicals, toxic substances, heavy metal fumes, pesticides. For this reason, it is important for people in direct contact to use all appropriate equipment;
- Suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- Inflammatory processes in the brain area;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Demodecosis. This is a skin disease caused by a parasite called demodex mite;
- Abuse of bad habits;
- Violation of the fat metabolic process;
- Poor quality food;
- Regular non-compliance with work and rest schedules;
- Stress and nervous breakdowns;
- HIV.
Bad habits can be the cause of brain lipoma.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that the presence of absolutely any cancer in relatives increases the risk of brain lipoma.
What causes the occurrence
Lead to the appearance of a wen on the head:
- metabolic disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal disbalance;
- chronic diseases;
- influence of allergens;
- diabetes;
- abuse of immunosuppressants;
- pathologies of the liver, kidneys;
- exhaustion due to severe illness;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- genetic predisposition (60%) – familial lipomatosis;
- the appearance of excess weight;
- expression of the “obesity gene,” or HMG IC;
- failure of innervation of individual zones;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vascular malformations;
- vegetative-vascular disorders;
- blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- lack of vitamins;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Since the list of factors is very large, in each specific case the cause is identified individually. Lipomas on the head can be either multiple or single.
Classification of types of pathology
It is customary to classify a lipoma according to its location in the brain. This factor directly determines which symptoms manifest themselves most clearly.
Interhemispheric lipoma
This type of neoplasm can be characterized by almost any signs. For example:
- Twitching of the upper and lower extremities;
- The appearance of hallucinations;
- Severe headaches;
- Nausea and vomiting.
Lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure
If the tumor is located here, then the patient is likely to experience the following unpleasant phenomena:
- Problems concentrating;
- Deterioration of vision. This is reflected in the fact that the patient is increasingly lost in space;
- Headache.
The last factor in case of lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure of the brain becomes especially pronounced with any attempt at mental stress. The pain becomes especially severe.
Lipoma of the corpus callosum
A feature of lipoma of the corpus callosum is involuntary movements of the limbs. This phenomenon is unusually called “alien hand syndrome.”
Lipoma of the falx cerebri
This type can also be found under the name “falx lipoma”. It is usually accompanied by:
- Sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- Headaches, mainly in the frontal lobe of the head. Their character is most often oppressive;
- Twitching and nervous tics characteristic of the left arm and leg.
Clinical manifestations
Lipoma in the initial stages, and also if it does not grow, is not accompanied by any symptoms. It can only be discovered by chance during this period. But this state does not always persist. If the tumor begins to grow in size, it becomes large enough to put pressure on nearby tissues and receptors. The patient begins to notice the first suspicious signs of the disease. They include:
- Constant feeling of weakness, rapid fatigue;
- Dizziness;
- Periodic headaches. This should especially alert those people who have practically never encountered them before;
- Blood pressure surges. As a rule, they are expressed in hypertension;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Increased sweating;
- Tremor of limbs, nervous tics;
- Decreased concentration and overall intellectual abilities;
- Deterioration of vision. This can happen quite abruptly;
- Sleep disorders;
- Loss of appetite;
- Irritability or apathy.

Undoubtedly, the larger the lipoma grows, the more strongly it affects areas of the brain. All this affects the severity of clinical signs. Accordingly, the sooner treatment is started at the first symptoms, the lower the risk of serious consequences.
What is and symptoms of brain formation
The lipoma is located in different parts of the brain: the corpus callosum, in the interhemispheric fissure and compresses anatomical formations. A small tumor in the primary stage is not detected by symptoms and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
After the first signs appear, urgent examination is necessary; if the tumor grows, there is a risk of complications. Acquired lipomas are formed as a result of impaired functioning of the body, severe stress or brain injury.
According to the ICD, the international classification of diseases, disease code C00-D48.
The rarity and asymptomatic nature of the disease make it difficult to study tumor growth and surgical practice in removing tumors from adipose tissue in the central nervous system.
As the tumor grows, symptoms increase. The lipoma begins to put pressure on nearby parts of the brain. Innervation and blood circulation are disrupted.
General complaints of patients:
- frequent and sudden migraines. Frequent headaches, most often occurring during physical activity. Can take place at rest and in a horizontal position of the body;
- dizziness, darkening of the eyes, loss of consciousness;
- frequent feeling of nausea and vomiting.
In addition to the main symptoms, specific ones arise that help differentiate the tumor and indicate its location. Single or multiple wen can form in the brain. Together they influence the functioning of the central nervous system. Diagnostics is necessary to accurately determine the diagnosis and size of the tumor.
Diagnostic methods
If a patient goes to a medical facility with the previously mentioned symptoms, the doctor will first of all:
- Performs physical examination;
- Collects anamnesis: is there a family history of cancer, what are the signs of the disease;
- Interested in the patient's immediate sensations.
In order to confirm or refute the diagnosis, the patient will have to undergo examination procedures such as:
- X-ray of the skull. Not always prescribed. This is the most accessible, but at the same time not the most informative diagnostic method;
- Neurosonography. This is an ultrasound examination of the brain. It is able to accurately determine the location of the tumor, as well as its size and approximate structure.
The most informative methods are:
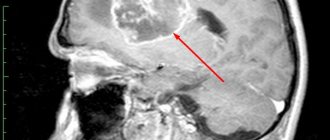
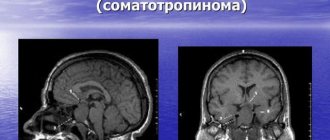
- CT scan. This study allows us to determine the exact size of the brain lipoma, its location, shape, as well as the condition of the vessels directly connected to it;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This is a more advanced version of tomography, which is additionally capable of assessing the condition of tissues located next to the tumor.
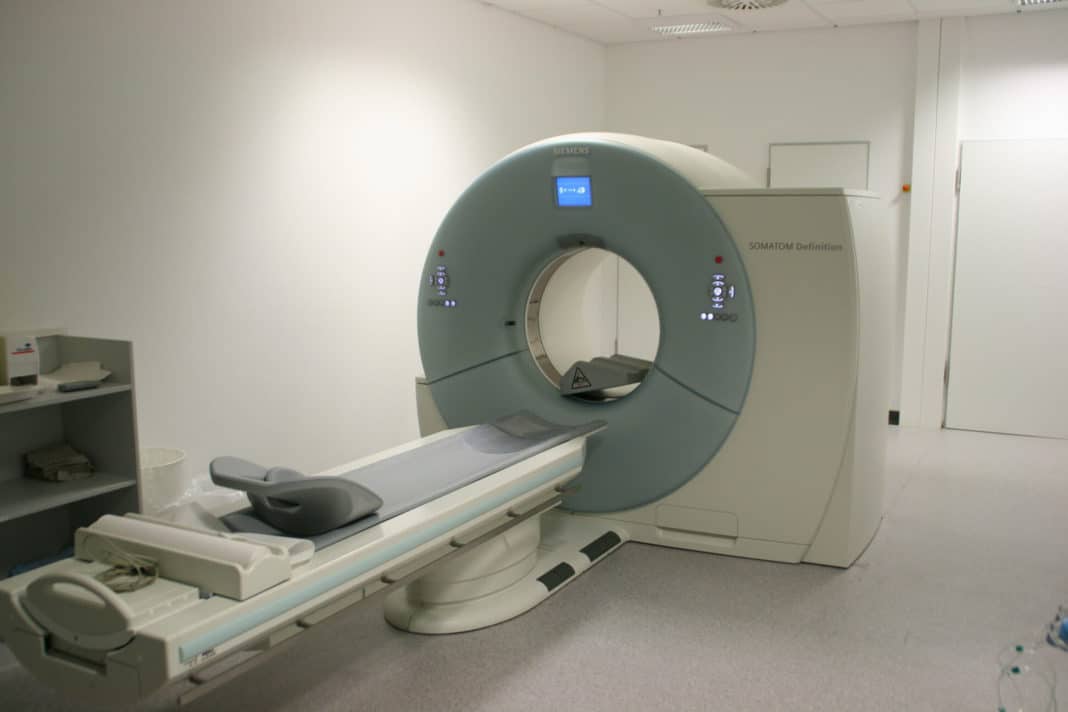
The last two examination procedures are more expensive. Equipment for them is not found in every medical institution.
Differential diagnosis
Since lipoma does not produce symptoms for a long time, it is often diagnosed accidentally, during preventive and periodic examinations or during research for other pathologies.
If the clinical picture has already formed, then pay attention to the following complaints of the subject: nausea, increasing pain, insomnia. During a neurological examination, the doctor assesses the state of the patient’s reflexes, skin and deep sensitivity, muscle strength, checks whether there are disorders of the sphere of consciousness, and inquires about the facts of epileptic seizures.
Instrumental studies remain the main ones in identifying a tumor.
X-ray examination
On an x-ray, this tumor appears as a cleared area with a smooth contour.
But the internal structure of the formation cannot be determined from an x-ray. Therefore, they turn to neuroimaging methods.
Neuroimaging
The following methods are used:
- Ultrasound . The location, size, and structure of the lipoma are visualized. The tumor is visible as a hypoechoic (lighter compared to the surrounding tissues) formation of a regular shape, without swelling around.
- CT differentiates lipoma from other neoplasms. In the photographs, the tumor appears as a non-enhancing homogeneous structure with reduced density (down to –100 units N).
- MRI accurately identifies tumors because the resonance from lipomas is the same as from fat. On T1 and T2 images, the tumor gives a pronounced signal; complete disappearance of resonance occurs on fat-suppressed MRI.
Treatment options
If a patient has been diagnosed with a brain lipoma, doctors resort to one of two main tactics: watchful waiting or surgery.
Waiting tactics
It is appropriate if the tumor is small in size, has no tendency to grow, and the patient’s general condition is good. As a rule, congenital lipomas are characterized by such properties. The patient must be monitored by an oncologist, who periodically conducts examinations and monitors his condition.
Radical tactics
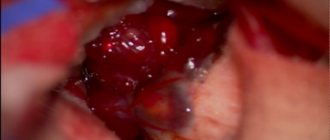
It involves surgical resection of the tumor. This is a serious operation that requires highly qualified surgeons. There are three main methods for doing this:
- Trepanation of the skull. This is the riskiest option, since the patient's skull is opened. Accordingly, there is a possibility of bleeding and infection. But it is most convenient for the surgeon to remove the tumor, since he has a good view;
- Endoscopic surgery. This is a more gentle option, since the patient’s skull is not opened, but special instruments and a microscopic camera are inserted through small holes, allowing the surgeon’s actions to be monitored. This operation has virtually no risk of bleeding and infection. And in general, the patient recovers faster. But not all lipomas can be removed in this way, especially if they are in a hard-to-reach place;
- Puncture-aspiration method. This is the most minimally invasive option and removes the tumor through a very thin tube. It is worth considering that the lipoma capsule remains in the body. This may affect the possibility of its recurrence.
Regardless of which method is chosen, each of them has its own risks and characteristics. Therefore, if the lipoma does not cause concern for the patient’s health, it will not be removed.
Traditional methods
It is necessary to immediately stipulate that self-medication when diagnosed with “brain lipoma” is strictly prohibited. All non-traditional folk methods of treatment are also prohibited.
On the Internet you can actually find many different recipes based on herbs and roots, but they are usually aimed at lipomas located in the subcutaneous space. In the case of tumors localized in the brain, these recipes will be powerless and meaningless.
Conclusion
Any phenomena in the form of lumps and lumps in the head area cause extremely unpleasant feelings. The question of how to get rid of a wen on the head cannot be resolved without turning to doctors, as this poses a great danger. Opening or other mechanical impact on the emerging tubercle without maintaining sterility can lead to complications and blood poisoning.
In addition, fatty growths often turn out to be carbuncles or boils, which are treated not by a surgeon, but by a trichologist or dermatologist. Patients choose what methods will be used to remove wen on the head, but only after a visit to the doctor.
Source
Forecast
If we talk about brain tumors in general, lipoma has a more favorable prognosis than others. In some cases, it does not have any negative effect on the body at all. If the tumor tends to grow, then there is a risk of various complications, including life-threatening ones. But this is only if the patient does not take measures to treat it. After complete removal of the lipoma, the patient can expect to return to a full life.
Consequences
Despite the fact that the wen has a benign course, when located in the brain, this pathology is very dangerous.
If timely treatment is not carried out, the following serious consequences are possible:
- mental disorders;
- cerebral edema;
- stroke;
- circulatory disorders;
- decreased vision and hearing impairment;
- development of pituitary adenoma.
More often than not, doctors are able to provide treatment before any complications arise. However, the risk of serious consequences still remains.
Prevention measures
Lipoma, like many other types of cancer, cannot be completely prevented. The best thing a person can do to reduce their risk is to follow general rules for improving their health. These include:
- Healthy lifestyle;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Sufficient activity. This does not mean that it is necessary to engage in professional sports. You can simply take daily walks in the fresh air, visit the pool, limit passive viewing of TV and gadgets;
- Compliance with the principles of proper nutrition;
- Avoidance of stressful situations;
- Maintaining a rational balance between work and rest;
- Using all necessary protective measures when in contact with radiation and hazardous substances;
- Timely treatment of diseases. It is very important not to start inflammatory processes and try to prevent them from becoming chronic.

One of the most important preventive measures is regular preventive medical examination. After all, this is how a tumor can be detected at an early stage.