Headache in the parietal part of the head, the causes of which will be discussed below, rarely occurs as a minor event.
It can be sudden, chronic, recurrent, but it always signals a malfunction in the body.
The type of pain requires a combination of drug therapy with non-drug treatment.
Loading …
Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
↑
Why might the top of your head hurt?
The parietal part of the head can hurt due to many reasons. Sometimes this symptom is present as an independent phenomenon or is accompanied by a number of other signs. Even if there are no other symptoms besides headache, you should not ignore this condition; still seek medical help. Information will be provided by the nature of the pain, its duration, etc.
Does the top of your head hurt? Causes:
- An acute condition when attacks of pain occur suddenly and are not regular. They occur due to injuries, infections, or stress; this condition causes a stroke or rupture of an aneurysm.
- The chronic condition is characterized by regular headaches, which sometimes do not go away even after taking medication. This happens due to a tumor in the brain, constant stress, frequent lack of sleep or due to osteochondrosis.
- If pain occurs in periods, for example once every few days or weeks, and is easily relieved with analgesics, then this may indicate VSD, blood pressure disorders, neuralgia, or female menopause.
- Relapsing syndrome. It manifests itself in hypertension, cluster pain, VSD or a tumor process.
An experienced doctor will be able to guess the cause of vertex pain based on clinical manifestations, but additional research will be needed to clarify the diagnosis.
Headache in the parietal part of the head: causes and treatment
Headache in the parietal part of the head, the causes of which will be discussed below, rarely occurs as a minor event.
It can be sudden, chronic, recurrent, but it always signals a malfunction in the body.
The type of pain requires a combination of drug therapy with non-drug treatment.
Loading …
Use search
Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease. ↑
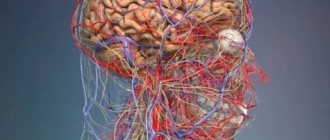
The parietal lobe of the brain is abundantly supplied with blood and innervated. It is closely related to skeletal muscles, pain and sensory receptors.
The causes of pain can be of various origins and are accompanied by specific symptoms:
- Vascular dystonia caused by changes in blood pressure. Cephalgia increases gradually. Feels like a pressing hoop. It has a descending nature, covers the parietal, frontal, and occipital regions of the head. Often there is a flashing of black dots before the eyes, a feeling of stuffiness in the ears.
- The cranial cavity contains a viscous fluid - cerebrospinal fluid, which maintains optimal intracranial pressure. Its amount is small and stable, but if this balance is disturbed, intracranial hypertension develops. Increased ICP is described as pressure at the top of the head that increases with changes in position and exercise. Cephalgia can be mild, but long-lasting and painful, accompanied by dizziness, blurred vision, and periodic nausea.
- Osteochondrosis of the upper cervical spine, spondylosis, intervertebral hernia are the most common causes of pain in the crown area. The sensations spread along the back of the neck, the back of the head, and are concentrated at the top of the head. The attacks are intense, pulsating, radiating to the lower jaw, neck, and shoulders. Caused by compression of the nerve roots and impaired blood flow.
- The consequences of a traumatic brain injury can take months to reverberate and develop into chronic cephalalgia. Exacerbation occurs after viral infections, emotional overload, and when playing sports. The pain is dull, aching, accompanied by attacks of nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, and pressure instability.
- Neoplasms of the parietal region, tumors and cysts, growing, compress the brain tissue. The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, from pressing to unbearable. Possible temporary impairment of vision, speech, fainting, signs of epilepsy. This pathology is a direct threat to human life and requires immediate diagnosis.
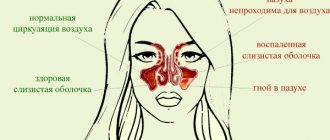
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the meninges are recognized by high fever, spastic state of the neck muscles, severe headache in the crown area. Secondary symptoms will be signs of general intoxication.
- Muscle tension in the back of the head and shoulder girdle is caused by prolonged exposure to a static position or occurs due to inflammation of the muscle itself - myositis. In the first case, headaches are aching in nature with a feeling of twisting, and the inability to relax the muscles. With myositis, acute local cephalgia occurs along the course of inflammation with limitation of movement.
↑ https://gidpain.ru/bolit/golovnaya-temennoj-chasti.html
Treatment of pain in the parietal part of the head
It is important to understand that self-administration of medications will help relieve symptoms, but will not eliminate the culprit of cephalalgia. They fight unpleasant sensations in the head by combining medications and non-drug therapy.
Depending on the reason, the following is prescribed:
- If blood pressure changes: antihypertensives or analeptics, moderate activity, adequate sleep, changes in diet.
- To combat increased ICP: nootropics, cerebral circulation correctors, diuretics, avoidance of bending work, overstrain of the optic nerve.
- In case of osteochondrosis, headaches are eliminated by manual therapy, massage, gymnastics, and taking antispasmodics and analgesics.
- Antibacterial and antiviral agents are prescribed to treat infections.
- If the top of your head aches due to muscle spasms: antispasmodics, sedatives, local analgesics, acupressure, walks in the fresh air.
- Neoplasms require specific treatment, often surgery.
It is important to remember that the parietal region does not hurt without a serious reason. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the more timely and effective the treatment will be.
↑
Often, after physical exertion or mental stress, people feel worse. The nature of the pain can be varied. Compressive, pressing, throbbing pain in one side of the head is possible.
Pain during exercise is often functional in nature. They can occur for many reasons:
- Changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure;
- Stressful state during physical activity;
- Heat and stuffiness in the room;
- Dehydration is often the cause of headaches;
- Eat a large meal before training;
- Overweight people often suffer from hypoxia during exercise.
The likelihood of illness is higher in people with specialties: programmer, accountant, driver, who spend many hours at the computer or constantly strain the muscles of the eyes and neck.
The initial appointment should be made by a therapist. He will conduct a general examination, measure blood pressure, write out directions for tests and refer you to specialists.
If you have unpleasant sensations in the head and neck area, it is good to have a home blood pressure monitor, with which you can track pressure surges in different life situations. A rise in blood pressure after physical activity can often be the cause of pain.
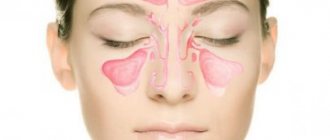
The doctor gives a referral to an otolaryngologist to rule out chronic otitis media, sinusitis or inflammation of the maxillary sinuses (sinusitis).
The doctor can give a referral to an ophthalmologist to identify changes in the fundus and possible vision defects.
Most of the causes of discomfort in the head are associated with neurological symptoms, so diseases accompanied by head pain syndrome are treated by a neurologist.
↑
What tests are usually prescribed?
At an appointment with a neurologist, a physical examination of the patient is performed: basic neurological reflexes are checked and the neck muscles are examined.
The doctor writes out a referral for tests: general blood test, biochemical blood test, blood sugar test.
A general blood test with an increase in ESR or an increased content of leukocytes indicates inflammation in the body.
Low blood glucose levels are often accompanied by cephalgia, dizziness and weakness.
The doctor may write a referral for additional tests:
- The gas composition of arterial blood can reveal cerebral hypoxia.
- A blood test for hormones determines various abnormalities in the functioning of the hypothalamus.
A neurologist can give a referral to one or more diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - excludes the presence of various neoplasms (tumors and cysts), aneurysms. The photographs clearly show post-traumatic defects, neurodegenerative abnormalities, and changes in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) is the most informative method for studying the brain. It gives a clear idea of pathological changes in the skull and brain, pathology of bone tissue, blood vessels and brain structures. Provides information about the consequences of traumatic brain injuries. The disadvantage of this method is the significant radiation dose during the study.
- Electroencephalography gives an idea of the presence of pathological changes in blood vessels and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Doppler ultrasound (ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck) - shows the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries; narrowing and tortuosity of the arteries, leading to brain hypoxia; peripheral vascular resistance.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - gives an idea of the tone and blood flow of blood vessels. Using REG, the following are diagnosed: hypertension, atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- MRI of the cervical spine - the presence of cervical osteochondrosis can cause pain in the head and neck, which intensifies when turning the head.
- Rheovasography of cerebral vessels (RVG) - shows the quality of blood flow through the great vessels, evaluates collateral circulation.
- Radiography will be less known. In the image you can only see the bone structures of the skull, soft tissues are not visible.
There is no need to panic when scheduling such a serious examination. The doctor excludes rare severe pathologies and looks for the causes of the pain process.
Based on the studies, if no serious organic lesions are found, the cause of the disease is usually diagnosed. It develops as a result of: vascular spasms, cerebral hypoxia, hypertonicity of cerebral vessels, hormonal imbalances, vegetative-vascular dystonia or osteochondrosis, provoked by physical or psycho-emotional stress.
↑
Safe medications and pills
When planning a visit to the doctor, the patient should be prepared to answer questions about how often pain occurs and what its intensity is. This will help the doctor develop the correct treatment tactics.
↑
Groups of drugs effective for episodic attacks of pain
Medicines to treat this pathology are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have an analgesic effect, relieve inflammation, and eliminate swelling.
Often prescribed:
- Ibuprofen-400 mg per day;
- Ketoprofen-100 mg/s;
- Naproxen-500 mg/s;
- Meloxicam-7.5-15 mg/s;
- Celecoxib-200 mg/s.
Most NSAIDs have a negative side effect: with long-term use, they negatively affect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, including the development of drug-induced gastritis.
Medicines Meloxicam and Celecoxib are new generation drugs that do not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The disadvantages of using these drugs include the relatively high price.
Analgesics are often used at home to relieve an attack. They do not treat the disease, but only relieve pain. Drugs in this group are suitable for stopping episodic attacks, but their systematic use leads to the occurrence of abuse syndrome.
During an attack of pain, you can take Paracetamol-100 mg, Citramon, Analgin-500 mg or Mig 200-400 mg.
If the examination revealed the appearance of cephalgia after exercise as a result of increased blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe medications prescribed at an early stage of the development of hypertension. These include: vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel blockers.
Self-prescribing antihypertensive drugs is unacceptable. Self-medication leads to serious consequences.
For muscle tension, drugs from the group of muscle relaxants are used as part of complex treatment. They relax the spasmodic muscles of the head and neck, relieving pain of a spastic nature, and help restore blood flow.
Often prescribed:
- Mydocalm-150-450 mg per day;
- Sirdalud (Tizanidine) - 4 mg/s;
- Baclofen-15 mg/s.
Nootropic drugs are often prescribed as part of complex treatment: Phenibut, Nootropil, Glycine. Nootropics have an activating effect on brain function and increase its resistance to damaging factors. The drugs improve cerebral circulation and eliminate the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
Sedatives in combination with basic drugs lead to muscle relaxation and decreased vascular tone. Taking tranquilizers helps relieve pain, but this type of medication quickly causes drug dependence with withdrawal symptoms.
Sedatives that are not addictive: Afobazol, Atarax; alcohol tinctures of valerian, motherwort, Maryina root.
For severe attacks, a combination of drugs is used: Sirdalud 2 mg + Aspirin 500 mg or Analgin 250 mg + sedative.
The use of vitamin B complexes has proven itself. Vitamins B1, B6, B12 have a beneficial effect on the central nervous system and restore the structure of nerve tissue. Vitamin complexes are often prescribed: Neuromultivit, Milgamma, Neurovitan.
If attacks of pain recur more than 10 times a month, a course of treatment with Ibuprofen at a dose of 400 mg per day for 2-3 weeks and treatment with muscle relaxants is prescribed for 2-4 weeks.
There is no single scheme for pain relief. Depending on the cause, each patient needs an individual selection of drugs.
↑
Treatment of chronic disease
Sometimes cephalalgia becomes chronic. The pain occurs every day, continuously, with varying degrees of intensity.
Amitriptyline 10-100 mg/s is most often prescribed, the dose is increased gradually. The drug relieves pain well, but has many negative side effects and is addictive.
As an alternative, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are prescribed: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline. The course of treatment is at least 2 months. These drugs have less toxicity.
In addition to prescribing drug therapy, the doctor will recommend massage, a course of physiotherapy or acupuncture.
Source: https://GidPain.ru/bolit/golovnaya-temennoj-chasti.html
Traumatic brain injuries
Post-traumatic pain in the head can bother a person for the next two months. This condition may be associated with a concussion. The pain in this case is dull and pulling. Sometimes it pulsates.
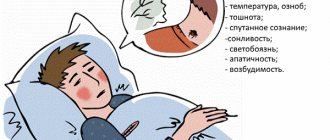
Additional symptoms of cephalalgia are:
- nausea and weak appetite;
- unstable blood pressure;
- weakness and craving for sleep;
- change of mood.
Ways to get rid of pain:
- bed rest and examination by a doctor;
- analgesics and nootropics;
- sedatives.
What to do if the upper part of your head hurts
Help and elimination of unpleasant symptoms in the head includes the use of drug therapy in combination with non-drug methods. Treatment of conditions depends on the causes that caused them.
| States | Medications |
| Tension cephalalgia |
|
| Vascular pathology | Depends on the diagnosis:
|
| Osteochondrosis |
|
| Migraine-like symptoms |
|
| Increased ICP |
|
When the top of your head hurts, you need to adjust your work-rest schedule, get into the habit of daily exercise and, of course, consult a doctor. Only a specialist can prescribe appropriate and timely therapy.
Migraine
This disease can be divided into different types:
- Vasomator migraine - pain occurs in the parietal region or on one side, for example, the left upper part of the head hurts. The cause is vascular changes in the brain.
- Neuralgic migraine - pain in the temples and upper part of the head. Causes include weather changes, stress, overexertion and lack of sleep. Sometimes a person complains of nausea, decreased vision and poor coordination of movements.
- Migraine with aura is accompanied by a number of symptoms, which is why this condition is called a syndrome. A person experiences dry mouth, loss of appetite, nausea, dizziness, decreased vision, etc.
Causes
Symptoms can appear for several reasons. Among them:
- Severe muscle strain and fatigue.
- Stress.
- Migraine.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Cluster pain.
It is worth considering each point in more detail to understand the characteristics of pain.
Overexertion and muscle fatigue
If you stay in an uncomfortable position for a long time, pain may occur in the parietal region of the head. Pain often occurs in people sitting at a computer screen, a machine, or during agricultural work, when they have to stand in an uncomfortable position for a long time. The muscles tense, causing pain. The parietal area often hurts due to improper daily routine, nutrition, and severe overload, both mental and physical.
Headaches often occur not only in men, but also in women. And this is not just an excuse, but a consequence of a constant repetitive lifestyle and significant overexertion.
Stress
The muscles in the head become very tense due to negative emotions, so a person may experience severe pain. It can give in the shoulders and neck. Pain of this kind cannot be called severe; it is stable, moderate, and does not change, even if additional stress occurs. Sometimes exacerbations occur, when the unpleasant feelings intensify and the stabbing begins to be much stronger.
When there is pain in the parietal region, when dizziness occurs, a feeling of motion sickness, limbs go numb, one of the reasons is psycho-emotional disorders. Long-term stress that occurs in people often leads to such developments. The brain is trying to correct the situation, to make it clear to the person that his work is deteriorating, the limit is coming when something needs to be done. For most people, the top of their head begins to hurt.
Cluster pain
A similar type of pain occurs in one part of the head and lasts from several minutes to 2-3 hours. Men 30-50 years old and women during menopause are susceptible to pain. The attacks are accompanied by redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, increased sensitivity, vomiting and nausea. Increases with fatigue and with any physical exertion.
The property of cluster pain is that its nature often changes. They are either strong or weak, becoming almost invisible. The upper part of the head hurts, the middle part, inside. Sometimes it is difficult to determine where the source of pain is; it feels like the entire surface is subject to unpleasant sensations.
Migraine
This type of pain is the most common. They happen at any age, in any gender. It all starts with aching pain and spasms. The pain begins only in the upper part of the head, and the duration of pain lasts from a couple of hours to several months. Manifestations of migraine:
- The head in the area of the crown hurts severely, an unpleasant feeling begins sharply. Pulsations permeating the entire surface.
- Severe pain in the parietal part of the head, worsening after eating or waking up. It turns out this is due to changes in pressure due to a change in the state of the body.
- Pain in the upper part of the head while walking or exercising.
- Vomiting, nausea.
The main cause of migraine is degenerative disorders of the nervous system, when they appear in the blood or, conversely, there is a lack of any substances. Migraines can occur due to increased consumption of alcohol, food, frequent smoking, numerous stress, and increased physical activity.
Traumatic brain injuries
After a person has suffered a traumatic brain injury, a post-traumatic condition may occur. There is an unpleasant sensation of pain in the parietal region. There is both acute and chronic pain that appears several weeks after the injury. Often such sensations are accompanied by a traumatic brain injury that was not detected. Therefore, you should consult a doctor for advice, especially if the following symptoms occur:
- blurred vision;
- deterioration of health;
- memory impairment;
- increase in pain intensity;
- vomiting, dry mouth;
- temperature increase.
Osteochondrosis
If the upper part of the spinal column is affected, then blood circulation is disrupted, first in the cervical region, and then in the brain. Due to this, a radicular pathology occurs - neuralgia, when the upper part of the head hurts severely. The pain can radiate to the temples, back of the head, cheekbones, shoulders and even to the shoulder blades. As accompanying symptoms, the following signs of cervical osteochondrosis appear:
- Loss of sensation in the upper limbs and occiput.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Double vision.
- Weakness of muscle tone in the cervical spine.
- The head and upper part of the skull may hurt.
Treatment is expected to be comprehensive. First of all, the manifestations of osteochondrosis, including headaches, are eliminated.
Nature of pain
As a rule, starting with a feeling of discomfort in the crown area, the pain gradually intensifies until it becomes pronounced. More often they are compressive, causing the feeling of a tight helmet on the head. But they can also have a bursting, pulsating, aching, and in rare cases, stabbing character.
In some patients, the pain remains localized in the upper part of the skull, while in others it can spread to other parts (back of the head, temples), becoming diffuse, and can radiate to the ears or eyes.
Pain in the parietal region can occur almost daily or manifest itself in attacks, aggravated by sound and light stimuli, reminiscent of a migraine. Moreover, over time, these manifestations intensify. Frequent attacks significantly reduce the quality of life of patients. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the reasons for their occurrence
Tumors
Often the culprits of headaches are benign or malignant tumors located in the brain. These circumstances cannot be eliminated with pills or improvised means of treatment; serious therapy will be required under the supervision of the attending physician.
The pain in the presence of a tumor will be constant and intense. Painkillers do not help in this case. The pain is worse in the morning or after physical activity.
Among other things, other symptoms are present:
- Nausea, often turning into vomiting.
- Decreased vision or hearing.
- Poor motor coordination.
- Memory loss.
- Mood swings.
- Drowsiness and lethargy.
Treatment methods and self-help
Severe forms of cephalgia can be cured in only one way - by contacting a therapist. He will prescribe appropriate medications and tell you what to do next. Some moderate and mild forms of parietal pain can be cured on your own, at home, but seeing a doctor will not hurt even in this case.
The lack of severity of headache symptoms in the crown area does not mean that they will not intensify later! When you know for sure that cephalalgia in the crown area was provoked by stress factors or atmospheric pressure, then self-medication is acceptable!
The best help is all kinds of herbal infusions (they can be prescribed by a herbalist), which have a beneficial effect on the nervous system and blood vessels. Infusions of peppermint and decoctions of St. John's wort relieve fatigue well. Melissa added to tea will calm you down and allow you to get a good night's sleep. A diet that limits the consumption of coffee and chocolate that excites the nervous system helps a lot.
Symptoms that may accompany a headache on the top of the head
Often, headaches are accompanied by additional symptoms that may indicate a specific disease. Some of them can pose a significant health threat, so you should seek medical help immediately. Additional symptoms of headache may include:
- Sudden vision loss.
- Irregularity of blood pressure.
- The headache does not stop even after taking painkillers.
- Increased body temperature due to headaches.
- Dry throat and nausea accompanying pain in the upper part of the head.
Symptoms
Headache in the parietal region can be of varying intensity and duration (several minutes or several days) depending on the cause of its occurrence.
On this topic
Some distinctive features of such pain, depending on its cause:
- injury : Headaches may be accompanied by impairment of memory and ability to concentrate, last several months, and become chronic.
- Stressful situations are prolonged or frequently repeated: pain is accompanied by dizziness, sometimes numbness of the limbs.
- Migraine: headache can be unilateral or, less commonly, bilateral, accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Most often it occurs in paroxysms, although it can last for several hours or even days. Its intensification is observed with light and sound stimuli, physical activity, and even when walking. The onset of an attack can be triggered by overeating, smoking, drinking alcohol, psycho-emotional or physical stress.
- Cluster pain: characterized by sharp intensity, short duration of attack, appearance at the same time, accompanied by nausea or vomiting, feelings of chills and weakness, severe dizziness, redness of the sclera of the eyes, sensitivity to light and sound stimuli.
- Problems of a vascular nature: pain can be combined with deterioration of hearing or vision, numbness of the limbs, and speech impairment.
- Tumor process: headaches are characterized by severity and persistence, increasing in intensity over time.
- Infectious diseases: damage to the brain and membranes manifests itself against the background of fever and other symptoms of infection, severe headache, accompanied by vomiting (which does not bring relief), intensifying with changes in the position of the head, sound and light stimuli.
Only a doctor can identify and take into account all the distinctive symptoms of a parietal headache, which help in correct diagnosis.
Examination methods
You should consult a specialist if you constantly have a headache in the upper part of your head. Even the most qualified doctor will not be able to determine the cause of the pain on his own, so the patient is sent for examination.
Fortunately, nowadays, thanks to innovations in the field of medicine, identifying the cause of this condition is not particularly difficult. The most informative method is MRI. Using this device, the doctor can examine the brain of a sick person in detail and determine the pathological condition.
But if there is a circulatory disorder, a CT scan will have to be performed. The vascular condition is determined by the MRA method (magnetic resonance angiography).
To detect the presence of infection, it is necessary to take a blood test. If, in addition to the pain in the upper part of the head, your vision has also decreased, you will need to consult an ophthalmologist. He will examine the fundus of the eye and determine possible abnormalities.
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient is treated by a general practitioner who begins the diagnosis. It includes several methods.
- Taking an anamnesis is a mandatory and very important step in making a diagnosis. We need all the signs of past illnesses, and even the patient’s lifestyle.
- Functional diagnostic methods : MRI (helps determine the most accurate picture of pain) and CT (detects foci of circulatory disorders), magnetic resonance angiography (assesses the condition of blood vessels).
- Laboratory tests : mainly blood tests, including for the presence of infections.
- Consultation with doctors of a narrow specialization (surgeon, ophthalmologist, ENT specialist, etc.) is possible
All therapeutic measures are prescribed after the necessary diagnostic procedures. Before making a diagnosis, the doctor can only prescribe medications that relieve painful contractions and accompanying symptoms. It is unacceptable to take any medications on your own.
Principles of treatment
If the head and upper part of the skull hurt, treatment will be prescribed only after a complete examination of the patient. This must be done, especially if the pain bothers you frequently or regularly.
It is not prohibited to take painkillers on your own, but if the headache is a one-time headache, with repeated discomfort in the head, the pills can even be harmful. If the problem is minor, you can use the “Star” balm. It will temporarily relieve headaches.
When purchasing any medicine at a pharmacy, first read the instructions for it. This is especially true for children. Remember that many medications may be contraindicated for young children.
Symptoms and main characteristics of pain
Depending on the cause, cephalalgia can manifest itself in different ways. It can be sharp and pulsating, or it can spread with general tension from the crown over the surface of the entire head. A number of cases are accompanied by weakness of patients, drowsiness, sometimes the pain in the parietal region is characterized by heaviness: “the head feels like it’s filled with lead.”
Some people tend to tolerate symptoms and wait for them to go away on their own. Others prefer to take analgesics on their own and self-medicate, which can only worsen the situation in the future. Only some people take a responsible approach to their health and consult a doctor on time.
If the pain is acute, if it began suddenly and affects vision and perception of reality, you must immediately go to a therapist, and not wait until it goes away. Such pain signals the presence of a serious pathology; delay can cost you your life!
How to treat headaches?
This treatment is provided for headaches not associated with serious pathologies:
- Analgesics. They will help to get rid of pain for a while, but will not eradicate the cause. It is also worth remembering that the pills can be addictive, and each time the pain will intensify, and you will need even more medicine.
- For moderate pain, you should not take pills; just take a walk in the fresh air and apply an alternating compress - hot and cold. Usually these measures help if your head hurts from overwork or nervous tension. You should not smoke or drink alcohol at this time, they will only worsen the situation.
- Acupuncture or acupressure can also help with occasional headaches. It is advisable to contact a specialist who knows which points to influence.
- Head massage helps with minor pain and migraines. The person relaxes and the discomfort goes away.
- Music therapy. It is better to include classical or ethnic music. But not all types of headaches can tolerate extraneous noise; for example, if you have a migraine, it is better to abandon this idea.
- Introduction of the drug "Botox". If you administer this remedy intramuscularly, it will create a lasting result that will eliminate tension and spasms in the head.
All these methods can be effective if the pain occurs as a result of stress, tension, overwork, etc.
What to do if there is pain
Headaches should not be tolerated. However, before you decide to take a pain reliever, you need to determine the cause of its occurrence.
On this topic
If it is known (overwork, stress, changed weather conditions, etc.), then the condition can be alleviated using the following measures:
- stop work and rest;
- go out into the fresh air or at least ventilate the room well;
- drink herbal tea (with chamomile, valerian, mint) or tea with honey and lemon;
- relax in a warm bath (you can add aromatic oils or sea salt);
- apply compress to the top of the head (ice in a rag or a wet towel) or hot - whichever helps;
- carry out a massage: acupressure, collar area, head (with your hands or a stream of warm water from the shower).
If the reason is not specified, then you need to contact a medical institution. Headache may be the only symptom of a serious pathology in some patients. Only a doctor can determine the cause of its occurrence and prescribe treatment.
On this topic
You should immediately call an ambulance in the following cases:
- the occurrence of severe pain for the first time and for no apparent reason;
- increasing intensity of headache;
- change in its localization, nature and severity;
- decreased visual that occurred suddenly;
- impaired speech and coordination of movement due to headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- the appearance of additional symptoms: dizziness, vomiting, severe weakness, numbness of any part of the body;
- lack of effect from painkillers;
- prolonged headache attack.
If any of the listed symptoms are present, immediate consultation with a doctor is necessary.
And only in cases where a previous examination has been carried out and the cause has been established, can medications prescribed by a doctor be used for periodic headaches.
Drug therapy
To know which medications help with pain in the crown, you should familiarize yourself with this list:
- "Citramon", "Askofen" are indicated if a decrease in pressure is observed.
- "Farmadipine", "Captopril" - these drugs are indicated for high blood pressure.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes are indicated for migraines.
- "Sedalgin" is prescribed for cluster pain.
- “Spazmalgon”, “Ibuprofen”, “Nurofen” are painkillers that are recommended to be taken for paroxysmal pain in the head. After this, the patient should lie down.
- Walking in the fresh air is recommended for neuroses, depression or after stress. Such people are often prescribed antidepressants, psychotherapy courses and a relaxing massage.
It is recommended to take all medications after consulting a doctor.
Traditional therapy for headache relief
The following folk recipes have proven themselves:
- Application of cabbage leaf. This method has been tested for years. The sheet is applied to the top of the head and left there for 30 minutes.
- Place your feet in a basin of hot water; for greater effectiveness, wrap your head with a cloth soaked in cold water.
- If the upper part of your head hurts, prepare soothing teas based on herbs such as mint, valerian, and marjoram.
- Aromatherapy will be useful for migraines; the aromas of herbs such as sage, mint, marjoram or lavender can temporarily relieve headaches.
- Try wearing amber beads or a bracelet, they help with headaches.
- Oddly enough, by applying a mask of fresh cucumber to your face, you will also help yourself get rid of headaches.
- Applying a cold compress to the head reduces soreness.
Pain in the crown
Depending on the cause, the headache can be localized in a specific area or cover the entire head.
The nature of the sensations may also vary, as well as their frequency. One of the most debilitating is considered to be a headache in the crown of the head. The crown is a part of the surface of the head located between the back of the head and the forehead, i.e. on top. It is worth noting that no one is immune from headaches in the crown area. It can even appear in a child. If the crown of your head hurts, the nature of the pain may be different. There may be a feeling of squeezing, bursting from the inside, sometimes even tingling. Often, pain symptoms can be pulsating in nature or radiate to the ears or optic nerve.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic – 4,500
Make an appointment
The reasons why the parietal part of the head hurts can be very different. The most common is considered to be increased intracranial pressure, but it is not the only one.
Prevention
To prevent pain in the upper part of the head, the following preventive measures are necessary:
- No need to sit in one place, be active, exercise and walk.
- Reduce your consumption of coffee and alcohol, they contribute to increased blood pressure; the healthiest and safest drink is regular drinking water.
- Pain will not bother you if a person includes foods rich in vitamin B2 in his diet. It is found in nuts, spinach, eggs and broccoli.
- Food must be balanced; if some foods are missing, then there will be a shortage of necessary microelements. It is also necessary to avoid foods that are too fatty, fried, spicy and salty. The diet should always include fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals and dairy products.
- Lack of sleep can cause headaches, so you need to get enough sleep, which is an average of 7-8 hours of sleep a night. Before going to bed, ventilate the room; fresh air helps you fall asleep faster.
- Don't allow stress in your life, don't get overtired. Remember about proper rest, which perfectly prepares you for the upcoming work. Often, pain in the top of the head occurs due to overexertion; after proper rest, it usually goes away.
- You should give up bad habits.
When the upper part of the head hurts, interest in life disappears. I would like to do everything possible and impossible to eliminate the discomfort. Early diagnosis will help begin timely therapy, so do not delay your visit to the doctor.
Consequences
Ignoring pain in the crown area and self-medicating can have serious consequences. A disease that is not recognized in time will progress, it will become increasingly difficult to cope with it, and in some cases it will even be impossible.
Thus, ischemic attacks can once again result in the development of a stroke. Conditions such as hemorrhagic stroke (brain hemorrhage) and brain tumor pose a direct threat to life.
It must be remembered that painkillers cannot be taken for a long time. First, they have side effects. Secondly, with long-term use, analgesics cease to have an effect at the usual dosage due to addiction, requiring increasingly higher doses.
On this topic
In the absence of the next dose of the drug, rebound pain occurs. The toxic effect of using higher doses will also provoke severe headaches.
Therefore, it is very important not to delay contacting a doctor and examination.