Today in our article we will talk about sexually transmitted diseases. Or rather, about one of the most famous diseases - syphilis. We will pay closer attention to neurosyphilis, which occurs due to infection with syphilis.
This disease is assigned code A52.1 according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases).
In general, syphilis is a disease caused by a microorganism called Treponema pallidum.
Treponema
It has a spiral shape, like a corkscrew. When it enters the body, it moves through the lymph and blood flow and reaches the organs.
In Russian history, many famous historical figures suffered from syphilis:
- Ivan groznyj;
- Peter I;
- Nicholas II;
- Vladimir Ilyich Lenin.
They say that syphilis was brought to Europe by Christopher Columbus after he discovered America and it is believed that this disease appeared as a result of bestiality. The indigenous people of America were very partial to llamas, who were carriers of this infection. Before antibiotics were invented, this was a fairly common disease.
Treponema is transmitted sexually. The whole horror of this disease lies in the fact that it takes on a chronic, protracted form and the person in fact becomes a walking vessel of treponema pallidum and passes it on.
The incubation period after infection is approximately four to six weeks. That is, only after this time can some symptoms begin to appear. Primary syphilis lasts for another two months, during which time hard chancre may appear on the human body.
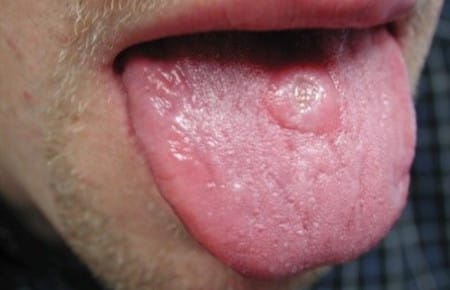
Chancre
One of the early manifestations indicating syphilis is chancroid. In this article you can find out what it looks like and is it possible to cure this disease?
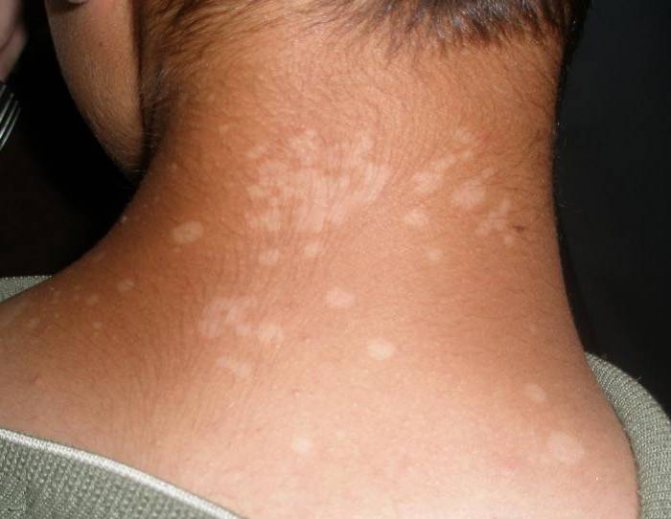
There is also a high probability of pigmentation appearing on the neck with the very romantic name “Venus necklace”. These are white spots that are located on the chest and neck.
In addition to these symptoms, there is another one that can appear only 4 years after the fact of infection - guma. Guma appears already during secondary syphilis. After this, internal organs, tissues, bones are affected, neurosyphilis develops, the central nervous system, spinal cord, etc. are affected.
Let's talk more about neurosyphilis (NS).
Causes and routes of infection
Infection occurs through sexual contact, after which the virus moves further to the organs. Therefore, answering the question of whether neurosyphilis is contagious, we can say with confidence, yes, it is contagious. At first, the body is able to produce antibodies to fight treponema, but the more advanced the process becomes, the less antibodies are produced. Because of this, bacteria have the opportunity to penetrate the central nervous system.
Infection occurs from a carrier of bacteria. Below are the ways in which the disease appears:
- Sexual intercourse is the main method of transmission of infection. The virus enters the body through the mucous membrane and small lesions on the surface of the skin. To protect yourself, you need to use condoms, but they do not guarantee 100% protection.
- Blood transfusions . Blood transfusion or dental treatment.
- Domestic. When a healthy person shares cutlery or a toothbrush with a person with syphilis, who has already begun to develop gum in the mouth, there is a high probability of infection.
- Intrauterine infection or transplacental route - transmission of the virus directly from mother to fetus.
In addition, the following list of factors contributes to the progression of the disease:
- reduced immunity caused by viral or inflammatory diseases;
- mental stress;
- incorrect or untimely treatment of syphilis;
- frequent stress or emotional outbursts;
- professional activity - the risk group includes honey. workers who have constant contact with various kinds of biological human secretions, such as saliva, semen and blood. Infection can occur during surgery, autopsy, or childbirth.
The greatest risk to others is posed by virus carriers in the early stages of disease progression—the first two years. Patients with a prolonged illness—more than five years—pose less of a threat.
Stages and symptoms
Depending on the time of infection, NS is divided into:
- Neurosyphilis early — it can really be diagnosed two or five years after infection. Treponema pallidum affects the blood vessels of the brain and its membrane. Because of this, you can observe the development of various anomalies, such as:
- Latent NS is also called asymptomatic, so it can only be identified, so to speak, “by chance.” It can only be detected by changes in the cerebrospinal fluid - the fluid surrounding the spinal cord and brain.
- Syphilitic meningitis. It is often found in young people. It manifests itself as severe headaches, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. Rarely increased temperature. Possible visual impairment and development of hearing loss due to the involvement of cranial nerves in the defective process.
- Meningovascular syphilis causes a disruption in the blood circulation of the brain. Sensitivity is impaired, attention decreases and memory deteriorates. Lack of therapy can lead to ischemic stroke, which is preceded by insomnia, severe headaches, and often epileptic seizures.
- Neurosyphilis late. It can be detected more than five years after the virus enters the body. During this period, nerve cells begin to break down. There are also several ailments that manifest the virus:
- Progressive paralysis or chronic meningoencephalitis. It often becomes active six to fifteen years after infection. The virus penetrates brain cells and destroys them. At first, the patient may experience a decrease in attention, memory, and vision. Later, mental disorders appear: hallucinations, depression, delusions. The disease develops quite quickly and the likelihood of death is high.
- Tabes dorsalis.
- Gummous NS.
- Optic nerve atrophy is quite often an independent symptom of late-stage neurosyphilis, which greatly reduces the patient’s quality of life. If left untreated, complete blindness occurs.
- Meningovascular syphilis (symptoms are similar to the early stage).
- Congenital NS is diagnosed very rarely. During pregnancy, the expectant mother undergoes many tests to detect various infections. And if the infection does occur inside the womb, then it will not be difficult to detect it. The symptoms are the same as in adults, but there is no tabes dorsalis. Particular symptoms of congenital NS are deafness, deformation of the upper incisors and keratitis. If you consult a doctor in time, you can really stop the process. However, neurological symptoms remain for life.
Neurosyphilis
Neurosyphilis is a lesion of the nervous system caused by Treponema pallidum.
The pathological process manifests itself in secondary and tertiary forms of syphilis, which occur in the absence of timely and adequate treatment. Pathogens enter the bloodstream, lymph flow and nervous tissue - this is the cause of the development of neurosyphilis. The incidence of neurosyphilis is 0.3-0.4 per 100 thousand population. 15-20% of patients infected with syphilis suffer from nervous system pathology. The disease accounts for 8-9% of all organic disorders of the nervous system caused by brain damage.
Routes of transmission of neurosyphilis
Treponema pallidum, the causative agent of the pathology, is transmitted primarily through sexual contact. The disease occurs as a result of the spread of a sexually transmitted infection called syphilis (lues).
An STD occurs in several stages. The patient is contagious in the primary and secondary forms, in the presence of chancre and rashes.
Neurosyphilis develops deep within the body and cannot be transmitted. The exception is when gummas form on the skin.
The infection is transmitted through blood during transfusion or intravenous injections using a single syringe. The spread of infection is possible at any stage of the disease.
Congenital neurosyphilis occurs in infants when spirochetes are transmitted from mother to fetus through the placenta, during childbirth, and is extremely rare. Women are examined during pregnancy, and the pathogen can be identified in advance. The child is prescribed syphilis therapy immediately after birth.
Household transmission of spirochetes is theoretically possible, but in practice it is rare. In a humid environment, treponema pallidum lives for several hours, but on a dry and hot surface it quickly dies; antiseptics also kill it.
Stages of neurosyphilis
There are 2 forms of the disease: early and late. Early is divided into the following types:
- meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- meningomyelitis - inflammation of the membranes, substance and spinal roots;
- meningoencephalomyelitis - inflammation of the membranes and substance of the brain and spinal cord;
- polyneuritis - multiple inflammation of the nerves;
- endarteritis or meningovascular neurosyphilis - inflammation of large vessels and their narrowing;
- gummous neurosyphilis - the formation of deep ulcers that heal with the formation of scars.
Late disease is divided into the following types:
- tabes dorsalis - inflammation of the posterior columns of the spinal organ and spinal roots;
- progressive paralysis or Bayle's disease is a mental pathology with the development of dementia, together with somatic and neurological disorders;
- amyotrophic spinal syphilis - damage to the membranes and anterior roots of the spinal cord.
There is a concept of asymptomatic (latent) neurosyphilis, when symptoms of the disease do not occur, but are diagnosed by changes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Pathology is the only neuroinfection in which, in the absence of pronounced symptoms, a change in the cerebrospinal fluid is noted.
Then the development of meningitis, meningoencephalitis, vascular pathology and the formation of gummas occurs.
Damage to the lining of the brain
Neurosyphilis begins with meningitis, brain damage. As it develops, it can be acute or subacute, chronic and gummous. At the initial stage, it may be asymptomatic or accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Asthenic syndrome or increased fatigue.
- Absent-mindedness, bad mood, forgetfulness, irritability.
- Decreased mental activity, slowing down of mental processes.
- Senesthopathy is unpleasant sensations throughout the body.
- Insomnia.
- Speech and movement disorders.
- Symptoms of meningitis are headache, vomiting, fever, tachycardia, convulsions, etc.
If there are no symptoms, serological tests of the cerebrospinal fluid will help detect the disease. With neurosyphilis, an increase in leukocytes, protein and polynuclear cells is observed.
Exacerbation of syphilitic meningitis
At the initial stage of syphilitic meningitis, there are no specific symptoms of inflammation. In the secondary period, the symptoms of meningitis increase. The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 38;
- headaches and tinnitus;
- dizziness and weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- photophobia.
The disease lasts 10-15 days; if left untreated, it becomes chronic and tertiary syphilis develops. The disease develops 4-5 years after infection with spirochetes and occurs without pronounced symptoms. The patient experiences headaches, especially at night. The oculomotor nerve suffers, which leads to impaired visual function and strabismus.
Basal meningitis
This form of brain inflammation occurs in a chronic form with periodic remissions; the lower part of the organ is affected. The diagnosis is made by complaints of prolonged headaches and damage to the cranial nerves. In case of pathology, the following signs are of concern:
- frequent urination and thirst due to dysfunction of the pituitary gland, symptoms of non-diabetes mellitus;
- Pechkranz syndrome - progressive obesity;
- acromegaly - changes in appearance and well-being due to increased production of growth hormone.
The pathology is accompanied by general cerebral symptoms: changes in the level of consciousness, headaches and vomiting, dizziness and convulsions. Sometimes focal signs appear: speech and movement disorders, paralysis, paresis, lack of sensitivity.
Damage to the dura mater of the brain
Inflammation of the hard membrane is almost always accompanied by damage to the soft membrane, and manifests itself in the form of cerebral syphilitic pachymeningitis. The pathology occurs in acute and chronic stages, and according to the nature of the course it can be purulent, serous and hemorrhagic.
The serous form is asymptomatic. With hemorrhagic manifestations depend on the degree of damage. With extensive hemorrhage, severe headache, vomiting, delirium and impaired mental function occur.
The pathological process is accompanied not only by inflammation, but also by the proliferation of connective tissue and thickening of the meninges, the formation of a hematoma tumor. The patient suffers from stroke and paralysis. A change in an organ at an advanced stage leads to the death of the patient.
Spinal cord lesion
Neurosyphilis affects the hard and soft membranes of the spinal cord. The disease of hard membranes occurs in 3 stages:
- inflammation of the roots;
- loss of sensitivity;
- organ compression.
Inflammation of the soft membranes can be widespread and focal.
The acute stage of spinal cord damage is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the back of the head and neck, back, lower back;
- pain and lack of sensitivity in the ulnar and median nerves;
- muscle atrophy, paresis, paralysis;
- Klumpke's paralysis - the disease affects the hands;
- formation of bedsores.
When the disease occurs, dysfunction of the spine and pain occur, the patient is in a forced position, and meningeal symptoms may appear.
The chronic stage of organ damage is recorded more often and is accompanied by the following disorders:
- Meningoradiculitis is an inflammation of the membranes and roots.
- Meningomyelitis is an inflammation of the membranes, roots and substance of the spinal cord.
The chronic inflammatory process can be asymptomatic, in which case the disease is diagnosed by cerebrospinal fluid.
Damage to cerebral vessels
Vascular neurosyphilis is accompanied by damage to the soft membranes and cranial vessels. Accompanied by depression of blood circulation, mental disorders, and the development of paralysis.
At the same time, as paralysis progresses, mental abnormalities become less pronounced, the disease manifests itself in the form of spontaneous remissions and exacerbations.
Damage to large vessels is reversible if the pathology is diagnosed at an early stage.
Inflammation of the blood vessels of the brain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- stroke;
- pathology of speech and motor function;
- epileptic seizures;
- general cerebral signs;
- paresis, loss of sensitivity;
- mental disorders - euphoria, delirium, memory problems, verbal hallucinations (auditory).
Damage to blood vessels in the back area is very dangerous. The pathology occurs secretly and asymptomatically. The patient slowly loses sensitivity and develops paresis. Different parts of the body are affected, depending on the affected area of the spine.
Tabes dorsalis
Syphilitic myelopathy or tabes dorsalis is an advanced stage of the disease, which develops 10-12 years after infection, against the background of a complete lack of treatment. Occurs in 3% of those infected with spirochetes, and in 20% of patients with neurosyphilis.
Men get sick more often than women, and the first signs of tabes dorsalis appear in patients after 30-40 years. Tabes dorsalis is a pathological change in the spinal cord.
The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- paresthesia;
- severe cutting pain in the limbs and torso;
- hypothalamic crises with increased temperature;
- when the gastrointestinal tract is affected, rapid weight loss is observed;
- decreased sensitivity;
- poor coordination of movements;
- disturbance of urinary function and defecation;
- damage to the optic and auditory nerves.
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the spinal cord and spinal area. In the last stages, complete atrophy of the limbs is observed, the person cannot move independently.
Taboparalysis
The pathology is a combination of tabes dorsalis and progressive paralysis. It is accompanied by disorders characteristic of myelopathy and progressive paralysis, but occurs in a milder form, as it develops slowly.
First, spinal manifestations characteristic of tabes dorsalis occur, and after 5-10 years insanity, visual hallucinations, and paranoid psychosis begin to occur. The symptoms are similar to alcoholic encephalopathies, so differential diagnosis is required.
Progressive paralysis
Paralytic dementia, which has many forms. The most common is dementia, in which there is an increase in dementia with complete indifference to what is happening and others, a decrease in memory, all this is accompanied by ridiculous actions. The patient does not remember his own address and name, and is unable to learn.
There is also a manic form, with delusional ideas of greatness. The patient is sure that he is the Lord of the World, there is euphoria and causeless joy.
In the depressive form, on the contrary, the patient blames himself for all the negative phenomena occurring on the planet and suffers from tearfulness and low mood.
Manic and depressive forms can change each other, then the circular type is diagnosed.
The most severe stage is complete dementia. The patient cannot take care of himself, makes illogical conclusions, and does not answer questions. At the same time, sudden mood changes occur from euphoria to complete apathy. In severe cases, marasmus develops, swallowing functions disappear, and involuntary urination and defecation occur.
Gumma brain
Gummous nodes form in the hard and soft membranes of the brain and spinal cord, grow into the organ, and compress it. At first, gumma is a tumor, which over time disintegrates in the center and turns into an ulcer. Gumma causes necrosis of the affected tissue, and after healing it forms an area of sclerosis, that is, a scar.
Ulcers develop 5 years after infection with Treponema pallidum, in the absence of treatment. The disease is accompanied by headaches and vomiting, impaired visual and auditory function, epileptic seizures, and paralysis. Clinical signs largely depend on the location of the gumma.
Congenital neurosyphilis
Juvenile neurosyphilis is a very rare disease that occurs as a result of the progression of congenital syphilis.
As a rule, the infection is diagnosed in the maternity hospital, immediately after the birth of the child. There, the neonatologist prescribes specific antibiotic therapy, and the child is cured.
If untreated, neurosyphilis manifests itself up to 2 years of age, accompanied by symptoms of tertiary syphilis and deviations in the development of the child. Requires long-term rehabilitation after primary treatment.
Diagnosis of neurosyphilis
The pathology is often asymptomatic, with negative serological reactions, which greatly complicates diagnosis. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood samples should be examined carefully.
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- History taking and neurological examination.
- Serological studies of cerebrospinal fluid - PRP, RIF, ELISA, RPGA.
- Spinal function for collection and examination of cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment methods
The pathological process is treated with antibiotics. The drug of choice is penicillin, since Treponema pallidums are not resistant to it. The treatment regimen is drawn up individually, depending on the stage of the disease. An example of a treatment regimen for early forms of neurosyphilis:
- Benzylpenicillin intravenously, 2-4 ml units 6 times a day, for 2 weeks. Or intramuscular benzylpenicillin novocaine salt, 2 million units per day, divided into 4 doses.
- Prednisolone 60-90 mg for 3 days, as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
At a late stage of the disease, the course of treatment is carried out twice. If you are allergic to penicillins, the drug is replaced with ceftriaxone.
6 months after treatment, repeated puncture of cerebral fluid is recommended to monitor recovery.
Forecasts
Untimely treatment of the disease leads to irreversible changes in the nervous system. Syphilis can be cured with antibiotics, but if changes have occurred in the organs, it will no longer be possible to recover.
At the initial stage of neurosyphilis, when the inflammatory process has only affected the membranes of the brain, the prognosis is quite favorable. In the later stages, with the development of dementia, it will not be possible to achieve a complete cure.
Sources
- https://pmarchive.ru/nejrosifilis/
- https://www.eurolab.ua/diseases/724/
- https://polovye-infekcii.ru/sifilis/sifilis-nervnoy-sistemyi
- https://med-lib.ru/books/nerv_bol/96.php
- https://doctor-neurologist.ru/nejrosifilis-simptomy-i-lechenie#i
- https://bme.org/index.php/SPINAL_TABES
- rmj.ru/articles/infektsiya/sovremennyy_neyrosifilis_klinika_diagnostika_lechenie/
Source: https://venerolog-info.ru/nejrosifilis/
Diagnostics
Above we explained what NS is. But how can this diagnosis be confirmed? There are three criteria by which this can be done:
- test results for syphilis;
- characteristic symptoms;
- detection of changes in the composition of cerebrospinal fluid.
A neurological examination of the patient is carried out, as well as an examination by an ophthalmologist. Blood tests such as RIF (immunofluorescence reaction) and RIBT (treponema pallidum immobilization reaction) play a serious role. If the doctor deems it necessary, they will be performed many times.
If there are no pronounced symptoms, a lumbar puncture is prescribed. Thus, with NS, the virus itself and an increased level of protein will be detected in the cerebral fluid.
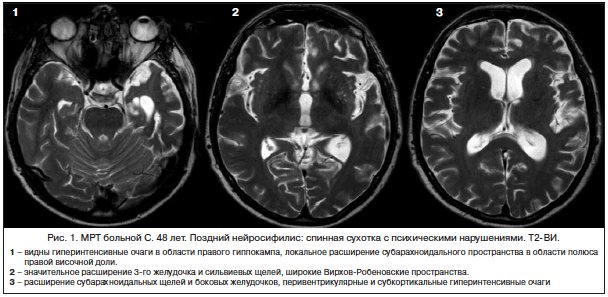
Absolutely all patients with suspected neurosyphilis are prescribed MRI and CT scans of the spinal cord. This helps detect medullary atrophy.
Recommendations
A consultation with a neurologist and a serological test of blood/cerebrospinal fluid are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, head of the department of the Russian State Medical University, professor, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Evgeniy Ivanovich Gusev. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Treatment
Therapy is carried out exclusively inpatient. The patient is administered a drug with a high concentration of penicillin. The course lasts at least two weeks. Doctors often prescribe complex therapy using several medications at once. funds. Standard scheme:
- penicillin;
- probenecid;
- ceftriaxone.
Medicines are administered intravenously, and penicillin is also injected into the spinal canal. After two weeks, a check is made to see if the virus has been eliminated; if not, the course is extended.
On the first day of treatment, headaches may intensify, so the patient is also prescribed corticosteroid and anti-inflammatory medications. facilities.
At a later stage, bismuth and arsenic are used, which, as you can imagine, are very toxic.
Consequences
If the disease is detected and treated at an early stage, the probability of completely curing the patient is very high. If the brain vessels and nerves were severely damaged, then some symptoms may remain with the patient for life. A congenital disease leads to lifelong deafness or disability.
NS carries a bunch of unpleasant consequences, so you can’t ignore some of the initial symptoms. And try not to have promiscuous sex and always use protection. If, for example, you went on vacation, met someone and had unprotected sex, then it is better to immediately go get checked so as not to risk your health and life.
You can also watch this video, where a neurologist will tell you in detail about neurosyphilis and what its main symptoms are.
What tests should I take after treatment of late forms of syphilis?
Getting tested once is not enough, as with other sexually transmitted infections.
Late syphilis requires a minimum of 3 years of observation of the patient after treatment.
Non-treponemal tests are performed every six months.
This can be an anticardiolipin test or the Wasserman reaction, which determines not only the presence of antibodies, but also their titer (quantity).
Treponemal studies are carried out once a year.

Although their results are not particularly significant.
Based on these serological reactions, the diagnosis of syphilitic infection is not removed.
In most cases, their positivity lasts for a very long time, sometimes throughout their lives.
The first cerebrospinal fluid analysis is performed 6 months after completion of therapy.
In the future, monitoring is carried out every six months.
If sanitization of the cerebrospinal fluid occurs, the patient is removed from the register.
It does not matter whether he still has neurological symptoms.