Atherosclerosis of the brain. What is this? Classification
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels is a specific disease in which the vessels of the head, which supply the organ with oxygen and nutrients, are narrowed due to the deposition of cholesterol on their inner surface. The disease is often called cerebral atherosclerosis, but this is not entirely true. With cerebral atherosclerosis, all vessels are affected, including capillaries, and with cerebral atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques form only in large main and medium-sized arteries.
With cerebral atherosclerosis, acute or chronic cerebral circulatory failure or ischemia of organ tissue develops. At the same time, the indicated pathological changes have a sluggish development with manifestation (exacerbation) after 50 years.
Patients suffering from cerebral atherosclerosis are unaware of the existence of the pathology for a long time.
The classification of the disease distinguishes the following groups of diseases depending on the location and name of the vessels in which cholesterol deposition occurs:
- With atherosclerosis of the extracranial segments of the main arteries of the head, damage occurs to the carotid arteries (common, external and internal), brachiocephalic trunk, lingual and facial arteries, maxillary, occipital and vertebral arteries. In addition, the superficial temporal and posterior parotid arteries are affected.
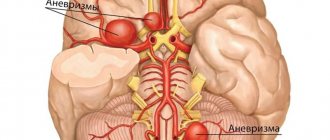
- With atherosclerosis of the intracranial arteries of the brain, damage occurs to the right anterior and right posterior cerebral arteries, the left central cerebral artery, the basilar and right internal carotid arteries.
- With diffuse atherosclerosis, both groups of arteries are affected (both extracranial and intracranial), and small vessels of the brain and capillaries are also damaged multiple times.
Both groups of cerebral artery atherosclerosis lead to significant impairments in the throughput of smaller vessels and capillaries, which inevitably affects the functioning of the central nervous system.
Based on the type of changes in large vessels during pathology, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- With non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the head, the vessels do not lose flexibility, and the narrowing of their lumen is achieved due to a layer of cholesterol deposited on the walls.
- With stenotic atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the head, the walls of blood vessels in certain areas become less elastic due to an increase in the number of connective tissue fibers. They cannot stretch (relax), which is why pronounced narrowing (stenosis) is constantly present in pathological foci.
As for the classification according to the type of course, the disease may have the following features:
- with a remitting course, the disease progresses in waves - symptoms gradually increase, but between exacerbations there are long periods of rest or remission;
- with slowly progressing atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head, symptoms are constantly present, but their intensity increases slowly, and periods of their complete absence are not recorded;
- in an acute course, symptoms arise suddenly and become severe with extensive damage to organ tissue;
- with malignant development, patients experience rapid development of ischemic stroke, and then dementia and dementia.
If cerebral atherosclerosis is not diagnosed in time and treatment is not started, in 90% or more patients will develop irreversible changes in the central nervous system.
Causes of the disease
Experts have identified many causes of cerebral atherosclerosis, which in most cases are combined with each other. The main and most common phenomenon that leads to the deposition of cholesterol plaques in the blood vessels of the brain is age. After 50 years, this disease occurs to one degree or another in 8 out of 10 people. The reasons for this are not fully understood, but scientists are inclined to believe that the body’s inability to remove harmful lipids from the body is caused by a natural slowdown in metabolism and changes in hormonal levels.
In addition, the risk of atherosclerosis at a young age can be affected by:
- unbalanced diet with a predominance of fatty, fried foods rich in carbohydrates and fats, hot spices in the menu against the background of an insufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits;
- irregular eating, when periods of acute hunger alternate with eating excessive amounts of food;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders - diabetes, obesity, hypo- and hyperthyroidism and others;
- physical inactivity or lack of physical activity and resulting obesity;
- bad habits - smoking and alcoholism, which provoke vasoconstriction and affect the circulatory system as a whole.
Doctors do not rule out the influence of a genetic factor. According to statistics, 9 out of 10 people suffering from cerebral atherosclerosis have immediate relatives who also encountered diseases caused by the deposition of cholesterol in the circulatory system.
Since atherosclerosis very often occurs against the background of hypertension, experts classify this disease as a provoking one. Since stress is the main cause of high blood pressure, it is also considered indirectly involved in the occurrence of pathology. Under the influence of psycho-emotional factors, blood vessels can change their tone several times during the day (contract and relax), as a result of which microdamages form on their inner surface. On such wounds, cholesterol settles quite quickly, forming plaques.
Despite identifying the main sources of the disease, doctors cannot identify the main cause of cerebral atherosclerosis. They call this disease polyetiological, that is, developing as a result of a combination of several factors.
Why is cerebral atherosclerosis dangerous?
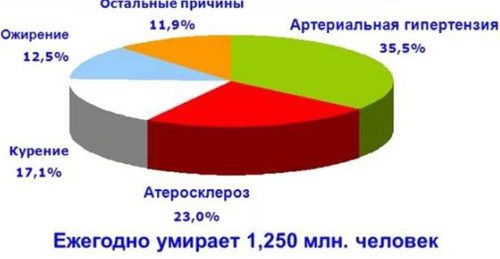
Despite the efforts that doctors make to prevent the disease, atherosclerosis remains one of the most common diseases. It ranks second in the ranking of the most dangerous causes of neurological disorders and 45% of cardiovascular pathologies. The main dangers of atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the brain are the following consequences:
- single neurological disorders - decreased vision, impaired hearing, memory, inability to perform logical operations, to foresee the consequences of one’s actions;
- vasomotor disorders in the form of absence or decreased sensitivity of individual parts of the body and limbs, paresis and paralysis, decreased motor skills;
- mental disorders in which a person loses his own identity, cannot interact with the outside world and sometimes poses a threat to others due to deviant behavior.
But this is not the worst thing about this pathology of cerebral vessels. With this disease, there is a high probability of acute, irreversible processes occurring. According to statistics, with cerebral atherosclerosis, disability of varying degrees is assigned to 80% of patients who seek help from a doctor.
If the disease was not monitored by specialists, and the patient did not undergo comprehensive treatment, the prognosis for life with cerebral atherosclerosis is more dismal:
- 75% of patients develop persistent neurological disorders that are not amenable to therapy;
- in 60% of patients, mental activity deteriorates to the point of dementia;
- In 90% of patients, an exacerbation occurs, which ends with ischemia of various parts of the brain, in which systemic pathologies are observed that require constant medical care for the patient.
It is noteworthy that even with timely and adequate therapy, negative consequences are inevitable. Modern medicine offers treatment regimens that help reduce their severity and reduce the likelihood of death, but completely getting rid of symptoms is only possible if the disease is detected at the initial stage.
Stages
Patients interested in the question of whether atherosclerosis can be treated first of all need to identify the degree of development of the disease. The stages of atherosclerosis are classified according to the following criteria:
- clinical manifestations;
- location;
- microscopy;
- macroscopy.
Features of clinical manifestations:
- First stage. Blood circulation is impaired, and sufficient oxygen does not reach the tissues. Dystrophic changes are reversible, the pathology often has no characteristic symptoms.
- Second stage. Degenerative and dystrophic disorders appear, and a fatty plaque forms. There may be minor pain in the affected area.
- Third stage. Scars form in the vascular cavity. Symptoms become more pronounced.
By location there are:
- damage to the coronary arteries:
- damage to the blood vessels of the legs;
- damage to the renal arteries.
Damage to the coronary arteries occurs in several stages:
- Dystrophic changes at the ischemic first stage are asymptomatic. Identification of pathology simplifies angina pectoris syndrome. Deviations in the cardiogram are possible, ST shift occurs. At the initial stage, during physical activity, the heart rate and breathing increase.
- The necrotic phase is characteristic of the second stage. The risk of developing a prolonged heart attack increases, and a relapse is possible.
- The third stage is characterized by cardiosclerosis. During this period, patients develop atrial fibrillation and cardiac asthma. The systemic and pulmonary circulation is disrupted.
Important information: Exercise therapy exercises for atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
The following symptoms are characteristic of each stage of vascular lesions of the lower extremities:
- The first stage is accompanied by mild lameness, which occurs due to impaired blood flow. Lower limbs hurt.
- Tissue thrombosis develops at the second stage. Necrosis affects the skin of the fingers and feet.
- Necrosis spreads to healthy areas of the lower extremities - muscle and bone tissue are affected.
Stages of the renal arteries:
- The ischemic phase is accompanied by impaired blood flow in the kidneys. There are no other violations. The risk of developing arterial hypertension increases.
- The patient's condition worsens, and in the second phase the necrotic process begins.
- The third stage is characterized by the appearance of symptoms of renal failure.
Microscopic criteria:
- prelipid stage;
- lipoidosis;
- liposclerosis;
- atheromatosis;
- atherocalcenosis.
The appearance of lipid bands and spots, fibrous plaques, and atherocalcinosis are considered macroscopic criteria.
Symptoms of pathology
Obvious clinical signs of cerebral atherosclerosis appear long after the onset of cholesterol deposition. Symptoms appear after the internal diameter of the main arteries and smaller capillaries of the brain narrows so much that the volume of blood flowing to the organ decreases by 15% or more.
Clinical symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis vary depending on the stage of development of the disease:
- At the initial stage, in patients, signs of pathology appear only with an increase in physical and psycho-emotional stress and disappear quite quickly upon transition to rest. They are expressed in asthenia, which is accompanied by weakness, fatigue, lethargy and deterioration of concentration and attention. In isolated cases, sleep disturbances occur in the form of insomnia or daytime sleepiness. Most patients complain of headaches and tinnitus. The ability to remember new information is noticeably reduced.
- With further progression, atherosclerosis is accompanied by mental disorders in the form of increased suspiciousness, mood swings, a tendency to depression and anxiety. Memory impairments become more pronounced: the patient forgets the events of the current day and gets confused in his memories. Headache and tinnitus become permanent. With progressive atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the brain, persistent speech disturbances (blurredness, changes in diction), vestibular disorders in the form of dizziness and gait instability are observed. Productive activity is rapidly declining due to deterioration of vision and hearing, tremors of the limbs and head, and inability to think clearly and logically.
- The final stage of atherosclerosis of the head is accompanied by dementia or dementia. The intellect weakens significantly, the patient reasons and behaves like a child or acquires unusual aggressiveness or tearfulness. Most patients experience complete or partial loss of memory, detachment, and lack of interest in the objects and events around them. Patients lose the ability to navigate in space and time. Such patients require constant monitoring and care due to the complete loss of self-care skills.
The last stage of the disease is irreversible and has no tendency to regression (weakening and reduction) of symptoms. Therefore, it is important to identify atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the head at the initial stages. This is the only way to preserve the patient’s basic self-care skills and preserve memory.
Symptoms
In the early stage, cholesterol deposition on the inner wall of the vascular bed shows virtually no signs. In the absence of preventive measures, plaques begin to accumulate and the first symptoms appear:
- Headache;
- Fainting, darkness in the eyes;
- Fatigue, weakness, apathy;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Blood pressure surges.
Narrowing of the lumen by atherosclerotic deposits leads to an increase in symptoms, you can find:
- Visual, hearing, speech disorders;
- Memory losses;
- Trembling in the limbs;
- Fatigue;
- Feeling of heaviness in the head;
- Psycho-emotional instability;
- Hypoxia of the cortex and cerebellum.
In advanced states, a person loses the ability to think and self-care. Acute cerebral insufficiency develops. Brain cells atrophy. Stroke and paralysis occur.
Diagnostics
Neurologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis of large and smaller vessels in the brain. It is to them that the patient is referred when presenting complaints that directly or indirectly indicate pathology. To begin with, an oral examination of the patient is performed to collect anamnesis and complaints, then a series of tests are performed. Evidence in favor of the disease is:
- the patient’s inability to look up (horizontal nystagmus);
- atypical increase or decrease in reflexes, most often asymmetric;
- inability to maintain balance in a standing position (legs together) and with arms extended forward;
- weakness and trembling of fingers on outstretched arms;
- inability to bring a finger to the tip of the nose with eyes closed.
Such signs of the disease are still considered indirect, so the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination with the involvement of other specialists. So, if you have visual impairment, you will need to consult an ophthalmologist, and if you have hearing impairment, you will need to consult an otolaryngologist.
In addition, the comprehensive diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis includes instrumental vascular studies:
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- radioencephalogram (REG);
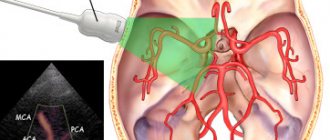
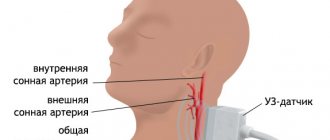
- Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels (USGD);
- duplex scanning of the head;
- MRI of cerebral vessels.
If the patient is admitted with signs of ischemic stroke, one of the common complications of atherosclerosis of the head, visualization of cerebral tissues will be required through CT or MRI. The functional state of the brain is checked using an electroencephalogram (EEG).
Dynamic studies of intracranial great vessels and carotid arteries play an important role in the diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis. They make it possible to determine the degree of narrowing of the lumen of these areas of the circulatory system.
Based on the data obtained during the examination, the doctor selects a treatment regimen and determines the list of medications necessary for the patient.
Treatment of the disease
Therapy for atherosclerosis is always a set of measures aimed at restoring metabolic processes, in which harmful cholesterol will not be absorbed and deposited in the vessels. In addition, it is important to pay attention to restoring blood circulation and nutrition of brain tissue, and preventing attacks of arterial hypertension.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment for cerebral atherosclerosis plays a leading role. In this case, several groups of drugs with different properties are used:
- Antiplatelet agents are drugs that make the blood less viscous and prevent the formation of blood clots. These include “Tiklid”, “Cardiomagnyl”, “Thrombo Ass” and their analogues.
- Statitis are drugs that reduce the size of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels. These include the drugs Zocor, Atoris, Atorvastatin. The use of statins for vascular atherosclerosis helps reduce the risk of life-threatening narrowing of the main arteries of the brain. The drugs either reduce their size or stop their growth.
- Fibrates are drugs similar in action to statins that do not affect the size of cholesterol deposits and plaques, but reduce the concentration of this triglyceride in the blood. Thus, the drugs slow down the progression of the disease.
- Bile acid sequestrants are specific drugs that interfere with the absorption of cholesterol from food.
- Drugs for restoring the functional state of blood vessels - Vinpocetine, Nifedipine, Pentoxifylline.
- Nootropics and drugs that improve neurometabolism - Piracetam, Glycine, Picamilon, products with ginkgo biloba extract. These drugs improve the functioning of the central nervous system and reduce the neurological symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis.
- Antihypertensive drugs that help stabilize blood pressure. With their help, it is possible to avoid life-threatening complications (strokes).
Vitamin and mineral complexes will help improve the general condition of the body. They must contain vitamins B, A, C and nicotinic acid.
The choice of how to treat cerebral atherosclerosis is the doctor’s priority, since many medications have contraindications.
You will need to use medications in long courses. Most of them are taken for life without interruption, periodically adjusting the dosage.
Surgery
Surgery for various forms of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head is a last resort. It is used in the following situations:
- with occlusion of the carotid arteries (narrowing of the lumen) by 70% or more;
- after a minor stroke with total blockage of small vascular branches of the brain;
- with repeated transistor ischemic attacks.
Several types of surgical interventions are used:
- Endarterectomy - removal of plaques and cholesterol deposits along with a small area of tissue lining the vessel from the inside (intima).
- Bypass surgery is the creation of a new vessel that bypasses the area affected by cholesterol deposits.
- Endoscopic stenting is the installation of an expanding structure into a vessel, which is impregnated with a composition that dissolves cholesterol.
After the operation, you continue to take the medications prescribed by your doctor, since the risk of plaque formation in other areas of the vessels cannot be ruled out.
Diet
Before treating cerebral atherosclerosis with special drugs, patients need to adjust to lifestyle changes. Since the disease very often progresses against the background of poor nutrition or lifestyle, they will have to follow a strict diet:
- reduce the amount of meat consumed, especially red and high-fat;
- reduce the amount of eggs (yolks) in the diet;
- limit the consumption of vegetable solid fats (margarine);
- limit the consumption of baked goods and sweets;
- give up fast food, canned food and sausages;
- give up alcohol.
Despite strict restrictions, the diet of a patient with cerebral atherosclerosis is varied, because the menu must always include cereals (buckwheat, rice, millet, barley, flax, oats and others), fresh, dried and pickled vegetables, fresh, dried and dried fruits, chicken or turkey fillet, sea and river fish.
Treatment or how to remove cholesterol plaques
Depending on the severity of the disease, there are different methods and methods of treatment.
Lifestyle change
It is always required, but at the initial stage you can get by only with it - under the influence of certain foods and physical activity, cholesterol plaques can gradually dissolve. Must include:
- Diet change . You need to eat at least five times a day, little by little. Reduce the amount of fried, smoked, salty and fast food. If possible, reduce the consumption of animal fats (fatty meat, full-fat milk and fermented milk products). Eat vegetables and fruits more often. Be sure to include olive oil, nuts, herbs, and lean fish in your diet. Drink vegetable juices more often, get used to eating citrus fruits, garlic and onions.
- Changing your daily routine . You need to sleep at least eight hours, get up and go to bed at the same time every day.
- Engaging in physical activity. It is not necessary to go to the gym, sign up for aerobics or dancing. It is enough to go for a walk to the nearest park once a day or at least walk to work. It will be useful to buy a bicycle and ride it, or buy rollerblades. The main thing is constant movement.

Drug therapy
At deeper stages, it will not be possible to destroy plaques using only the correct regimen - stronger means are needed. Most often these are medications, including:
- Bile acid sequestrants . They reduce the production of cholesterol in the liver and at the same time lower its concentration in the blood vessels. If the dosage is incorrect, it can negatively affect your health - a lack of cholesterol is just as harmful as an excess.
- Cholesterol absorption blockers . They are very diverse - these are anion exchange resins, fibrates, statites, nicotinic acid, and plant sorbents. They can also be harmful in the wrong dosage.
- Unsaturated fatty acids . They promote the destruction and utilization of lipoproteins, which, accordingly, leads to a decrease in cholesterol levels.
- Endotheliotropic agents . Destroy already formed plaques.
Surgical intervention
It is used in cases where other methods will not give an effect - or will not give it fully. For example, if a plaque has already blocked a vessel or the patient is allergic to specific drugs. Happens:
- Laser correction . The most modern, simple and safe of the methods is that the plaque is burned out with a special laser, after which the patient’s recovery occurs in the shortest possible time.
- Micro section . It is more difficult for the surgeon - the wall of the vessel is carefully incised and the plaque is removed through it, after which the incision is sutured. Requires skill and a relatively long recovery.
- Prosthetics . The most expensive and complex option is that the part of the vessel plugged with plaque is removed and replaced with a special tube. A long rehabilitation is required until the body accepts the prosthesis as part of itself.
People's Councils
Traditional medicine often helps in treatment - but before starting therapy, you need to consult with your doctor and find out about possible contraindications.
Among the most famous traditional medicine recipes:
- Honey, ginger and lemon - ginger is grated, diluted with water, brought to a boil and cooked for some time. The lemon is cut and added to the resulting infusion after filtering it. Honey interferes with the final result. Drink hot.
- Garlic . You should just add it to all dishes - but be careful, it can affect the health of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Decoctions of rowan, nettle, hawthorn, rosehip, tansy, strawberry.
- Vegetable and fruit juices - citrus, beet, carrot, tomato.
Traditional medicine by itself is not capable of ridding the body of plaques. Only in combination with official treatment methods and a complete lifestyle change.
Prognosis and prevention
Prognosis for atherosclerosis cannot be unambiguous and equivalent for everyone. The outcome of the disease can be influenced by factors such as compliance with the doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition and lifestyle, regularity of taking medications, genetic characteristics of the patient, his age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The most unfavorable prognosis is for patients who have been unable to give up smoking and other bad habits, as well as for those who move little, are overweight, have poor nutrition, or are regularly stressed (angry, irritated, offended, or worried about loved ones). This category of patients in 80% of cases is subject to severe disability with loss of self-care skills and interaction with the outside world. In addition, they have a high risk of death.

Prevention of the development and occurrence of complications of cerebral atherosclerosis consists of quitting smoking, moderate physical activity and a balanced diet. It is also necessary to exclude negative psycho-emotional reactions. Sometimes this requires a course of sedatives.
Video: “Live Healthy” program about cholesterol, diet
Cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain are the result of the influence of a number of factors on the human body, including genetics, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, etc. Such formations are considered extremely dangerous, since their separation from the wall of the vessel can lead to blocking its lumen and the development of ischemic stroke. Cerebral atherosclerosis is a common disorder in people over 40–45 years of age.

The appearance of plaques that narrow the lumens of blood vessels is due to hormonal changes that are observed in the body at this age. In addition, young people suffering from obesity are at particular risk of developing this pathological condition. According to statistics, cerebral atherosclerosis is approximately 2–3 times more likely to be detected in middle-aged men.
Preventive measures
Preventing cholesterol plaques is very important for maintaining health. Experience shows that people who lead a healthy lifestyle and maintain proper nutrition rarely suffer from such problems.
The following recommendations should be followed:
- Eliminate smoked and fried foods from your diet;
- Use the fractional feeding method;
- Eliminate fatty foods from your diet;
- Consume more fermented milk products;
- Add dried fruits, seafood and plant foods to your diet.
If the disease has already begun to manifest itself, then it is worth increasing the amount of fruits and vegetables in the daily diet. It is necessary to make your diet balanced, corresponding to the person’s height and weight.
Etiology of cholesterol plaques in brain vessels
The exact reasons for the development of this pathological condition still remain a mystery. A long-term study of patients with a similar problem made it possible to identify factors that may contribute to the appearance of cerebral atherosclerosis. A special risk group includes people who tend to systematically eat poorly. This leads not only to the accumulation of fatty deposits, but also to increased cholesterol levels.
This substance is the main building material for the formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels. Factors that help speed up this process include:
- inactive lifestyle;
- bad habits;
- viral infections;
- high blood pressure;
- metabolic disorders of various etiologies;
- endocrine diseases.
Poor ecology plays an important role in the formation of cholesterol plaques in the blood vessels of the human brain. Relatively recently, it was noticed that people who work in hazardous industries, as well as residents of large cities, are much more likely to encounter this problem than those who are engaged in agriculture and live in the countryside all year round.
Considerable attention is currently being paid to the genetic component. Many people suffering from cerebral atherosclerosis have relatives with a similar problem.
Therapy
First of all, it is worth remembering that prevention is the best method to combat the disease. Preventing atherosclerosis in most cases is easy - just follow a diet and an active lifestyle.
One of the most effective medical methods is extracorporeal hemocorrection. The patient's blood is taken, divided into components, and cholesterol is removed. Almost all cholesterol leaves the blood, which significantly reduces the risk of further development of the disease.
In severe cases, surgical correction is used: endarterectomy. Plaques and correction of arterial tortuosity are performed during open surgery.
Other operations are endovascular, which involve the installation of a stent to widen the stenotic areas.
Main manifestations of the disease
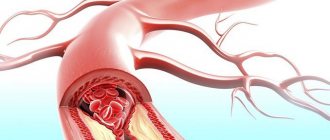
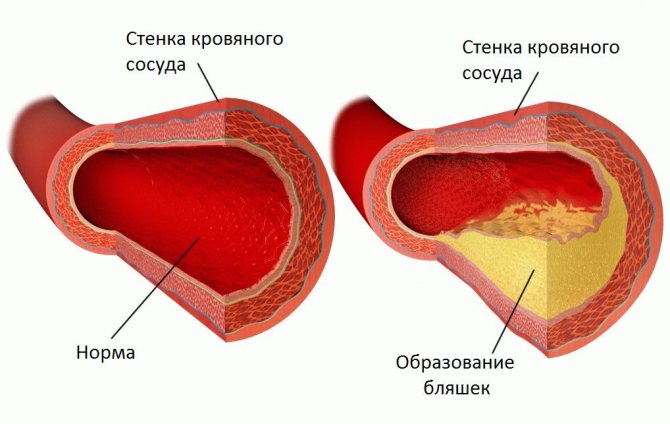
In this pathological condition, the entire brain suffers from cholesterol plaques. As such formations increase, they gradually narrow the lumen of the vessels, which helps slow blood flow.
In addition, they tend to spread throughout the vascular bed. At the attachment points of such formations, the vessel wall becomes deformed and thinned, which significantly increases the risk of rupture when blood pressure rises.
Disruption of normal blood circulation in the vessels of the brain leads to the fact that the cells do not receive the required amount of oxygen. Cholesterol plaques that completely or partially block the blood flow can affect large areas of this vital organ.
With atherosclerosis of this type, symptomatic manifestations increase slowly. Depending on the degree of circulatory impairment in the brain, people suffering from this pathological condition may complain of short-term or prolonged headaches.
Usually, unpleasant sensations do not have a clear localization. The intensity of pain can vary from mild to very severe. Among other things, people suffering from atherosclerosis often complain of dizziness and tinnitus. Similar symptoms often appear when lifting heavy objects, changing weather conditions, being in extreme heat, or making sudden movements.
In some cases, sleep disturbance is observed against the background of the development of this pathological condition. You may have frequent nightmares. With cerebral atherosclerosis, daytime drowsiness and nighttime insomnia may occur. In most cases, against the background of this pathological condition, there is a significant decrease in short-term and long-term memory, as well as rapid fatigue. Often people with cerebral atherosclerosis complain of a significant decrease in performance. In the future, a person may become overly irritable, suspicious, meticulous, etc.
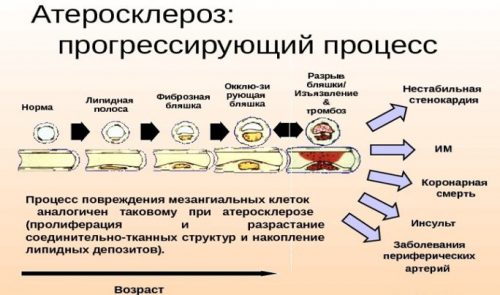
In especially severe cases, when the cerebellum is damaged, against the background of increasing hypoxia, impaired coordination of movements and slowness may appear. In addition, in some cases, people suffering from this pathological condition experience the appearance of unclear speech.
Medications
Treatment of atherosclerosis with medications requires compliance with all medical prescriptions. The dosage regimen and regimen are determined individually depending on the stage of the disease. The course of application is at least 14 days. The following groups of medications are used in the fight against vascular disease:
- statins;
- fibrates;
- ion exchange resins.

The main purpose of using drugs for medicinal purposes in vascular sclerosis is to reduce blood cholesterol levels. Medicines help reduce fat synthesis at the cellular level. With regular use of medications, accelerated removal of cholesterol metabolites from the body is observed.
Statins
The inclusion of statins in therapy helps cleanse blood vessels of cholesterol plaques. They must be taken by patients with high LDL (low-density lipoprotein) levels. Statin drugs prevent the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, which is considered a precursor to cholesterol. Regular use of statins can reduce the risk of sclerotic plaque formation.
Medicines in this group have contraindications. These include:
- severe liver pathologies;
- individual intolerance to certain components of medications;
- elevated levels of liver enzymes;
- any stage of pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- age restrictions (up to 12 years).
The presence of relative contraindications (epilepsy, kidney pathologies, chronic alcohol abuse, myalgia) requires adjustment of the dosage regimen and careful administration.
Fibrates
Treatment of vascular atherosclerosis with fibrates is based on correcting lipid metabolism. A group of medications intensively affects LDL, accelerating lipid metabolism. Fibrates can increase the activity of enzymes responsible for the breakdown of cholesterol. Fibrates are compounds derived from fibroic acid. They accelerate the removal of harmful cholesterol from the body.
With regular use of fibrates, the following is observed:
- improvement of the general condition of the arteries;
- increasing the elasticity of the walls;
- normalization of cholesterol levels.
Fibrates prevent the growth and spread of sclerotic plaques. They are taken orally before or during meals. It is strictly forbidden to give medications to children, pregnant and lactating women. Hypersensitive patients should take medications under the supervision of a specialist. Absolute contraindications include chronic alcoholism, renal and liver failure, chronic and acute pancreatitis.
Ion exchange resins
With the help of bile acid sequestrants (ion exchange resins), you can get rid of cholesterol plaques. Medicines in this group are hypolipidemic. With elevated cholesterol levels, the absorption of bile acids is reduced. The synthesis of additional receptors leads to normalization of lipid metabolism. Taking drugs in this category may be accompanied by problems with bowel movements and rectal prolapse.
Important information: Effective medications for the treatment of atherosclerosis of the lower extremity vessels
Possible complications
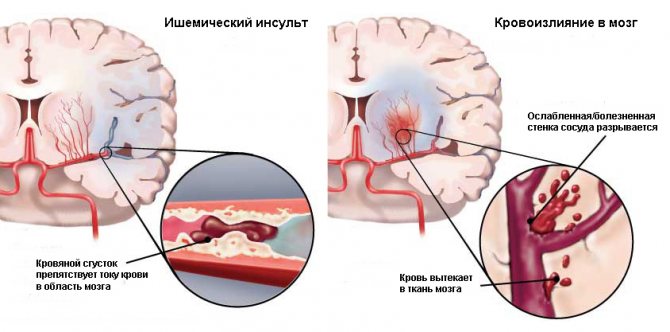
The gradual narrowing of the lumens of the blood vessels that supply brain tissue, in the absence of targeted treatment, can cause the development of severe disorders. The risk of developing hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke increases several times. These conditions can pose a danger to human life, and in addition are fraught with the development of paralysis, paresis, cognitive and mental disorders.
Ischemic stroke usually develops when atherosclerotic plaques in the blood vessels of the brain completely block the lumen, or such a formation breaks off and blocks blood flow. This leads to the fact that oxygen ceases to flow into a certain part of the brain, which first causes hypoxia and then tissue death.
Hemorrhagic stroke in cerebral atherosclerosis is observed in people who have arterial hypertension. In this case, the vessel, which is narrowed in a particular place due to the presence of a cholesterol plaque, cannot withstand the increased load and therefore ruptures.
Among other things, cerebral atherosclerosis significantly increases the risk of developing a transient ischemic attack. In addition, a person with multiple cholesterol plaques in the vessels located in the brain is likely to develop severe dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Operations for atherosclerosis
Any surgical intervention for atherosclerosis is a radical treatment method. The main goal is to normalize blood flow in the affected artery. Surgical intervention requires preparation; the operation itself is performed under general anesthesia. During the rehabilitation period, it is important to provide the patient with proper care. The following types of operations for vascular sclerosis are distinguished:
- bypass;
- angioplasty;
- endarterectomy.
The radical method is not suitable for all patients. It is prescribed in extreme cases, if drug treatment does not bring results.
Bypass surgery
There is no point in treating atherosclerosis at the fibrotic stage with medications. In this case, atherosclerotic plaques can be removed using arterial bypass surgery. During surgery, a shunt (an additional path) is created through which blood flow is restored to the affected area of the artery. Atherosclerotic fatty formations interfere with normal blood flow and lead to narrowing of the vascular lumen.
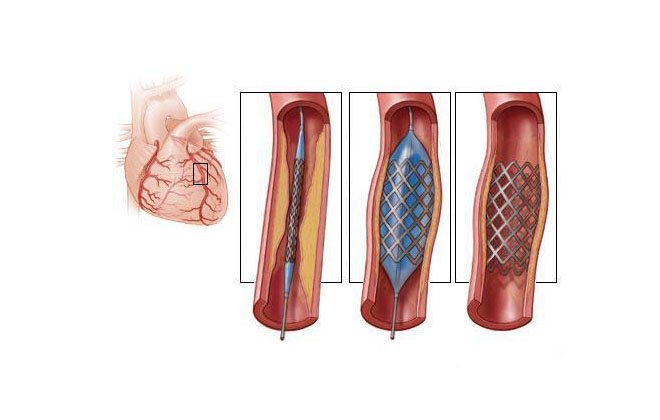
The saphenous vein or an artificial synthetic prosthesis can act as a shunt. The surgeon makes an incision in the affected area and sews the ends of the shunt to the artery. The stitches are removed after 6-8 days. Blood circulation is restored gradually, the safety electrode is removed after 9-10 days.
Angioplasty
In order to remove fatty streaks on the vascular walls and expand their lumen, the patient may be prescribed balloon angioplasty. During surgery, a balloon is inserted into the affected area of the artery, expanding the lumen. Instruments required for the operation:
- catheter;
- angiograph;
- conductor;
- stent;
- introducer.
The patient is placed on his back and connected to the monitors. A catheter is inserted into a vein, through which anesthesia or sedatives are released into the blood. A guidewire is inserted into the affected artery, followed by a balloon catheter. It swells, normalizing blood flow and increasing the vascular lumen. After the required time, the catheter is deflated and checked to see if blood flow has been restored. If necessary, angioplasty is supplemented with stenting - the stent expands the vessel, pressing against its walls. The introducer is removed last.
Endarterectomy
Cholesterol plaques in blood vessels can also be removed using endarterectomy. Reconstructive surgery involves removing the fatty strip from the artery. There are several types of operations:
- straight;
- eversion;
- carotid.
The direct type of surgery is considered classic. During the operation, the skin over the affected artery is cut and the vessel is isolated. The introduction of a shunt connecting the sections of the vessel is mandatory. The artery is incised and an instrument is inserted inside to cut off the fatty strip. A patch is applied to speed up healing. The shunt is removed last. Drainage is inserted into the wound and removed after 2-3 days.
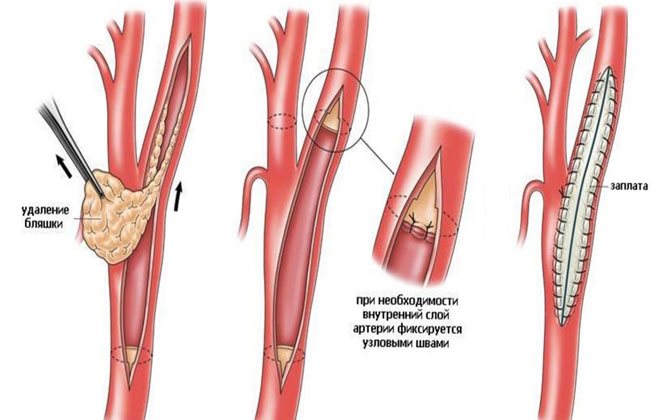
The eversion type of operation involves a transverse incision below the location of the fatty plaque in the affected artery. The vessel is turned inside out, the fatty strip is removed, after which the artery returns to its normal position. The wound is sutured and a patch is applied if necessary.
The carotid type of surgery is performed when the carotid artery is damaged. Through the incision, the fatty plaque is scraped out and the wound is sutured. For hypertension, cancer, heart failure, Alzheimer's disease and diabetes, surgery is not performed.
Diagnosis of cholesterol plaques in brain vessels
With this pathological condition, you should not self-medicate. If there are characteristic signs of cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain, you need to contact a specialist to conduct a series of studies. First of all, a lipid profile is performed. This study allows you to determine the risk of atherosclerotic plaque formation.
Often a necessary measure is to conduct color duplex scanning. This is a special type of ultrasound. Typically, this test can detect obstruction of blood flow in the lower extremities, aorta, and blood vessels leading to the brain. In addition, this type of ultrasound can detect cholesterol deposits in the blood vessels that supply the retina.
A triplex scan may be recommended. This is another type of ultrasound that allows you to examine the vessels that are located inside the skull. To clarify the location of cholesterol plaques on the walls, angiography is often performed.
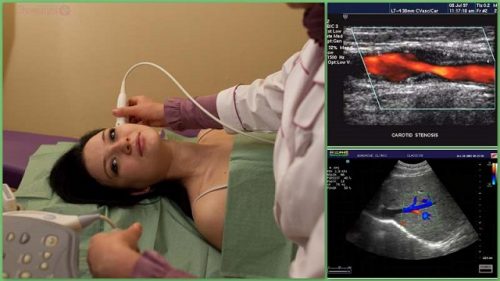
Among other things, doctors may prescribe a number of additional blood tests. After a comprehensive diagnosis, a specialist can determine the best treatment option, taking into account all the existing features.
Causes of exacerbations
Exacerbations occur against the background of sudden stress, metabolic disorders, sudden weight gain or starvation. Atherosclerosis is a systemic chronic disease, and any severe stress on the body can lead to a sharp exacerbation and general deterioration of the condition.
This could be moving to a different climate zone, a change in diet, a change in sleep patterns, a nervous shock, the onset of menopause, a sudden and abrupt start to training or a healthy lifestyle.
In some cases, the development of the disease moves upward from the cervical regions. Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease and affects the entire body, all veins and arteries. Cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain may remain invisible for a long time and appear during an exacerbation of the disease.
Symptoms of plaques in the brain
Any disruption of the blood supply to the brain produces behavioral reactions. A sharp change in character, constant fatigue, headaches and tinnitus most often indicate problems.
With more serious injuries, lesions of the central nervous system become noticeable to others, such as tremors in the arms and legs, impaired coordination of movements, awkwardness, and disruption of the vestibular apparatus.
Many people mistakenly perceive the characteristic manifestations of the disease as special personal characteristics and do not pay significant attention to the symptoms of atherosclerosis.
The main symptoms of cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain are as follows:
- Severe and prolonged headaches. Headache is always an alarming symptom, indicating problems with blood vessels. You cannot tolerate a headache; you must consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
- Drowsiness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, difficulty with intense mental activity, memory impairment, tinnitus. No, it's not just fatigue. If you detect at least two of the listed symptoms, immediately contact a neurologist and insist on an MRI of the brain. This is an expensive procedure, but only it can accurately diagnose problems. Cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain are clearly visible during diagnosis. Understanding the exact location and size of plaques in the head will allow doctors to choose the right treatment.
- Emotional changes. Increased irritability, loss of control over emotions, tearfulness, nervous tension. In this case, advertising advises drinking valerian in various modifications and eating vitamins. By doing this, you risk triggering the development of atherosclerosis. In case of changes in blood vessels, the appearance of plaques in the vessels of the brain, or vascular injuries, what is needed is not sedatives for the nervous system, but powerful vasodilators and blood thinners. At the initial stages of plaque formation, they are still soft and can be washed away by the bloodstream during its restoration. If there are large and dense plaques, when they break off they form a blood clot. Decisions about medications should be made by a qualified physician. Vitamins and mineral supplements can cause irreparable harm and contribute to the hardening of atherosclerotic deposits and calcification.
- The most obvious symptoms of plaques in the vessels of the brain can be seen on the inner and outer surfaces of the eyelids. The presence of wen, yellowish stripes under thin skin or on the surface of the mucous membrane is lipid deposits. Their presence on the eyelids is a symptom of atherosclerotic plaques in the brain. If you notice such changes, consult your doctor immediately. This is not a cosmetic problem like clogged pores and the formation of subcutaneous wen. When plaques on the eyelids are removed, they will soon form again. Metabolic and lipid metabolism disorders require systemic treatment.
Treatment
Atherosclerosis of the brain is a serious disease that requires comprehensive medical treatment.
To improve vascular health, you will certainly have to give up bad habits that cause vasoconstriction. This is alcoholism and nicotine addiction. To strengthen blood vessels, special medications and blood thinners are prescribed.
Plaques in the vessels of the brain and deposits of lipid tissue on the walls of blood vessels resemble fatty tissue in structure. More recently, treatment methods for “vascular obesity” have been practiced using special diets or even refusal of food.
It was assumed that plaques in the vessels of the brain from fasting treatment would dissolve and resolve without the slightest harm to the vessels. In fact, lipid tissues are more likely to be proteinaceous, that is, protein in nature.
When atherosclerotic plaques are destroyed, serious injury to worn-out vessels and destruction of their walls often occur. If the destruction of blood vessels occurs in the brain, hemorrhage automatically means a stroke. Extensive hemorrhage can lead to death.
Folk recipes
Treatment of atherosclerosis using traditional medicine is a gentle method. You can remove plaques using decoctions and infusions of garlic, onion peels and medicinal plants. The products have contraindications, which are identified by a specialist when interviewing the patient.
Treatment with garlic
Garlic tincture will help get rid of plaques in blood vessels. Garlic is combined with other vegetables and fruits. For atherosclerosis, use a remedy that contains lemons. Ascorbic acid in citrus fruits improves blood properties. Required ingredients:
- garlic - 200 g;
- lemon - 7-8 large fruits;
- water - 2.5 l.

The garlic is peeled and passed through a meat grinder. It is not necessary to zest the lemons, just remove the seeds. Cut the fruits into small bars and grind in a blender. The ingredients are mixed in a separate container and filled with water at room temperature. The container must be closed with a lid and stored in a dark place. The product is infused for 72-80 hours. Take 50-75 ml on an empty stomach before breakfast. The course of application is 30-60 days.
Dandelion roots
Treatment of vascular atherosclerosis with infusions based on medicinal plants requires long-term use of traditional medicine. Dandelion roots are poured with boiling water or alcohol. You can prepare them yourself or buy a ready-made mixture at the pharmacy. The leaves of the plant are added to the root.
Cooking algorithm:
- Dried parts of dandelion (root and leaves), taken in equal parts (1:1), are pre-crushed.
- The raw materials are poured into a glass jar and filled with 100 ml of vodka or alcohol.
- Close the jar with a nylon lid and put it in a dark place for 14 days.
The product is taken orally 20-25 drops before each meal. The course of treatment is 30-40 days. The infusion is not allowed to be given to children.
Onion peel
You can fight atherosclerosis with products based on onion peels. Onion peel has vasodilating properties, restores elasticity and strengthens blood vessels. The husk must be rubbed in the palms of your hands and filled with 250 ml of alcohol. The infusion is poured into a dark glass jar and stored in a dark place. The product is ready for use after 14 days. Take 15-20 drops orally before meals. The infusion is poured into vegetable (sunflower) oil. The course of application is 2 weeks. Treatment can be repeated after 10-12 days.

Avoiding cholesterol in food
The influence of cholesterol on the formation of atherosclerotic plaques is obvious. Under a microscope you can even see cholesterol crystals. The problem is that only a small portion of cholesterol enters the body through diet. In addition, entry into the gastrointestinal tract does not mean automatic penetration into the blood plasma.
Cholesterol is produced in the liver and from there enters directly into the blood. Restricting cholesterol in food will not bring significant positive results except in cases of obvious abuse.

For example, when eating only chicken yolks, an increase in cholesterol in the blood is natural. In experimental animals, atherosclerosis immediately develops. However, perhaps this was due to the excessive load of heavy food on the liver.