Definition of pathology
Anoxic damage to the tissues that form the brain is a pathology that is associated with oxygen deficiency, which determines the nature of damage to nerve cells. Oxygen is an essential component involved in maintaining brain functions. The brain mass makes up about 2% of the total body weight. At the same time, the brain consumes more than 20% of the oxygen entering the body through the respiratory organs.
Oxygen reserves are necessary for the accumulation of nutrients. The brain substance continues to function for 4-5 minutes without access to oxygen. After this period, children and adults experience anoxic damage to the tissues that form the brain. The longer oxygen starvation lasts, the higher the degree and greater the volume of damage to brain structures. Within 15 minutes of complete disruption of gas exchange, 95% of the nervous tissue of the central nervous system dies.
Classification of the disease
There are pathological conditions that lead to disruption of gas exchange in nerve structures. Hypoxemia is a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood, anoxia is a complete lack of oxygen in the tissue, anoxemia is a lack of oxygen in the blood. True anoxia and anoxemia are rarely observed. Typically, states of oxygen deficiency in medical practice are called hypoxia. It is important to distinguish between ischemia and hypoxia.
Ischemic processes occur against the background of deteriorating blood supply to parts of the brain. Impaired blood circulation is associated with a reduction in the volume of incoming oxygen and incomplete removal of metabolic products, which leads to the accumulation of toxins and aggravation of the pathology.
Hypoxic processes are associated with a decrease in the supply or absorption of oxygen. Hypoxia of the isolated area is compensated by protective mechanisms - increased blood flow. In contrast to rapidly progressing ischemic changes, ATP synthesis during hypoxia slows down gradually. Types of hypoxic damage to brain structures:
- Anoxic anoxia. Occurs due to a person’s stay at a high altitude relative to sea level. The air in the mountains is rarefied, which affects the body's activity. The pathology develops as a result of complete or incomplete suffocation, drowning, throttling (a decrease in gas pressure due to a narrowing of the passage channel), destruction (blockage) of the respiratory tract. The condition can be triggered by attacks of bronchial asthma or anaphylactic shock.
- Anemic anoxia. The pathology is associated with a reduced content of hemoglobin, which normally transports oxygen. Disorders may occur due to the inability of hemoglobin to bind to oxygen molecules.
- Ischemic anoxia. It occurs as a result of weakened blood flow in parts of the brain, which in turn is provoked by vascular pathologies or low blood pressure. It is the main cause of anoxic encephalopathy. Factors that may be involved in the pathogenesis include acute hypotension, hemorrhage in the brain structures, and cardiac arrest.
Cardiac arrest often occurs against the background of arrhythmia and is considered a significant risk factor for the development of anoxic damage to brain tissue. Anoxia of toxic etiology occurs when poisoned by chemicals that bind oxygen molecules. Potentially dangerous compounds include carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, cyanide, narcotic drugs, ethyl alcohol, and acetone.
Causes
Sometimes physiological hypoxia of brain areas develops as a result of intense mental activity. In contrast to pathological hypoxia, in the physiological form, the balance of gases is restored independently, and disturbances in brain function are temporary. A reduction in the volume of incoming oxygen occurs for various reasons:
- Heart failure.
- Diseases of the respiratory system.
- Electric shock.
- Birth injuries. Anoxic damage to brain tissue in newborns is almost always associated with birth trauma. Usually the condition is provoked by factors: malpresentation, entanglement of the umbilical cord, weak labor, premature birth or post-term pregnancy.
Damage to the brain of a hypoxic nature in the fetus occurs as a result of maternal circulatory disorders, placental abruption, and compression of the umbilical cord arteries feeding the fetus. Hypoxia in infants is detected as a result of intoxication, uterine bleeding, gestosis (toxicosis) suffered by the mother during gestation.
Anoxic damage to brain structures in newborns is provoked by factors such as apnea (short-term cessation of respiratory activity), congenital heart defects, sepsis and infectious diseases, and hemolytic disease. In early childhood, a common cause of hypoxia is the entry of foreign objects into the respiratory tract.
Damage to brain tissue due to severe disruption of gas exchange occurs as a result of injuries and pathologies that provoke terminal conditions requiring rehabilitation measures. Emergency methods of restoring the activity of organs and systems are used in the agonal (the last stage of dying, which is characterized by activation of compensatory mechanisms) period or at the stage of clinical death.
Typically, terminal conditions are provoked by severe tissue damage of a traumatic nature, heavy blood loss, shock, and suffocation. Resuscitation is impossible if clinical death occurred as a result of a long-term, chronic or acute disease, which led to irreparable changes in the morphological structure of tissues, gross, irreversible dysfunction of vital organs (brain, heart, lungs).
After resuscitation, a period of post-resuscitation illness begins. At this stage, pathological processes and conditions are possible - repeated cessation of breathing, cessation of heart activity, death of brain neurons. It is during this period that anoxic-type encephalopathy often develops, which is one of the common causes of death of a patient after rehabilitation therapy.
Pathogenesis is associated with edema and swelling of the brain matter, which is caused by acute hypoxia, increased permeability of vascular walls, and infiltration of physiological fluid into the brain tissue. Necrotic-ischemic processes lead to the death of neurons and irreversible changes in the morphological structure of the white matter.
Similar processes occurring in the cortical regions provoke brain death. If brain death occurs while the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are functioning, the death of a person occurs as an individual in society. The patient becomes unable to think. The progression of necrotic changes in the brain leads to the absence of reflex activity and the cessation of its bioelectrical activity. Total necrosis of the brain substance is a condition incompatible with life.
Anoxic brain damage in children
One of the most serious damage to brain structures is considered to be anoxic pathology, which is characteristic especially of newborns. Anoxic brain damage is hypoxic in nature, as a result of which there is a failure in ventilation, blood circulation, respiration and tissue metabolism.
Description of the disease
The problems of treating children with neurological pathologies are extremely relevant in our time.
This is directly related to the general decline in the birth rate, and in addition, to the increase in the number of various unfavorable factors that provoke damage to the children's nervous system.
Among other things, this is largely due to the fact that in the modern world, cases of the birth of unhealthy, and at the same time physiologically immature, children have become more frequent.
Very often, the main causes of anoxic brain damage are hypoxic and ischemic processes due to insufficient oxygen supply to nerve tissues.
In the ICD-10 system, such a diagnosis is encrypted in several sections at once. The closest in pathophysiology are code P21.9 (it implies neonatal anoxia) and G93.
1 (in this case we are talking about anoxic brain damage, not classified in other categories).
Unfortunately, medicine has not yet identified the exact mechanism of anoxic brain damage. True, the anatomical picture of this pathology is quite simple.
The fact is that the nervous tissue ceases to receive oxygen in sufficient quantities; against the background of this, a hypoxic ischemic process occurs, which, even over a short period of time, is detrimental to the structure of the brain.
In other words, each neuron, as it were, does not receive the required amount of oxygen during the blood supply. Neurons in children are not yet as developed as they are in adults, so their relationship with the brain is only at the stage of formation. With little supply to the cell, it simply ceases to function correctly, and at the same time changes morphologically and internally.
Accordingly, anoxia is called a morphological degenerative process that has an extremely detrimental effect on healthy tissue. Symptoms of anoxic brain damage in children are extremely difficult to tolerate, which often ends in death. Next, we will figure out what causes are the provoking factors for the occurrence of this disease in children and newborns.
A single root cause for the occurrence of anoxic brain damage has not yet been identified. But it is worth noting that there are a lot of provoking factors that can precede such a terrible phenomenon. These factors can interfere with normal blood supply, and in addition, the supply of the required amount of oxygen to the child’s brain:
- We are talking about cardiac arrest or suffocation.
- The impact of intoxication with chemicals, for example, is sometimes even influenced by dirty ecology. It is worth noting that the child’s body is very sensitive to the cleanliness of the environment.
- Various viruses along with neuroinfections.
- Receiving sunstroke (or heatstroke) and electric shock.
- Performing surgery on the heart or brain.
- The onset of coma or clinical death.
- The effect of prolonged arterial hypotension (i.e. decreased blood pressure).
Symptoms of this dangerous pathology
Anoxic brain damage in newborns is usually extremely severe. The fact is that even the onset of short-term hypoxia can cause an attack of suffocation along with convulsions and internal necrosis. General symptoms and signs of anoxia include:
- The child has epileptic seizures and convulsions.
- The presence of involuntary trembling of the limbs.
- The occurrence of sensory disturbances.
- The appearance of malfunctions in the functioning of the organs of hearing and vision.
- The occurrence of photophobia and increased photosensitivity.
- The appearance of paralysis and paresis of the limbs.
- The occurrence of asthma attacks and breathing problems.
- The appearance of a heart rhythm disturbance.
- The occurrence of headaches.
Diagnosis of this brain pathology
Diagnosis of anoxic brain damage in children involves, first of all, magnetic resonance and computed tomography. Electroencephalography may also be needed. Based on the results of all these procedures, the doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and predict the further course of the disease.
Treatment usually includes two successive stages. Firstly, it is the removal of the root causes of the disease along with the restoration of the body.
At this stage, it is necessary to understand what exactly caused anoxia in order to eliminate it.
And directly at the second stage, taking vitamins is required along with breathing exercises and taking vascular medications in order to restore the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, among other things.
How and where is anoxic brain damage treated?
Methods to combat this disease
So, as has already become clear, the treatment of the disease that has arisen usually involves several stages. In case of an acute illness, it is urgently necessary to completely eliminate the influence of factors leading to anoxia:
- The child requires sanitation of the respiratory tract.
- Removal of a foreign body.
- It is necessary to remove the patient from the area of exposure to carbon dioxide.
- Strangulation must be stopped.
- Preventing the effects of electric current.
At this stage, it is necessary to maintain normal blood circulation and oxygen supply; in some cases, artificial respiration devices are used.
In this case, support is provided at a level that should not allow irreversible changes in the brain.
If natural breathing is preserved, the child requires oxygen inhalation and transportation to the hospital. If breathing is ineffective, intubation will be required.
Restoration of vital functions
The next stage involves the restoration of vital functions. Thus, it is necessary to restore blood circulation, breathing and normal heart function. Further therapy is aimed at restoring all previously lost functions. For these purposes, neurometabolites are prescribed along with nootropics, vascular drugs, neuroprotectors and antioxidants.
Symptomatic therapy is aimed at eliminating the main manifestation of the consequences of anoxia. In case of severe headache, analgesics are used, and against the background of epileptic seizures, anticonvulsants are required, and so on.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/409194/anoksicheskoe-porajenie-golovnogo-mozga-u-detey
Definition of pathology
Anoxic damage to the tissues that form the brain is a pathology that is associated with oxygen deficiency, which determines the nature of damage to nerve cells.
Oxygen is an essential component involved in maintaining brain functions. The brain mass makes up about 2% of the total body weight.
At the same time, the brain consumes more than 20% of the oxygen entering the body through the respiratory organs.
Oxygen reserves are necessary for the accumulation of nutrients. The brain substance continues to function for 4-5 minutes without access to oxygen.
After this period, children and adults experience anoxic damage to the tissues that form the brain. The longer oxygen starvation lasts, the higher the degree and greater the volume of damage to brain structures.
Within 15 minutes of complete disruption of gas exchange, 95% of the nervous tissue of the central nervous system dies.
Classification of the disease
There are pathological conditions that lead to disruption of gas exchange in nerve structures.
Hypoxemia is a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood, anoxia is a complete lack of oxygen in the tissue, anoxemia is a lack of oxygen in the blood. True anoxia and anoxemia are rarely observed.
Typically, states of oxygen deficiency in medical practice are called hypoxia. It is important to distinguish between ischemia and hypoxia.
Ischemic processes occur against the background of deteriorating blood supply to parts of the brain. Impaired blood circulation is associated with a reduction in the volume of incoming oxygen and incomplete removal of metabolic products, which leads to the accumulation of toxins and aggravation of the pathology.
Hypoxic processes are associated with a decrease in the supply or absorption of oxygen. Hypoxia of the isolated area is compensated by protective mechanisms - increased blood flow. In contrast to rapidly progressing ischemic changes, ATP synthesis during hypoxia slows down gradually. Types of hypoxic damage to brain structures:
- Anoxic anoxia. Occurs due to a person’s stay at a high altitude relative to sea level. The air in the mountains is rarefied, which affects the body's activity. The pathology develops as a result of complete or incomplete suffocation, drowning, throttling (a decrease in gas pressure due to a narrowing of the passage channel), destruction (blockage) of the respiratory tract. The condition can be triggered by attacks of bronchial asthma or anaphylactic shock.
- Anemic anoxia. The pathology is associated with a reduced content of hemoglobin, which normally transports oxygen. Disorders may occur due to the inability of hemoglobin to bind to oxygen molecules.
- Ischemic anoxia. It occurs as a result of weakened blood flow in parts of the brain, which in turn is provoked by vascular pathologies or low blood pressure. It is the main cause of anoxic encephalopathy. Factors that may be involved in the pathogenesis include acute hypotension, hemorrhage in the brain structures, and cardiac arrest.
Cardiac arrest often occurs against the background of arrhythmia and is considered a significant risk factor for the development of anoxic damage to brain tissue. Anoxia of toxic etiology occurs when poisoned by chemicals that bind oxygen molecules. Potentially dangerous compounds include carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, cyanide, narcotic drugs, ethyl alcohol, and acetone.
Causes
Sometimes physiological hypoxia of brain areas develops as a result of intense mental activity. In contrast to pathological hypoxia, in the physiological form, the balance of gases is restored independently, and disturbances in brain function are temporary. A reduction in the volume of incoming oxygen occurs for various reasons:
- Heart failure.
- Diseases of the respiratory system.
- Electric shock.
- Birth injuries. Anoxic damage to brain tissue in newborns is almost always associated with birth trauma. Usually the condition is provoked by factors: malpresentation, entanglement of the umbilical cord, weak labor, premature birth or post-term pregnancy.
Damage to the brain of a hypoxic nature in the fetus occurs as a result of maternal circulatory disorders, placental abruption, and compression of the umbilical cord arteries feeding the fetus. Hypoxia in infants is detected as a result of intoxication, uterine bleeding, gestosis (toxicosis) suffered by the mother during gestation.
Anoxic damage to brain structures in newborns is provoked by factors such as apnea (short-term cessation of respiratory activity), congenital heart defects, sepsis and infectious diseases, and hemolytic disease. In early childhood, a common cause of hypoxia is the entry of foreign objects into the respiratory tract.
Damage to brain tissue due to severe disruption of gas exchange occurs as a result of injuries and pathologies that provoke terminal conditions requiring rehabilitation measures.
Emergency methods of restoring the activity of organs and systems are used in the agonal (the last stage of dying, which is characterized by activation of compensatory mechanisms) period or at the stage of clinical death.
Typically, terminal conditions are provoked by severe tissue damage of a traumatic nature, heavy blood loss, shock, and suffocation.
Resuscitation is impossible if clinical death occurred as a result of a long-term, chronic or acute disease, which led to irreparable changes in the morphological structure of tissues, gross, irreversible dysfunction of vital organs (brain, heart, lungs).
After resuscitation, a period of post-resuscitation illness begins. At this stage, pathological processes and conditions are possible - repeated cessation of breathing, cessation of heart activity, death of brain neurons. It is during this period that anoxic-type encephalopathy often develops, which is one of the common causes of death of a patient after rehabilitation therapy.
Pathogenesis is associated with edema and swelling of the brain matter, which is caused by acute hypoxia, increased permeability of vascular walls, and infiltration of physiological fluid into the brain tissue. Necrotic-ischemic processes lead to the death of neurons and irreversible changes in the morphological structure of the white matter.
Similar processes occurring in the cortical regions provoke brain death. If brain death occurs while the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are functioning, the death of a person occurs as an individual in society.
The patient becomes unable to think. The progression of necrotic changes in the brain leads to the absence of reflex activity and the cessation of its bioelectrical activity.
Total necrosis of the brain substance is a condition incompatible with life.
Symptoms
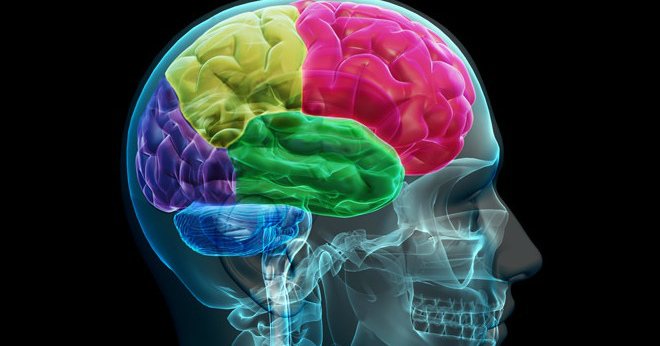
The clinical picture depends on the localization of the pathological process. Parts of the brain differ in different sensitivity to oxygen levels. Areas of increased sensitivity:
- Hippocampus (participates in the assimilation of new information).
- Basal ganglia (involved in controlling motor function).
- Cerebellum (regulates motor coordination).
- Cortical structures (responsible for cognitive abilities).
Signs of hypoxic damage depend on the etiology of the pathological process, the duration of the period of oxygen starvation, and the severity of changes in the brain tissue. Symptoms of anoxic damage to parts of the brain:
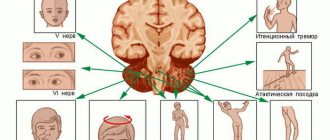
- Epileptic crises. Occurs with a frequency of about 33% of cases. Unlike ordinary epileptic seizures, they are often complex, partial (partial) in nature, accompanied by impaired consciousness and myoclonic twitching (sudden muscle spasms).
- Akinetic crises. They are characterized by akinesia (impossibility or decrease in the range of voluntary movements), muscle rigidity, tremor in the extremities, dysarthria (speech disorder), dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Tetraparesis (impaired motor function of the limbs), papaparesis (mild paralysis in both legs).
- Violation, depression of consciousness.
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities (deterioration of mental activity, memory).
The clinical picture varies significantly depending on the degree of neuronal damage. In a mild form, cognitive impairment may occur; in a severe form, brain death may occur.
Symptoms are variable, expanding due to specific signs that reflect the primary pathology that caused oxygen deficiency.
This could be a myocardial infarction, traumatic brain injury, or cessation of cardiac activity.
Source: https://golovnoj-mozg.ru/zabolevaniya/anoksicheskoe-porazhenie-golovnogo-mozga-u-detej
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the localization of the pathological process. Parts of the brain differ in different sensitivity to oxygen levels. Areas of increased sensitivity:
- Hippocampus (participates in the assimilation of new information).
- Basal ganglia (involved in controlling motor function).
- Cerebellum (regulates motor coordination).
- Cortical structures (responsible for cognitive abilities).
Signs of hypoxic damage depend on the etiology of the pathological process, the duration of the period of oxygen starvation, and the severity of changes in the brain tissue. Symptoms of anoxic damage to parts of the brain:
- Epileptic crises. Occurs with a frequency of about 33% of cases. Unlike ordinary epileptic seizures, they are often complex, partial (partial) in nature, accompanied by impaired consciousness and myoclonic twitching (sudden muscle spasms).
- Akinetic crises. They are characterized by akinesia (impossibility or decrease in the range of voluntary movements), muscle rigidity, tremor in the extremities, dysarthria (speech disorder), dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Tetraparesis (impaired motor function of the limbs), papaparesis (mild paralysis in both legs).
- Violation, depression of consciousness.
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities (deterioration of mental activity, memory).
The clinical picture varies significantly depending on the degree of neuronal damage. In a mild form, cognitive impairment may occur; in a severe form, brain death may occur. Symptoms are variable, expanding due to specific signs that reflect the primary pathology that caused oxygen deficiency. This could be a myocardial infarction, traumatic brain injury, or cessation of cardiac activity.
Treatment methods
Treatments for anoxia and life-threatening conditions include restoring a strong flow of adequately oxygenated blood to the brain. To this end, the cause of the lack of oxygen flow is determined and appropriate measures are taken:
- Removing foreign bodies from the respiratory tract.
- Removing the patient from the danger zone of carbon dioxide or electric shock.
- Stopping strangulation (loosening and removing parts of clothing from the neck - a tie, shirt collar, or other objects that impede blood flow).
If necessary, artificial (using devices) maintenance of gas exchange and cardiac activity is carried out. Correction of mild oxygen deficiency is carried out with the help of antihypoxic drugs and antioxidants.
Antihypoxants (Amtizol, Bemitil, Mexidol) alleviate the reactions of the body, which is experiencing an episode of oxygen starvation, and accelerate the process of cell recovery after hypoxia. Treatment of oxygen starvation in infants and adult patients is aimed at eliminating the causes of the pathological condition, taking into account the primary pathology that provoked the oxygenation disorder.
Anoxic damage to brain tissue is associated with a lack of oxygen. Impaired oxygenation can be due to various reasons. Treatment is carried out taking into account etiological factors and symptoms.

Anoxic brain damage is serious damage to organ structures. Pathology develops in infants. The disorders are hypoxic in nature. With the disease, disturbances in breathing, blood circulation and tissue metabolism are observed.
Treatment
Treatment of organic brain damage involves a long process, so the relatives of a sick adult or child need to devote more time to him, caring for him, and, if possible, tolerate his antics and negative mental states.
With timely detection of the lesion and proper therapy, the prognosis gradually improves.
If we talk about drug treatment, then you need to take sedatives, nootropics and vitamins.
Also, physiotherapy, therapeutic baths, and massages should not be neglected.
Author of the article: Neurologist of the highest category Tatyana Mikhailovna Shenyuk.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of pathology are not fully established. There are provoking factors that lead to the disease. Under the influence of these factors, circulatory disturbances and insufficient blood flow to the brain are observed.
The pathology appears in patients and develops against the background of cardiac arrest. The cause of the disease is suffocation. In newborns, the disease appears after drowning.
If a child’s body is exposed to toxic substances, this leads to poisoning. A polluted environment has a negative impact on a child's body. Anoxic brain damage occurs with neuroinfections and various viral lesions. In case of electric shock, the development of the disease is diagnosed.
If a child is diagnosed with clinical death or coma, this leads to the development of pathology. Low blood pressure over a long period of time leads to pathology.
The anoxic type of disease occurs against the background of various provoking factors that affect the brain.
Degrees and symptoms of the disease
Anoxic brain damage has three stages of development, according to which the development of symptoms is observed:
Hypoxic disorders are mild. In patients at this stage of the disease, neuro-reflex excitability increases. Diagnosed with the disease is decreased muscle tone. Reflexes may increase or decrease. Trembling in the extremities is noted in the pathology.
After a week, the symptoms of the disease go away on their own. Normalization of the child's condition is observed. In case of illness, the absence of gross neurological disorders is diagnosed.

With moderate severity of the lesion, severe symptoms are observed. The child's sucking and other reflexes are suppressed. The disease is accompanied by a decrease or increase in muscle tone, blue discoloration of the skin, and an increase in intracranial pressure. In case of illness at this stage, the occurrence of autonomic disorders is diagnosed.
The pathology is accompanied by diarrhea and constipation. This pathological process is accompanied by bradycardia or tachycardia. Some patients stop breathing due to pathology. As intracranial pressure increases, an increase in anxiety in the baby is diagnosed. Poor sleep, bulging fontanel, trembling limbs are diagnosed.

In some cases, convulsions are observed. With intensive treatment, the child's condition improves. it is impossible to eliminate neurological disorders. If the condition worsens, the baby falls into a coma.
When pregnancy is complicated, severe hypoxic disorders occur. In women, swelling, increased blood pressure, and the development of kidney disease are diagnosed. A newborn girl or boy has signs of developmental delay. With a difficult labor process, the situation worsens.
After birth, the baby is unable to breathe. A decrease in tone and reflexes is diagnosed, and blood circulation is impaired. In this form of the disease, urgent cardiopulmonary resuscitation is recommended. Otherwise, the chances of survival are reduced to zero.
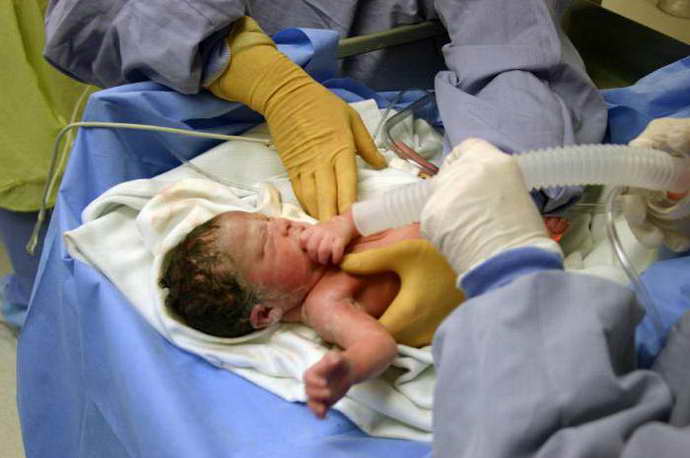
Anoxic brain damage - what is it?
Anoxic brain damage is serious damage to organ structures. Pathology develops in infants. The disorders are hypoxic in nature. With the disease, disturbances in breathing, blood circulation and tissue metabolism are observed.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of pathology are not fully established. There are provoking factors that lead to the disease. Under the influence of these factors, circulatory disturbances and insufficient blood flow to the brain are observed.
The pathology appears in patients and develops against the background of cardiac arrest. The cause of the disease is suffocation. In newborns, the disease appears after drowning.
If a child’s body is exposed to toxic substances, this leads to poisoning. A polluted environment has a negative impact on a child's body. Anoxic brain damage occurs with neuroinfections and various viral lesions. In case of electric shock, the development of the disease is diagnosed.
If a child is diagnosed with clinical death or coma, this leads to the development of pathology . Low blood pressure over a long period of time leads to pathology.
If the body of a newborn is exposed to electric current, then the little patient develops a disease. Surgery on the brain or heart leads to illness.
The anoxic type of disease occurs against the background of various provoking factors that affect the brain.
Degrees and symptoms of the disease
Anoxic brain damage has three stages of development, according to which the development of symptoms is observed:
Hypoxic disorders are mild . In patients at this stage of the disease, neuro-reflex excitability increases. Diagnosed with the disease is decreased muscle tone. Reflexes may increase or decrease. Trembling in the extremities is noted in the pathology.
After a week, the symptoms of the disease go away on their own. Normalization of the child's condition is observed. In case of illness, the absence of gross neurological disorders is diagnosed.
With moderate severity of the lesion, severe symptoms are observed . The child's sucking and other reflexes are suppressed. The disease is accompanied by a decrease or increase in muscle tone, blue discoloration of the skin, and an increase in intracranial pressure. In case of illness at this stage, the occurrence of autonomic disorders is diagnosed.
The pathology is accompanied by diarrhea and constipation. This pathological process is accompanied by bradycardia or tachycardia. Some patients stop breathing due to pathology. As intracranial pressure increases, an increase in anxiety in the baby is diagnosed. Poor sleep, bulging fontanel, trembling limbs are diagnosed.
In some cases, convulsions are observed. With intensive treatment, the child's condition improves. it is impossible to eliminate neurological disorders. If the condition worsens, the baby falls into a coma.
When pregnancy is complicated, severe hypoxic disorders occur . In women, swelling, increased blood pressure, and the development of kidney disease are diagnosed. A newborn girl or boy has signs of developmental delay. With a difficult labor process, the situation worsens.
After birth, the baby is unable to breathe. A decrease in tone and reflexes is diagnosed, and blood circulation is impaired. In this form of the disease, urgent cardiopulmonary resuscitation is recommended. Otherwise, the chances of survival are reduced to zero.
If the disease is particularly severe, intensive therapy is performed. The absence of a positive result is diagnosed within 1-2 weeks.
Features of treatment
Diagnosis of the acute form of the disease is carried out in accordance with the results of a survey of the patient himself or his relatives.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to use magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalogram, computed tomography, single-photon emission computed tomography.
During the diagnosis of the disease, evoked visual and auditory potentials are assessed.
Therapy of anoxic lesions is carried out using several techniques. If the pathology is acute, then the child is protected from the negative factors that led to the disease . Foreign objects are removed from the patient's respiratory tract, sanitation is carried out, exposure to electric current is prevented, and strangulation is stopped.
In order to maintain gas exchange and blood circulation at an optimal level, therapeutic techniques are recommended. To avoid pathological changes in the brain area, the child is connected to special equipment.
While breathing is maintained, the patient is treated in a hospital setting. In this case, oxygen is inhaled. If breathing stops, the patient is placed in an incubator.
At the next stage of therapy, it is recommended to normalize blood circulation and restore the functionality of the cardiovascular system. To restore brain function, treatment is carried out:
- Nootropics;
- Metabolites;
- Vascular drugs;
- Neuroprotectors;
- Antioxidants.
It is recommended to carry out symptomatic therapy, with the help of which the severe symptoms of the disease are eliminated. If the disease is accompanied by headaches, then their elimination is carried out with the use of analgesics. Anticonvulsants can help ease epileptic seizures . If the patient experiences muscle cramps, they are eliminated with Clonazepam.
After complete restoration of the blood circulation process in the brain, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures is recommended. Treatment is carried out using psychological correction, massages, and special exercises.
Anoxic brain damage is a serious pathological process that can lead to a number of serious complications. The disease develops in childhood under the influence of various provoking factors. In case of pathology, it is recommended to carry out urgent treatment, which is prescribed by the doctor in accordance with the characteristics of its development.
Source: https://nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/patologii-golovnogo-mozga/anoksicheskoe-porazhenie.html
Features of treatment
Diagnosis of the acute form of the disease is carried out in accordance with the results of a survey of the patient himself or his relatives. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to use magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalogram, computed tomography, single-photon emission computed tomography. During the diagnosis of the disease, evoked visual and auditory potentials are assessed.
Therapy of anoxic lesions is carried out using several techniques. If the pathology is acute, then the child is protected from the negative factors that led to the disease. Foreign objects are removed from the patient's respiratory tract, sanitation is carried out, exposure to electric current is prevented, and strangulation is stopped.
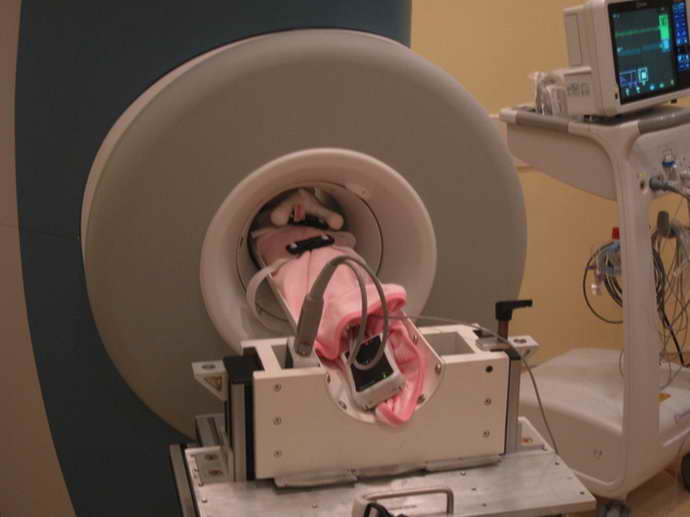
In order to maintain gas exchange and blood circulation at an optimal level, therapeutic techniques are recommended. To avoid pathological changes in the brain area, the child is connected to special equipment.
While breathing is maintained, the patient is treated in a hospital setting. In this case, oxygen is inhaled. If breathing stops, the patient is placed in an incubator.
At the next stage of therapy, it is recommended to normalize blood circulation and restore the functionality of the cardiovascular system. To restore brain function, treatment is carried out:
- Nootropics;
- Metabolites;
- Vascular drugs;
- Neuroprotectors;
- Antioxidants.
It is recommended to carry out symptomatic therapy, with the help of which the severe symptoms of the disease are eliminated. If the disease is accompanied by headaches, then their elimination is carried out with the use of analgesics. Anticonvulsants can help relieve epileptic seizures. If the patient experiences muscle cramps, they are eliminated with Clonazepam.
After complete restoration of the blood circulation process in the brain, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures is recommended. Treatment is carried out using psychological correction, massages, and special exercises.
IMPORTANT! To save an article to bookmarks, press: CTRL + D
DOCTOR, and get a FREE ANSWER, you can fill out a special form on OUR SITE, follow this link >>>
Anoxic brain damage in children: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
The problems of treating a child with neurological pathology are extremely relevant in our time. This is due to a general decline in the birth rate, an increase in the number of unfavorable factors that provoke damage to the nervous system, and an increased incidence of the birth of unhealthy, physiologically immature children.
Very often, the direct causes of brain damage are hypoxic-ischemic processes as a result of insufficient oxygen supply to the nervous tissue. In ICD-10, the diagnosis is encrypted in several sections. The closest in pathophysiology are codes P21.9 (neonatal anoxia) and G 93.1 (anoxic brain damage, not classified elsewhere).
Anoxic damage to the nervous system in children is caused by a lack of adequate oxygen supply to neurons . Under such conditions, the cell quickly changes its functional properties and is not able to function fully.
Subsequently, the morphology of neurons is also disrupted. Oxygen deficiency leads to cellular necrosis and/or apoptosis and forms foci of ischemia in the brain.
Symptoms of cerebral anoxia can be severe and fatal.
Neurons begin to die after only 4 minutes of acute anoxia. Under conditions of hypothermia, this time is extended to 20-30 minutes, and at high temperatures it is reduced to 120 seconds.
Etiology and pathogenesis
There are a number of unfavorable factors that can lead to the development of anoxic damage to the nervous system.
Even minimal deviations significantly disrupt the functioning of the brain due to the fact that they affect immature nervous tissue.
Subsequently, this may manifest itself as a neurological deficit, a slowdown in the rate of formation of cerebral zones and centers, and a delay in overall development. Prolonged anoxia leads to death or the formation of a vegetative state .
The root causes of anoxia may include acute thrombosis, suffocation, strangulation, drowning, electric shock, cardiac arrest, alcohol or drug intoxication, neuroinfections, as well as other factors that prevent the supply of oxygen to the brain. Separately, anoxic lesions of the nervous system of the perinatal period are distinguished. This is facilitated by:
- pathological course of pregnancy (somatic diseases of the mother, gestosis, threat of miscarriage, symptoms of qualitative and quantitative starvation, intoxication, general immaturity of the pregnant woman, etc.);
- intranatal (arising during childbirth) damaging factors. This includes symptoms of premature abruption, placenta previa, entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck, umbilical cord nodes, premature and late, rapid and protracted labor, weakness of labor;
- postnatal (postpartum) disorders. These include meconium aspiration, repeated apneas, cardiovascular defects, sepsis, and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
All of the above provocateurs cause the development of foci of ischemia. In parallel, as a compensatory reaction, the permeability of cerebral vessels increases. On the one hand, this reduces cerebral perfusion and aggravates ischemia, on the other, it serves as one of the mechanisms for the development of hypoxic-hemorrhagic lesions.
Due to it, the process of diapedetic impregnation of red blood cells begins through the altered vascular wall. In addition, under conditions of oxygen starvation, glucose utilization occurs along the anaerobic pathway with the formation of lactate. During perinatal anoxia, acid compounds irritate the digestive and respiratory centers of the brain stem.
During childbirth, this provokes premature passage of meconium and its aspiration into the child’s respiratory tract, which contributes to even greater hypoxia.
Morphologically, deviations are observed in the form of:
Classification
Depending on the predominant morphological result of the development of disorders, anoxic pathology can manifest itself in the form of cerebral ischemia, intracranial hemorrhages of hypoxic origin, and combined non-traumatic ischemic-hemorrhagic lesions of the central nervous system.
The mechanism of development of anoxia allows us to classify it into the following types:
- anoxic, formed as a result of the cessation of oxygen supply through the respiratory tract;
- anemic, occurring as a result of massive blood loss, vascular spasm, thrombosis;
- congestive, which is a consequence of cerebral circulation discirculation;
- metabolic – a manifestation of metabolic disorders.
In addition, there is acute anoxia, which develops suddenly, and a chronic form of pathology with a gradual increase in oxygen deficiency (hypoxia).
The duration of the decrease in oxygen supply determines the gradation of anoxia into mild (oxygen starvation for up to 80 seconds), moderate (up to 120 seconds) and severe (up to 240 seconds) forms. Such a division is quite arbitrary, since the severity of anoxic manifestations will depend on the ambient temperature, the age of the patient and the condition of the body itself.
Clinic
Clinical symptoms are primarily determined by the cause of anoxia and the duration of its effects. Acute anoxia is manifested by loss of consciousness, which may be accompanied by convulsive paroxysms. Subsequently, profound amnesia occurs. Severe and moderate forms of anoxia provoke persistent neurological disorders:
Severe anoxic lesions can lead to decortication syndrome - functional shutdown of the cerebral cortex, and the development of a vegetative state.
Diagnostics
Acute anoxia can be diagnosed based on the results of a survey of the patient himself, his relatives or nearby people. The doctor finds out the cause of this condition and, if possible, the duration of exposure to the traumatic factor. Additional diagnostic methods are:
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- electroencephalogram;
- single photon emission computed tomography;
- assessment of evoked auditory and visual potentials.
Methods to combat anoxia
Treatment of anoxic brain damage involves several stages. In case of acute pathology, it is necessary to urgently exclude the influence of the factor leading to anoxia:
- sanitize the respiratory tract;
- remove foreign body;
- remove the person from the area exposed to carbon dioxide;
- stop strangulation;
- prevent the effects of electric current.
At the same stage, blood circulation and gas exchange (artificial if necessary) are maintained at a level that does not allow irreversible changes in the brain. If breathing is maintained, oxygen inhalation and transportation to the hospital are required . If breathing is ineffective, intubation is necessary.
The next stage is to restore vital functions - restoring blood circulation, breathing, and adequate heart function.
Subsequent treatment is aimed at restoring lost functions. For this purpose the following is prescribed:
- neurometabolites;
- nootropics;
- vascular drugs;
- neuroprotectors;
- antioxidants.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at eliminating the main manifestations of the consequences of anoxia - analgesics are used for severe headaches, anticonvulsants are used for epileptic seizures, etc.
Additionally, after restoration of independent blood circulation, physiotherapeutic methods (hyperbaric oxygenation, darsonval, laser and magnetic therapy), physical therapy, massage, and psychological correction are used.
Oxygen deficiency is the basis for the development of various pathological symptoms in many diseases and critical conditions.
Anoxic brain damage is quite often observed in the clinic and is considered one of the central problems of medicine. Brain cells are the most sensitive to anoxia.
Studying various aspects of pathology can significantly improve the results of treatment of patients with anoxic damage to the nervous system.
Sholomova Elena Ilyinichna, neurologist
Rate this article:
Total: 120
4.25 120
Source: https://mozgius.ru/bolezni/nevrologiya/anoksicheskoe-porazhenie-golovnogo-mozga-u-detej.html
How does organic damage to the central nervous system manifest itself, what are its symptoms?
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. However, due to the fact that the defeat...
Organic damage to the central nervous system can be congenital or acquired. The cause of congenital pathology is diseases, stress suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy, her bad habits, and exposure to toxic and natural factors. This group also includes conditions that arose during childbirth and in the early postpartum period. Acquired ones occur after a stroke, trauma, cerebral infarction, infections, tumors.
The clinic will largely depend on the number, location of dead cells and the function they perform. Symptoms can vary. In adults, this is primarily paralysis (complete lack of movement) and paresis (decreased strength) in the limbs. Along with them, changes in coordination of movements, decreased vision and hearing, headaches, and dizziness may occur. A rather serious symptom indicating organic damage to the central nervous system is dysfunction of the pelvic organs (urinary and fecal incontinence).
Epileptic seizures, sleep disturbances, fatigue, irritability, and mental disorders are not excluded. Against this background, a decrease in immunity may also be observed.
In children, organic damage to the central nervous system, especially congenital, causes much more serious manifestations, and the consequences are more severe the earlier the damage to brain cells occurs. In young children, in addition to the above, serious developmental delays are observed:
- Speech. There is a late development of speech, a poor vocabulary, and in severe cases, a complete lack of speech skills: such children are able to pronounce only sounds and some single words
- Motor skills. Children with organic pathology of the central nervous system later begin to hold their heads, sit, and walk. Voluntary movements are impaired: difficulties in eating, playing, and self-care. With severe damage, there is a high probability that the child will remain recumbent for life.
- Psyche. An organic lesion of the central nervous system in a child is indicated by his poor performance in school and kindergarten. At the same time, problems such as memory impairment, developmental delay, intellectual disability (from a slight decrease in intelligence to debility, idiocy, mental retardation), defects in the perception of the surrounding world, new information, and the inability to learn may also arise.
Symptoms
As already mentioned, in children the symptoms of residual organic damage are observed immediately after birth, in some less pronounced, in others more, but this does not change the essence. Based on the baby’s behavior, the doctor may immediately suspect certain neurological problems, for example, tremors of the limbs, constant crying and restlessness, delay in certain movements, unhealthy facial expressions, tone disorders.
In adult patients, symptoms appear in the same order, only at a different level, that is, more vividly.
If the doctor suspects possible neurological problems in the baby, he can immediately send the mother and newborn for a neuroimaging procedure, neurosonography, or, in extreme cases, an MRI of the brain.
So, the clinical picture of residual organic damage to the brain and central nervous system consists of the following symptoms:
- external mental disorders - fatigue, moodiness, constant crying, anxiety, restlessness;
- rather rapid exhaustion of the body, this is visible not only through the baby’s food intake, but also by his weight - instead of gaining weight, some newborns stop in their development;
- mental instability, unhealthy behavior towards oneself and others - applies not only to children, but also to adults. A person may begin to hurt himself, and he also behaves inappropriately towards those close to him, turning against them in a very aggressive way;
- absent-mindedness, significant impairment of attention, lack of perseverance, sometimes increased activity of the limbs;
- apathy, indifference to everything that happens;
- encephalopathy;
- headaches and dizziness - especially if the frontal lobe of the brain is affected;
- disorders in the mental and emotional sphere - stress, irritability;
- insomnia, increased excitability even at night;
- disruption of the visual and auditory organs - in particular, with damage to the brain stem;
- impaired coordination of movements - with disorders in the cerebellum.
Organic damage to the brain and the entire central nervous system: from myths to reality
1. Place of pathology in the ICD 2. What is OPCNS? 3. Types of organic lesions 4. What cannot cause OPCNSL? 5. Clinic 6. Diagnosis 7. Treatment 8. Consequences
The main feature of our time is an accessible information space in which everyone can contribute. Medical sites on the Internet are often created by people who are vaguely related to medicine. And, when it comes to specific diagnoses, for example, diabetes mellitus or thrombophlebitis, you can glean useful knowledge from the article.
But when search engines try to find a problem or something unclear, knowledge is often lacking and confusion begins. This fully applies to such a topic as organic brain damage.
If you take a serious reference book on neurology and try to find a diagnosis such as organic damage to the central nervous system (that is, the brain and spinal cord), you will not find it. What is it? A passing disease or a more complex disorder leading to irreversible changes in the structure of the central nervous system in adults and children? Or is it a whole group of diseases? There are many questions, we will try to start from the position of official medicine.
Types of disease
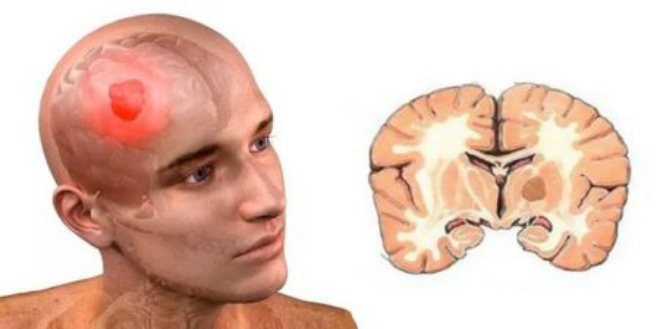
Organic brain lesions are usually easily identified through certain procedures, for example, magnetic resonance or computed tomography, neuroimaging, electroencephalography. Their peculiarity lies in visible damage to certain areas of the brain; damage to the frontal lobe and temporal regions is very often observed. Organic lesions include both foreign bodies present in the structure of the brain and problems with blood vessels and the general state of blood circulation.
So, medicine identifies several types of organic lesions of the central nervous system and brain:
- vascular lesions - most often occur in diseases such as atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, cardiovascular diseases localized in other areas of the body, and spinal osteochondrosis. In many cases, brain damage is caused by squeezing or damage to blood vessels, disturbances in the speed and rhythm of blood circulation, and a state of hypoxia—oxygen starvation of the brain;
- intoxication with chemicals, narcotic substances, alcoholic beverages. In case of poisoning, individual brain tissues and cells localized in a certain area are affected. The affected area may increase in size, very often poisoning leads to rapid dementia and other pathologies of the nervous system, as evidenced by external signs of neurological disorders of the body;
- foreign bodies are malignant or benign tumors that can increase in size, which contributes to damage to brain tissue and compression of blood vessels.
Thus, all types of organic brain lesions are closely intertwined - one type may in the future cause other signs of lesions and damage. That is why doctors recommend regular observation in the clinic, since a disease detected at an early stage, of course, provides a huge chance of salvation.
Separately, medicine distinguishes residual organic damage to the brain and central nervous system, which incorporates the symptoms and causes of all three of the above types.
Place of pathology in the ICD
Each case of any disease, both a functional disorder and a life-threatening condition, must be submitted to medical statistics and encrypted, receiving the ICD-10 code (International Classification of Diseases).
And the central nervous system can also suffer, while the damaging factors can be firmly established, the pathogenesis of the disorder, signs are known, and there is a final separate diagnosis. Therefore, even just on the basis of the official classification of diseases, it is possible to draw a conclusion and create a definition of what this mysterious pathology is.
Definition of OPCNS
Organic brain damage is a persistent disorder of both the structure of the brain and its individual functions, which manifests itself in various symptoms, is irreversible, and is based on morphological changes in the central nervous system.
This means that all brain diseases in adults and children, including young children, can be divided into two large groups:
- functional disorders. They do not have any morphological substrate. In simple words, this means that, despite complaints, according to all examination data, MRI, lumbar puncture and other research methods, no pathological changes are detected.
Such diseases, for example, include vegetative-vascular dystonia with diencephalic crises, or migraine headaches. Despite a thorough ultrasound of both the cerebral vessels and the vessels of the head and neck, no pathology may be detected. This is due to a sharp change in vascular tone, which leads to severe, throbbing pain with nausea and vomiting, against the background of normal test results.
We have given an example of organic damage to the central nervous system associated with stroke and trauma, occurring against the background of atherosclerosis in an elderly person. What diseases in general are associated with the subsequent appearance and development of organic disorders?
So what does this mean that the patient has an organic lesion? This is where the most interesting part of the story begins: purely formally, morphologically, from the point of view of pathological anatomy - yes. But, since the patient does not complain, neurologists do not give him any diagnosis. In addition, if these changes in the brain occurred quietly and asymptomatically, and one of the following diagnoses was not documented, then the basis for OPCNSL does not seem to exist.
- acute cerebrovascular accidents. These include ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, intracerebral hemorrhages, and, to a lesser extent, subarachnoid and subdural hematomas. If the hematoma is removed in a timely manner, everything can go away without a trace. In addition, there are disorders of the spinal and cerebrospinal circulation. Spinal stroke with consequences is also a sign of OPCN;
- Parkinson's disease, parkinsonism syndrome, hyperkinesis, damage to the basal ganglia: globus pallidus, putamen, substantia nigra, caudate and red nucleus (subcortical structures have amazing names);
In addition, systemic diseases of the whole organism, such as atherosclerosis, in its cerebral form, leading to dementia, and persistent cognitive disorders, which were previously called intellectual-mnestic, can lead to organic damage.
Peculiarities
The main feature of residual organic brain damage is that it is residual in nature after structural damage to brain and nerve tissue. Such a lesion is mainly characteristic of newly born babies, and they are at risk until the seventh day after birth. It's all about the pathological intrauterine processes that occurred during the perinatal period. This happens as follows: at the stage of fetal development, for some reason, a certain local area of the brain is affected, which after the birth of the child leads to neurological disorders and other pathologies.
You need to know that even the smallest area of damage can provoke various bodily anomalies in all internal systems. That is why the term residual organic brain damage is not used by doctors as the name of the disease. This concept is extremely general, which includes a lot of possible pathologies, dangerous symptoms and their development.
Despite the fact that newborn children often suffer from residual organic damage to the central nervous system and brain, nevertheless, there is a possibility of the disease occurring in adults. For example, damage to the frontal lobes or white matter due to poisoning, viral diseases, inflammatory processes.
The symptoms of residual organic damage in both adults and children depend on the degree of the disease, because each element in this organ is responsible for a certain set of body functions; accordingly, the more areas are affected, the more clearly various dangerous signs will manifest themselves.
Diagnostics
In recent years, neuroimaging techniques have been widely used: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, angiography with contrast, and myelography. Of course, diagnosing cognitive impairment and consequences from higher cortical functions involves, for example, testing for memory, attention, concentration, vocabulary, exhaustion, and so on. The results are also important for making the diagnosis of OPCNSL.
There is a certain paradox: OPCNS are persistent and lifelong. Timely and competent treatment of the cause, or underlying disease, can lead to the fact that the organic lesion simply does not form. On the other hand, if a massive focus of necrosis has already appeared in the brain due to a major stroke, then this change occurs immediately and forever, since it is determined by the pathogenesis of the disease itself.
If it is unknown whether there will be any consequences or not, then they are not talked about yet: therefore, while a person is sick, for example, with meningitis, and this underlying disease is being treated, then there is no diagnosis of OPCNSL, and there is nothing to treat.
Disability for organic pathology is granted, but this is decided not by the doctor, but by experts from the medical and social bureau. Currently, they are given a strict task of saving public funds, and everything is determined by the degree of dysfunction. Therefore, with arm paralysis, the chance of getting a group 3 disability is much higher than with complaints of memory loss.
The problem of diagnosing organic damage, as you can see, is not so simple and unambiguous. We can say that only one thing is known for sure: to avoid consequences, you need to immediately treat all diseases, and do not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Organic damage to the central nervous system: causes, diagnosis and treatment
The entire human nervous system can be divided into central and peripheral.
The central nervous system includes the spinal cord and brain. The spinal cord is located in the spinal column and is presented in the form of a cord that starts from the foramen magnum and ends in the lumbar region. The brain is located inside the skull. Organic damage to the central nervous system means that the human brain is defective. Doctors say that the first stage of this disease can be detected in 99% of people. This stage has no symptoms and does not require treatment. However, stage 2 is a more severe type of lesion, but stage 3 is a severe disease with serious deviations.
Brain damage can be congenital or acquired. Congenital pathologies develop if during pregnancy a woman:
- drank alcohol, drugs or smoked
- had the flu, ARVI
- took certain medications that have toxic effects
- experienced severe stress.
Other reasons include hereditary predisposition and too young age of the expectant mother. In addition, organic brain damage can occur due to improper management of childbirth and birth trauma.
Acquired damage to the central nervous system occurs after:
- stroke
- traumatic brain injuries
- alcohol and drug use
- infectious diseases (meningitis, meningoencephalitis)
In addition, damage can occur against the background of autoimmune diseases and tumor processes in the brain.
Symptoms of damage to the central nervous system:
- fast fatiguability
- urinary incontinence during the daytime
- lack of coordination
- decreased vision and hearing
- sleep disturbance
- easily distractible
- reduced immunity
Children with organic damage to the central nervous system are called mentally retarded. Their normal mental development is disrupted, active perception, speech, logical thinking and voluntary memory are inhibited. Such children are characterized by either increased excitability or inertia. They have difficulty developing interests and communicating with peers.
In addition, the child’s physical development also suffers. Such children have an irregular skull shape, their gross and fine motor skills are impaired, and difficulties arise in the formation of motor automatisms.
Diseases of the central nervous system caused by organic brain damage:
Oligophrenia is a disease characterized by mental retardation. Such children have reduced intelligence, their speech, motor skills, and emotions lag behind. The disease is often congenital or develops in the first year of life. These people are able to take care of themselves independently.
The human central nervous system is made up of neurons and their processes; when these neurons begin to deteriorate, dementia occurs. Dementia is a disease in which there is a loss of skills and knowledge and the inability to acquire new ones.
The disease is acquired in nature and occurs as a symptom of many diseases:
- Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia (55–60% of cases)
- vascular
- alcoholism
- brain tumors
- traumatic brain injury
There are 3 degrees of severity of dementia. At grade 1, the patient is capable of self-care, but social activity is already impaired. At degree 2, the patient requires self-monitoring. In grade 3, the patient does not understand what is being said to him and does not say anything himself. Incapable of self-care. Needs constant monitoring.
Reasons for origin
Medicine identifies four types of perinatal pathologies that increase the risk for the child due to the possible appearance of residual organic damage to the brain and central nervous system, which can manifest itself immediately after birth. These include:
- traumatic;
- hypoxic;
- dismetabolic;
- viral.
So, the traumatic nature of perinatal pathology is caused by falls of a pregnant woman, blows to the abdominal area. Thus, the child may experience congenital brain injuries associated with mechanical impact. Therefore, expectant mothers are advised to be careful when moving, to stay at home in bad weather, especially when it’s icy, and to eliminate as much as possible all the risks of external influences on the child.
Hypoxic damage can be caused by certain pathologies of the mother or her bad habits, in particular, smoking and drinking alcohol. At the same time, the child in the womb experiences oxygen deficiency, and even a short-term state of hypoxia can cause irreversible damage to the structures of the brain, since both the nervous system and the brain of the fetus are still only at the stage of their formation.
The dismetabolic nature of residual organic brain damage is a consequence of a malfunction in the endocrine system in the body of the expectant mother. Metabolic disorders are directly related to hypoxia - the fetus, even at the development stage, begins to receive less nutrients, which negatively affects the condition of the brain.
Finally, the viral or infectious nature of the lesion is nothing more than existing or severely suffered in the past infections and viruses of the expectant mother. This also includes intrauterine infections that enter through the woman’s vagina and directly affect the child’s body in the perinatal period.
Medical experts include the following parameters as risk factors that can cause residual organic damage to the central nervous system and brain:
- malfunction of genes, gene mutations;
- hereditary predisposition;
- influence of environmental quality. This includes possible air pollution with chemicals and toxins, radiation exposure above the norm, harmful emissions from cars, reduced levels of oxygen in the air, in general terms, poor and ruined ecology;
- toxic and chemical intoxication with vapors, gases, alcohol, drugs, other compounds, including certain medications;
- pregnancy pathologies, for example, too early birth, umbilical cord abnormalities, bleeding;
- infections and viruses that occurred during pregnancy or in the past;
- weakened immunity of women;
- unbalanced poor nutrition, lack of proteins, vitamins of all groups, minerals (calcium, potassium, magnesium), fiber. At the stage of pregnancy, any diets are prohibited; nutrition must be standardized, not necessarily regimented, the main thing is that the expectant mother gets all the substances she needs into her body. After all, you need to remember that by eating, the mother is already feeding not only herself, but also her baby;
- pathologies of the birth process itself - either rapid or too prolonged labor;
- chronic maternal diseases, mostly associated with damage to the nervous system, endocrine processes, cardiovascular diseases;
- frequent stress during pregnancy, mental and emotional instability of the expectant mother.