Drug treatment for Parkinson's disease
Contents
Medicines can replenish the reserves of the hormone dopamine, which ceases to be produced due to the death of brain cells. There are also medications that can slow down the process of death of brain neurons, resulting in prolongation of life and elimination of symptoms of the disease. Only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment for Parkinson's disease.
In the hospital, for the treatment of Parkinson's syndrome, drugs are prescribed that do not have side effects of the amantadine series (midantan, glutantan, PC-Merz), selegiline series (Yumex, deprenyl, Niar). They may also prescribe medications for Parkinson's disease with possible side effects - dopamine receptor agonists (pramipexole, piribedil, etc.), anticholinergics, drugs with levodopa (nakom, sinemet, madopar) and their long-acting analogues (nakom R, sinemet CR, madopar GSS).
In public clinics you can sometimes get free medications for Parkinson's disease.
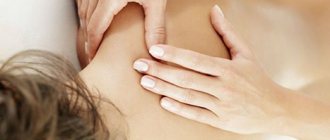
Massage
The purpose of massage for Parkinson's disease is to restore muscle mobility. It is recommended to conduct sessions every day or every other day. The average duration of the procedure is 40 minutes. Massage for Parkinson's disease includes the following techniques:
- stroking is a preparatory stage, promotes relaxation;
- rubbing - improves blood microcirculation in the soft tissue area, increases skin elasticity;
- kneading is a direct effect on the muscles.
Each technique alternates on different parts of the body. It is recommended to do the massage in the following order: back, chest, stomach, limbs.
How to alleviate the manifestation of the disease with natural ingredients
For paralysis, it is recommended to brew a decoction of crushed and dried lavender, oregano, snakehead, and purslane. You need to mix 1 tbsp. spoon of each of these herbs and pour a liter of boiling water, leave for 3 hours. Drink one third of a glass before meals three times a day.
To relieve trembling in the legs, you can make a tincture: 30 g of dry Lafanta inflorescences or 100 g of fresh ones should be poured with half a liter of vodka and left for 7 days in a dark place, shaking occasionally. Take the prepared tincture 3 times a day before meals, 25 g with honey.
Treatment of Parkinson's syndrome with folk remedies to improve the general condition of the body is possible with rosehip decoction. For cooking you need 2 tbsp. Boil tablespoons of rose hips in a glass of water for 20 minutes. You should drink this decoction half a glass 30 minutes before meals.
For brain function, it is useful to take a decoction of angelica - boil a tablespoon of angelica roots for 5 minutes in a glass of water. You need to drink this remedy half an hour before meals 3 times a day.
Therapy for severe parkinsonism
Now we will talk about methods of therapy that can help improve the condition of people who have not long-standing Parkinson's disease. Treatment with folk remedies described below will be effective if there are no associated ailments.
A decoction of oats can eliminate the symptoms of the disease. A glass of unhusked grains should be poured into an enamel bowl and filled with three liters of water. Then you need to put the container on the stove, bring to a boil and cook over low heat for an hour. The prepared decoction should be drunk instead of water. You should drink it within two days, and then prepare a new one. Treatment must be continued for three months.
If the acidity of the gastric juice is normal and there is no constipation, you can use freshly squeezed cherry juice or juice from spinach leaves. The drink must be prepared immediately before consumption. Drinking 1/3 cup of one juice or another two or three times a day will help alleviate Parkinson's disease.
Treatment with folk remedies for this disease also includes the use of propolis. You should chew it every day for a month and swallow saliva while doing so. In the first fifteen days, two to three grams of propolis are used daily, and in the next fifteen – one to one and a half grams.
Stronger medications must be used if there is advanced Parkinson's disease. Treatment with folk remedies described above may not be effective in this case. When other methods are ineffective, you can try using poisonous plants such as hemlock, fly agaric (mushroom), aconite, datura, belladonna, henbane.
Prevention and treatment of Parkinson's disease with a healthy lifestyle
The effect of drugs to treat the disease can be enhanced by proper nutrition and exercise. It is easier to achieve positive dynamics from a set of procedures. Food should contain the maximum amount of foods containing vitamins and microelements necessary for the brain and nerves. The diet must also include fruits, vegetables, herbs and garlic. Food should only be cooked boiled, steamed or stewed, without frying. It is good for the body to drink 2 liters of water, periodically drink linden tea.
To prevent the disease from overcoming itself, it is very important to remain physically active throughout your life. Performing exercise therapy helps you feel a surge of strength and energy, gives you vigor and the opportunity to live a full life. The physical therapy complex is prescribed to develop all muscle groups, so that over time, movements will no longer be constrained.
Physical exercise
1. Place your palms in front of your chest and rub them together forcefully (vertical motion) for 2 minutes.
2. Carefully massage the tips of your fingers and especially the tip of your index finger with the tips of the fingers of your other hand; perform the exercise either with your right or with your left hand.
In parkinsonism there is often muscular
, impaired coordination and balance. To combat these phenomena, it is imperative to engage in physical exercise. I recommend doing exercises with dumbbells, it’s much more effective than just waving your arms. Jump rope, do squats, adding one squat per day, if possible, do exercises, walk more, jog. Take a contrast shower if
allows - go to the bathhouse, just be sure to wear a knitted cap in the steam room: overheating the head can increase the tremor. An exercise bike is well suited: it allows you to accurately dose the load and exercise in any weather.
Try these exercises: sit on a chair, concentrate and try to get up as quickly as possible. Do the same on the bed from a lying position. Practice changing your body position on the bed.
However, don’t try to give yourself a big load right away. Start with your usual level of physical activity, and then gradually increase the intensity.
New developments and innovations in treatment
Medicine is constantly evolving, experts are conducting research in search of more and more effective and simple treatment methods. The latest news about Parkinson's treatment includes stem cell therapy, which is capable of producing dopamine in the body. Individually grown stem cells are injected into the patient intravenously or endolumbarally.
Among the new methods of treating Parkinson's syndrome, the Neumyvakin method is also proposed, according to which you need to rub the patient with a 3% peroxide solution and make 15-minute compresses on the affected areas of the body.
Russian scientists are also striving to make a breakthrough in medical capabilities and are trying to discover something new in the treatment of the disease. Recent developments include the RANC method. According to this method, the activity of the nerve centers of the brain responsible for the production of dopamine can be restored from the influence of severe stress.
Surgery
If drug treatment is ineffective, doctors resort to surgery. The following operations are prescribed:
- Stereotaxy. The method is based on the destruction of pathological zones using a gamma or cyber knife. Refers to radiofrequency electrosurgery. As a result, a targeted effect occurs on the affected areas of the brain. Stereotaxy is considered an effective method of combating Parkinson's disease.
- Electrical stimulation. The most popular technique among minimally invasive interventions. The essence of the operation is to implant a neurostimulator into the patient in the area under the collarbone.
- Gene surgery using stem cells. The operation is based on the transplantation of neurons into the brain.
Causes of the disease
The causes of this disease have not yet been definitively determined.
Medical research on this topic merely puts forward a number of theoretical assumptions.
They are, to one degree or another, responsible for the development of Parkinson’s disease:
- Presence of a history of traumatic brain injury. A concussion, especially a repeated one, can cause problems in its functioning.
- People suffering from atherosclerosis are at risk.
- The presence of inflammatory processes in brain tissue.
- Genetic pathologies that result in damage to brain neurons.
- Insufficient amount of vitamin D in the body, which may be due to lack of exposure to sunlight.
Due to age-related changes, the body’s ability to accumulate vitamin D due to solar radiation disappears. For this reason, older people need to diversify their diet with products containing it. - The hereditary factor also plays a big role. Most people with Parkinson's disease have relatives with the same condition.
- Poisoning with toxic substances that negatively affect brain neurons.
- The effect of free radicals on the body. By interacting with brain cells, they cause electron oxidation.
Why does Parkinson's disease occur? It is known that it affects mainly older people (over 50 years of age), but in a small percentage of patients it is detected at a relatively young age. Neither gender nor place of residence affects the incidence rate; the origin of the disease is still not fully understood. Among the identified factors are:
- Aging. The number of brain neurons decreases with age - according to statistics, approximately 8% are lost within 10 years of life. This indicator does not depend on the aging model, since symptoms of the disease can appear even during its normal course. However, the human brain has impressive compensation capabilities. Therefore, Parkinson's disease does not always occur in older people, but only in cases where the loss of neurons amounted to 80% of the total mass.
- Genetic predisposition. For a long time, scientists have been discussing the theory that Parkinson's disease is hereditary. Genetic disorders coupled with unfavorable environmental factors can lead to the development of this disease. Exposure to toxins triggers a mechanism of organic changes in the human brain. To date, it has been revealed that 28 chromosomal mutations are responsible for the disease. Recent studies have shown that it is possible to diagnose the presence of damaged genetic code in a fetus as early as 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Exposure to toxic substances. It has been proven that Parkinson's disease can be triggered by various chemical elements that trigger destructive processes in the neurons of the brain.
Parkinson's disease can also occur for other reasons, either separately or in combination. These include: vascular atherosclerosis, traumatic brain injuries (severe, repeated), circulatory disorders, viral infections that provoke chronic parkinsonism. Long-term use of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs that stop the production of dopamine can lead to the appearance of symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Therefore, before making a diagnosis, it is important to study the patient’s medical record and clarify what therapy he received.
Symptoms and signs
The first symptoms include the presence of tremor of one of the limbs at rest. Gradually, the disease begins to progress and symptoms increase.
When excited or restless, the patient's hands tremble or his head begins to shake. When trying to concentrate, the shaking may get worse.
In advanced situations, in addition to tremors of the head and limbs, trembling of the lips or eyelids and increased blinking may occur.
The main signs of Parkinson's disease include:
- slowness and stiffness in movements;
- freezing in an unchanged position for several tens of minutes;
- the gait becomes “shuffling”;
- mask effect on the face;
- monotonous and quiet speech without emotional coloring;
- muscle rigidity or increased tone;
- the patient, being in constant tension, becomes stooped. The joints of the limbs are always slightly bent;
- late stages of the disease are characterized by postural instability;
- vegetative disorders appear. The surface of the skin becomes more oily;
- there is increased salivation and sweating;
- There may be problems with bowel movements and urination.
In Parkinson's disease, the patient's intellectual abilities are rarely affected. Most often, patients retain the ability to think clearly.
However, with this disease, thinking abilities slow down, memory deteriorates, and it becomes more difficult for the patient to express his thoughts. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by a depletion of emotions and the development of depressive states.
Treatment with bee death
In the spring, when beekeepers are putting things in order in bee farms, ask them for a jar (3 liters) of dead bees. Dry them in the oven until they turn into dust when rubbed with your fingers, then grind all the bees into powder, which you then sift through a sieve. You will receive flour, which will need to be mixed with honey until smooth, similar in consistency to toothpaste.
Leave the mixture to mature for three days. After this time, take one to three teaspoons of the medicine with water every day after meals. The mixture contains a lot of silicon, which the body really needs in advanced stages of Parkinson's disease. Bee bees contain substances that thin the blood, so if you are prone to bleeding and have high blood pressure, you should take the medicine in minimal doses. You must continue taking it for at least three months.
Diagnostic standards
There is a certain difficulty in diagnosing Parkinson's disease at the earliest stage, since the symptoms may be similar to the manifestations of other diseases - diffuse Lewy body disease (a type of primary dementia), progressive supranuclear palsy, severe head injury, etc.
Diagnosis is made in three stages:
- examination and interview of the patient;
- laboratory research;
- instrumental studies.
Let's take a closer look at each of the above points. So, when a patient with suspected Parkinson's disease approaches, the symptoms of the disease should be recorded in his own words. Next, the specialist conducts a thorough survey, finding out how long ago the signs of the disease were discovered, whether their manifestation was sudden or gradual, and whether any of the patient’s family members have parkinsonism.
The doctor should also clarify whether the patient has had severe head injuries or contact with toxic substances, whether he is taking medications (if so, which ones), and whether he has problems swallowing. Based on the answers received, the specialist differentiates Parkinson's disease from other ailments with similar symptoms.
To make a preliminary diagnosis, it is necessary that at least two symptoms coincide with the clinical manifestations of the suspected disease. These include: muscle rigidity, unilateral tremors at rest, impoverished movements, instability of body balance. During the neurological examination, the patient must perform certain tasks on balance, muscle tone, and limb mobility.
In some cases, the patient may be prescribed a drug based on L-dopa to see how the body responds to it. The patient's condition will need to be monitored for some time. A persistent, significant response to a drug will support a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease.
It is very important that the doctor has enough experience to distinguish between neurological diseases with similar symptoms. In the early stages of Parkinson's disease, symptoms may be nonspecific. To help a specialist, use the following studies:
- blood test for the presence of cerruloplasmin and cuprum to exclude liver diseases and hormonal imbalance in the thyroid gland;
- urine test for copper to exclude the possibility of Wilson-Konovalov disease.
Two-photon emission tomography has shown high efficiency in determining parkinsonism. It makes it possible to confirm the diagnosis, even if the disease is in the preclinical stage. Electromyography is used to determine increased bioelectrical activity of muscle fibers; electroencephalography allows recording changes in brain activity.
Symptoms such as loss of balance when moving, rare blinking and poor facial expressions are additional confirmation of the diagnosed disease. If the patient is elderly, severe depression, low thyroid function, and other diseases that may lead to decreased movement should be ruled out before a definitive diagnosis is made.
When a patient or people from his close circle notice certain disturbances in behavior and movements, as a rule, they turn to a general practitioner.
Based on complaints and characteristic symptoms, the doctor assumes the development of Parkinson's disease.
Next, the patient receives a referral to a neurologist. The diagnosis is confirmed through a series of diagnostic procedures and clinical manifestations.
The neurological examination evaluates gait, coordination, and the performance of some simple manual tasks. Particular attention is paid to the functions of the human sense of smell.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are used:
- Blood collection for tests. This is necessary in order to assess the condition of the thyroid gland and liver.
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography. Helps to fully study the state of the brain and exclude the presence of tumor processes in it.
- Positron emission tomography.
Allows you to determine the reduced level of dopamine in the brain. This method is quite informative, but today it is not available in all medical institutions. - Efficacy of drugs. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed drugs that are used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease with dopamine. Some time after the start of therapy, their effect is assessed.
Parkinsonism and its main nosological forms
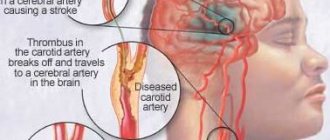
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic, steadily progressive disease of the central nervous system with degeneration of nigrostriatal neurons and dysfunction of the basal ganglia. It is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, which ranks third among the causes of death after cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
Parkinsonism has been known for a long time; the first reports of the treatment of similar disorders were made 1000-2500 BC.
The first clinical description belongs to the English physician James Parkinson, who published “An Essay on the Shaking Palsy” in 1817.
A detailed clinical analysis of the pathology complex was made in 1879 by the famous French neurologist Jean Martin Charcot.
Currently, the classification of parkinsonism includes: I. Parkinson's disease (it accounts for about 70-80% of all registered cases). II. Secondary (symptomatic) parkinsonism (about 15%) includes the following options: drug, toxic, post-hypoxic, encephalitic, traumatic, with volumetric processes, with hydrocephalus, vascular. III. Parkinsonism in various degenerative diseases with damage to the extrapyramidal system (“Parkinsonism-plus”, about 10%): multisystem atrophies (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar degeneration), progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski disease), corticobasal degeneration, dementia with Lewy bodies , parkinsonism-ALS-dementia, Wilson-Konovalov's disease, Huntington's disease (juvenile variant of Westphal), Fahr's disease (idiopathic calcification of the basal ganglia), Alzheimer's disease, others.
The main nosological form of parkinsonism is Parkinson's disease.
The worldwide prevalence of PD is approximately 1%.
The etiology of PD is unknown. Its pathogenesis is based on the degeneration of so-called dopaminergic neurons. PD is predominantly sporadic, but if close relatives have PD, the risk of developing it increases.
Clinical manifestations of PD occur when the amount of dopamine in the caudate nucleus and putamen decreases by at least 70%. Symptoms of PD develop gradually, initially affecting the limbs on one side. The clinical picture of PD is characterized by a combination of hypokinesia, rigidity, resting tremor, and postural disturbances.
Hypokinesia is manifested by a decrease in motor activity, slowness of movements, and a decrease in the amplitude of actions.
Rest tremor classically begins in the distal upper or lower extremity and resembles hand movements “counting coins or rolling pills.” Subsequently, the tremor involves the homolateral limb, lower jaw, and opposite limbs. Sometimes there is postural tremors of the hands.
Rigidity in PD is manifested by a plastic increase in muscle tone, often with a “cogwheel” phenomenon that increases during the study. Postural instability, which occurs in advanced stages of PD, is characterized by instability when turning, staggering when walking, and falls. In the future, patients are forced to use support devices.
In addition to motor disorders, non-motor manifestations develop in PD: neuropsychiatric disorders; sleep disorders; autonomic disorders; sensory disorders.
Depending on the predominance of a particular symptom in the clinical picture of PD, it is customary to distinguish the following clinical forms of the disease: trembling, akinetic, as well as mixed forms - akinetic-rigid and rigid-tremulous.
There are five degrees of severity of PD (stages of the disease according to Hoehn and Yahr): stage 1 - unilateral symptoms of parkinsonism; Stage 2 - bilateral symptoms of parkinsonism without postural disturbances; Stage 3 - moderate postural instability occurs; Stage 4 - significant limitation of motor activity, falls, but the ability to move independently is still retained; Stage 5 - the patient is bedridden or wheelchair-bound.
In the later stages of PD, the clinical picture changes; additional motor (motor fluctuations, drug-induced dyskinesias, walking disorders, falls, freezing and akinetic crises) and non-motor (vegetative, cognitive, neuropsychiatric) syndromes appear.
Patients may experience long periods of decompensation - from several days to several weeks, as well as akinetic crises - severe episodes of akinesia, accompanied by dysphagia, autonomic disorders, hyperthermia, oliguria, and confusion. The reasons for this may be: violation of the regimen for taking antiparkinsonian drugs, their complete o); taking drugs that block DA receptors (primarily antipsychotics); exacerbation of concomitant somatic diseases, stress; operations, injuries, dehydration of the body.
PD can be diagnosed with certainty only through autopsy. Clinical diagnosis of parkinsonism syndrome requires the presence of hypokinesia and at least one of the three main symptoms of parkinsonism: resting tremor, rigidity and postural instability.
An MRI of the brain is mandatory if the patient has parkinsonism syndrome. This study is primarily necessary to differentiate idiopathic Parkinson's disease and secondary parkinsonism, as well as “parkinsonism-plus”.
The main directions of treatment for PD are: 1. Pharmacotherapy. 2. Medical and social rehabilitation. 3. Therapeutic physical education (PT). 4. Neurosurgical treatment.
Pharmacotherapy for PD is aimed at normalizing the biochemical imbalance and requires constant use of medications, since when treatment is stopped, the symptoms of PD return to their original level.
At an early stage, treatment of PD consists of prescribing monotherapy followed by a transition to combination treatment.
In the early stages of the disease, it is generally accepted to prescribe DA receptor agonists and MAO-B inhibitors in the form of monotherapy or combination to patients under the age of 70 years.
In patients over 70 years of age, when the patient's life expectancy is shorter, and there are cognitive impairments, therapy can be started immediately with DOPA-containing drugs in the minimum effective dose, which is adjusted gradually.
Anticholinergics (Cyclodol, Akineton) are prescribed mainly at the early stage of PD - as monotherapy or in combination with other antiparkinsonian drugs; they predominantly affect resting tremor.
Currently, they are prescribed only to young patients with severe rest tremor and intact cognitive functions. The high incidence of side effects and low effectiveness compared to other groups significantly limit their use. Amantadine preparations (Midantan, PC-Merz).
Amantadines can be prescribed both at the initial stage as monotherapy and in combination with other antiparkinsonian drugs in the later stages of PD. The drugs are also effective in reducing the severity of dyskinesia caused by taking levodopa. The infusion form of amantadine sulfate (PC-Merz) is used in the treatment of decompensations and akinetic crises in PD.
Dopamine receptor agonists have the ability to directly stimulate DA receptors in the brain. Non-ergoline DA receptor agonists (Pronoran, Mirapex, Requip Modutab, Newpro) are widely used at all stages of PD. In addition to controlling movement disorders, they showed an antidepressant effect, which is very important, since the frequency of depressive syndrome in PD is quite high.
ADAR monotherapy in the early stages of the disease makes it possible to delay the prescription of levodopa drugs, as well as the development of motor fluctuations and drug-induced dyskinesias.
MAO type B inhibitors (Rasagiline). The administration of drugs in this group leads to an increase in the amount of dopamine in neurons. They are also believed to have a neuroprotective effect. They can be prescribed in the early stages as monotherapy, as well as in combination with levodopa.
COMT inhibitors. COMT inhibitors increase the bioavailability of levodopa by reducing the level of its inactive metabolites.
Peripherally acting COMT inhibitors do not cross the BBB and interfere with methylation of levodopa in the gastrointestinal tract and bloodstream. Thanks to this, they maintain the concentration of levodopa at a certain level. These drugs include entacapone.
The combination of entacapone with levodopa drugs can reduce the daily dose of DOPA-containing drug by 15–30%.
It is prescribed only in combination with levodopa drugs (Stalevo), since when prescribed as monotherapy it does not have an independent antiparkinsonian effect.
Levodopa preparations (Madopar, Nacom, Tremonorm, Tidomet-forte, Duellin, Sindopa). Dopamine does not cross the BBB, so a metabolic precursor of dopamine, levodopa, has been proposed as a drug, which crosses the BBB and is metabolized into dopamine in the brain. Today, levodopa drugs are the most effective drugs, the “gold standard”, used for the treatment of PD. However, they do not stop the progression of PD. Moreover, after an average of 5 years of using DOPA-containing drugs in patients with PD, their effect decreases, motor fluctuations and drug-induced dyskinesias appear.
The timing of treatment with levodopa depends on the severity and rate of progression of the disease, the professional activity of the patient, and family and household status. In general, it is necessary to prescribe drugs from this group when there are severe motor disorders that cannot be relieved by other antiparkinsonian drugs.
Neurosurgical treatment.
A decrease in the effectiveness of pharmacotherapy, the appearance of motor fluctuations and drug-induced dyskinesias are indications for the use of neurosurgical treatment, which over the past two decades has firmly taken its place in the algorithm for the management of patients with PD. Currently, three types of neurosurgical interventions are used for PD: stereotactic destructive methods (ventrolateral thalamotomy, pallidotomy, subthalamotomy and their combination), stimulation methods (implantation of electrodes into subcortical structures followed by chronic electrical stimulation) and intracerebral transplantation of dopaminergic neurons of the mesencephalon of the human embryo, effectiveness which continues to be studied.
The most modern method of surgical treatment of PD is deep electrical stimulation of the brain. The DBS procedure consists of implanting electrodes with 4 contacts into target areas within the subcortical formations of the brain; The electrodes are connected to a stimulator implanted under the skin, which delivers high-frequency electrical impulses to the stimulated nucleus.
Medical and social rehabilitation.
The high degree of disability with steadily progressing PD, the socio-economic losses suffered by society necessitate the creation of a system of medical and social rehabilitation, which should include dispensary observation of patients; creating schools for patients and their relatives, conducting training programs and psychotherapeutic classes, creating public organizations and support groups. Exercise therapy is of great importance, which can be selected individually depending on the severity of the disease in a particular patient, exercise therapy classes in groups, dance therapy, as well as occupational therapy and physiotherapy.
Literature: 1. Shtok V.N., Diagnosis and treatment of extrapyramidal disorders. - M., 2000. - P. 138. 2. Shtok V. N., Fedorova N. V. Treatment of parkinsonism. - M., 1997. - 194 p. 3. Yakhno N. N. Modern approaches to drug treatment of Parkinson’s disease // Clinical pharmacology and therapy. - 1994. - No. 3-4. - P. 92 - 97. 4. Levin O.S., Fedorova N.V., Parkinson’s disease. - M., - 2012. 5. N.V. Fedorova, I.P. Chigir, Parkinson's disease - Attending physician - 2005. -№8.- p.26-28.
What to do and how to treat: where and which doctor treats an illness in an elderly person
Therapeutic measures for Parkinson's disease, which progresses rather slowly but steadily, consist of the following principles:
- Elimination of present symptoms and reduction of its manifestations.
- Elimination of the appearance of new symptoms and progression of the disease.
- Improving the quality of human life and his general condition.
The main principle of treatment is an integrated approach.
There is a simultaneous impact on all components of the disease in any possible way.
Despite the fact that the main method of treatment is medication. In some situations, therapy is carried out without the use of drugs.
How to remove or reduce tremors in Parkinson's disease? The main treatment method for Parkinson's disease. Most of the symptoms of this disease occur due to decreased dopamine levels.
Therefore, patients are prescribed medications that increase the level of this hormone, stimulating its production, or imitate its effect.
Taking dopamine does not bring a positive effect because it does not reach the brain cells.
Medications are selected individually to influence the mechanism of the disease itself and relieve symptoms.
To treat Parkinson's disease, groups of medications are used, which are presented in the table below.
| Group | Drugs | Action | Side effects |
| Levodopa preparations | Hexal, Senemet, Levocarb, Madopar, Nakom | In the body, the active substance is transformed into dopamine and replenishes its deficiency. In addition to levodopa, they contain cardidopa and benserazide, which increase the effect of levodopa. | The use of drugs from this group may be accompanied by vomiting and nausea, abdominal pain, hypotension, increased psychomotor agitation, dilated pupils, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract and other side effects. As a rule, levodopa is well tolerated by patients |
| Amantadins | Gludantan, Amantin, Neomidantan, Midantan | Helps maintain the required concentration of dopamine | Their use may be accompanied by headaches, dizziness, nausea, anxiety, visual hallucinations, hypotension and related symptoms |
| Dopamine receptor agonists | Pronoran, Cabergoline, Bromocriptine, Pergolide, Pramipexole | The action is to stimulate dopamine receptors | Nausea, swelling, sleep disturbances, visual hallucinations |
| Monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors | Segan, Yumex, Selegiline | Reduce the breakdown of dopamine, which helps maintain its concentration | Use may be accompanied by decreased appetite, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, anxiety and insomnia. The risk of side effects is minimal |
| Anticholinergic | Akineton, Parkopan, Cyclodol, Cogentin | Help relieve tremors. Restores the balance of dopamine and acetylcholine | Stopping their use is accompanied by withdrawal syndrome. They are addictive. Their use may be accompanied by: dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, increased intraocular pressure, increased heart rate, and impaired excretory functions. Used quite rarely |
| Kakhetol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors | Entacapon, Tolcapon | Helps block enzymes that destroy levodopa and thereby prolong its therapeutic effect | Dyskinesia, insomnia, digestive disorders, loss of appetite. Withdrawal of drugs or a sharp reduction in dosage is accompanied by withdrawal syndrome |
Indicated in advanced conditions or when drug treatment does not bring the desired result.
Through surgical intervention, symptoms that have a negative impact on a person’s quality of life are eliminated: muscle stiffness, uncontrollable trembling of the limbs, difficulty moving.
There are several types of surgeries that are indicated for Parkinson's disease:
- Deep brain stimulation. An electrode is inserted inside the brain, and a control device is inserted into the upper part of the chest, which are connected to each other using a thin wire under the skin. The electrical impulses sent by the neurostimulator interfere with the activity of the electrical signals, causing symptoms to develop. This intervention is effective in patients who respond positively to levodopa treatment.
- Thalamotopia. The operation destroys the thalamus, a tiny part of the brain. This intervention effectively eliminates tremors that cannot be treated with medication. Unfortunately, this procedure does not solve other problems.
- Subalamotomy. Surgical destruction of the subthalamus.
- Pallidotomy. Damage to a small part of the brain that is responsible for excessive motor activity in patients with this disease.
Alternative medicine has been used with great success in treating this disease. Medicinal herbs are often used: hemlock, oak bark, sagan-dail grass.
In recent years, the method of Academician Neumyvakin using hydrogen peroxide has been widely used.
He claims that most neurotic disorders arise due to a lack of oxygen in the tissues. Peroxide, penetrating into the bloodstream, turns into water and O2.
He advises using it for compresses and rubbing in a 1:1 concentration with water.
Research conducted by reputable scientists in Israel has shown that smoking cannabis helps relieve symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease. For this reason, the production of raw materials was legalized for therapeutic purposes back in 2011.
Hardware technique
Recently, the use of Diamag Almag 3 physiotherapy devices has received good reviews.
They are generators of low-frequency magnetic pulses. The device block is fixed on the head. It works from the network.
Its use is to stimulate cerebral circulation, normalize the activity of the cardiovascular system, and reduce muscle tone.
The result of treatment is to improve a person’s quality of life and stop the progression of Parkinson’s disease. It is quite suitable for use at home.
Almag 1 is used by attaching to problem areas of the body. It acts directly in the place where it works using electromagnetic pulses.
The positive effects of using Almag 1 include increased blood circulation and normalization of metabolic processes in tissues.
The best results will be obtained from the combined use of both types of devices. Before starting treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Daily routine, physical therapy and home procedures
Patients are often bothered by insomnia; they may wake up several times a night and wander around the house in a half-asleep state, bumping into things and risking injury. Therefore, it is necessary, firstly, to create the most comfortable sleeping environment for a person suffering from Parkinson’s disease, and secondly, to arrange his bedroom in a place where you will immediately hear the noise and be able to come to the rescue.
Therapeutic baths have an excellent warming and relaxing effect. It is these procedures that have the most beneficial effect on the well-being and mood of those suffering from Parkinson's disease, since hot water and the state of immersion relieve muscle spasms, reduce tremors and simply bring pleasure.
It is recommended to add decoctions of medicinal herbs to the water to enhance the positive effect of the procedure. Thyme, chamomile, lavender, linden, sage, and St. John's wort are best suited. In fact, a bath for patients is prepared according to the same principle as for restless infants with prickly heat, since with Parkinson's disease dry skin and severe nervous excitability are observed.
- Sit on a chair, legs together, hands on your knees. Raise your shins one at a time so that your leg is parallel to the floor and remains pressed against the knee of the other leg. Repeat the exercise 10-20 times.
- Sitting on a chair in the same position, tilt your body forward 45 ° C, arch your back, then straighten completely, moving your shoulders back, and return to the starting position. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Stand at the back of a chair or bed and grasp it firmly with your hands. Slowly rise up on your toes and lower down. Repeat 10-20 times.
- A great exercise for your hands: alternately touch your thumb to the pads of the other four fingers, trying to gradually increase the pace. It can be performed several times a day in any environment, 10-20 times.
- To avoid the frozen facial expression characteristic of Parkinson's disease, you need to train your facial expressions: alternately raise your eyebrows and open your mouth, feigning extreme surprise, and then frown and purse your lips as if you are very angry. Repeat the same as the previous exercise, whenever possible, 10-20 times.
- While standing or sitting, place your hands on your shoulders and turn your whole body first to the left, then to the right, slightly straining as you do so. Repeat 10 times.
- Stand with your back to the wall and try to press your whole body into it, from the back of your head to your heels, count to five and relax. Repeat 10-20 times.
You need to do exercises every day, and several times a week it would be good to visit the pool or dance studio, depending on the age and condition of the patient. If this is a very elderly and frail person, he needs to demonstrate the exercises by personal example, since he himself will not remember them, and will not want to do them.
Modern methods of rehabilitation
Absolutely all patients who suffer from Parkinson's disease require rehabilitation. Programs are selected individually in each specific case for all patients.
The measures are aimed at correcting movement disorders, including restoring fine motor skills of the hands, as well as preventing side effects of treatment for Parkinson’s disease.
All patients are given a physical therapy program with a specific set of simple exercises. Most of them are aimed at maintaining coordination.
In especially advanced cases, robotic simulators with biological feedback are used.
The principles of successful rehabilitation include systematic training, as well as guidance of the process by an experienced instructor.
How was the disease treated in the old days?
In the old days, people diagnosed with Parkinson's disease were given very unusual treatments. They underwent a rite of purification, accompanied by reading in church, anointing and communion. Before this, a person had to observe strict fasting for several days; some were allowed to limit themselves to a fast diet.
After such events, traditional methods of treating Parkinson's disease were put into use. The person was bathed in potions, given medicinal teas, and fumigated with the smoke of medicinal herbs. The patient was given holy water to drink and the body was washed with it. They did this until the unfortunate illness left the body.
Nowadays, most of these rituals have already been forgotten and are not used. However, the practice of various purifications is still encouraged. This is especially true when a person is diagnosed with Parkinson's disease. Treatment with folk remedies for this disease gives good results. Let's talk about the methods used in more detail.
Nursing care for patients at home: clinical recommendations
Caring for a patient who is able to care for himself or herself is not required.
In this case, it is only necessary to monitor his compliance with the doctor’s prescriptions.
In advanced cases, it is necessary to constantly have a sensitive, attentive and calm person nearby who will ensure the patient’s vital functions and provide him with medical and physical assistance.
It is advisable for a relative or qualified healthcare professional to fill this role.