/rak-mozga/
Tumors of the pineal gland (epiphysis)
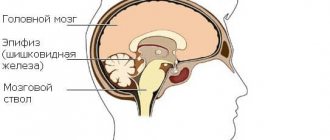
The pineal gland (epiphysis) is an organ that performs an endocrine function. The gland consists of neuronal cells (pinocytes) associated with light-sensitive cells in the retina. The pineal gland is responsible for memory, curiosity, aggressiveness, and sexual desire.
A tumor of the pineal gland, regardless of the degree of malignancy, requires urgent treatment. Due to compression of brain structures, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted (manifested by symptoms such as severe headaches combined with nausea and vomiting), other focal neurological manifestations are observed: paralysis of upward movements of the eyeballs, impaired coordination of movements and walking, tremor and hypotension ( as a result of damage to the cerebellum). An important symptom for correct diagnosis is early puberty in children, caused by an effect on the inhibitory function of the hypothalamus.
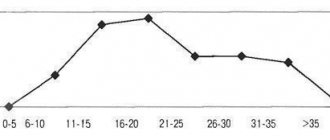
Tumors of the pineal gland are uncommon and affect people mainly in adolescence (13-20 years)
Peculiarities
A benign tumor develops in the pineal region—the epiphysis. This area is located in the deep layers of the brain; the full range of its functions is not fully defined. When the pineal gland is damaged by a cyst, the outflow of hormones responsible for the cycle of sleep and wakefulness and puberty changes.
The outflow of hormones responsible for the cycle of sleep and wakefulness and puberty changes.
A cavity with liquid contents is rarely identified during a routine visit to a therapist. This usually occurs during a comprehensive examination for the presence of other pathologies.
Sometimes a cyst in the pineal region of the brain forms before birth. The patient can live with it all his life, sometimes experiencing minor symptoms.
Classification of pineal tumors
- pineocytoma (pinealocytoma) is a slow-growing tumor that consists of mature pinealocytes. It is observed in approximately 45% of patients with tumors of the pineal gland. Develops at the age of 25-30 years equally often in men and women.
- pineoblastoma is a high-grade tumor, an embryonic tumor with poor differentiation, which has many common features with medulloblastoma. Accounts for about 45% of all pineal gland tumors. Has a tendency to metastasis. It is detected mainly in adolescence (childhood), although it is very rare in adults.
- Tumor of the pineal gland parenchyma is characterized by the least predictable course. They are more often observed in adults and account for only 10% of all tumors of the pineal gland.
Causes of the disease
- Blockage of the channel through which endocrine secretions are removed. The outflow of melatonin is disrupted, which leads to its constant accumulation. This process often occurs as a result of various injuries. The flow is slow.
- Helminthiasis is the cause of a parasitic cyst in the epiphysis of the brain. The larva of echinococcus enters the tissue through the circulatory system. The parasite is enveloped in a protective capsule. Products and toxins from its development constantly accumulate in it.
- Hemorrhages can be one of the reasons for the appearance of a cyst in the pineal gland. Active blood supply to the pineal gland for unknown reasons leads to the formation of a capsule.
Hemorrhages lead to the formation of a capsule. - A microcyst of the epiphysis may be congenital. It is formed due to defects during embryonic development, infections during pregnancy and lack of oxygen.
Possible complications
As the volume of the tumor increases, fluid accumulates between the hemispheres of the brain. This leads to blocking the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which provokes hypertensive crises. This condition is characterized by frequent vomiting, headache and confusion.
Subsequently, intracranial pressure increases, due to which the patient loses the ability to perceive new information and sleeps longer. Large pineocytomas compress the brain, resulting in the death of local tissue.
Prolonged development of the tumor process leads to irreversible consequences: persistent neurological disorders occur.
On this topic
- central nervous system
Causes and consequences of cyst formation in the head in children
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
Compression also causes dislocation syndrome, in which brain tissue is displaced. Such processes are accompanied by multiple symptoms, which are determined depending on the severity of the case.
Brain damage negatively affects the performance of internal organs. Compression provokes pulmonary edema, pneumonia, tachycardia, arterial hypotension, and apnea. If the tumor process causes dysfunction of the medulla oblongata, respiratory and heart failure occurs. Such complications lead to the death of the patient.
Possible complications of pineocytoma include the risk of tumor malignancy. Malignant transformation of the tumor is characterized by the spread of cancer cells throughout the internal organs and increased growth of pineoblastoma.
Signs
A pineal cyst in the brain manifests itself in rare cases. As the capsule grows, symptoms similar to other pathologies that are not associated with neuropsychic disorders are observed. The main symptom of a pineal cyst is recurrent or constant headaches. As the pineal organ tumor grows, other symptoms appear, but they may not be intense:

Double vision, blurred images as with cataracts.
- visual disturbances (diplopia or double vision, blurred images as with cataracts);
- change in coordination of movements (unclear gait, staggering);
- nausea or vomiting due to severe headaches;
- dropsy (formed after compression of the pineal gland duct and slowing down the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid).
The number and intensity of manifestations depend on the size of the cystic formation of the pineal gland. The larger the cavity in diameter, the more it compresses the surrounding tissue. One of the complications of an epiphysis cyst is blocking the movement of the spinal substance, which leads to persistent disorders in the body.
Echinococcal lesions of the pineal gland pose a great danger. The parasite can grow into a large capsule in just a few years. It is with a parasitic tumor that mental disorders clearly manifest themselves - depression, mental retardation, delusional consciousness and epileptic seizures.
Indications for the study
In 80% of cases, diseases of the pineal gland are discovered by chance. Indications for research are the following symptoms:
- periodic headaches for no reason;
- signs of intoxication accompanying headache;
- pain when trying to raise your eyes up;
- decreased visual acuity, double image;
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system;
- loss of coordination and unsteadiness of gait;
- increased drowsiness.
These signs indicate the development of a tumor in the structure of the pineal gland. Symptoms occur only when the tumor increases in size. Medications do not help cope with pain.
Not only cancerous formations pose a health hazard, but also some benign tumors (hydatid cysts). The waste products of an hydatid cyst poison the body and provoke neurological disorders:
- partial paralysis, which covers one half of the body;
- impaired perception of temperature, pain and tactile sensations;
- epileptic seizures;
- frequent depression of an unreasonable nature.
It is important to study the state of the brain and determine in which of its parts the pathological process develops. MRI allows you to diagnose cystic and cancerous tumors with 90% accuracy and differentiate them from each other.
Diagnosis of pineal gland neoplasm
Cystic transformation of the pineal gland can only be detected by extensive instrumental examination. Early diagnosis practically does not yield results due to weak manifestations.
At later stages of development of a cyst in the pineal gland of the brain, a neurological examination reveals a violation of the motor function of the eye. The optic discs become swollen.
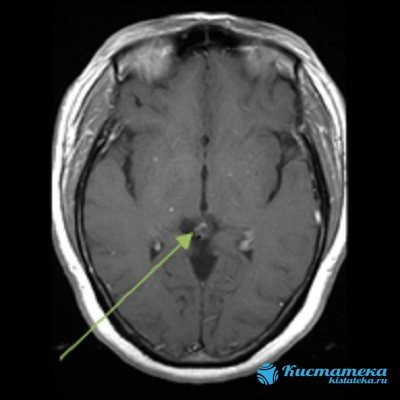
MRI determines the size and localization of the pathology.
When cerebrospinal fluid is taken through a puncture from the spine, the level of protein mass and the number of cells - lymphocytes and monocytes - are determined. The study of cerebrospinal fluid allows us to determine other disorders, for example, hidden inflammatory processes and chronic pathologies.
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered the most informative diagnostic method. Layer-by-layer images are displayed on the monitor and photographs. MRI of the brain clearly determines the size, location and level of spread of the cystic process of the pineal gland. An analogue of MRI is computed tomography.
Pineal gland cyst of the brain: causes of development
The main causes of the development of pineal gland cysts in the brain are:
- Blockage of the excretory canal, as a result of which the outflow of melatonin produced by the gland is disrupted. When the excretory duct is blocked, secretions accumulate;
- Echinococcosis is a helminthiasis that provokes the formation of parasitic cysts in various organs. In other words, damage to the pineal gland by echinococcus that enters the gland through the bloodstream. The parasite forms an echinococcal capsule, protecting itself from the body's immune attacks. The pineal cyst, formed by the membrane of the echinococcus, is filled with waste products of the parasite and may increase slightly in size.
Due to the fact that this brain structure is poorly understood, other reasons for the formation of pineal gland cysts in the brain still remain unknown. This is also explained by the fact that the formation and development of a pineal gland cyst is practically asymptomatic.
Treatment
For microcysts of the pineal gland, treatment is abandoned if it does not progress and there are no symptoms. Usually such a tumor is discovered by chance. To control the formation, the patient is prescribed a scheduled MRI once every 12-24 months.
Drug therapy
For microcysts in the epiphysis of the brain that have pronounced manifestations, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. Pain in the head helps to eliminate diuretics, which remove a significant part of the fluid from the cystic cavity of the epiphysis. If the tumor has reached a large size and affects the electrical impulses of the brain, the patient requires antiepileptic drugs.

Diuretics help relieve pain.
Sedative medications will help reduce psycho-emotional stress. For small echinococcal cysts of the pineal gland, antiparasitic treatment is carried out. The use of medications is necessary for patients who are contraindicated for surgery. In other cases, radical treatment is used.
Cyst removal
Before preparing a patient for surgery, the doctor tells him why such a cyst is dangerous and what consequences may occur after surgical treatment. Sometimes, before intervention, several years of constant monitoring of the cavity in the pineal gland take place. And only for serious indications that threaten the health and life of the patient, one of the radical treatment methods is used.
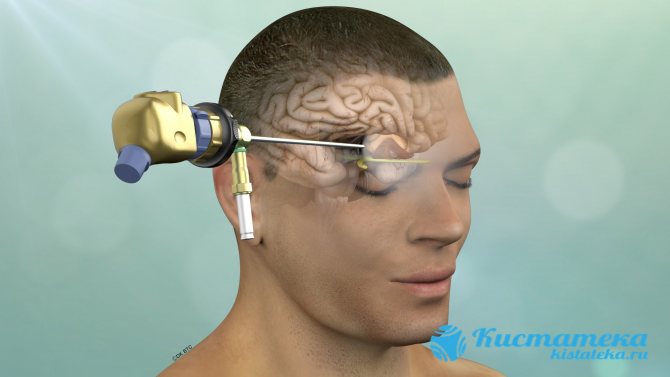
The fluid is removed using an endoscope.
- Shunting. Thanks to the implantation of an artificial vessel into the pineal organ, the outflow of fluid is restored to the patient. After the shunt is installed, various side effects may occur, but without increasing intracranial pressure.
- Endoscopy. A relatively gentle surgical method. The fluid from the pineal cavity is removed using an endoscope, after which its walls collapse. The outflow of secretory substances through the drainage is resumed.
- Trepanation of the skull. One of the most difficult brain surgeries, associated with a high level of injuries and complications. Surgical intervention is advisable for persistent brain disorders, progression of the cyst or growth of its walls into malignant tissue. Successful surgery depends on the type of education and experience of the neurosurgeon. In 70% of cases, neurological disorders are observed after treatment.
Symptoms
The disease has symptoms such as:
- Unexpected, irregular, causeless severe headache, which has a pressing nature due to increased intracranial pressure. Attacks of pain are not periodic, but are quite long-lasting. Headache resistant to painkillers.
- Violation of visual function: characterized by doubling of objects, the appearance of blurred outlines, and a veil before the eyes. Often there is pain in the eyeball when moving the eyes.
- Dysuric disorders in the form of nausea. This may cause a slight headache.
- A noise in the head that is constant and intensifies as the intensity of the headache progresses.
- Movement coordination disorders: unsteadiness, instability, imbalance when moving, difficulties when working with small objects and in assessing the speed of movement of objects.
- Disturbance of the body's biorhythms. There is a desire to sleep during the day and vice versa to stay awake at night;
- Paralysis of the limbs, hypo- or hypertonicity of muscles;
- Mental disorders, loss of consciousness, convulsions;
- Sensitive skin disorders;
- Feeling of pulsation in the head;
- Involuntary movements of the limbs;
- Pulsating fontanel and vomiting in young children.
- Lethargy.
- epileptic seizures,
- mental disorder,
- delusional state and inability to assess the real situation,
- limb paralysis,
- development of dementia,
- noticeable hypertension.
The combination of symptoms depends on the area of localization of the cyst and its pressure on nearby brain structures.
Consequences of the disease
Epiphysis cysts are not dangerous if they are of normal size. A threat to humans is the growth of a tumor, which provokes hydrocephalus and epilepsy. As well as formations that exceed 1 cm in diameter and capsules with parasitic contents.
A tumor size of 2 cm carries a great danger of neurological abnormalities.
Children with congenital complicated cysts are sometimes diagnosed with autism, but a direct relationship between the pathologies is not observed. Most often, the cause is more complex defects.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
Preventive actions
Prevention of epiphysis cysts includes routine examinations of the brain. It is necessary to promptly pay attention to changes in the child’s behavior and complaints of headaches. The main indicator of a brain disorder is neurological disorders. It is necessary to undergo an MRI to accurately establish the diagnosis and begin early therapy.
A brain cyst is not a death sentence. But if the patient is already aware of his diagnosis, he will need regular thorough examinations and consultations with a neurologist.
The essence of pathology
The pineal gland, also called the pineal gland, is a brain structure. This is a small unpaired organ responsible for performing endocrine functions. This formation has a gray-red tint and is located between the hemispheres of the brain in the area of the interthalamic fusion. On the outside, the gland is covered by a connecting capsule.
Since the gland is very small and has a specific location, its functions are not yet fully understood. But scientists were able to establish that the organ is involved in regulating circadian rhythms.
There is also evidence that the pineal gland is responsible for the synthesis of melatonin. This body performs the following functions:
- regulation of puberty, transformation of sexual behavior;
- slowing down the production of growth hormone;
- inhibition of the development of neoplasms.
So what is it - an epiphysis cyst? This term refers to a benign formation that does not transform into a malignant tumor. This small cyst is diagnosed very rarely. However, it is rarely characterized by dynamic growth. Education does not affect the functioning of the gland and almost never disrupts the function of adjacent brain structures.
Prevention of pineal microcysts
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to regularly visit a neurologist and conduct an MRI scan every six months.
In order to prevent pineal gland cysts, you need to take basic measures: periodically undergo a medical examination, give preference to a healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet, correctly alternate the time of rest and sleep, and minimize radiological effects on the head and neck area.
To prevent infection with echinococcus, you should maintain personal hygiene, handle culinary products properly and limit contact with animals that carry parasites.
The phenomena that provoke the occurrence of cystic neoplasms of the pineal gland require further in-depth study. Medical data indicate that with timely diagnosis of the disease and regular monitoring of its dynamics, the patient’s quality of life will not be affected.