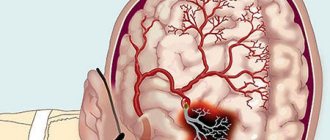
VSD and osteochondrosis
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a neurological problem. It develops primarily in adolescents and young adults. But still, pathology is often caused by other diseases, which are more common in mature and elderly patients. Such reasons include osteochondrosis.
Cervical osteochondrosis and VSD are often observed simultaneously
In 90% of cases, the development of VSD in adulthood occurs due to osteochondrosis. The symptoms of dystonia are caused by impaired cerebral circulation and, as a consequence, changes in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Relationship between diseases
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine creates optimal conditions for the occurrence or aggravation of VSD. This is caused by deformation of the intervertebral discs and subsequent compression of blood vessels by the cervical vertebrae. As a result, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. With VSD, a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system occurs and hypoxia develops. Osteochondrosis interferes with normal blood flow in the damaged area and increases vascular dystonia.
The causes of osteochondrosis can be:
Osteochondrosis can be caused by shocks and stress
- curvature of the spinal column, poor posture, scoliosis;
- sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work;
- neck injuries;
- uneven physical activity;
- emotional shocks, stress;
- poor nutrition, strict diets;
- metabolic disease;
- intoxication, allergies, abuse of bad habits;
- burdened heredity.
The main factors influencing the development of VSD and osteochondrosis are impaired cerebral circulation and instability of the body's nervous system. The relationship between vegetative-vascular dystonia and cervical osteochondrosis follows from the pathogenesis of the diseases.
Due to degenerative changes in the vertebrae, their structure changes. The disorder spreads to the nerve and vascular columns running along the spine, and the nutrition of brain tissue deteriorates. This affects the amount of hormones produced that control the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, advanced osteochondrosis smoothly flows into progressive vegetative-vascular dystonia.
There are several types of VSD, which differ in symptoms:
Cardialgic type of VSD
- cardialgic;
- tachycardial;
- hypertensive;
- hypotonic;
- asthenic;
- respiratory;
- visceral;
- mixed.
The cardialgic type is characterized by dull or sharp pain in the area of the heart muscle. The symptoms in this case do not depend on physical activity and are not relieved by heart medications.
The tachycardial type is characterized by increased heart rate up to 130-150 beats, redness of the face and neck, and pounding in the temples.
Hypertensive and hypotensive types are accompanied by an increase and decrease in blood pressure, respectively. Jumps occur rarely, for a short period of time, and may be accompanied by weakness and increased sweating.
The tachycardial type is characterized by increased heart rate and redness of the face and neck
The asthenic type of vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by low-grade fever and trembling in the fingers. Fatigue, loss of performance, and decreased endurance often appear.
Manifestations of the respiratory type are associated with difficulty breathing, sensation of a foreign body in the throat, and dry cough.
If gastrointestinal diseases are excluded, but the patient experiences dyspeptic digestive disorders, pain and bloating, then there is a high probability of a visceral type of VSD.
In advanced forms of the disease, a mixed type develops, which is a combination of several.
When diseases are combined, almost all types of disease appear, except visceral.
Symptoms of the general manifestation of osteochondrosis and VSD may look like:
- headache, often in the back of the head or temple, constant or paroxysmal;
- blood pressure surges;
- dizziness, weakness;
- increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, panic attacks;
- numbness of the upper limbs, fingers;
- noise and congestion in the ears, blurred vision, the appearance of spots before the eyes;
- discomfort in the area of the heart muscle;
- increased irritability, excitability, anxiety.
The cardialgic type of vegetative-vascular dystonia can be confused with diseases of the thoracic spine, and the visceral type with lesions in the lumbar region. However, VSD is much more difficult to diagnose.
Etiology of the disorder
Due to the fact that VSD is often caused by the development of dystrophic changes in the structure of the spine, the causes may be common. Often, dystonia becomes more pronounced during periods of exacerbation.
The most common etiological factors for the development and aggravation of VSD are:
- Curvature of the spinal column.
- Excessive stress on the discs between the vertebrae.
- Mechanical damage to the spine.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Allergic reactions.
- Decreased immune system activity.
- Physical inactivity (inactivity).
- Impaired blood flow in the spine.
- Hormonal dysfunctions.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Diseases of internal organs.
A sedentary rhythm of life contributes to the development of both pathologies.
These conditions contribute to disorders of the nervous system, including its autonomic department. At the same time, emotional stability is significantly reduced and the intensity of negative symptoms increases.
VSD and cervical osteochondrosis, connection, features of clinical manifestations
In the pathogenesis of the development of the disease, the presence of two mechanisms is of particular importance: damage to the musculoskeletal system and a violation of the neurohumoral regulation of the body.
Damage to the musculoskeletal system manifests itself in the destruction of the joints of the spine along its entire length.
Namely, what happens:
- development of destructive and degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue of the spinal joints;
- narrowing of the joint space;
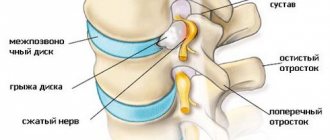
- compression of intervertebral discs and their protrusion from the spinal canal (formation of hernias);
- deformation of bone tissue (growth of osteophytes); curvature of the spinal column;
- damage to nerve endings, up to their atrophy and loss of nerve impulses.
The formation of destructive processes in the cervical vertebrae (C5, C6, C7) leads to the occurrence of reflex manifestations that limit the mobility of the cervical spine. Pinching of the spinal cord roots at this level is accompanied by severe pain, shooting in the head and shoulder girdle.
Often, during an exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, the patient takes a forced, gentle position, in which he tries to move as little as possible, so as not to cause himself additional pain. Myositis is a frequent “companion” of cervical osteochondrosis. The pain spreads across the shoulder girdle, down to the level of the shoulder blades, limiting movement in the shoulder joints. Palpation of the paravertebral points of the cervical spine is quite painful.
Violation of neurohumoral regulation largely explains the existence of a close connection between the progression of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
One of the most common companions of cervical osteochondrosis is VSD. Destruction of the intervertebral discs, compression of the nerves and vessels supplying the brain, atrophy of the muscles of the back and neck lead to the development of VSD in cervical osteochondrosis. Dysfunction of the nerve plexus in the vertebral artery leads to the appearance of neurological symptoms reminiscent of transient ischemic attacks or acute cerebrovascular accidents.
These include:
- severe severe headaches and dizziness in the morning, even to the point of fainting;
- numbness and paresthesia in the upper extremities, neck and shoulders;
- fatigue, chronic fatigue syndrome;
- depression, depression, panic attacks;
- increased irritability, exposure to stressful situations;
- weather dependence;
- sleep disturbance, insomnia;
- noise in the head, ears;
- blurred vision, double vision, flickering spots before the eyes;
- nausea;
- blood pressure surges;
- a feeling of heaviness and tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, palpitations.
In order to consider VSD not as a separate disease, but as a consequence of cervical osteochondrosis, there are several characteristic signs inherent in this combined pathology.
VSD and cervical osteochondrosis, symptoms:
- Panic attacks are attacks of unjustified anxiety and increased feelings of fear, accompanied by difficulty breathing, pain in the chest, nausea, fainting, weakness, and numbness in the legs. A distinctive feature of a panic attack (one of the signs of VSD in cervical osteochondrosis) is the spontaneity of its occurrence when the patient remains in an uncomfortable position for a long time or after physical activity.
- Disruption of the cardiovascular system often manifests itself in a feeling of lack of air that occurs during walks or after physical activity. There may even be dyspnea - a breathing disorder that requires qualified medical care. Breathing with a diagnosis of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis and VSD is superficial with rhythm disturbance. In addition to breathing problems, there are heart rhythm disturbances and increased blood pressure. Finding a patient in an uncomfortable body position for a long time is often accompanied by paresthesia and numbness in the cervical spine, shoulder girdle, and occipital region.
- Neurological symptoms are quite diverse. The patient complains of decreased vitality, fatigue, dizziness, and tension headaches. Characteristic is the close connection of headaches with motor activity in the shoulder girdle, movements of the head and neck. It is often possible to determine damage to the facial nerves, a small amount of movement of the eyeballs when turning the head to the side. The localization of the headache is mainly one-sided with lumbago in the ear canal and temporal region.
- Violation of thermoregulation manifests itself in a sharp change in body temperature in the presence of a stress factor. A peculiarity of hyperthermia associated with the diagnosis: VSD, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, is that it is accompanied by a throbbing headache and decreased visual acuity.
VSD and cervical osteochondrosis are two serious diseases, which, if ignored, can greatly harm the body. They have the same symptoms, and there have often been cases where the diagnosis was made incorrectly. The difference between these two ailments lies in the mechanism of their origin. Accordingly, the treatment method (with medications) is also different.
Osteochondrosis is a disease in which there is complete or partial destruction of the intervertebral discs, which in turn reduce the distance between the vertebrae and infringe on the nerve endings. Depending on the location of the lesion, there are several types:
- Cervical osteochondrosis (occurs in 7 vertebrae of the neck);
- Thoracic (affects the part of the spine at chest level);
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region.
VSD is a disease that can occur in the body due to malfunctions of various organ systems. And doctors do not define this illness as a disease of anything. This is a consequence of one disease or another, and most often the cause is osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra. Once the disease is detected, you should immediately consult a doctor to begin a course of treatment. In such cases, a serious course is prescribed, based on a comprehensive method.
VSD and cervical osteochondrosis can arise from a number of different reasons. Starting from the simplest – incorrect sleeping position, ending with the complete absence of any physical activity. Here it is very important to study the causes of the manifestation of VSD, to conduct research on the course of the disease, in order to understand what treatment method to prescribe (if it occurs due to osteochondrosis).
VSD, as a consequence of neck disease, can occur in obese people, those who have suffered from spinal injuries, as well as those whose body position is constantly in an incorrect position (sedentary work, taxi drivers). Of all the reasons listed, the most common is sedentary work.
As terrifying statistics show, in 100% of cases of cervical osteochondrosis, VSD manifests itself. This pair of diseases also occurs in young people. And the reason is the wrong lifestyle. Here we are talking not only about the lack of physical activity. From an early age, people eat “empty” food that does not enrich the body with useful substances.
If, in addition to pain in the neck and head, there is a sharp increase in pressure (increases upward), gait is disturbed, and general malaise is felt, it is worth visiting a neurologist to check for the presence of VSD, or its absence. A correct diagnosis allows you to prescribe smart treatment. Self-medication, in this case, is not recommended.
Symptoms
Attention! The similarity of the manifestations of osteochondrosis and dystonia sometimes does not allow making an accurate diagnosis.
Both pathologies can affect the general well-being of the patient. The activity of individual organs and systems is also disrupted.
But there are still differences in symptoms. For a doctor, one of the main tasks is to identify the most important disorders and determine what they indicate.
The cardiovascular system
The circulatory system actively responds to any disturbances in the body. The development of both osteochondrosis and VSD also negatively affects her activities. The symptoms of pathologies are similar:
- Heartache.
- Change in pulse rate.
- Deterioration of cerebral circulation.
- Headaches in the back of the head.
- Frequent feeling of numbness in the hands.
- Dizziness.
- Migraine.
- Tachycardia.
- Cold extremities, their cyanosis.
Increased heart rate is one of the signs of dystonia in osteochondrosis.
In addition, patients often note increased sweating of the hands (this is more typical for VSD). Changes in blood pressure levels are also possible. It can either increase or decrease.
Respiratory system
The respiratory organs are also affected. Most often, shortness of breath develops, the person complains of difficulty in breathing. He often complains of a feeling of obstruction in the airways.
Shortness of breath is a common manifestation of the disease
Pain in the chest area may also occur. A feeling of heaviness in the chest often accompanies VSD.
Nervous system
The central nervous system reacts most strongly to any disorders associated with VSD and degenerative processes in the back. Patients especially often suffer from headaches, and it is not entirely clear what disease this provokes and what the pathological origin of this condition is.
Also, lesions of the central nervous system are manifested by the following symptoms:
- Sleep disturbance (superficiality, intermittency).
- Frequent neurotic disorders.
- Apathy.
- Insomnia.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Mood lability.
- Emotional depression.
- Increased irritability.
Insomnia and interrupted sleep are signs of neurological changes in VSD.
Patients usually find it difficult to focus on something. Pathological processes in the cervical spine disrupt tissue trophism, resulting in severe pain in the morning. This is especially intense when trying to turn the head. Sometimes visual acuity decreases, which is a sign of optic nerve atrophy. In severe cases, panic attacks are possible.
Digestive system
As a result of osteochondrosis, the course of dystonia is aggravated. At the same time, all its symptoms become more pronounced, including gastroenterological manifestations. Therefore, nausea is often observed with VSD and accompanying osteochondrosis.
Cases of heartburn, bloating, and vomiting are also becoming more frequent. The consistency of stool is often disrupted due to changes in the innervation of certain parts of the organs.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis with vegetative-vascular dystonia
Pathologies have physiological and psychological manifestations. The clinical picture at the initial stage of the disease, be it osteochondrosis or VSD, is weakly expressed. As degenerative processes progress, symptoms become more severe and become chronic.
Physiological signs of degenerative processes in the spine with VSD are:
- recurrent or constant back pain;
- dizziness when standing up and sudden movements of the head;
- temporary or permanent visual impairment;
- the appearance of “flies” before the eyes;
- hearing impairment;
- tinnitus;
- headache;
- numbness, loss of sensation and low temperature of the extremities.
VSD against the background of cervical osteochondrosis is characterized mainly by psychological manifestations. These include symptoms such as:
- panic attacks;
- sudden attacks of irritability;
- apathy and depression;
- tearfulness;
- sleep disorders.
Physiological signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia appear in the form of:
- digestive disorders;
- fainting states;
- chills or hot flashes;
- frequent urination;
- itching and burning in the genital area;
- flatulence;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating.
If you notice the above symptoms, you should go to the doctor with suspicions of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine or VSD. Only a doctor can find out the cause of the clinical picture and make a diagnosis based on a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Diagnostics
In order to begin treatment, it is important to determine the cause of the patient’s poor health. To do this, the doctor must take into account the symptoms. A number of important studies also need to be conducted. The list of tests for each patient is individual. This is due to the variability of clinical manifestations.
But in any case, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. This is a highly specialized specialist who will help reduce the list of examinations to the most important and effective ones. For a proper examination, it is necessary for the doctor to palpate the vertebral column. Next, you can proceed to instrumental methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT scan.
- Radiography.
MRI and CT are among the most informative. They have a minimum number of contraindications, are painless and quick. But their main disadvantage is their high cost. Radiography is cheap. But this diagnostic method is not very informative.
It is also necessary to examine those organs and systems that have suffered due to dystonia. First of all, it is necessary to study the condition of the heart. This can be done with ECG, Echo-CG, and ultrasound of the heart. Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is also recommended to study other organs.
Clinical picture
The characteristic symptoms of VSD appear individually and depend on the underlying cause of the pathology, general condition, and age of the patient. Possible signs of a problem:
- deterioration of the patient’s general condition (weakness, drowsiness, lethargy);
- vascular manifestations (fainting, pressure surges, dizziness);
- cardiac dysfunction (pain, arrhythmia);
- change in the emotional background (increased irritability, the appearance of causeless fear);
- sleep disturbances (drowsiness or inability to sleep);
- decreased sensitivity of the limbs, “goosebumps”;
- feeling hot or cold;
- disturbance of urination, interruptions in the gastrointestinal tract.
The listed symptoms of VSD are not associated with the development of pathologies of internal organs, but are caused by disruption of the normal functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac symptoms
Manifestations of cardiac and vascular disorders in spinal osteochondrosis are the most common. These include:
- increased heart rate;
- arrhythmia;
- pale or red skin;
- trembling hands;
- heart pain;
- dyspnea;
- pressure surges.
These symptoms of VSD have an important feature - they do not depend on the patient’s state of activity or rest, and do not decrease when taking nitroglycerin and similar drugs.
Respiratory system
Panic attacks and cervical osteochondrosis are interrelated: the first is a consequence of the second. During an attack, the patient feels suffocated, something is pressing on his chest, and does not allow him to take a large breath of air. Unpleasant sensations are provoked by physical activity, riding in public transport, and temperature fluctuations. The discomfort is complemented by a growing sense of fear.
Digestive system
The patient suffers from irritable bowel syndrome, the characteristic manifestations of which are:
- stomachache;
- bloating;
- increased gas formation;
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- frequent need to go to the toilet.
The symptoms do not depend on the type of food consumed by the patient and can be eliminated after complex treatment of osteochondrosis.
Nervous system
Impaired blood supply to the brain leads to the development of nervous symptoms:
- migraines;
- impairment of vision, hearing;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- ear ringing;
- decreased sensitivity of the limbs.
To eliminate these symptoms, it is necessary to stop the compression of the vertebral artery that supplies blood to the brain.
Other symptoms
VSD and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can lead to swelling and myalgia. The patient suffers from urinary disorders: frequent urge, pain, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Sexual function is inhibited.
Treatment
Therapy for this condition requires a special approach. This is due not only to the manifestations of dystonia, which come to the fore.
Often patients are driven by what the symptoms are, treatment should be etiological - it is important to treat the root cause of the pathology. In this case – osteochondrosis. The disturbances provoked by this condition contribute to the aggravation of the course of VSD.
Treatment with medications
This method of therapy is traditional and very important. Taking medications must be included in the treatment regimen. Necessary medications must be discussed with the doctor. The following groups of drugs are most often prescribed:
- Chondroprotectors.
- NSAIDs.
- Painkillers.
- Antidepressants.
- Muscle relaxants.
Chondroprotectors are designed to stimulate the processes of restoration of cartilage tissue. Also, the use of these drugs slows down dystrophy in the joints. NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, help relieve swelling from the affected areas, which reduces irritation of the nerve endings. It is also recommended to eliminate pain with analgesics and muscle relaxants. Antidepressants are rarely prescribed; they are recommended for patients with severe neurological disorders (for example, irritability, apathy).
Massage
This method is also very useful. Its effectiveness can significantly reduce pain by stimulating blood circulation at the site of the lesion. The processes of cartilage regeneration are also accelerated and muscles relax.
Massage procedures in the neck area help improve the patient's condition
But it is important to remember that massage in the neck area should not be performed by non-professionals. Incorrect massage technique can cause harm to the patient - possible pinching of the nerve fiber.
Physiotherapy
These procedures are particularly effective in the case of a combination of osteochondrosis in the cervical region with dystonia. Some types of physical therapy are not widespread enough, despite all their benefits and effectiveness.
Most often, it is recommended to carry out procedures using magnetic fields and low-voltage stimulating electric current. Leech therapy and acupuncture are rarely recommended. But these methods are effective in treating pathology due to active stimulation of blood flow.
Beneficial physical exercises
Advice! You can relieve tension from the muscles and spine with the help of gymnastics.
Therapeutic exercises can restore skeletal mobility and normalize blood flow. The muscles of problem areas are also strengthened, due to which the spine is slightly fixed in the required position, the load on it is reduced, and the severity of spasms is reduced.
Gymnastics for VSD and osteochondrosis are very simple. Its main principles are smooth and slow movements. The list of exercises includes slight turns of the head while sitting or standing, and bending. Stretching your arms high above your head is also helpful. Regular exercise is the key to success in treatment.
Psychological help
If dystonia greatly affects the nervous system, then negative neurological symptoms may occur. Often this manifests itself not only in headaches and mild irritability, but also in emotional lability, panic attacks and sleep disturbances.
Such disorders provoke worsening depression and depressed state. Some patients cannot cope with this on their own, so they need psychological support. If the doctor helps the patient improve his emotional state and reduce the severity of neurosis, then recovery will occur many times faster.
Traditional methods
Therapy for VSD, which is caused by osteochondrosis, is well complemented by a variety of traditional medicine. But these medications often have contraindications, so consulting a doctor is necessary.
It is often recommended to make compresses with horseradish leaves. To do this, you need to pour boiling water over the raw material and wait until it cools completely. Then, for two to three weeks, it is recommended to apply moistened gauze or a bandage to the problem area.
Horseradish and its leaves are a good substrate for medicinal compresses
Compresses with honey are also considered beneficial. Before using the product, you need to warm the skin of your neck.
Drinking a decoction of celery is also effective. To prepare it you need to take 3 grams of vegetables and 900 ml of water. After boiling for a short time, the product needs to brew and cool. It is recommended to take a tablespoon before meals.
Osteochondrosis
Spinal osteochondrosis is an acquired pathology in which degenerative-dystrophic disorders affecting the vertebrae and intervertebral discs are noted. The consequence of such disorders is constantly increasing pressure on the nerve endings of the spinal roots and on the vessels passing there. With such processes, symptoms are clearly manifested, very similar to the signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Modern studies have shown that 90% of people with VSD were also diagnosed with osteochondrosis.
This disease is characterized by classic symptoms:
- Headaches of varying intensity that do not go away after taking painkillers. The pain gets worse with head movements and can be felt in the shoulder complex or chest area.
- Loss of coordination and even dizziness caused by a sudden turn of the head.
- Flashing of black flies before the eyes.
- Tinnitus.
- Feeling of weakness in the muscles of the arms and legs. Sometimes there may be a feeling of numbness or pins and needles.
As we see, the symptoms are very similar, but still osteochondrosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia are completely different pathologies, which, unfortunately, very often overlap. In such cases, all the symptoms of the disease overlap each other, which confuses the diagnosis. In addition, both VSD and osteochondrosis can develop as complications of each other.
Prevention methods
Preventing dystonia in the case of osteochondrosis is a difficult task. Back diseases are irreversible, but stable remission can be achieved. This requires a lot of effort. First of all, you need gymnastics, but you should avoid excessive exercise. Inadequate exercise significantly worsens the condition - muscles become overstrained and blood circulation worsens. It is also important to completely eliminate bad habits. Stressful conditions also negatively affect the body. With dystonia, which is already developing, nervous shocks make neurological symptoms more pronounced.
Physiotherapy exercises play one of their main roles in the treatment of osteochondrosis. It significantly smoothes out the symptoms of dystonia and reduces the severity of pain. The patient must understand that the payload is dosed. Only adequate exercise, proper food and well-chosen medications can prevent the worsening of pathological processes. To better understand the problem, it is recommended to watch the video:
Treatment methods
VSD and cervical osteochondrosis are treated comprehensively: with medications, physiotherapy and psychotherapy. Treatment with medications for vegetative-vascular dystonia and osteochondrosis is aimed at strengthening cartilage tissue, vessel walls and improving blood flow. As a rule, the following are used for this:
- vitamin complexes, which necessarily include B vitamins; a course of vitamins B1 and B6 may be prescribed,
- vascular drugs: Cavinton, Cinnarizine, Actovegin,
- vasodilators: chondroprotectors (“Teraflex”, “Aflutop”, etc.),
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: “Baralgin”, “Ketorol”,
- herbal-based sedatives: valerian extract, motherwort,
- antidepressants or tranquilizers: Rispolept, Flucosetine, Sertraline.
It is very effective to treat cervical osteochondrosis with gymnastic exercises and physiotherapeutic methods. The following physiotherapeutic methods are popular nowadays:
- cupping massage,
- stone therapy,
- manual therapy,
- physical therapy exercises,
- yoga,
- circular shower,
- radon baths,
- magnetic laser therapy,
- electrophoresis,
- Darsonval currents,
- acupuncture.
All these techniques produce analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The use of Darsonval currents restores blood microcirculation, relieving the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia and improving trophism of the spine.
The main method of treating orthopedic diseases is traction, which can be used to eliminate various deformities. With traction, the stagnation of venous blood decreases and microcirculation improves, and the pressure of the spinal roots decreases. But these positive changes occur only during the stretching period. After its completion, the spine returns to its previous position, so the patient can receive short-term relief from symptoms.
Massage procedures in the collar area are carried out by a specialist. Therapeutic massage improves blood circulation and relieves muscle spasms. As a rule, the initial stages of massage are characterized by deterioration of the condition. Patients complain of severe pain, even with a light touch to the collar area. Improvement occurs within 10-14 days. It should be borne in mind that cervical osteochondrosis and VSD are treated with massage for 2 weeks, then pause for 3-6 months and repeat the course.
For VSD and cervical osteochondrosis, it is very useful to engage in so-called beach swimming - without tension and overload. Long walks in the fresh air are very useful; they help relieve muscle spasms and reduce brain hypoxia.
Patients who, due to professional activities during working hours, are constantly in one position, should do a warm-up every 45 minutes or an hour in the same type of body position. Thanks to exercises and gymnastics, the blood does not stagnate and the body remains healthy.
In addition to physiotherapeutic procedures and medications, all patients suffering from VSD are recommended to undergo a course of psychotherapeutic assistance. Special techniques used by a psychotherapist help get rid of the consequences of panic attacks and attacks of fear. The psychotherapist helps the client take control of his negative manifestations in unpleasant situations and change his attitude towards situations that provoke the development of an attack.
Prevention
It must be remembered that complete recovery from vegetative-vascular dystonia against the background of cervical osteochondrosis cannot be achieved. Prevention will be aimed only at slowing the progression of the pathology. These measures include:
- regular examinations, as well as courses of maintenance therapy; avoiding prolonged sitting. To do this, you need to regularly warm up, which will improve blood circulation;
- inclusion of physical activity in your lifestyle, selected based on your health status;
- change in diet. It is necessary to increase the number of meals and also eliminate foods containing large amounts of salt or cholesterol;
- exclusion of stressful situations;
- normalization of the work and rest regime with sufficient rest.
These preventive measures help smooth out osteochondrosis and VSD for a long time.