Causes
There are many reasons for the development of cerebral palsy. The most common ones should be highlighted:
- Intrauterine brain damage
- Hypoxia during childbirth
- Intoxication
- Somatic and endocrinological diseases of the mother
- Rhesus conflict between mother and child
- Anomalies of labor (including birth injuries)
- Past infections
Under the influence of these and other reasons, direct damage to brain tissue occurs, and disturbances in its development processes begin to form. In this case, special attention should be paid to infectious diseases of the mother, which, today, account for more than half of all causes of cerebral palsy in a child.
Morphological changes in brain tissue are varied. Often, a child develops hemorrhages in the interthecal spaces and the brain tissue itself, degeneration of the structures of the cerebral cortex, and cicatricial changes occur. The lesion often affects (but is not limited to) predominantly the anterior parts of the brain.
Occupational technique and assessment of autism
An occupational therapist conducts research, studies children, and observes them to see if they can perform the tasks they are expected to perform at that age. It happens that the doctor receives a home video on which you can track how the child behaves during the day, how he interacts with people and objects around him. An occupational therapist may evaluate autism based on the following factors:
- concentration;
- endurance;
- play activities;
- response to the touch of other people;
- aggression or melancholy;
- does he need personal space?
Symptoms (forms of cerebral palsy)
The symptoms of cerebral palsy vary greatly. Based on the clinical picture, it is customary to distinguish several different forms of cerebral palsy, each of them will be discussed below.
— Hemiplegic form is the most common form of development of cerebral palsy. Its development is associated with damage predominantly to one of the cerebral hemispheres. In this case, the symptoms of the disease are as follows: paresis of the limbs develops on one side, contractures of the joints of the arms and legs are observed. The muscle tone is increased according to the pyramidal type. In the neurological status, attention is drawn to an increase in all tendon reflexes; pathological reflexes are often caused. Most often, the severity of the phenomena is greater in the arm than in the leg. During active movements, frequent synkinesis attracts attention - hand movements to the side, violent movements. The limbs on the affected side are developmentally delayed. Also quite often, this form of cerebral palsy is accompanied by the development of symptomatic epilepsy and mental development disorders.
— Diplegic form (Little's disease). It is a variant of cerebral palsy, expressed in spastic paresis of mainly the lower extremities. The child is clearly lagging behind in motor development; often such children never begin to walk independently. At the same time, a pronounced increase in muscle tone in the calf muscles makes the gait of such patients very peculiar: patients rely only on their fingers, their knees touch each other while walking, and it seems as if the patient is about to fall forward. This sign is so bright that it allows one to diagnose this form of cerebral palsy at a distance. The neurological examination also shows increased reflexes and pathological foot signs. In most cases, intelligence suffers little.
— The hyperkinetic form develops with damage to the subcortical ganglia (often with Rh conflict). Among the symptoms of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy, hyperkinesis itself comes to the fore - violent movements such as athetosis, chorea, etc. Usually hyperkinesis is varied, but one of them is still of leading importance. As the child grows and develops, the nature of hyperkinesis may change.
— The atonic-astatic form is manifested by a decrease in muscle tone of all extremities and the inability to maintain a vertical posture. Motor skills are practically not developed. Dysarthria often occurs.
— A rare cerebellar (atactic) form develops with predominant damage to the cerebellum. Vestibular disorders, ataxia, disorders of gait and coordination of movements acquire leading importance.
Where is occupational therapy used?
This technique has found wide application in various fields of medicine, as it is included in the program of many rehabilitation measures. In most cases, occupational therapy is used in neurology (a group of medical and biological scientific disciplines that studies the nervous system in both normal and pathological conditions).
An occupational therapist helps a person recover from the following disorders and illnesses:
- body paralysis;
- musculoskeletal disorders;
- after a stroke;
- with traumatic brain injury.
Occupational therapy is also very often used in the treatment of mental illness (doctors help people with psychological trauma to live a normal life and take care of themselves, outside the boundaries of a medical institution). The doctor draws up an individual communication and training program for each patient. For this purpose, various computational methods are used.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is usually based on the presence of a cause that led to cerebral palsy, as well as the clinical picture and neurological status. In modern medicine, neuroimaging methods such as MRI and MSCT are also important, but their use is limited by the need for anesthesia during the study. *MRI image for cerebral palsy
Also, in the presence of symptoms such as epileptic seizures, delayed mental and motor development, research methods such as EEG, Echo-EG, psychological testing, etc. can be useful.
History of occupational therapy education
This technique has existed for more than sixty years and arose in the post-war period, when crippled soldiers, both physically and mentally, returned home from the front. These people required a complex of pedagogical, psychological and medical measures that are aimed at restoring or compensating for the normal mental and physical needs of a person that were disrupted or completely wasted during the course of illness or injury. As a result, this therapy arose, whose workers helped people return to life again and adapt to current circumstances.
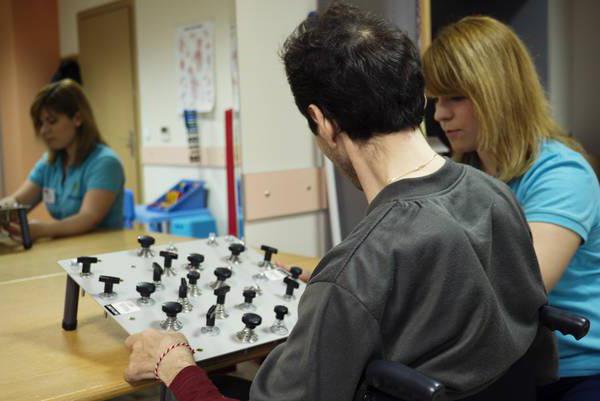
In addition, occupational therapy is fraught with a certain mystery. Medical professionals confirm that this treatment is intended to enable a person to learn new knowledge that he has lost (he becomes uninitiative and inert, his taste for life disappears). Occupational therapy forces the patient to think more, helps him to abstract himself and accept his disability.
Interesting!
In Russia, occupational therapy appeared relatively recently, within ten years, and to this day it helps people with disabilities learn to live again.
Course of the disease and life prognosis
Cerebral palsy, especially at an older age, is not a progressive disease, but the presence of persistent residual consequences of brain damage. In this case, as a rule, there is regression of symptoms to one degree or another. The possibilities for compensating for impaired functions are quite large in early childhood, and sometimes make it possible to achieve almost complete recovery.
It is difficult to assess the signs of cerebral palsy at three months of age, or, say, at the age of 6 months. The phenomena of developmental delay and signs of paresis of the limbs come to the fore. However, each case is individual, and it is impossible to identify the exact signs of cerebral palsy in the first year of life.
The life prognosis of patients with cerebral palsy is usually favorable. Patients live to a ripe old age and can have offspring. A decrease in average life expectancy is often associated with mental underdevelopment, lack of social adaptation, as well as the frequent presence of symptomatic epilepsy.
Is it possible to cure cerebral palsy if you try hard?
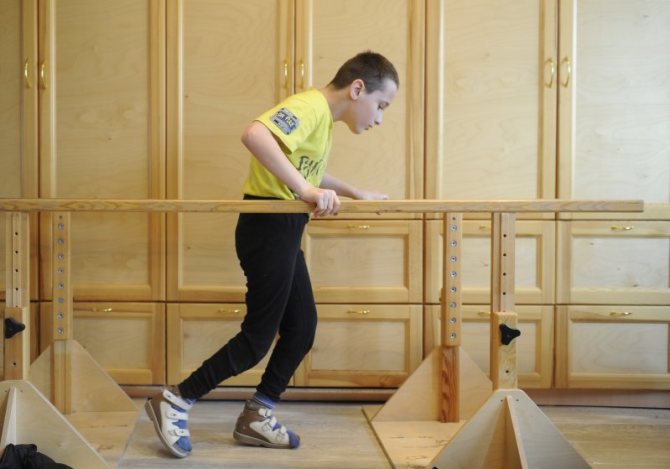

Photo: Evgeny Kurskov/TASS Demosthenes puts stones in his mouth and shouts over the sea. Hockey player Kharlamov goes on the ice for the first time after the accident and trains with the boys. We love stories about overcoming and believe in them - perhaps this is why the belief is so widespread that willpower can overcome any disease. Physical therapist Ekaterina Klochkova told “Takim Dela” whether it is possible to “cure” cerebral palsy if you try really hard.
Ekaterina Klochkova, physical therapist, director of ANO rehabilitation

Photo: from personal archive
The perception of cerebral palsy as a disease that can be cured is a myth: “Parents worked 24 hours a day and got the child on his feet, while others didn’t work and didn’t.”
Cerebral palsy is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive conditions that are associated with damage to the brain early in its development (in utero, during childbirth, or in the first two years of life). It follows from this that it is impossible to “cure” cerebral palsy, since we cannot eliminate the cause of the motor deficit - structural disorders in the central nervous system. But the consequences of this damage can be compensated to varying (sometimes significant!) degrees.
We do not saturate the media space with examples and stories about what cerebral palsy is. Therefore, what do people focus on? To those heroic stories that exist around us - about rehabilitation. Here is Valentin Dikul (a circus performer who learned to walk after a spinal fracture - TD's note). No one is interested in what type of spinal lesion he had, that he would have regained his movements anyway... But there is a whole myth around this, how he raised himself to his feet, how all the doctors refused him, and he made these exercise machines himself, and so on Further. Or Alexey Meresyev (a military pilot who continued to fly after the amputation of both legs - TD's note) - here he is without legs, he was given prosthetics, he bled everything there, but he flew again. And the fact that these were adults who had disabilities due to injury or injury does not bother anyone at all.
It is impossible to “cure” cerebral palsy
On the one hand, people say the right things: rehabilitation of a child with cerebral palsy, or rather even habilitation (the process of developing abilities for everyday, social and other activities - TD), should really start early and be intensive. But on the other hand, the meaning that is put into this concept in our country is completely different. In our country, rehabilitation is what is done with a child in a special place: that is, for rehabilitation you need to go to a special place and have a specially trained person rehabilitate the child there.
In modern Western programs, habilitation is also very intensive and is carried out almost 24 hours a day. But this is not a hired masseuse or some kind of rehabilitation center where the child is not allowed to breathe. This is a trained mother who receives the support of specialists. All events in which the child participates - feeding, changing clothes, bathing - they will all occur in the correct position, with the correct movement, the correct rhythm. Mom, for example, will stimulate the hand that works worse. Of course, this child will be seen by certain specialists, but they will not do this every day, but will provide long-term support.
Treatment
Therapy for cerebral palsy is a multifaceted task. It must be comprehensive and include medications, physiotherapy, psychotherapy, speech correction, massage, the use of special orthopedic devices, and physical therapy.

— Among drug therapy, the most important is given to neuroprotective drugs (Cortexin, Actovegin, Cerepro), as well as muscle relaxants (baclofen, mydocalm) to relieve spasticity. Vitamin and other metabolic drugs are widely used. If necessary, sedatives are used. The presence of symptomatic epilepsy presupposes the use of antiepileptic drugs.
— Physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage are aimed at reducing the lag in motor development. Also, activation of motor function helps to improve the mental development and social adaptation of a patient with cerebral palsy.
Recently, methods of treating cerebral palsy such as hippotherapy (treatment with contact with horses) have become fashionable. However, these techniques are not always available and, as a rule, expensive, so they are not widely used.
Work principles
Rehabilitation in the occupational therapy system implies a whole range of measures that is aimed at resuming a person’s natural, daily life activities with a specific and strict consideration of diseases and disorders that already exist. Only an occupational therapist can help a patient relearn how to communicate, have fun, and take care of himself.

The main rules of occupational therapy are as follows:
- When drawing up a treatment plan, the doctor must take into account all the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Treatment is aimed at taking the necessary measures together with a medical professional to help the person recover.
- Continuously developing medical science contributes to the emergence of new techniques and methods for performing occupational therapy.
- When providing treatment, the doctor must take into account and acknowledge the culture and customs of the patient.
Therapy
When treating this form of cerebral palsy, the following methods are used: massage, therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy.
They help eliminate movement disorders: the patient walks better, gets tired more slowly, his muscular system becomes stronger, coordination improves, his gait is straightened, and the affected limbs develop better.
For best results, you need to engage with your child as much as possible and treat him warmly, express feelings: this improves emotional reactions and general condition, gives an incentive to improve, especially in older children.
It is also useful to develop mental abilities and memory: learn poems, give information about the world around you, read books aloud, talk, discuss events, and gradually the results will make themselves felt, even if mental retardation is severe.
Communication with animals has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease: children become more open, their emotional state improves, and games and walks with them help eliminate motor disorders.
It is known that the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is characterized by the fact that the patient experiences frequent involuntary muscle and tendon contractions. About the disease of foot paresis, see here.
In the treatment of cerebral palsy, a specific but widely used method is used: hippotherapy. Riding a horse has a positive effect on children’s mood and their development (mental, mental, physical), and also helps restore motor skills, improves motor skills and coordination.
The prognosis for this form with timely initiation of treatment is positive, especially if minor impairments in mental activity are observed: children learn to walk without support and use the injured arm; other impairments can also be corrected or eliminated completely. And the sooner treatment begins, the greater the chance that the child will be able to fully adapt and live independently as an adult.
Double hemiplegia
The double hemiparetic form of cerebral palsy is the most severe. It manifests itself as impaired movement in all extremities. These changes are often asymmetrical and differently expressed. In addition to movement disorders, swallowing and speech disorders are characteristic, up to its complete absence (anarthria). Seizures often occur.
Primary brain damage, lack of speech, which leads to the impossibility of contact with peers and learning, ultimately cause mental and intellectual disorders.
This form of cerebral palsy is often accompanied by various developmental anomalies. For example, microcephaly - small head size.
The prognosis for this severe form of cerebral palsy is extremely unfavorable.
Late manifestations
As the child gets older, other symptoms of cerebral palsy appear:

- Speech appears late, some children (30-40%) have speech disorders;
- a quarter of children have various delays in mental development (mental retardation is usually mild, but significant deviations also occur), half have delayed mental development;
- difficulties arise in the process of mastering writing and reading;
- if the right hemisphere is affected, children are irritable, show aggression, and are easily excitable;
- there are gait disturbances;
- Some children experience partial seizures of epilepsy;
- due to a specific gait, spinal curvatures develop;
- bone growth is slowed down, the affected limbs are noticeably shorter and weaker than healthy ones.
The effectiveness of occupational therapy for autism
Autistic people often have problems communicating with other people. The actions of people suffering from this disease are quite limited. The main group of patients for the use of occupational therapy are children who suffer from cerebral palsy, with damage to the musculoskeletal system, and with autism.
Occupational therapy for children can combine several different rehabilitation schemes. They help a child with autism respond better to the world around him, allowing the child to become closer to peers, correctly express feelings and emotions, and focus his attention on assigned tasks.