Emerging abnormalities in the vascular system of the human brain are currently considered one of the most common pathologies, which causes the development of many diseases and often death.
Violations of this nature can be provoked by an incorrect lifestyle, bad habits, frequent stressful situations and nervous strain.
For timely diagnosis of vascular disorders, a modern method called transcranial Doppler sonography is used. Despite the fact that the method exists recently, it allows one to obtain the most extensive information about the state of the patient’s brain.
What is research
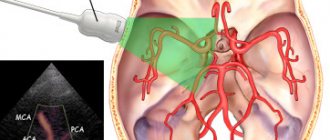
Transcranial Dopplerography (TCDG) is an ultrasound scan that evaluates the speed, pressure and nature of blood circulation through the vessels and arteries of the human brain.
By the word “ultrasound” it is necessary to understand that the main research method is the use of ultrasound, which does not pose any danger to the patient’s health. This is what makes TCD accessible to people of any age.
Doppler sonography is recommended for a thorough study of the cerebral vessels, as well as the craniovertebral cervical spine.
Dopplerography method
Today, one of the most advanced techniques is digital Dopplerography in M-mode, which allows transcranial examination of cerebral vessels. This mode allows you to scan blood flow at a depth of 30-90 mm. The result is presented on a computer monitor in the form of a scale colored in different colors.
Red color displays the characteristics of flows directed towards the sensor, blue, on the contrary, from the sensor. The main difference between the M-method and the standard technique is that there is no need to change the depth to evaluate the vessel, since all flows are scanned automatically at the entire depth. The depth can only be selected if display and measurement of the Doppler signal is required.
The computer has the ability to display from 1 to 8 Doppler spectrum windows at different depths, either in turn, or simultaneously online. The final indicators are formed in a graphic report with digital indicators and the conclusion of the doctor who conducted the study.
What can transcranial Doppler ultrasound reveal? Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels helps the doctor:
- understand the cause of the headache (spasm of cerebral vessels, increased ICP - intracranial pressure);
- diagnose vascular lesions of the head and neck in the early stages;
- detect disturbances in the lumen of blood vessels, including narrowing (stenosis);
- characterize blood flow in the vertebral arteries;
- characterize the functioning of the cerebral venous system, as well as venous outflow through the vessels of the head and neck.
Application of the technique for diagnostic purposes
Today, transcranial Doppler sonography of cerebral vessels is increasingly used in neurology, cardiology and other areas of medicine. With its help, it is possible to determine the presence of the following deviations and violations:
- development of thrombosis, stenosis;
- the course of hypertension;
- macroembolism;
- angiopathy;
- vasculitis;
- symptoms of vascular pathologies that appear in the initial stages;
- aneurysms of arterial and nervous origin;
- arteriosinus anastomosis;
- abnormal brain asymmetry;
- changes in blood vessels that are atherosclerotic in nature;
- suspicion of coronary heart disease;
- altered blood circulation in the structures of the brain;
- encephalopathy;
- congestion in veins and arteries;
- vasospasms of cerebral nature;
- arteriovenous malformations.
In addition, urgent diagnosis using Doppler sonography may be needed when providing emergency medical care (for example, if coronary heart disease or stroke is suspected).
Who needs to be tested?
To understand that there is insufficient nutrition of cells in the brain, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
Doppler sonography of the head is indicated for patients with certain chronic diseases. A specialist may prescribe an examination for people who:
In addition, the study can be prescribed before cardiac surgery, as well as for children with mental development disorders.
Based on the patient's complaints, the neurologist can determine where the blood flow in the body has been disrupted.
Main indications for the study
Transcranial diagnostics can be recommended according to a doctor’s indications, and also as a screening method for studying the condition of cerebral vessels. It is also mandatory during the period of prevention after previous vascular pathologies.
Doppler sonography is mandatory when a person exhibits alarming symptoms or existing diseases. These include the following:
- constant migraines and headaches;
- fainting, fatigue, loss of consciousness;
- frequent noises in the ears and head;
- trembling of the lower and upper extremities, as well as a feeling of tingling and burning in the face and legs;
- diagnosing cervical osteochondrosis;
- the patient has vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- previous traumatic brain injuries;
- circulatory disorders in brain structures;
- injury to the cervical spinal system;
- dysfunction in the cardiac system;
- diabetes;
- decreased level of visual acuity;
- change in coordination of movements;
- age range from 45 to 55 years;
- the presence of mental and mental retardation in childhood;
- genetic predisposition to vascular pathologies.
The main advantage of transcranial Doppler ultrasound is that this procedure has absolutely no contraindications. It is not capable of harming the human body. For this reason, the study can be carried out both in childhood and adulthood.
Transcranial Dopplerography
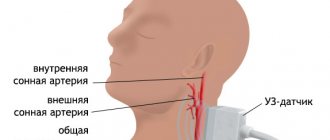
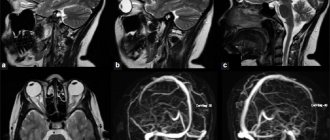
Transcranial Dopplerography (TCDG) is a method of ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels, which allows one to evaluate the speed of blood flow through intracranial vessels - the carotid, subclavian, vertebral arteries, large arteries of the brain, as well as large veins of the neck.
This examination allows the doctor to evaluate not only the diameter of the vessels, the features of their anatomy, but also the patency and speed of blood flow.
Why do you need Dopplerography of cerebral vessels?
Dopplerography of cerebral vessels allows:
- find out the cause of the headache (angiospasm, increased intracranial pressure)
- identify early vascular lesions of the neck and brain, including aneurysms of the cerebral arteries
- identify stenoses (narrowing of the lumen) of the arteries of the neck and brain, determine their significance
- determine the condition of the vertebral arteries
- determine the state of venous blood flow in the vessels of the neck and head
To assess blood circulation in the brain, we recommend that you undergo an examination using modern ultrasound techniques - transcranial Doppler sonography.
Dopplerography in children
In children, Doppler ultrasound is used for:
- delayed speech development
- restlessness, disinhibited behavior
- manifestation of asthenic conditions with increased fatigue, decreased memory and attention
Indications for transcranial Dopplerography
- different types of headaches
- dizziness, both associated with turning the head and changing body position, and occurring in other situations
- noise in the head or ears
- fainting states
- attacks of general weakness, poor health, spots before the eyes, feeling of lack of air
- episodes of sudden loss of consciousness
- episodes of sudden weakness or numbness in an arm or leg, speech problems
- vegetative-vascular dystonia
- consequences of traumatic brain injuries
- pathology in the cervical spine
- pronounced osteochondrosis
- suspected cerebral vascular abnormality
- clinical signs of cerebrovascular accident
- coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction
- vertebrobasilar circulatory failure (VBI), cerebrovascular disease, transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- If you have suffered a stroke, then Doppler ultrasound is necessary to predict the degree of recovery of disorders, the development of complications and relapses of the disease.
- age over 55 years, with a family history of heart attacks, strokes, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis
- poor adaptation to external loads (motion sickness in transport, weather dependence, etc.)
How the research works
Dopplerography of cerebral vessels does not require special preparation, except for the exclusion of vascular drugs immediately before the procedure. You should also not smoke or drink alcohol.
During the examination, you lie on your back on a special couch. The doctor sits behind your head and, touching certain points on your neck and head with an ultrasound sensor, locates the blood flow. During the examination, you need to follow the doctor’s commands - hold your breath, breathe frequently, turn your head (when necessary).
During the procedure, you cannot talk or turn your head. The examination does not cause any unpleasant sensations. The only thing that can cause slight inconvenience is short-term pressure on the neck area (for 3-4 seconds), which the doctor must perform several times during the examination to assess the patency of the blood vessels.
The method is absolutely painless and has no contraindications, which makes this procedure possible for young children.
Getting ready for research
There is no need for special preparation before performing the diagnosis.
All the patient needs to do is stop taking all medications (especially those that stabilize blood pressure) on the day of the Doppler ultrasound.
It is also best to reduce or completely abandon the consumption of coffee, strong tea and alcoholic beverages. After all, the substances included in these drinks can negatively affect the condition of blood vessels and arteries, which will cause distortion of the results.
Preparation and technique
TKDG does not require special training. On the day of the examination, you should refrain from smoking, drinking coffee, alcoholic beverages, and tranquilizers.
Until the end of the procedure, it is prohibited to take medications containing narcotic substances. All drugs for cardiovascular pathologies are also prohibited.
Technique
The patient sits on a chair or lies down on a couch (in this case, a small cushion is placed under the head). After turning on the device, the sensor is pressed against the head next to the ear, then moves upward (to the parietal and temporal region). Then it returns to the starting position and to the back of the head.
This helps to assess blood flow throughout the brain. If necessary, the doctor may ask you to change your position, turn around, hold your breath, or take intense breaths. You cannot move or talk during the scan. The duration of the procedure is 30-60 minutes.
Half an hour for everything
The duration of transcranial Doppler ultrasound in most cases is about 30-40 minutes. During this entire time, the patient will need to follow all the commands that the specialist will tell him (for example, roll over to the other side or hold his breath).
It should be noted that at the time of diagnosis the person does not feel any pain or discomfort. Diagnosis is quick and painless.
The procedure goes as follows:
- the first thing you need to do is lie down on the patient’s back in a specially prepared place;
- after this, the doctor sits behind the patient himself, namely behind his head;
- after this, with the help of special ultrasonic sensors, they are fixed on the head and neck;
- to obtain correct results, the patient should not talk during the event;
- At the end of the procedure, the doctor will definitely inform the patient about this, only after that he will be able to perform motor acts and speak.
All diagnostic results are provided electronically and transcribed by a specialist. Based on them, an accurate medical diagnosis is established and further treatment is prescribed (if necessary).
Performing an ultrasound procedure of the cerebral vessels
All blood vessels that supply the brain are best examined with the patient in a comfortable supine position and the physician examining the vessels from behind the patient's head. In accordance with the normal direction of arterial flow, extracranial examination should be performed before intracranial vascular examination. During extracranial ultrasound, the patient's head should be elevated only slightly or not at all to provide maximum space for insonation in the neck.
Results
The results of the study are interpreted as follows:
- the carotid artery should arise from the aorta on the left side, and from the brachycephalic brain stem on the right side;
- the blood circulation speed in the central and carotid arteries should be uniform and equally palpable (diagnosed);
- the internal branches of the carotid artery should not have any branches before the direct entrance to the cranium;
- a large number of additional branches must be traced from the external artery (carotid);
- the waveform in the internal branches of the carotid artery is monophasic, and the bleeding rate should be slightly greater than in the vein itself;
- the external form of the carotid artery must have a three-phase character, and the bleeding rate must be an order of magnitude lower than in the carotid artery itself;
- the thickness of the tissues of all vessels should not exceed 0.12 centimeters.
If a specialist diagnoses significant thickening of the blood walls, we can talk about the development of atherosclerosis.
When diagnosing abnormalities during diabetes mellitus, it is advisable to say that the disease is in the stage of decompensation.
Contraindications and expected risks
There are no unconditional contraindications that prohibit the procedure. Limitations are the patient’s serious condition and other factors that do not allow the patient to take a lying position (chronic heart failure, exacerbation of bronchial asthma). Dopplerography is absolutely safe for the human body and does not cause radiation exposure. This procedure has no age restrictions. It is performed on the elderly, infants, nursing mothers, and pregnant women. During pregnancy, the doctor may refer you for testing if there is a possibility of circulatory problems in the placenta.
TCD DS of head and neck vessels can be performed multiple times. Due to its harmlessness and high accuracy, the technique is used to control the ongoing treatment. In addition, it is prescribed for the prevention of serious diseases.
When conducting a study, certain difficulties may arise: it is more difficult to assess the condition of small vessels than large ones; It happens that the cranial bones prevent a full analysis of the condition of all brain vessels. Results often depend on the qualifications of the specialist and the instruments. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCDG) is often used instead of angiography.