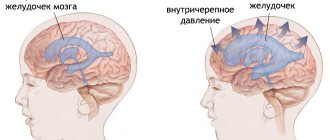
Agenesis of the corpus callosum in the fetus is a congenital brain disease that is formed under the influence of genetically determined factors. This disease is an intrauterine pathology and occurs in very rare cases.
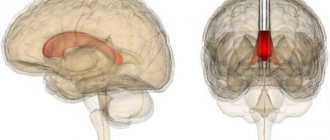
The corpus callosum is formed by nerve endings that intertwine with each other. The function of this anatomical formation is to connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain. The shape of the corpus callosum is wide and flat, and it is located under the cortex of the brain.
The formation of agenesis is observed in the complete absence of adhesions that connect both hemispheres. In terms of incidence, agenesis of the corpus callosum accounts for no more than 1 case per 2000 newborns.
Causes
The most likely factor in the occurrence of this congenital anomaly is genetic defects that affect the development of central nervous system structures. There are two variants of the course of agenesis. In the first case, the newborn child does not suffer from motor and intellectual activity, while the disturbances affect the quality and speed of transmission of nerve impulses from the right hemisphere to the left, and vice versa. Such children, as they grow older, are not able to determine in which hand this or that object is located. In addition, disorders may affect speech function.
If we talk about the second option for the development of agenesis, then such children have serious malformations of central nervous activity. Manifestations of this variant of agenesis include seizures, hydrocephalus, impaired neuronal migration, and mental retardation.
The period for the formation of this structure in the fetus is the period from 10 to 20 weeks of gestation. According to the nature of the course, medical practice distinguishes the incorrect formation of the corpus callosum, its partial or complete absence. Despite the fact that the true cause of this developmental defect has not yet been established, the following predisposing factors for the development of agenesis are identified:
- Chromosomal rearrangement;
- Launching the process of uncontrolled gene mutation;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Persistent disruption of metabolic processes in the body of the expectant mother;
- Drinking alcohol and smoking while pregnant;
- Insufficient intake of vital components into the body of the developing fetus;
- Toxic damage to the body of a child in the womb. We are talking about the entry of certain medicinal components and other toxic substances into the mother’s body;
- Various injuries suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- The presence of an infectious-inflammatory process in the body of a pregnant woman.
History of the study
The corpus callosum has long remained a mystery of human anatomy. Scientists could not determine exactly what function this part of the brain has. By the way, in 1981, the scientist who discovered the corpus callosum received the Nobel Prize for this. His name was Roger Sperry.
The first operations on the corpus callosum were aimed at treating epilepsy. Thus, by disrupting the connection between the hemispheres, doctors actually cured many patients from epileptic seizures. But over time, scientists drew attention to the occurrence of specific side effects in such patients - behavioral reactions and abilities changed. Thus, as a result of experiments, it was found that after an operation affecting the corpus callosum, a person could write exclusively with his right hand, and draw only with his left. So the corpus callosum, the functions of which were still unknown to scientists, was no longer dissected in surgery to treat epilepsy.
A few years later, scientists discovered a connection between the focus of the corpus callosum and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of agenesis, as well as their intensity, are closely related to the level of underdevelopment of the corpus callosum. After the child is born, he may develop the following clinical manifestations of agenesis of the corpus callosum:
- Developmental defects of the visual apparatus;
- Microcephaly;
- Brain tumors;
- Atrophy of the nerves responsible for the functional state of the organs of vision and hearing;
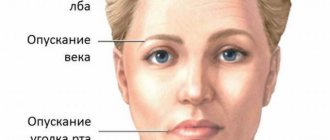
- Facial dysmorphism;
- Risk of seizures;
- Fundus pathologies;
- Early puberty;
- Gastrointestinal pathologies;
- Delayed psychomotor development.
In addition to the above-described clinical manifestations of agenesis, children with a similar diagnosis often develop a rare genetic disease called Aicardi syndrome. The pathology is accompanied by visual disturbances, as well as functional disorders of the central nervous activity.
Along with this pathological condition, agenesis of the ductus venosus develops in the fetus. We are talking about the so-called combined malformations of the child. Such babies may develop defects such as facial anomalies, diaphragmatic hernia, renal agenesis and other types of anomalies.
corpus callosum of the brain is absent in a newborn
With this developmental anomaly, there are no fibers of the large tract connecting the two hemispheres of the brain. Sometimes partial agenesis is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner; in most cases the etiology remains unknown. With this anomaly, two clinical syndromes are distinguished.
Firstly, the patient has preserved intelligence and motor functions, and the anomaly itself is manifested only by a violation of the transmission of information from one hemisphere to the other: for example, a right-handed patient finds it difficult to name an object placed in his left hand, since this requires that information from the right sensory zone of the cortex entered the speech zone, localized in the left hemisphere. Secondly, most often agenesis of the corpus callosum is combined with other malformations of the brain, including lack of neuronal migration and hydrocephalus. In this case, from a very early age, children experience severe seizures, mental retardation, an increase in head size, and often hypertelorism. The diagnosis is made based on data from pneumoencephalography or computed tomography.
Porencephaly is a defect in the medullary mantle resulting from a cyst-like expansion of the lateral ventricle that may extend into the pia arachnoid. Sometimes its cause is a primary anomaly in the development of the cerebral mantle; in this case, the defect is usually bilateral with displacement of the fluid-filled temporoparietal areas of the brain.
In children with a bilateral process, complete amentia occurs. More often, porencephaly is unilateral and develops secondarily as a result of focal brain damage in the last period of intrauterine development or in the early postpartum period. Possible etiological causes include cerebral vascular occlusion, encephalitis and brain puncture.
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, children develop with
Source
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a congenital pathology, the development and spread of which is played by genetic factors. The corpus callosum itself is the largest structural formation of the brain, which connects both hemispheres to each other.
The intersection of fibers, as well as their connection with the hemispheres, begins already at twelve, thirteen weeks.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum, the consequences, treatment and symptoms of which will be discussed below, occurs with the partial or complete absence of it itself, as such.
The corpus callosum is a dense plexus of nerves in the brain. It is designed to connect the right and left brain hemispheres. It consists of up to two hundred and fifty million neurons. The corpus callosum is flat and wide, consists of axons, and is located directly under the cortex.
The fibers mainly run in the transverse direction and connect the symmetrical parts of the brain, but there are also longitudinal fibers that connect the asymmetrical parts of the opposite hemispheres, or one part.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum, the consequences of which are reflected in the intellectual abilities of a person, is part of many widespread congenital developmental disorders, pathologies and diseases.
The main callosal commissure in this case is partially or completely absent; it is replaced by transparent columns of the fornix, short and incomplete septa. The frequency of occurrence of this kind of defects is one case in two thousand conceptions, the reason for this is heredity or spontaneous unexplained gene mutations.
Symptoms of agenesis of the corpus callosum
Symptoms of agenesis of the corpus callosum can manifest themselves in different ways, one way or another, expressed in intellectual retardation of various levels, epileptic seizures, disorders of motor physical activity, as well as anomalies in the formation and growth of internal organs of people
Source
Hello. My daughter has agenesis of the corpus callosum, a congenital malformation of the brain. We are being observed and treated at the Kalinin hospital. But I have never met any children there or in general with such a diagnosis. I would really like to talk about this topic and share my experience. Are there really no more children with this diagnosis in Samara?
We were diagnosed after a CT scan. But for many, agenesis of the corpus callosum is diagnosed during pregnancy, when an ultrasound is done around 20 weeks. I had ultrasounds done 3 times during my pregnancy, and all 3 times everything was just fine. We were diagnosed when our daughter was one year old.
My daughter started sitting at 10 months, standing up in her crib at 1.3 years, crawling at 1.5 years, and walking at almost 3 years. But she does not follow instructions, even the most basic ones... She does not understand spoken language. She knows her name and has been responding to it since she was 5 months old. Our hearing and vision are good...
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is incurable, I know. But I think that there are some methods of brain development that will suit and help us. Doctors say just wait, either the brain will find a communication path between the two hemispheres besides the corpus callosum or not...
But I don’t want to wait, I want to act...
The corpus callosum (lat. corpus callosum) is a plexus of nerve fibers in the brain of placental mammals, connecting the right and left hemispheres.
In addition to the corpus callosum, the hemispheres are connected by the anterior commissure, posterior commissure and commissure of the fornix (commissura fornicis). But the corpus callosum, consisting of 200-250 million nerve fibers, is the largest structure connecting the hemispheres.
The corpus callosum has the shape of a wide, flat strip, consists of axons and is located behind the cortex.
We were diagnosed with agenesis of the corpus callosum from birth, since the tomogram step never fell on it. Then the ultrasound doctor Kotlyarov showed me the callus on the monitor at the IDK
Source
The corpus callosum of the brain is a strong adhesion of huge hemispheres located in the brain, which formed along with the development of neopallium. The corpus callosum of the brain is a white organ that has a long shape and a slightly compacted formation.
The corpus callosum extends over its entire area from the back to the front, and its total length is approximately 9-10 centimeters, making it the largest commissure in both hemispheres of the human brain.
General information
The corpus callosum is located in the deep part of the longitudinal fissures of the brain. In general, such an organ can be divided into three large sections - posterior, middle and anterior. Now I would like to consider in more detail what each part of the corpus callosum is.
If we talk about the anterior section, then it bends forward, then down and at the very end back. Thus, an organ is formed, which is called the knee of the corpus callosum, which smoothly passes into the lower parts of the carina or directly into the beak of the corpus callosum. Then, the latter continues to advance to the final plate, located in front of the common commissure and slightly below it.
The middle section of the corpus callosum is also called the brain stem. It has the appearance of a certain convexity, which, in turn, resembles the shape of a rectangle. It is this part that is considered the longest of all that are present in the adhesions of the human brain.
Rear end. Here is the splenium of the corpus callosum, a thickening. By the way, the roller hangs in a free style over the epiphysis of the brain, as well as over the plate of the lid, located in the middle part of the brain.
At the very top of the corpus callosum there is a very thin layer of gray fluid, the so-called gray vesture. In some specific situations
Source
Among the anomalies of brain development, one of the most common diseases is congenital structural pathology, agenesis of the corpus callosum, in which there is a violation of associative connections between the two hemispheres.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum: causes
A disease associated with abnormal development of the brain, congenital, quite rare, manifested in the complete or partial absence of a structural formation connecting the hemispheres of the brain, is called adhesion of the corpus callosum.
Normally, the corpus callosum, or major commissure, is represented by a dense junction of nerve fibers that unites the cerebral hemispheres, left and right, and ensures coordination between them.
The formation of this structure from a morphological point of view corresponds to the period of 10-20 weeks of pregnancy; the beginning of differentiation of the tissue of the corpus callosum is attributed to the middle of the sixth week.
This pathology can have varying degrees of structural manifestation and be expressed in the form of a total absence, partial (hypogenesis) or incorrect (dysgenesis) formation, underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the corpus callosum.
Instead of the normal structure, which looks like a wide, flat strip, the large commissure takes on the appearance of shortened septa or transparent pillars of the arch.
To date, it is not possible to unambiguously name the cause of agenesis of the corpus callosum; we can only identify the factors causing its occurrence.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The clinical manifestations of the disease vary; depending on this, it can be detected in a severe form in childhood, usually up to two years, or in adults, asymptomatically and sometimes completely by accident.
Causes of hoarseness in a newborn's voice Hoarseness of voice is a rather unpleasant condition. It is not a disease, but rather a symptom of some illness or its consequence. Young children encounter this quite often.
When a child has
Children whose disease, for one reason or another, was not diagnosed in the prenatal period, at birth
Source
In this publication you will learn why hydrocephalus occurs in a newborn baby, what kind of disease it is, what symptoms appear, what measures need to be taken so as not to harm the body even more.
Hydrocephalus is a brain disease that occurs due to excess fluid in the ventricles. This phenomenon affects the size of the ventricles of the brain and can lead to an increase in their size.
Three types of hydrocephalus in newborns
The first type of hydrocephalus develops in older people. Newborns may experience hydrocephalus of the second and third types.
With replacement hydrocephalus, fluid accumulates in the intracranial space, and with uncompensated hydrocephalus, damage to brain tissue occurs. Hydrocephalus in the first months after birth can occur for various reasons.
Hydrocephalus in newborns can be congenital and develop during fetal development, while acquired hydrocephalus can be associated with exposure to external factors. The formation of a tumor or infection can be the impetus for the disease hydrocephalus.
cause the development of fetal hydrocephalus, possibly an infectious disease suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy, especially in the early stages;
Fetal hydrocephalus is diagnosed using ultrasound after sixteen or twenty weeks of pregnancy. Moreover, past infectious diseases cause more harm in the early stages due to the fact that during this period all the organs of the unborn child are formed.
a newborn may be allergic to dill water. Bathing is one of the most favorite activities of all babies, but even it can pose a potential danger to their health. Who would have thought that an activity that is absolutely harmless at first glance could turn
About eighty percent of hydrocephalus in a newborn is caused by improper development of the brain or spinal cord, as well as infections during development. Twenty percent of newborns may develop hydrocephalus as a result
Source
The corpus callosum is a strong connection of nerve fibers, which in turn connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain. There are more than 250 million nerve fibers in the structure of the corpus callosum; they are the largest structure that connects the hemispheres.
A little history
A group of scientists led by neuropsychologist Roger Sperry discovered the corpus callosum. This event took place in the first half of the 60s, and in 1981 Sperry received the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
While conducting research to cure epilepsy, scientists conducted several successful experiments on animals. Then surgery was performed on the human brain. The essence of the operation was to separate the hemispheres of the brain, which are connected by nerve fibers. This connection of fibers is the corpus callosum of the brain.
The result of such operations was relief from epileptic attacks. However, after surgery in the corpus callosum, some behavioral characteristics of a person changed, as well as some of his abilities.
For example, people who operated with their right hand in everyday life could not write anything with their left hand, but draw anything with their right hand. Or another example: with their right hand, those operated on felt an object and recognized it, but could not name it out loud.
As a result of these operations, patients were able to be relieved of epileptic seizures, but at the same time, some unusual features and problems were added to their lives. This was the beginning for scientists to study the various functions of the cerebral hemispheres.
A thin layer of gray matter covers the upper part of the corpus callosum and in some places appears as longitudinal thickenings - stripes. The fornix and pro
Source
Source: https://bornechal.ru/post/1046-mozolistoe_telo_golovnogo_mozga_otsutstvie_u_novorojdennogo
Diagnostics
To reliably detect structural abnormalities in the fetus, the following diagnostic techniques are used:
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- Echography;
- MRI.
It is possible to obtain reliable information about certain changes only in the second half of pregnancy.
Diagnostic difficulties regarding agenesis of the corpus callosum are due to the fact that this intrauterine pathology is most often combined with other types of developmental anomalies. Medical specialists often determine agenesis of the cerebellar vermis in the fetus. In clinical practice, both partial agenesis of the cerebellar vermis in the fetus and its complete absence occur with equal frequency.
Localization
Spatially, this part of the brain is located under the hemispheres along the midline. From anterior to posterior, the corpus callosum can be divided into several different zones: genu, midsection, body, posterior end, and splenium. The knee, curving downwards, forms the beak, as well as the rostral plate. On top, the corpus callosum is covered with a thin layer of gray matter.
Another structure of this part of the brain is radiance. Strands of fan-shaped neurons extend to the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres.
Treatment
Modern medicine does not have effective methods for correcting the abnormalities that arise in a child when diagnosed with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Drug therapy for this condition is selected for the baby individually, taking into account the degree of agenesis, as well as the presence of concomitant developmental anomalies. To correct functional disorders, the following groups of medications can be used:
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example Prednisolone and Dexamethasone;
- Phenobarbital and benzodiazepines;
- Neuropeptide drugs, for example, Cerebrolysin and nootropics, for example, Piracetam, Semax;
- Diazepam drugs and antipsychotics.
In addition, children with a similar developmental anomaly are prescribed Mexidol, Diacarb and Asparkam.
In addition to the listed conservative treatment methods, some children are prescribed surgery to stimulate the fibers of the vagus nerve. This procedure is recommended for those children who have persistent functional disorders in the functioning of internal organs.
Taking into account the fact that agenesis of the corpus callosum is a potential cause of structural and functional abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system, such children very often develop S-shaped scoliosis.
That is why medical experts recommend that children regularly perform physical therapy and hardware physiotherapy sessions. Share:
Sexual dimorphism
A number of Russian and foreign scientists believe that the difference in thinking and behavioral reactions between men and women is associated with the different structure and size of the corpus callosum. Thus, Newsweek published an article explaining the nature of women's intuition: women have a slightly wider corpus callosum than men. This fact, according to the same scientists, also explains the fact that women, unlike men, are able to cope with several different tasks at the same time.
After some time, a group of French scientists reported that, as a percentage of brain size, men have a larger corpus callosum than women, but scientists did not draw any clear conclusions. Be that as it may, all scientists only agree that the corpus callosum is one of the most important structural components that performs a number of vital functions.