Concussion is one of the most common diagnoses in pediatric traumatology. Overall, traumatic brain injury (TBI) ranks first among all childhood injuries requiring hospitalization. Approximately 120 thousand children with concussion are admitted to Russian hospitals every year.
According to the severity, traumatic brain injury is divided into mild (concussion), moderate (mild to moderate brain contusion, with possible fractures of the cranial vault) and severe (severe brain contusions, intracranial hematomas with compression of the brain, fractures of the base of the skull). Fortunately, up to 90% of childhood TBIs are concussions, which is what this article will discuss.
The high level of injuries in children is explained by the child’s increased motor activity, restlessness and curiosity, which is combined with imperfect motor skills and coordination of movements, as well as a reduced sense of danger and fear of heights. In addition, in young children, the head has a relatively large weight, and the skill of belaying with hands has not yet been developed, so small children, as a rule, fall upside down and do not use their hands.
The causes of childhood TBI are very specific to each age group. Newborns in the total mass of victims make up 2%, infants - 25%, toddlers - 8%, preschool children - 20% and school-age children 45%.
Injuries in infants are primarily the result of the inattention and carelessness of their parents. Children under 1 year of age most often (more than 90%!) receive head injuries after falling from changing tables, beds, from parents' arms, from strollers, etc. You should never leave your baby alone in a place where he could fall. If you need to move away from your child at a distance greater than an outstretched hand, do not be lazy, put him in a crib, in a stroller with sides, in a playpen! One or two seconds is enough for the baby to roll to the edge of the changing table and fall.
From 1 year
babies begin to walk. The main cause of TBI is a fall from one’s own height, and a little later - falls from stairs, trees, roofs, windows, slides, etc. The episode of TBI itself is not always possible to identify. It should be borne in mind that if the child remained under the supervision of relatives, neighbors or a nanny, then they can hide from the parents the fact that the baby fell.
Older children
For various reasons, they themselves often hide the trauma.
In addition, children may experience brain damage without direct head trauma. These injuries usually occur when a child's body is subjected to sudden acceleration or deceleration (shaken baby syndrome). “Shaken baby” syndrome is most often observed before the age of 4-5 years
and can occur with rough handling, jumping from heights, and in young children even with excessively intense rocking.
Child's body
Childhood is a time of active changes in the body, because from a newborn baby a person needs to grow into an adult. Activity and curiosity are the main features of a growing individuality. Moreover, this is typical both for a baby who begins to crawl and walk, and for a teenager who considers himself a completely grown-up and independent teenager. And it often happens that a concussion becomes a consequence of a child’s worldview. Whether the child is 2 years old or 12 years old, it doesn’t matter; in case of a head injury, consultation with a medical specialist is required in any case.
Concussion as an injury
Impacts and unintentional sudden movements of the head in most cases lead to a concussion. This phrase refers to the mildest, so to speak, form of injury to this most important organ, which precedes a bruise. However, concussion is also divided by experts into several degrees:
- mild degree - no loss of consciousness, slight lethargy, the child may experience nausea, after 20-30 minutes the condition returns to normal;
- moderate degree - there may be a loss of consciousness for a short time, the child periodically feels sick and vomits, you can see external signs of injury - a mark from an impact, a hematoma; health status may return to normal after a few hours;
- severe degree - sufficiently long-term loss of consciousness or disorientation in space, paroxysmal vomiting and nausea, severe headaches; Mandatory hospitalization and round-the-clock monitoring by medical staff are indicated.
They are characterized mainly by the time of loss of consciousness during injury, as well as the severity of symptoms and consequences. For example, a concussion in a one-year-old child is diagnosed precisely by external signs, since the baby cannot yet independently talk about his condition.
A concussion itself is a slight contact of the gray matter, surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid, with the hard walls of the skull. This occurs with sudden movements of the head: falls, collisions. A stronger contact of the brain with the bones of the skull is called a bruise. It is noteworthy that with this form of traumatic brain injury, pathomorphological changes can be detected only at the cellular and subcellular levels, but external, let’s say, signs are diagnosed as a consequence of a concussion.
Symptomatic signs of childhood TBI
Reference! Approximately 120 thousand children with concussion are admitted to hospitals in Russia every year. Therefore, it is not even worth talking about the prevalence of this disease. It ranks first among childhood injuries.
- Pale skin followed by redness. In children with a concussion, one of the first signs is often pallor of the facial skin, which then, several hours or even days after the injury, is sharply replaced by erythema (redness of the tissues). This symptom is observed most often, but it may not exist.
- Vomit. This is another symptom indicating a possible concussion - vomiting. Both immediately after the injury and several hours and even days later.
Astigmatism.
When a child has a concussion, the movement of the pupils may be out of sync.- Very severe headache. When it comes to babies who cannot speak, it is simply impossible to know about this symptom. But children who have already “found the gift of speech,” so to speak, often complain that they often have a headache. And strongly.
- Loss of consciousness. Sometimes it can be short-term, sometimes it can last for a very long time.
- The pulse has changed. If your heart rate changes, this may be another sign of a concussion. It can be either too slow or too fast.
- Breathing has changed. If a child has a head injury and there is shortness of breath, the cause may be a concussion.
- There is blood coming from the nose. This may also indicate a concussion or even more serious injury.
- The size of the pupils changes. Both increase and decrease are possible.
Sometimes some of these symptoms may occur, sometimes all of them.
Is there any other way to check whether it is there or not?
If your baby's concussion is not detected immediately, the symptoms may become less severe.
- The baby becomes lethargic and is uninterested in even the activities that he loved before the injury.
- He often complains of aching pain in his head.
- And for tinnitus.
- And for dizziness, i.e. the vestibular apparatus is impaired.
- And for poor sleep. At the same time, excessive drowsiness is possible.
Before your eyes, the baby fell and hit his head. What should you pay attention to in order to watch out for a concussion and avoid possible complications?
- Did he cry, did he become restless in his behavior, was there any disturbance in coordination of movements?
- Preservation of appetite.
- Was there excessive spitting up or vomiting and, if so, how long after the injury.
- What is the size of the pupils, their change when reacting to light.
- Time to fall asleep and quality of sleep.
Test to check the child's condition
Children of preschool and primary school age cannot always tell themselves what worries them. Help them.
Carry out diagnostics. Ask a few simple questions to assess your post-injury condition.
- How do you feel?
- How old are you?
- Does your head hurt?
- Does it hurt to move your eyes and sides?
- Is there any nausea?
- Do you feel unsteady when walking?
- What were you doing before the injury?
- Are you sleeping well?
What should you be wary of?
The first signs of a concussion in a child may not alert parents if they did not see the moment of injury, and the child either cannot tell on his own or hides it. But sudden lethargy, drowsiness, nausea or vomiting should alert and force parents to take their child to a specialist who can determine the extent of the injury. Signs of a concussion in children may be mild and occur not as a group, but as if separately, but in any case, examining the child and consulting a doctor will not be superfluous.
How does concussion manifest in infants and young children?
It would seem, is it possible for a concussion to occur in an infant? Symptoms of the problem indicate brain damage associated with a blow or bruise. But harsh, rough treatment is enough for a baby, when a concussion is defined as “shaking syndrome.” Parents may not even realize that the child has suffered a mild form of traumatic brain injury, attributing crying, whims, refusal to eat, regurgitation, and drowsiness to other reasons. A child who cannot speak and explain what is bothering him, in the absence of pronounced manifestations of a concussion, such as loss of consciousness, open wounds, may behave differently than usual for only a few days. This should be the reason for contacting a pediatrician.
As for older children, they may not talk about a head injury due to fear or punishment from the parents themselves, or having received threats from the person who indirectly or directly caused the head injury. Therefore, changes in the child’s behavior, as well as attacks of nausea and vomiting, and complaints of headaches require contacting a specialist who can determine the cause of the ailment and prescribe treatment that is appropriate to the situation.
What is a concussion and why is it dangerous?
A child's fall, violation of rules of conduct on the playground, or simply an unfortunate set of circumstances can result in not only a bump or a cut in the skin, but also a more serious head injury.
Concussion is the most common type of consequence among all types of damage to the brain. It is characterized by reversible disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system. The mechanism of development of the condition is based on disruption of connections between the cells of the medulla.
Experts distinguish three stages of development of a bruise:
- acute – the period of onset of symptoms of pathology, which lasts up to 10 days;
- intermediate – six months from the moment of injury, during which brain functions should be fully restored;
- long-term – up to 2 years from the moment the first symptoms appear, when either complete recovery should occur, or pathological consequences may appear.
In childhood, as a result of bruises and falls, a mild degree of pathology is usually observed, which does not threaten any permanent negative consequences. In some cases, there is still a possibility of developing serious complications. These include cerebral edema, hemorrhages, and post-traumatic epilepsy. Among the long-term consequences, early aging of the central nervous system organ stands out. It significantly reduces life expectancy and affects the general condition of a person.
A teenager has a problem
A concussion in a child in adolescence can also be a health problem. After all, children are curious, do not think about their safety, and extreme hobbies, one might say, simply boil in the blood of teenagers. Such traumatic brain injury manifests itself, depending on the severity, with the following symptoms: nausea, frequent vomiting, loss of consciousness and disorientation, headache, external signs of head trauma. Unfortunately, teenagers can often hide an incident that happened to them from their parents, and therefore the period of the problem can pass without medical supervision, but if the injury is severe enough, then its consequences can be quite unfavorable for the child’s health. Attentive attitude on the part of adults to a teenager, a trusting relationship between a child and his parents will help to cope with any difficult situation correctly, without fear of punishment and misunderstanding.
What to do if you have a concussion
Regardless of the severity of the injury, the child should be shown to a specialist. A traumatologist or neurologist will assess the baby’s general condition, decide on hospitalization, and provide first aid. It is not recommended to take independent actions. It is better to limit yourself to the simplest activities. The patient should be laid down and calmed down, if there is a wound, its edges should be treated, and cold should be applied to the lump.
The child needs an influx of fresh air, for which a window is opened indoors, and space around the victim is cleared outside. You should not let your baby fall asleep, especially if he complains of drowsiness. Due to the high likelihood of vomiting, the patient's head is turned to the side so that he does not choke. If the patient has lost consciousness and shows no signs of life, begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Medical aspects of the problem
The degree of concussion in children can vary; only a specialist can determine the quality of the injury. Modern neuroscience, unfortunately. acknowledges the fact that today it is quite problematic to accurately diagnose a concussion. This is due to the non-specificity of the result of the injury, since the signs that appear during a concussion serve as indicators of a number of health problems. Many experts start from the fact that a concussion is made as a diagnosis by the method of differentiation, that is, the gradual exclusion of pathologies with similar manifestations from the list of potential problems. As a result, a concussion of a certain severity is diagnosed.
Traumatic brain injury can manifest as individual, single symptoms or as a complex of them. In addition, an uncharacteristic symptom may appear - temperature during a concussion in children. This is associated more with the body’s reaction to a traumatic situation than with the development of the inflammatory process. Although a brain contusion, the appearance of a hematoma and the lack of adequate treatment can cause inflammation at the site of the skull injury.
Consequences
Typically, with a concussion, symptoms subside within three days. In such cases, parents interrupt therapy. The consequences may not appear immediately, but closer to adolescence. The type of complications depends on the causes and the severity of the resulting disorders. This may include frequent headaches, dizziness, and convulsions. Character traits change, the child becomes more whiny, capricious and irritable. There is retardation in mental development.
Urgent measures at home
Any symptoms of a concussion in children require contacting a specialist for consultation and a thorough examination. Whatever the reason for the deterioration in health, the child needs to receive quality therapy. If parents or other adults saw the injury or the child was able to talk about what happened, you must first take the following steps:
- call an ambulance, explaining the situation;
- place the child on a flat surface;
- calm the victim emotionally without resorting to special medications, even seemingly harmless ones like valerian;
- apply something cool to the site of injury, such as a towel soaked in cold water, to reduce the risk of complications - the development of edema and hematoma;
- if necessary, treat open wounds and abrasions with special agents, for example Chlorhexidine.
A concussion in an infant is accompanied by crying, since the baby cannot talk about what is bothering him and what happened. And if there was no clearly recognized moment of injury, for example, the child did not fall from the changing table, but there was rough handling of the baby, for example, sudden shaking, then parents should assume the potential danger of a concussion in the baby and also call an ambulance.
If you suspect a brain injury, there is no need to give your child any medications, even symptomatic ones, to eliminate nausea, for example, without consulting a doctor.
Signs of a concussion in a baby
June 23, 01:14
The child fell and what should I do?
There are mothers who complain that their child fell... from the sofa, bed, when they, the mothers, turned away or walked away for just a couple of seconds... What to do in a situation when a child has fallen? A child’s skull is a more fragile and vulnerable structure.
The likelihood of brain injury from a head impact is much higher in children than in adults. Especially in the first year of life, when the bones of the skull have not yet fused and are easily displaced upon impact. We, adults, are obliged to know where the baby is in danger. Fall to the floor from the changing room...
Continue reading →
If the baby fell off the sofa
It probably doesn’t happen that a child grows up and never falls, but a young mother is especially worried when this happens in infancy.
Rolled off the sofa, off the bed or fell from the changing table - almost all babies will experience such an unpleasant story, but there is no need to become hysterical and blame yourself, the main thing is to calm down and carefully monitor the child’s behavior.
The baby's head weighs much more than the body, so when falling, it is the head that babies hit most often. The severity of the bruise depends on the height... Continue reading →
What to do if a child falls?
First aid for a baby after a fall and what you should pay attention to: Continue reading →
Visit to a neurologist
After Thursday’s fall, we went to see a neurologist... Read more →
Fell out of bed and hit his head.
As you know, between the bones of the skull and the brain there are meninges and a special liquid - cerebrospinal fluid, which additionally protects the brain. During a head impact, the brain continues to move by inertia, that is, it moves inside the skull, sharply colliding with the bones of the skull.
Liquor dampens this movement, but not always. And in case of severe trauma, if there is a fracture of the skull bones... Continue reading →
Girls! Read it, it’s important... the baby’s fall...
We, adults, are obliged to know where the baby is in danger. Falling onto the floor from a changing table or falling out of a stroller is a “hobby” for infants. Older children master the world by testing its strength with their own foreheads.
Continue reading →
Cperla)
We, adults, are obliged to know where the baby is in danger. Falling onto the floor from a changing table or falling out of a stroller is a “hobby” for infants. Older children master the world by testing its strength with their own foreheads.
The young traveler doesn’t even need sharp corners - he will hit a bump literally out of the blue. And it’s good if there’s a bump. And when the baby grows up and starts running, it is not known who grabs his head more often - the frightened mother or himself.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely protect a child from injury. If your child falls… Read more →
falls
Approximately from the third month, the child’s motor activity increases (begins to roll over from back to stomach), and with it the danger of falling. Children fall from strollers, from cribs and this happens with lightning speed; You won’t always have time to react, even standing nearby! Continue reading →
GOOD TO KNOW.
Hitting your head: why is it dangerous?
For some reason I turned out to be unprepared for today’s incident... oh, mother... “Children under one year old Infants most often roll onto the floor from changing tables, so you need to swaddle the baby not on the table, but, for example, on the sofa. He's shorter.
Also, to cushion a possible fall, place a rug under a table or next to a sofa.
Three more simple recommendations: do not take your eyes off the baby for a second while swaddling; try to hold him with your hand; if you need to go away (to get a bottle, or pick up the phone, or open the door), take the baby with... Read more →
If the baby falls
Approximately from the third month, the child’s motor activity increases (begins to roll over from back to stomach), and with it the danger of falling. Children fall from strollers, from cribs and this happens with lightning speed; You won’t always have time to react, even standing nearby! Continue reading →
Source: https://www.BabyBlog.ru/theme/priznaki-sotryaseniya-mozga-u-grudnichka
Diagnostic principles
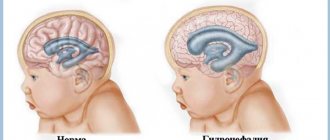
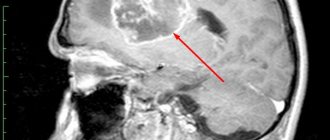
Diagnosis of a concussion in children is a whole range of measures that work both to identify the cause of deterioration in well-being and to identify the depth and extent of the injury. To do this, the specialist uses a survey of either the child himself or adult relatives, an external examination, and the appointment of standard tests - the baby needs to donate urine and blood to determine the inflammatory process, for example, which can cause the disease. Then MRI, CT, and radiographic examination are prescribed. Which method of examining a child to choose in each individual case is decided by a specialist depending on the situation.
An informative method for diagnosing traumatic brain injury, as well as congenital pathologies, is electroencephalography. It allows you to identify the electrical activity of brain cells and draw conclusions about the pathological processes occurring in a particular area of the organ. Also, in establishing the fact and extent of brain trauma in infants, neurosonography is used, in which the baby’s brain is examined by ultrasound through an area of the skull not protected by bone tissue—the fontanel. But ultrasound encephalography allows you to literally “see” the state of the brain on the monitor screen - tumors, hematomas, injured areas.
The main causes of injury
Concussion in children is the most common type of traumatic brain injury. Increased activity, restlessness, and curiosity are not the only reasons for this.
Most often, concussions are observed in school-age children - they make up 45% of the total number of affected children. The lowest rate in newborns is 2%. In addition, 25% are infants, 8% are toddlers, and 20% are preschoolers.
Unfortunately, concussions in infants are the result of parental inattention and carelessness. In 90% of cases, children are injured as a result of falling from a changing table, bed, stroller, or even the gentle hands of their parents. At this age, children require maximum attention and care, and not only of a psychological nature.
Under no circumstances should you leave a child alone for several minutes if there is even the slightest chance that the precious child may fall. If there is a need to leave, leave the baby in a playpen, a crib with sides, or another place that is reliably protected from falling.
After the age of 1 year, when the youngest member of the family begins to walk, the main cause of concussion is a fall from one’s own height. The older the child becomes, the more the height of the fall increases: these already become stairs, trees, fences, slides, windows and even roofs.
Exploring the world, a child tries to discover everything new, unknown, to conquer new heights in the most literal sense of the word. And here it is not enough to simply tell what is good and what is bad, what can be done and what cannot be done.
Treatment options
Mild concussions in children most often do not require hospitalization. Treatment of such an injury is carried out on an outpatient basis, but the child must be provided with maximum peace, both physical and psycho-emotional. More severe forms of brain trauma will require hospitalization in a hospital, where the patient will be prescribed both additional examination techniques and appropriate treatment, which may include a whole range of medications:
- anti-allergenic medications (such as Fenkarol);
- vitamins;
- diuretics;
- nootropics;
- painkillers;
- sedatives.
Some concussion symptoms in children may require appropriate treatment. For example, vomiting can be controlled with antiemetics and fluid management agents. In a hospital, a small patient should also be provided with peace.
The child must remain in bed for the entire period of treatment - this is the main key to successful treatment of a concussion of any severity. Unfortunately, medicine today cannot guarantee that any disturbances in the activity of the central nervous system that may arise in later life are not a consequence of the trauma of the cranial structure experienced. Therefore, the more carefully all the recommendations of the treating specialist are followed, the better the result of therapy will be.
First steps if you suspect such a TBI
First of all, you need to provide the child with maximum peace (i.e., place him on a hard surface, cover him with a blanket).
- If there was a loss of consciousness, the child should be placed on the right side, the left arm and leg should be bent 90 degrees. Similar measures must be taken if vomiting occurs in a supine position.
- Examine him for abrasions and bruises. If there are any, process them.
- See a doctor as soon as possible!
If you suspect a child has a concussion, DO NOT:
- Get to the clinic on your own. You need to call an ambulance if possible.
- You cannot give him water or any medicine, because... this will increase the urge to vomit.
If diagnosed in the hospital, which doctor should I contact?
It depends on many factors.
- If the injury was not severe, then an examination by a pediatrician is needed. If necessary, he can refer you to a neurologist. Whether examination by other specialists is necessary depends on the nature of the injury.
- If there was damage to the face, the child needs to be examined by an ENT specialist and a dental surgeon.
- If there was a blow to the temple, then you need to see an otolaryngologist.
- An ophthalmologist is needed if the orbital area is damaged.
- An examination by a traumatologist or surgeon is needed if the blow fell on the forehead or back of the head and was with a sharp swing.
Diagnostic methods
If a child or teenager has a concussion, a clinical examination may be sufficient. But there are studies that help the doctor clarify the diagnosis. These studies include:
- fundus examination;
- sometimes: ultrasound – methods and/or laboratory;
- X-ray of the skull and cervical region;
- encephalography and echoencephaloscopy, with the help of these procedures it is possible to determine whether there are any focal lesions in the vessels of the brain;
- computed tomography will help detect changes in the farthest corners of the brain (it is prescribed only in serious cases).
If such a diagnosis has been made, treatment should be prescribed the sooner the better.
If a child has a concussion, it will not be enough to just take medication. It is also important to adhere to the regime as much as possible. The parent’s task is to monitor compliance with this regime.
How are they treated?
No one is immune from this injury. After the doctor has examined the patient and made the necessary appointments, the child can be taken home. Of course, if the doctor allows it. And if possible, provide him with full treatment and follow absolutely all the doctor’s instructions.
In order for your child to recover faster, you need to do the following:
- Compulsory bed rest is in order for the first three days (this is for adults, children - better than 5 days).
- It is forbidden to read, watch TV, work and play on the computer, play on a mobile phone and tablet, very long communication,
- Close people should protect the child from any worries;
- If severe headaches appear, there is no need to force your baby to endure them. He should take painkillers. Which ones exactly? Only a doctor can prescribe it. They are different for everyone.
- It is not recommended to turn on bright lights, especially if it is a sunny day. It is better that the windows are closed with curtains or even blinds.
If you follow all the listed rules, the child should feel better within 2-3 days, and after a week the child already feels normal. It is important to remember that if there are no positive changes or if the condition worsens, you need to go to the emergency room as quickly as possible. If the following symptoms are observed: nosebleeds or blood flowing from the ears, you need to call an ambulance. And urgently and without delay.
Rehabilitation period
A concussion in a child is a form of traumatic brain injury that can occur for the most seemingly harmless reason. For a baby, for example, a strong shake during rough handling is enough to get such a problem. Diagnosis of a concussion depends on its external manifestations, because a mild form of injury may not make itself felt after just a couple of tens of minutes. And if the parents are not too attentive to the baby, and the fact of the injury was not visually indicated and recorded, then it may happen that no one can even guess about it, attributing the baby’s crying and regurgitation to digestive problems.
An older child or teenager may also hide the injury for some reason, and a mild form of concussion may only manifest itself as weakness and slight nausea. Naturally, adults, having noticed changes in the condition of a little person, in any case should show the child to a specialist, especially if the brain injury was quite serious and manifested by loss of consciousness, disorientation, nausea and vomiting. In addition to the therapy itself, which helps normalize brain function, rehabilitation of the child after injury is important.
All measures that need to be provided to a small patient who has suffered a brain injury must be prescribed by a doctor or agreed with him. It is necessary to provide a daily routine appropriate to the child’s age, high-quality nutritious nutrition, maintain a gentle regime of physical activity for a certain period of time and, of course, avoid repeated traumatization. External signs of a concussion in children may go away within a few days, but changes at the cellular level can persist for a long time and lead to health problems even years later. Unfortunately, modern diagnostics are not yet able to detect such changes and prevent their consequences with a 100% guarantee.
Signs and symptoms of a concussion in an infant
Knowing the early signs of a concussion can help prevent or mitigate serious consequences. Children—especially those just starting to walk—fall frequently. Falls are often severe and bring parents a lot of anxiety, because babies can fall out of the crib or from a highchair.
How to identify a severe bruise from a fall
Despite the fact that young children fall a lot, most often there is only a bump, bruise or swelling at the site of the injury. Thanks to the elastic skeletal system of the skull, a concussion in infants due to a fall is unlikely. It is enough to apply a cold object to the bruised area, and the bruise will go away without consequences in a few days.
But there are times when, when falling, a baby can hit a sharp corner with its head, and then the first symptoms of a concussion appear.
If a large hematoma appears at the site of the injury, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- After the child falls, strong and prolonged crying appears. At the same time, he knocks his legs and waves his arms. In other cases, on the contrary, he becomes lethargic and drowsy.
- Vomiting occurs. The child refuses to eat and spits up after eating a small amount of milk.
- There is moodiness and irritability.
- Sleep is disturbed: the baby has trouble falling asleep and may wake up crying during sleep.
- Pallor of the skin is observed.
- Increased sweating and a sharp rise in body temperature may occur.
- Symptoms of visual impairment are likely - blurred vision, poor concentration.
- If a baby is seriously injured, the fontanel may swell.
At the first appointment with a specialist, they are usually immediately referred to a neurologist if fundus disorders and other neurological signs are observed.
How are head injuries in children treated?
After the child has fallen and signs of a concussion appear, emergency doctors should be called. Having determined the child’s condition, they will decide on further tactics - perhaps they will give some recommendations or decide on hospitalization for a detailed examination. There is no need to get to the hospital yourself.
Before the doctors arrive, the baby should be provided with rest, not given the opportunity to make unnecessary movements, and placed on a hard surface.
There is no need to let the child fall asleep. If he loses consciousness, turn him on his side. No medications or water should be given.
If a baby experiences loss of consciousness, you should not panic. You can bring a cotton swab dipped in ammonia and apply a cold object to your head. You should feel and count the pulse. Loss of consciousness in infants is extremely rare; signs of a concussion appear a few seconds or minutes after the fall.
Treatment of a child can be carried out both at home and in a hospital. The main condition is compliance with bed rest for several days or weeks. In some cases, surgical intervention is provided - it all depends on the severity of the condition.
The following medications may be required as therapy:
- to reduce intracranial pressure;
- to eliminate or prevent seizures;
- Diuretics may be prescribed to prevent cerebral edema;
- potassium preparations;
- analgesics for pain relief;
- sedatives;
- nootropics that improve brain metabolic processes.
The hospital will carry out the following tests to make a diagnosis:
- urine and blood analysis;
- examination of the eyes using an ophthalmoscope (intracranial pressure is determined);
- neurosonography reveals cerebral edema, hemorrhages, bruises and hematomas (it can be done on children under two years old, since the skeletal system is still soft, and the results are accurate);
- radiography (the method allows you to determine the integrity of bones after injury);
- brain tomography;
- electroencephalography (allows you to evaluate brain activity).
The child is examined by several specialists - an ophthalmologist, a traumatologist, a pediatrician, and a neurologist.
Attention is paid to the patient’s consciousness, mobility, sensitivity, motor activity, and the presence of reflexes.
If the blow was not strong, then you can take your time with the inspection, but you also cannot postpone it for a long time. First of all, you should consult a pediatrician. After examining the symptoms of falls and injuries, he will decide whether to refer you to other specialists.
- If a child has injuries to the face or mouth, doctors such as a surgeon and dentist may be needed.
- A blow to the temporal lobe can lead to hearing impairment, so it is worth visiting an otolaryngologist.
- If the blow falls on the frontal lobe, you need to consult an ophthalmologist.
- If the back of the head or cervical spine is affected, consultation with a neurologist, surgeon, or traumatologist is required.
Consequences of a severe injury
Symptoms from a concussion may not appear immediately, but may take several months or even years:
- weather-related headaches;
- asthenic syndrome;
- epileptic seizures;
- disruption of the cognitive (attention, memory, thinking) and emotional (irritability, depression) spheres;
- pathological changes in the muscular system.
In more severe cases, there may be disability or death (if the child is unconscious for a long time).
Small children should not be left unattended, even for a short time. Even if the child has not yet learned to roll over, he can slide off the surface of the changing table, actively moving his limbs.
The crib must have bumpers.
Most injuries under one year of age occur due to the carelessness of adults, so leaving a child on an open high surface (stroller, table, bed) is not allowed even for a second.
Source: https://grudnichky.ru/zdorove/sotryaseniye-mozga-u-grudnogo-rebenka.html
Avoid problems in the future
Modernity is full of risks of traumatization. This is especially true for children of any age: babies are curious and restless, older children are inquisitive and do not have a developed sense of self-preservation, teenagers have a feeling of invulnerability. That is why childhood injuries occupy the first position among medical problems. Signs of a concussion in children may be subtle if the traumatic brain injury is mild. But even if a child feels relatively well after a blow, fall, or collision with any object, it is necessary to show him to a doctor, undergo the necessary examinations and receive treatment and rehabilitation measures that are adequate to the situation. A concussion can go away in a matter of days, but manifest itself years later as disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
Treatment
A child with such a disorder should always be at rest, and his condition should be monitored by a specialist. To determine complex injuries, it is better for the child to be examined in a hospital for several days. This will prevent complications.
You need to move less, no matter how the child feels. You cannot watch TV, play on the computer, or play sports.
Treatment with medications involves the use of the following medications:
- Diuretics to prevent swelling of the brain after a stroke. These drugs are used together with tablets containing potassium.
- Medicines that stimulate blood circulation in the brain and supply it with nutrients.
- Sedatives.
- Antihistamines.
- Painkillers.
- Medicines to relieve nausea.
- Vitamin complex.