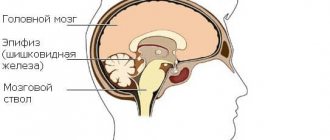
The pathology occurs during gestation up to 20 weeks, and already in an adult child.
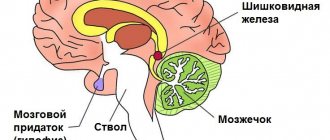
The choroid plexuses of the main organ, the brain, are not associated with the activity of nerve processes. Their main function is nutritional, carried out through the spinal substance. A choroid plexus cyst in newborns forms in the brain tissue. The cerebral substance quickly accumulates and fills the vascular areas. A similar pathology occurs during gestation up to 20 weeks, and already in an adult child. Does a benign tumor affect the further development of the body?
What is a cerebral pseudocyst in newborns?
To understand what a pseudocyst is, imagine a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid or other liquid, surrounded by a thin, clear membrane.
This brain pathology is a malformation of intrauterine development. It can appear in vascular tissue or meninges during embryogenesis or as a consequence of complicated childbirth.
The bones of the baby’s skull are still mobile and, when displaced, can compress the brain tissue during childbirth, leading to hypoxia or small ruptures of blood vessels.
What is the difference between a pseudocyst and a cyst?
There is a not entirely correct idea that differentiation of a cerebral pseudocyst is possible by the presence or absence of an epithelial layer inside it. However, this is a controversial point, since this layer is often absent inside a real cyst.
In addition, ultrasound, which is used to determine the nature of the cystic formation, does not make it possible to carefully examine the membrane and its walls from the inside. Also, shape and size are not indicative of diagnosis: they differ in variety both in the case of a pseudocystic cavity and in a true cyst.
In domestic medical practice, the concepts of cyst and pseudocyst are even used as synonyms in relation to any hollow structure. These two types of pathology differ in structure and area of occurrence.
The main signs indicating that the formation in the lateral ventricles of the brain is a pseudocyst are:
- location. It is found in the following areas: the lateral angles of the anterior horn, the lateral ventricles, the area bordering the optic thalamus and the caudate nucleus;
- the causes of formation, which lie in intracerebral bleeding, lack of oxygen. Hereditary factors are not involved in the mechanism of its development.
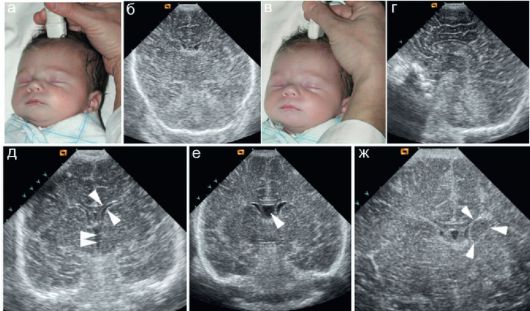
Subependymal pseudocyst in infants is formed as a result of birth injuries. It develops under the ependyma, which lines the inside of the ventricles and the spinal canal, in which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, washing the brain tissue.
The size of this pathology varies from two to ten millimeters. Pseudocysts are found in the ventricles on both the left and right sides.
Small formations resolve on their own after a year. But those that are larger are able to compress the surrounding tissues and do not go away for a long time, up to the age of six. With different locations, the formation can have different effects on the brain, causing a variety of symptoms:
- compression of the occipital area affects vision;
- effects on the cerebellum may impair motor functions;
- exposure to the temporal zones worsens hearing acuity;
- a large pseudocyst pressing on the pituitary gland can cause hormonal imbalances.
Is a choroid plexus cyst dangerous for a newborn?
1. Causes 2. What is the difference between a cyst and a pseudocyst?
3. What is a subependymal pseudocyst? 4. Signal to parents 5. What to do if a cyst is discovered in infancy? 6. Does the side matter - right or left? 7. Choroidal cyst In the vast majority of cases, a choroid plexus cyst is an accidental finding, since it does not manifest itself in any way. Most often, such a cyst disappears spontaneously by the end of the first year of life. If it is detected, the baby should be examined regularly at intervals of 3 months until the age of 1 year.
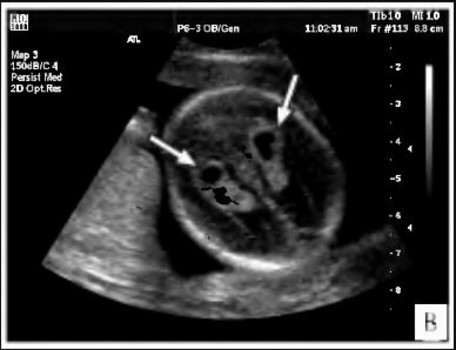
The presence of a choroid plexus cyst in the fetus can serve as evidence that during pregnancy, factors leading to disruption of embryogenesis were affected.
Difference between cyst and pseudoplasm
False formations that appear in the brain area have significant differences from the true ones. They are distinguished by:
- Place of appearance. In most cases, pseudoformation is located in the zone of the subcortical nuclei, or rather between them. The pseudocyst is localized near the lateral ventricles or in the area of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Reason for appearance. The disease can be secondary or acquired. An accurate diagnosis is made through instrumental diagnostics. If a specialist has directed you to undergo an examination, you should not abandon this step, since timely detection of pathology will prevent the occurrence of serious violations.
Reasons for development
False cysts of the pancreas usually form in people who already have some pathology of this organ. The most common causes of occurrence include:
- Acute and chronic forms of pancreatitis. If there are many false formations, then some of them may disappear as the severity of the process decreases, but the remaining ones will give a certain clinical picture.
- Traumatic damage to the gland and ducts. The integrity of the organ parenchyma is compromised, and a false cyst may appear at the site of damage.
- Hemorrhages into the parenchyma of an organ (vascular pathologies, trauma, etc.).
- Necrosis of the organ parenchyma (postnecrotic pancreatic cyst).
Is a pseudocyst dangerous and why?
The existing pseudocyst in the head of a newborn in all cases has a second cause of development. The following reasons may act as a catalyst for the appearance:
- lack of oxygen;
- problematic childbirth;
- presence of injury.
A false cyst in an infant is not dangerous to health. This pathology should cause alarm in cases where the formation rapidly increases in size.
There is no need to perform any specific therapeutic procedures in the treatment of pseudocysts in infants. All that is necessary is to regularly visit a neurologist and carry out restorative therapy designed to combat the emergence of possible complications that often appear against the background of injury.
If after 12 months the formation and the baby have not gone away, doctors diagnose a true cyst. In such situations, you should be observed by a neurologist throughout your life.
A pseudocyst is a small, non-malignant formation in the form of a capsule, inside of which there is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which forms in the baby’s brain structures in utero or during the prenatal and birth periods. Doctors diagnose similar benign structures in the head not only in newborn infants, but also in adult men and women. Another medical term for this abnormality is subependymal cyst.
Peculiarities:
- The pseudocyst is localized only in the lateral ventricles of the brain. The subependymal cyst is separated from the ventricles only by the ependyma (membrane) and a thin layer of medulla containing matrix tissue (germ layer).
- A pseudocyst can form on the left or right (in the right or left ventricle of the brain). Bilateral lesions also occur.
- The diameter of the formations does not exceed the limits from 1 – 2 to 7 – 9 mm.
- They can be either single or multiple.
- The disease is detected in approximately 5 newborn babies out of 100.
- A pseudocyst in the head of a newborn child does not pose a threat to life, physical or mental health. Often the cystic fraction resolves on its own before birth or in the first 12 months of life.
- This pathology requires constant monitoring of the child and periodic ultrasound examinations until complete disappearance.
A similar pseudotumor also includes a pseudocyst of the choroid plexus in a newborn, which occurs even in the embryo at the stage of active brain formation, when cerebrospinal fluid penetrates into the voids of the intertwining vessels. Experts detect this deviation using ultrasound at 16–21 weeks of gestation.
Causes
During embryogenesis, the formation of blood vessels precedes the formation of brain matter and the formation of neurons. The choroid plexus is located in the ventricles of the brain, its purpose is to produce cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid. It is formed from the tissues of the pia mater and contains blood vessels and nerve endings that transmit information.
The plexus is formed as follows: the wall of the brain bladder at the site of the future ventricle retains a single-layer structure, which does not differentiate into nervous tissue. Outside, it is adjacent to the pia mater, rich in blood vessels. Gradually it bends and penetrates into the lining of the brain bladder. They grow together, forming many new vessels, from which the plexus is formed.
Choroid plexuses in the fetus are formed at 18-19 weeks. It is during this period that an ultrasound scan can reveal the first signs of cysts, which look like echo-negative formations. Most often, between 20 and 24 weeks, when the brain is actively forming, the size of the cyst decreases and it completely disappears.
The development of the fetus is continuous, constant differentiation of organs and tissues occurs. But if something goes “wrong”, the “deficiency of building material” is replaced by a cyst. The replacement is temporary - the child will be born, and during the first year of life he will develop the necessary structural units.
All that is needed from parents and doctors is to control the development process and create optimal growth conditions for the baby. You only need to worry if the cyst increases in size and does not decrease.
What is the difference between a cyst and a pseudocyst?
A pseudocyst in a baby's head must be differentiated from a true cyst. The main indicator is the characteristic location. A false anomaly is formed either in the area of the bodies and lateral angles of the anterior horns of the right or left ventricle of the brain, or at the border of the thalamus (optic thalamus) and the head of the caudate nucleus.
The remaining cavity, fluid formations, if detected in other parts of the brain, are called cysts. False cysts resolve or significantly decrease in size by one year of age. True cysts in the head do not disappear, they can cause painful neurological symptoms and require constant monitoring by a neurologist.
Causes of subependymal pseudocyst in the head of a baby
Why does a pseudocyst develop in the head of a newborn baby? The mechanism that triggers the development of the anomaly in children is not reliably known and has not been fully studied.
The most likely causes of a pseudocyst in the head are:
- disruption of the process of formation of the germinal matrix - embryonic tissue in the embryo, where fragile vessels are concentrated and intense metabolic processes occur;
- lack of oxygen supply to the fetal brain due to impaired blood supply (ischemia) before or during childbirth. This condition can occur due to disruption of fetoplacental blood flow (between mother and fetus), early placental abruption, umbilical cord entanglement;
- brain injury during childbirth, hemorrhage in the cerebral tissue of a newborn child;
- damage to the fetus or newborn infected with infections from the mother (herpes, papillomavirus, sexually transmitted diseases);
- multiple births, preeclampsia, blood incompatibility according to the Rh factor;
- serious pathologies, infections during pregnancy, acute poisoning, difficult experiences during pregnancy;
- hereditary genetic factors.
An anomaly such as a pseudotumor is not considered as an independent disease, but is considered a consequence of pathological conditions in a woman or fetus.
Symptoms of a pseudocyst in the head of a newborn
Certain conclusions about the type of ventricular cystic formation and prognosis are made only based on the results of diagnostic studies and clinical examination by a pediatric neurologist.
If a subependymal pseudocyst in a newborn is up to 4–5 mm in size, found in a typical location, and is isolated (not accompanied by neurogenic manifestations, not associated with other diseases), then the prognosis for the baby is favorable. A pseudocyst in the head does not aggravate the disease with abnormalities in mental development. In the fetus, a subependymal pseudocystic neoplasm often resolves by 35–40 weeks, and if this does not happen, then up to 9–12 months of the child’s life.
Dynamic monitoring of the behavior of the pseudocyst and the development of the infant is mandatory.
Can a newborn baby have any symptoms of a pseudocyst in the head? False ventricular formations themselves are a sign of trauma, hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) during childbirth or during “intrauterine life” and indicate that the child’s brain tissue is damaged. Such infants often cry for no apparent reason, spit up, worry and sleep worse; they may experience trembling of the chin, fingers, and a slight and temporary (within normal) developmental delay.
Multiple pseudocysts in the left and right ventricles of the brain always indicate an existing causative disease (they are not an independent symptom), so doctors recommend periodic control ultrasounds even if the child has no signs of dysfunction of the nervous system.
If an ultrasound shows that by the 12th month of life the anomaly has not significantly decreased, has not disappeared, and even continues to grow, then doctors undertake additional examinations to clarify the diagnosis. It is important not to miss the fact of the growth of a true arachnoid, retrocerebellar cyst or other types of similar formations. When they begin to put pressure on the cerebral tissues, the child develops painful symptoms:
- headaches in a baby, during which he can cry for a long time;
- increased excitability or lethargy;
- trembling of arms and legs;
- signs of vision and hearing impairment, including strabismus;
- seizures;
- muscle weakness or hypertonicity.
The main thing that is required of parents is to regularly examine the newborn from the first days of life with a neurologist and follow all recommendations.
What to do if a cyst is discovered in infancy?
Basically, to ensure that the pathology does not interfere with the child’s development. A damaged subependymal area indicates that the child suffered several episodes of hypoxia in utero, or was infected.
The cyst can also replace the site of hemorrhage in the wall of the ventricle. A fairly common cause is the herpes virus; it is considered one of the causes of the formation of brain cysts. Brain damage is caused by difficult childbirth. The main thing is that the size of the cyst should not increase in the baby and development should be disrupted.
The size of the cyst is monitored using ultrasound, which is done at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months. Usually by a year, often earlier, the cyst disappears. It is also necessary to monitor the timing of development and the general condition of the child. The slightest delay requires help and correction.
The following complaints indicating increased intracranial pressure should cause alarm, especially if they appear for the first time:
- constant crying and screaming;
- general increased irritability;
- vomit;
- refusal to eat;
- convulsive attacks.
Such conditions are rare, but parental awareness is the key to ensuring that the baby grows up healthy. An enlarged cyst immediately changes the child’s behavior.
Does it matter whether the side is right or left?
Hardly ever. A cyst of the right choroid plexus is as little dangerous as a formation on the left. In half of all cases of diagnosis, the cysts turned out to be bilateral. This is especially true for formations found in the fetus. There are times when cerebrospinal fluid is already being produced, and the growth of the ventricle simply “does not have time.” Then the cerebrospinal fluid becomes blocked in the middle of the vessels, which can represent a cyst. Such cavities sometimes persist until adulthood, without revealing themselves in any way. Liquor, in contact with the villi of the plexus, has the ability to exchange substances.
Diagnosis of subependymal brain cyst
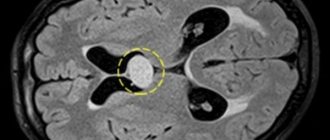
Only hardware diagnostics can confirm the presence of a pseudocyst in a baby’s head. Ultrasound examination (neurosonography) is considered an accurate, reliable way to detect abnormal tumors.
An ultrasound of the brain is informative until the baby’s fontanel is overgrown (up to one year). The method is indicated for premature babies, those who have suffered oxygen deprivation, or birth trauma.
Using neurosonography, the doctor determines the size, number and localization of cystic compactions, assesses the degree of expansion of the ventricles of the brain (which may indicate increased intracranial pressure and the risk of hydrocephalus), identifies signs of blockage of the liquor pathways and impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, and studies changes in the echostructure of brain tissue.
During a second ultrasound, the specialist compares the results and sees how the pseudocyst shrinks and gradually disappears. If echo signs of a true cyst are detected in a newborn child, ultrasound will allow timely treatment to begin in order to prevent complications as early as possible.
In addition to ultrasound, for the purpose of detailed study of pathology, the following can be performed:
- Doppler encephalography to evaluate the state of blood flow and cerebral vessels.
- Two-photon or positron emission tomography. Allows you to monitor the effectiveness of prescribed conservative treatment in accordance with changes in brain tissue.
- Cerebral scintigraphy.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI).
These tests are often performed on older children. These methods make it possible to distinguish (differentiate) pseudocyst, tumor and brain cyst, which is very important for the development of correct treatment.
If a neonatologist or neurologist prescribes an instrumental examination for a child, then refusing it to parents is irresponsible and dangerous. Early detection of any abnormal formations in cerebral tissues allows one to avoid serious consequences.
Prognosis and prevention
The patient's prospects may depend on factors such as:
- primary anamnesis – the presence of severe underlying pathologies (diabetes, cholecystitis);
- stage of pseudocyst development and complications;
- general condition of the body;
- diet.
According to existing data, the mortality rate in the postoperative period is up to 50%. However, it is noted that most of the patients had a history complicated by chronic and alcoholic pancreatitis.
You can prevent the appearance of a pseudocyst or promote the resorption of a developing cavity by following these recommendations:
- a diet with a large amount of easily digestible proteins and a minimum of fatty, salty, spicy foods or sauces, preference for steamed dishes and fractional meals;
- routine examinations and tests;
- rejection of bad habits.
The use of traditional medicine recipes can provide a good preventive effect:
- a collection of equal parts of yarrow, celandine and calendula. Brew 1 tablespoon of the mixture with 200 ml of boiling water and let stand for two hours;
- a mixture of plantain arrows, tansy and calendula in equal parts. Brew similarly to the previous one and leave for 3-6 hours. Then strain;
- Shilajit is famous for its filling effect. A mummy ball about 2 mm in size needs to be dissolved in water.
The long-term absence of symptoms and the risk of complications are the factors that allow us to say that the best treatment for a pseudocyst is prevention, including pancreatitis, cholecystitis and diabetes that “provoke” the cyst.
Treatment methods for pseudocysts
Are there ways to get rid of a pseudocyst in the head through therapeutic treatment without surgery? Yes, if this is truly a false formation, then it will resolve on its own. But medications will help improve brain function, strengthen the immune system, relieve increased excitability or stimulate the activity of the nervous system.
Conservative therapy
If a neurologist, based on the diagnostic results, has determined the presence of a pseudocyst in the newborn’s head, the doctor prescribes medications that eliminate the causes that led to the appearance of the anomaly. Similar conservative treatment is prescribed if a true cyst is suspected in the initial stage of growth.
Many of the pharmaceuticals, especially in tablets and injections, are contraindicated or limited for use in infancy, so it is unacceptable to prescribe them to a child on your own. Only a pediatric neurologist will determine whether the baby needs this or that drug and will calculate the safe dose and frequency of use, taking into account his age, the severity of neurogenic manifestations and concomitant diseases.
If a specialist notices that a child has certain signs of neurogenic damage, he can prescribe nootropic medications that improve cerebral circulation and drugs that eliminate the consequences of oxygen starvation (hypoxia) experienced by the child. But only if they are really indicated for a small patient, since many effective medications have serious side effects, cause acute allergic reactions or give complications to the nervous system and hematopoiesis.
Among the basic medications used to treat cerebral pseudocysts in newborns, doctors use:
- Cytoflavin (from newborns) in suspension;
- Encephabol (pyritinol) in suspension from the first months of life;
- Pantogam in syrup (infants) – activates cerebral circulation and helps with hypertension and convulsive manifestations;
- B vitamins, which have a beneficial effect on the nervous system;
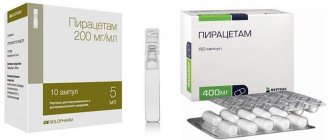
- Piracetam, Nootropil, Cortexin (up to a year - only with the permission of a neurologist);
- Glycine for sleep disturbances and overexcitability.
- Aloe in ampoules (from one year onwards) as a resolving and strengthening agent.
Active medications that have many contraindications and side effects (Mexidol, Cavinton (Vinpocetine), Actovegin, Cinnarizine, Cerebrolysin) are prescribed exclusively according to indications, after a joint decision of the neonatologist and neurologist, since contraindications include childhood.
To reduce intracranial pressure with a pseudocyst, the doctor prescribes weak diuretics (Diacarb, which can be used for children from 4 months).
To strengthen the nervous system and normalize muscle-motor functions, a special massage is used, which should be performed by an experienced pediatric specialist (in the absence of contraindications).
Highly active anticonvulsants prescribed to children suppress respiratory function, which is dangerous for infants (barbiturates, Hexenal, magnesium sulfate). Among the safest gentle drugs that have a weak effect on the respiratory center are the neuroleptic benzodiazepines, Lidocaine, Droperidol.
Methods for removing pseudocysts
At 9–12 months of life, the child must undergo a control ultrasound in order to make a final conclusion about the correctness of the diagnosis. If the size of the pseudocyst in the head of a newborn remains unchanged or an increase in the node is observed during the use of drug treatment, echo signs indicate the formation of a true cyst, then the question of further therapy or surgical removal of the tumor is raised.
A true cyst does not disappear on its own, it grows and puts pressure on the brain, blood vessels and cranial bones, causing severe neurological complications, developmental delay, epilepsy, and mental disorders.
Surgical treatment tactics include several methods of performing surgery to remove a large pseudocyst in the brain:
- Radical microneurosurgical operation with trepanation and complete removal of the tumor.
- Bypass surgery, during which the contents accumulating in the cavity are removed into the physiological cavities of the body through a special tube. After the fluid leaks out, the seal walls spontaneously close and the shunt tubes dissolve.
- Endoscopic method for pseudocyst removal. It is considered the most gentle, anemic and effective, but is not suitable for all types of pathological growths. The latest medical technologies make it possible to perform surgery without trephination using an endoscope and micro-instruments that are inserted through the nasal cavity.
Traditional treatment
To relieve unpleasant symptoms and improve the child’s condition, folk remedies and methods for treating pseudocysts can be used in parallel with medications.
But it is important to remember that plants contain poisons that can harm babies, so using them is extremely dangerous. Other decoctions and herbal infusions often lead to an acute allergic attack, swelling of the larynx and suffocation.
The most common recipes involve the use of:
- soothing and sleep-improving hawthorn decoction;
- infusions of horsetail, violet, and cinquefoil, which reduce intracranial pressure in cases of subependymal cyst;
- soothing baths with a decoction of 2 tablespoons of a mixture of equal parts of dry raspberry leaves, licorice and calamus root, chamomile herbs, yarrow and 500 - 700 ml of boiling water (infuse for 6 - 8 hours).
A small pseudocyst in an infant in the lateral ventricles of the brain is not life-threatening, but requires observation. Repeated examinations will allow the doctor to notice its growth and begin treatment immediately.
Features of treatment
In most cases, when cerebrospinal fluid bubbles appear in the choroid plexuses, therapy is not required. Cysts resolve on their own unless they are caused by injury or infection. In other cases, the neurologist himself determines the treatment tactics. It can be medical or surgical.
Conservative therapy

Medicines are prescribed when the formation in the plexus develops slowly. Then they use drugs that eliminate the cause of its appearance and help increase blood circulation. This gives the damaged area of the brain sufficient nutrition and distribution of cerebrospinal fluid.
If the abnormal development of a cyst is associated with an inflammatory viral or infectious process, antimicrobial drugs, antiviral agents and immunostimulants must be prescribed. The course of treatment continues until positive dynamics begin to be monitored.
Operation
Surgical intervention is necessarily prescribed for large capsules that develop rapidly. This treatment prevents the high risk of complications of symptoms, and can maintain the child's mental development at a normal level. Before treatment, parents must be notified of the consequences of the manipulations.
- Shunting. It is carried out with minimal trauma to the child through special tubes through which fluid is pumped out from the cystic cavity. The disadvantage of this operation is the high probability of infection through the tubes. At the same time, antibiotic therapy is carried out to exclude the development of an inflammatory process and damage to brain tissue. Also, after bypass surgery, there is a possibility of relapse, when the cavity can again fill with cerebrospinal fluid.
- Trepanation. An extremely dangerous method of treatment for a child. It is prescribed in critical situations when other methods are not effective. After surgery, a number of consequences occur, which parents learn about in advance. In a later period, the baby may experience various neurological pathologies.
Pseudocysts in adults
A pseudocyst in an adult patient is most often diagnosed in the pancreas, causing severe pain. Such a node threatens the life of the patient, as it is prone to suppuration, perforation, malignant degeneration, and the formation of fistulas. With this disease, competent surgical treatment is necessary.
Pseudocysts in the adrenal glands do not initially cause symptoms, but when they enlarge, they cause various manifestations due to compression of adjacent organs. Such neoplasms provoke an abnormal release of adrenaline and are complicated by acute bleeding into the lumen of the capsule. Urinary pseudocyst or urinoma can occur in retroperitoneal or perinephric tissue. When they grow, such structures require surgical removal.
The concept of pseudocyst also appears in the diagnoses of men and women with lesions of toxoplasma and cryptococcal infections, when massive intracellular foci with a concentration of parasitic microorganisms form in the brain and other organs. But most often in such cases the term “pseudocyst” is used.
Pancreatic pseudocyst (false cyst): what is it?
The leading cause of the formation of pancreatic pseudocysts is pancreatitis - acute, chronic or alcoholic. It is not surprising that this particular type of pathological cavities makes up more than 80% of all identified cysts of this organ.
A distinctive feature of pseudocysts is the unpredictable behavior of the neoplasm - it can develop slowly or, on the contrary, reach significant sizes in a short time. The growth of cystic cavities threatens with serious complications that are difficult to treat. Therefore, you should not neglect preventive examinations and observations of specific symptoms.
Reasons for education
It is still not possible to find out the exact reasons for the appearance of a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn. Practice and experience make it possible to outline the range of circumstances influencing the formation of cyst-like cavities.
The main factors causing the appearance of a bubble are injuries and various adverse consequences of childbirth. The reasons for the formation of pseudocysts include the following:
- intracerebral hemorrhage or brain hypoxia in the fetus;
- stress, excessive physical and emotional stress of a pregnant woman;
- infectious diseases caused by herpes virus, chlamydia, cryptococci and other pathogens;
- deficiency of some elements important for the normal development of the embryo, impaired blood circulation in the brain.
If the anomaly does not affect the lateral ventricles and periventricular region, the pathology usually does not manifest itself in any way.
The development of neoplasms of the choroid plexus is recorded by ultrasound, starting from the ninety-eighth day of embryogenesis.
Such a pseudocyst does not pose any threat to the fetus. Essentially, this is a temporary stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid that nourishes brain tissue.
Liquor is retained and forms bubbles in the rudiment of the central nervous system, where it is produced. The cavities disappear on their own over time, mainly by the one hundred and ninety-sixth day of pregnancy.
There are versions according to which the cause of their development is a hereditary factor. Mutations in genes lead to stagnation of fluid in cyst-like blisters.
At the same time, the baby is found to have congenital genetic pathologies that have a much greater significance and impact on the baby’s development than a pseudocyst, which does not pose any danger.
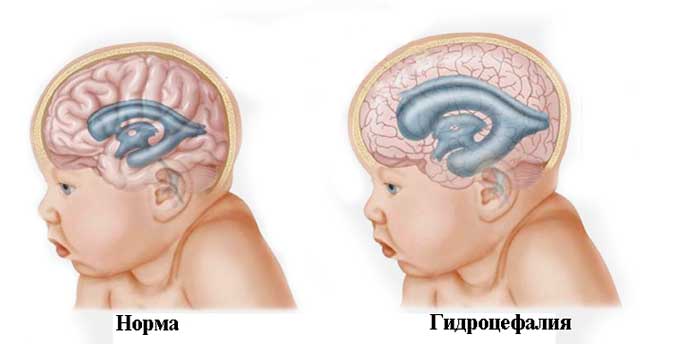
You need to take the situation seriously if, along with a pseudocystic cavity, the baby is diagnosed with the following disorders:
- hernia, hematoma of the diaphragm;
- Edwards syndrome;
- delays in the development of the upper jaw;
- disruption of the formation of the anterior peritoneal wall;
- hydrocephalus;
- neural tube pathologies;
- disorders in the development of the foot.
Be that as it may, you should remain calm and observe how the baby develops, intervening only if the formation grows and does not resolve.
Treatment tactics
Small, not fully formed pseudocysts measuring less than 60 mm allow conservative methods of therapy with constant monitoring of dynamics. The following groups of medications are used:
- proton pump inhibitors (PPIs);
- H2-histamine receptor blockers;
- anticholinergics.
The action of the drugs is based on reducing the secretion of hydrochloric acid and, accordingly, reducing acidity.
Often, such treatment is supplemented by the installation of a percutaneous catheter, which allows the cystic cavity to be washed with antiseptics for several months. During this time, the cyst will either show a tendency to resolve or will grow.
Large or complicated pseudocysts require surgical treatment . It is often preceded by taking the medications mentioned above - this helps to avoid postoperative complications.
Among the “gentle” surgical methods for treating pseudocysts are:
- Percutaneous (puncture) external drainage is a minimally invasive intervention that eliminates pathological fluid accumulation. It cannot be performed if the patient is in serious condition or has hemorrhage into the cystic cavity. The operation may result in bleeding, leakage of cystic fluid, and infection of the abdominal cavity;
- endoscopic operations to drain the cyst into the lumen of the stomach (cystogastrostomy) or duodenum (cystoduodenostomy), or anastomosis between the cyst and the small intestine. It is carried out only for certain localizations of the cyst and can lead to complications;
- laparoscopic operations for anastomosis are similar to the previous ones, but involve a combination of improved visualization and minimal trauma. Complications are also possible.
Among the operations with access through the open abdominal cavity, the following are used:
- Marsupialization - external drainage with suturing into the wound of the anterior peritoneal wall. Often the only solution for cysts complicated by peritonitis, sepsis or purulent inflammation;
- radical intervention - removal of the pseudocyst along with part of the pancreas. The technique cannot be used if the walls of the cyst are formed by tissues of neighboring organs.
The concept of pseudocyst
Formations of the cystic type are peculiar cavities, characterized by a round shape and having a small size. They are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (exudate or other substances). The bulges are concentrated on one or both sides at the same time. The mechanism of development of this pathology in infants has not been fully studied to this day. It may happen that, in the presence of alarming prognosis, a baby is born absolutely healthy, and a second newborn is born with damage to the nervous system, with completely normal prognosis.
With the rather rapid intrauterine development of the brain, the vacated territory located in the area of the choroid plexuses is filled with a special fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). These are the processes that are observed during the development of a pseudocyst. It is safe for the life of the baby and is most often detected during an ultrasound scan of the fetus in the womb.
A large percentage of cystic formations resolve before birth. If this does not happen, then experts explain this by the presence of a herpes infection in the mother.
Symptoms and causes of pathology
A pseudocyst in the head of a newborn is not accompanied by any specific symptoms. Doctors associate the appearance and development of this disease with pathology during intrauterine development.
The causes of the formation of cystic formations and cysts can be:
- hypoxia – lack of oxygen;
- birth injuries;
- metabolic disorders;
- infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy (rubella, measles);
- umbilical cord entanglement.
The presence of these factors in the pregnant woman's history must be taken into account when making a diagnosis.
Diagnostics
The leading method of examination for pseudocyst is ultrasound. However, it does not allow you to carefully examine the walls and interior of the cavity. They target specific areas where cerebral pseudocysts usually form in newborns.
Attention is paid to the cerebral hemispheres, lateral ventricles, the area where the head of the caudate nucleus and the visual thalamus are located. Features of localization make it possible to distinguish a pseudocyst and not confuse it with a true cyst.
The presence of a formation is indicated by echo signs of a subependymal pseudocyst in the region of the left or right ventricle. The use of ultrasonic waves is effective only until the baby is one year old, since his fontanelle is not yet covered by bones. Indications for examination are:
- premature birth;
- childbirth with complications, hypoxia;
- anxiety, tearfulness, insomnia in an infant;
- neurological symptoms: cephalalgia, dizziness, convulsive muscle contractions.

In combination with ultrasound, the following methods are used:
- Doppler encephalography;
- neurosonography;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- cerebral scintigraphy;
- positron emission tomography.
If genetic disorders are suspected in the fetus, chromosomal analysis of the amniotic fluid may be used. This is an invasive intervention, so it is used only when absolutely necessary.
It is also necessary to carefully differentiate the disease from meningitis. Its symptoms are described in detail in this publication.
Is a cerebral pseudocyst dangerous for a child?
The origin of a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn is not related to genes. It is most often caused by birth trauma, which affects the walls of the baby’s skull and brain tissue, and oxygen starvation.
As a rule, pseudocysts do not pose a threat to the child’s life and normal development. Usually it is enough to be observed by a neurologist to eliminate the consequences of birth injuries. Within twelve months, as a rule, the formation in the baby’s brain resolves on its own.
Otherwise, a true cyst is diagnosed (no more than in five percent of cases), which can already pose a certain danger to the child.
Depending on its location, type, and growth tendency, the doctor selects a treatment method. Particular attention should be paid to subependymal cavities that arise after extensive intracerebral bleeding.
Clinical picture
The stage of cyst formation can occur against a background of inflammation and be accompanied by pain. However, more often the cyst does not manifest itself for a long time and begins to cause discomfort only when it reaches a certain size (the cavity can grow up to 40 cm). The neoplasm compresses and displaces neighboring organs. This may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dull pain in the upper abdominal cavity, radiating to the back and left half of the body - diagnosed in 90% of patients;
- heaviness in the epigastric region, a feeling of early satiety;
- dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, stool disorders - observed in 70% of cases;
- general weakness;
- weight loss – occurs in a third of patients;
- icteric manifestations;
- attacks of fever.