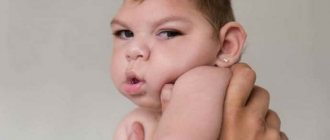
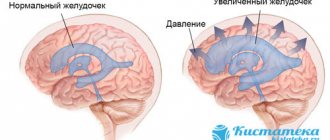
The structures of the brain matter in the cranium are a kind of “control panels”, under the guidance of which the entire human body functions. Any organic brain damage is a life-threatening condition
Recently, cases of ischemic cerebral strokes in relatively young people aged 25 to 40 years have become more frequent. Although a decade ago it was exclusively a disease of old age. There is a completely scientific basis for this, which is based on poor lifestyle and nutrition, frequent stressful situations and consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages and tobacco.
Ischemic cerebral stroke belongs to a group of neurological diseases. The cerebrovascular structure is affected, which may result in the death of the patient or his long-term persistent disability. The pathology is based on the pathological process of disruption of the normal blood supply to a particular area of the medulla. Acute disruption of cerebral blood supply can occur as a result of several mechanisms. The most common among them are:
- embolism of a blood vessel with a thrombus;
- vascular spasm due to smooth muscle impulses;
- “loss” of individual lacunae from the blood supply process.
The ischemic etiology of the disease involves tissue necrosis and subsequent death as a result of prolonged oxygen starvation. The mechanisms of oxidation and transformation of protein compounds are gradually activated.
Embolism of a vessel by a thrombus is a secondary process, which is based on long-term diseases affecting large veins and arteries. This may be deep vein thrombophlebitis, atherosclerosis with the formation of intravascular plaques, congestion in the pelvic cavity. Sometimes embolism is a side effect after surgical interventions, especially in the cervical and facial areas. Air embolism often develops with open fractures of the lower and upper extremities.
Congestion in the pulmonary circulation increases the risk of embolization and the occurrence of a clinical picture of stroke by 5-8 times, depending on the severity and form of heart failure.
Spasm of large blood vessels in the brain can develop due to prolonged exposure to nicotine after drinking a large dose of alcoholic beverages. This is facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet, which is dominated by animal fats and refined foods. Due to the spasm, the flow of blood to certain parts of the brain stops, ischemia and subsequent necrosis occurs with the loss of some functions.
Lacunar types of cerebral infarctions are relatively rare and are more often diagnosed as microstrokes. A diagnosis of transient cerebrovascular accident may be made. Restoration of all lost functions occurs quite quickly due to the compensatory reaction of nearby areas of the medulla.
Criteria for brain death [edit | edit code]
Russia [edit | edit code ]
According to the order of the Russian Ministry of Health [1], the following signs indicate brain death:
- Complete and persistent lack of consciousness (coma).
- Atony of all muscles.
- Lack of response to strong painful stimuli in the area of the trigeminal points and any other reflexes that close above the cervical spinal cord.
- Lack of pupil reaction to direct bright light. It should be known that no medications that dilate the pupils were used. The eyeballs are motionless.
- Absence of corneal reflexes.
- Absence of oculocephalic reflexes.
- Absence of oculovestibular reflexes.
- Absence of pharyngeal and tracheal reflexes.
- Lack of spontaneous breathing.
United States of America [ edit | edit code]
According to the recommendations of the US Presidential Commission [2], the following signs indicate brain death:
Ophthalmological examination [edit | edit code]
- “fixed pupils”: lack of pupillary response to light.
- Absence of corneal reflexes.
- Absence of the oculocephalic reflex (“doll eyes”).
- Lack of swallowing reflex.
- Absence of oculovestibular reflex (caloric test with ice water). The external auditory canal of one ear is washed with 60-100 ml of ice water (not performed if the eardrum is damaged) with the head raised 30° above the horizontal plane of the bed. Brain death is excluded if, in response to rinsing with ice water, the eyeballs turn towards the ear being rinsed. The procedure is repeated on the other side no less than 5 minutes after the previous examination.
- Apnea test: absence of spontaneous respiratory movements when the patient is disconnected from the ventilator (to determine the function of the medulla oblongata). An increase in the partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, which in turn can cause cerebral hernia and vasomotor instability, so this test should be performed last, when the causes of brain death are obvious.
- PaCO2 should be above 60 mmHg, and the absence of breathing confirms the diagnosis of brain death. The test is not evidence-based in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and chronic heart failure.
How to become a donor?
Usually the bone marrow that is transplanted into patients is taken from close relatives, but a complete stranger can also become a donor. Stem cell donation is no less common around the world than blood donation.
Any person between 18 and 50 years of age who has not had hepatitis or HIV and is not a carrier of infectious diseases can donate biological material.
Donors for specific patients are selected based on the so-called tissue compatibility - certain proteins on the surface of the cells of the donor and the patient must match.
There is a special international registry that includes millions of potential donors; in addition, such a registry exists in almost every country.
In the context of the financial crisis, many people are interested in the question of how much donors are paid in Russia, because many clinics offer money for seminal fluid and eggs.
It should be noted that bone marrow donation is voluntary, anonymous and free of charge.
Donors are paid for travel to the procedure site, accommodation and food, and are also compensated for financial losses at work.
In other words, it is impossible to sell bone marrow - saving someone else's life can already be considered a sufficient reward.
Clinical confirmatory studies [ edit | edit code]
Cerebral angiography [edit | edit code]
Nowadays it is rarely used due to the high cost, the need for transportation to the radiology department, the involvement of highly qualified workers, the waste of time and the potential danger of damage to organs intended for transplantation. Visualization of the absence of cerebral blood flow incompatible with brain life on angiography of 4 cerebral vessels is the Gold standard for brain death.
Electroencephalography - EEG [edit | edit code]
Can be performed at the patient's bedside [3] . Requires the participation of a qualified specialist - an interpreter. Does not detect brain stem activity. Electrocerebral silence (ECS) does not exclude the possibility of reversible coma. It is necessary to continue monitoring the patient for at least 6 hours after determining ECS. EEG can be used to clarify the diagnosis of brain death in patients in whom drug intoxication, hypothermia or shock have been reliably excluded. The definition of electrocerebral silence on the EEG is based on the absence of electrical activity > 2 microvolts under the following conditions:
- Recording electrodes from the scalp and neutral (referential) electrodes should be located at a distance of more than 10 cm
- Recording was carried out from 8 electrodes on the scalp and one on the ear
- Resistance between electrodes is less than 10,000 ohms (or impedance less than 6,000 ohms) but more than 100 ohms
- Sensitivity 2 µV/mm
- Time constants for parts of recording 0.3-0.4 sec (time constants for part of recording)
- Lack of response to stimuli (pain, noise, light)
- Recording over 30 min
- Repeated examination in doubtful cases
- Qualified technician and electroencephalographer with experience in intensive care units
- Transmission of EEG by telephone is unacceptable.
Cerebral radioisotope angiography - Cerebral Radionuclid Angiogram (CRAG) [edit | edit code]
Can be performed on a bed using a conventional scintillation chamber with a low energy collimator. May be ineffective in the presence of minimal cerebral blood flow, especially to the brainstem, so it is recommended to continue observation for 6 hours if there is no clear evidence of massive brain damage (trauma, hemorrhage) and other complications. The examination is carried out by an experienced interpreter.
Can be used to diagnose brain death in the following conditions:
- In the presence of conditions complicating the diagnosis - hypothermia, drug intoxication (patients brought out of a barbituric coma), metabolic disorders.
- In patients with massive facial trauma, when ophthalmological examination is difficult or doubtful.
- In patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or chronic heart failure (CHF), when the apnea test cannot be considered reliable.
- To shorten the observation period, especially when there is a question about organ transplantation.
- The scintillation chamber is placed above the head and neck in an anteroposterior projection
- 20-30 mCi 99m Tc labeled albumin or pertechnetate in a volume of 0.5-1.5 ml is injected into a peripheral or central vein, followed by 30 ml of saline.
- A series of dynamic images are taken at 2-second intervals for 60 seconds.
- Then a statistical analysis of images of 400,000 counts is carried out in the anteroposterior and then in the lateral projection.
- If the examination needs to be repeated for reasons of questionable results or inconsistency with the diagnosis of brain death, this may be possible after a 12-hour interval necessary to remove the isotope from the circulating blood.
The study confirms that brain death demonstrates the absence of blood flow in the carotid arteries at the base of the skull, the absence of filling of the middle and anterior cerebral arteries (with brain death, delayed and true visualization of the dural sinuses may be observed). The absence of the “candelabra effect” indicates a lack of cerebral blood flow over the base of the brain.
Brain Death and Religion [edit | edit code]
Brain death in Christianity [edit | edit code]
The Catholic Church considers the cessation of activity of the cerebral cortex to be a criterion for determining the death of a person [4].
In the Orthodox Church there is no clear opinion on whether brain death, given the functioning of other body systems, is the basis for declaring the fact of a person’s death. Death in Orthodoxy, based on Holy Scripture, is understood as the separation of the soul from the body (Ps. 146:4; Luke 12:20). Thus, theologian V.V. Zenkovsky writes that “the destruction of the body takes away from the soul the basis of its life (there is no brain, nervous system, through which the soul receives material for life)” [5]. Therefore, artificial maintenance of the vital activity of the organism is considered appropriate only when there is hope for the continuation of life and functioning of the organism as a whole [6]. For this reason, in case of brain death, it is allowed to stop artificial ventilation [7].
Disease prevention
To prevent the occurrence of senile dementia in old age, doctors recommend monitoring your health and lifestyle. The main prevention of dementia comes down to:
- Enriching your diet with foods that contain many antioxidants (vegetables, fish, nuts).
- Giving up bad habits.
- Timely treatment of pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, etc.
The pathology risk scale indirectly shows what determines the occurrence of dementia and how it can be avoided. Control your blood pressure and cholesterol, watch your weight, eat right and exercise
- Development of intelligence (self-education, solving crosswords and puzzles).
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and playing sports.
All these simple rules are available to each of us. It has been proven that this can subsequently protect a person from the development of senile dementia.
Source: ProMigreni.com
Treatment of brain death[edit | edit code]
Treatment of brain death at this stage of medical development is impossible. In 2020, American scientists began research on restoring brain activity after death, using modern biomedical technologies [14].
Sometimes it is possible to recover from a state of deep coma, the history of which is in many ways similar to brain death. Stimulation of the brain with electrical impulses is being considered as a treatment option for such conditions [15].
Radiation necrosis of the brain is a term denoting necrotic degradation of brain tissue after intracranial or regional radiation therapy for an intracranial pathological process (eg, astrocytoma, arteriovenous malformation) or as a result of irradiation of head and neck tumors (eg, pharyngeal cancer).
Terminology
Although post-radiation treatment effects include pseudoprogression, which occurs almost immediately after radiation, and especially with combination therapy for glioblastoma in combination with chemotherapy, this publication discusses more distant changes, collectively called radiation necrosis, which appear several months or even years after radiation therapy and include necrotic changes with mass effect and the presence of neurological deficits.
Pathology
There are numerous mechanisms of post-radiation necrosis:
- vascular lesion
- acute endothelial injury can lead to vasogenic edema
- chronic fibrosis, hyalinization and stenosis can lead to subsequent thrombosis and infarction
- with total irradiation, vascular ectasia and telangiectasia are common
- damage to oligodenthrocytes and white matter
- oligodendrocytes are sensitive to radiation
- loss of white matter substrate leads to volume reduction
- effect on fibrinolytic enzymes
- An increase in urokinase plasminogen activator and a simultaneous decrease in tissue plasminogen activator contributes to the development of cytotoxic edema and the formation of tissue necrosis
- immune mechanisms
Stages of the disease
Depending on how well the patient can adapt socially, there are several stages of senile dementia:
- Mild – there is a decrease in intellectual abilities, but the patient remains critical of his condition. The patient is able to do everything independently and does not need outside care.
- Moderate – characterized by gross impairment of intelligence. At the same time, his critical perception of what is happening decreases. The patient has difficulty working with household appliances, cannot use the telephone, door lock, etc. Leaving such a person alone can be dangerous.
- Severe – complete collapse of personality. Such patients require constant care, as they are unable to maintain basic hygiene.
MMST scale – Mini Mental Status Test. This is a rating scale for neuropsychological studies that allows you to identify various mental disorders