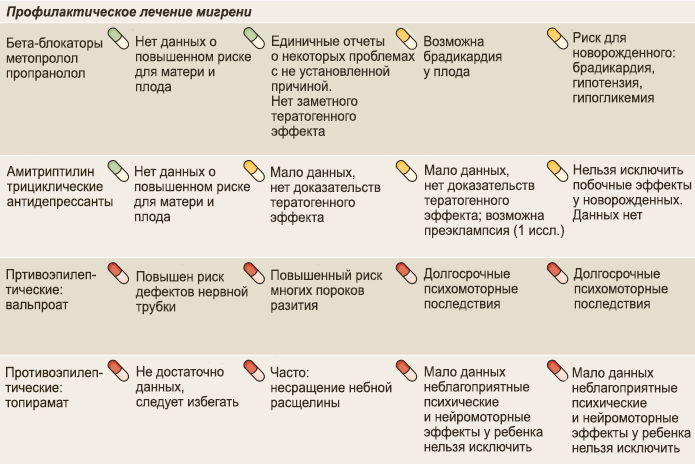
At-risk groups
Typically, focal changes in the white matter of the brain of a dystrophic nature most often occur in old age. Most lesions appear during life and as a result of hypoxia and ischemia. People who lead a sedentary and unhealthy lifestyle are also susceptible to the disease. Genetic predisposition also plays a role.
The white matter of the brain coordinates all human activity. It is what connects different parts of the nervous system. White matter is necessary for the two hemispheres to work together.
Diagnostics
The most informative, comprehensive examination that can objectively assess the functioning of neurons and blood vessels in the brain and their destruction is MRI.
Depending on where the MRI detected foci of destruction of the brain substance of a dystrophic nature, the following features of the disease can be assumed:
- Pathologies in the cerebral hemispheres may be accompanied by blockage of the vertebral arteries (due to congenital defects or atherosclerosis). This deviation also occurs with an intervertebral hernia.
- Focal changes in the white matter of the brain in the forehead are associated with hypertension and experienced hypertensive crises. Fine-focal changes found here may also be congenital; they are not life-threatening if they do not increase over time.
- Multiple lesions detected on an MRI image indicate serious pathology. Such results occur if dystrophy develops in the substance of the brain, which is typical for pre-stroke conditions, epilepsy, and the progression of senile dementia.
If an MRI reveals such a brain pathology, the person will have to regularly repeat the examination in the future, approximately once a year. In this way, it is possible to establish the rate of progression of destructive changes and the optimal plan of action to prevent a rapid deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other methods, in particular CT, can only provide information about traces of previous heart attacks, thinning of the cortex, or accumulation of fluid (CSF).
The essence of the problem
Nature has made sure that every cell of the nervous system receives plenty of blood: the intensity of blood supply here is very high. In addition, in the head there are special jumpers between sections of the vascular bed, which, if there is a deficiency of blood circulation in one section, can provide it with blood from another vessel.
But even such precautions did not make the nervous tissue invulnerable, and in many people it still suffers from a lack of blood supply.
In those areas where access to gas exchange and the exchange of nutritional components was difficult, even temporarily, neurons die extremely quickly, and with them the patient loses motor abilities, sensitivity, speech and even intelligence.
Depending on how numerous and extensive the destruction is, single focal changes in the brain substance of a discirculatory nature or multiple focal changes in the brain substance are distinguished.
This or that degree of focal destruction of the brain of a vascular nature occurs, according to some data, in 4 out of 5 people of mature or old age.
The causes of the pathology can be different:
- Dystrophic focal changes in the brain associated with a deficiency of cellular nutrition.
- Post-ischemic changes provoked by problems with blood delivery through the arteries.
- Focal changes of a dyscirculatory nature, caused by imperfect microcirculation due to defects in blood flow, including the spinal cord.
- Changes of a discirculatory-dystrophic nature.
It is important that single focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature, as well as multifocal brain damage, are not clinically expressed in their initial stages. External signs that may accompany the onset of pathological processes are similar to the symptoms of many other ailments.
This insidious feature is unfavorable for a person, because in the absence of a diagnosis, accordingly, no treatment is prescribed, and in the meantime, further damage to neurons and white matter of the brain continues.
What are focal changes in the white matter of the brain
The brain is the center that regulates the functioning of the entire body and is directly connected to the autonomic nervous system. Focal changes in the white matter of the brain are an irreversible process of death of sensitive neurons, even with slight oxygen starvation.
Forms of the pathological process
Depending on the damage caused by disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels and the delivery of nutrients to the brain tissues, there are:
- Discirculatory nature of the damage;
- Focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature.
Not only older patients are at risk. The pathological process in the brain structures also occurs with concomitant diseases not related to the vascular system:
- Age over 50 years;
- Metabolic disorders (obesity);
- Hypertension;
- Sedentary lifestyle (phenomena of stagnation in the vascular bed);
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Diabetes;
- Vegetovascular dystonia;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Heart rhythm disturbances (bradycardia, tachycardia);
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
Discirculatory disorders
The dyscirculatory form of the pathological process is the slow development of lesions of vascular origin and has a chronic course. The initial stage does not lead to significant disruptions in the nervous system and is felt as overwork or depression; it is extremely difficult to diagnose the developing pathology.
The proliferation of vasogenic lesions leads to tissue death and is expressed by mental instability and the appearance of headaches. Extensive tissue necrosis leads to irreversible changes, the person becomes incapacitated (motor activity and intellectual abilities are impaired).
What is included in the concept of genesis?
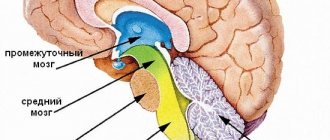
The essence of the process can be understood if you imagine how the blood supply system to the brain works.
How does this happen:
- There are three large branches (anterior, middle and posterior) in the cranial cavity, which receive arterial blood from the vertebral and carotid arteries.
- All arteries are connected by anostomoses, forming a collateral network.
- In the case of dystrophy (narrowing) of arterial vessels, blood does not pass through the arteries, but bypasses it through the collateral network - this is the initial stage of damage to the cerebral arteries.
- Arterioles have branches that pass into the capillary system, where the outflow of venous blood occurs.
- The capillaries connect into sinuses, which empty into the superior and jugular veins.
- Not only AC (arterial blood), but also an excess portion of the cerebrospinal fluid enters the venous bed from the cerebral ventricles.
Such vascular manifestations are classified as venous pathology, which contributes to the development of hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure and other diseases.
Damage to blood vessels can be of a general nature, form large or small focal changes, single or numerous foci.
Localization of lesions can be observed in any hemisphere, in the temporal lobes, in the frontal, parietal or occipital region.
The disease can be acute and appear suddenly or chronic over a long period of time.
The causes and symptoms of vascular origin are varied. Let's consider the main diseases that provoke the occurrence of pathology.
Arterial blockage
Another name is cerebral atherosclerosis, which is characterized by degeneration of the vascular bed. When blood vessels are narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques, the nutrition of the brain worsens or completely stops, which contributes to the death of tissues and cells.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Preparations for the blood vessels of the brain and heart
Main symptoms:
- increased sweating, facial redness;
- chin, head trimer;
- visual impairment;
- facial asymmetry;
- a sharp increase in blood cholesterol levels.
A special symptom is a severe headache. The disease can lead to stroke, aneurysm or paralysis of the cerebral lobes. In most cases, surgery is required.
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic changes in the brain or ischemic stroke is a brain infarction that causes a progressive deterioration of blood supply and cessation of brain functions.
The main symptom is a mental disorder. This condition requires immediate hospitalization and treatment of the patient.
The term "transistor ischemic attack" means the sudden onset of a focal deficiency that regresses in less than a day.
TIA has many syndromes, for example, migraine, ischemic or focal epilepsy syndrome.
Specific signs of an attack indicate pathology of a specific area or artery:
- carotid or midbrain;
- vertebrobasilar system (vertebral or basilar artery);
- small penetrating artery.
The duration, stereotypicality of symptoms and episodic frequency of ischemic attacks indicate a specific pathology. For example, weakness of the limbs, speech impairment, and a duration of about 12 hours are characteristic of the formation of an infarction in the frontal lobe.
Damage or swelling of the walls of blood vessels, veins or heart muscle is an extremely dangerous pathology. With a brain aneurysm, a growth forms that quickly fills with blood.
Delayed diagnosis can lead to rupture of the vessel, which often results in death or disability.
There are several types of aneurysm of different classifications and locations. No specific exact cause of the disease has been identified.
However, many factors are known that provoke the development of an aneurysm. For example, TBI, atherosclerosis, infections, smoking, drugs, tumor, etc.
What are foci in the white matter of the human brain?
20.03.2019
Lesions in the white matter of the brain are areas of damage to brain tissue, accompanied by a violation of the mental and neurological functions of higher nervous activity.
Focal areas are caused by infection, atrophy, loss of blood supply and trauma. Most often, affected areas are caused by inflammatory diseases. However, areas of change may also be of a dystrophic nature.
This is observed mainly as a person ages.
Focal changes in the white matter of the brain can be local, single-focal, or diffuse, that is, the entire white matter is moderately affected. The clinical picture is determined by the localization of organic changes and their degree. A single lesion in the white matter may not affect the dysfunction, but massive damage to neurons causes a disruption in the functioning of nerve centers.
Symptoms
The set of symptoms depends on the location of the lesions and the depth of damage to the brain tissue. Symptoms:
- Pain syndrome. Characterized by chronic headaches. Unpleasant sensations intensify as the pathological process deepens.
- Rapid fatigue and exhaustion of mental processes. Concentration deteriorates, the volume of operative and long-term memory decreases. It is difficult to master new material.
- Flattening of emotions. Feelings lose their sharpness. Patients are indifferent to the world and lose interest in it. Previous sources of pleasure no longer bring joy and desire to engage in them.
- Sleep disturbance.
- In the frontal lobes, foci of gliosis disrupt the control of the patient’s own behavior. With deep violations, the concept of social norms may be lost. Behavior becomes provocative, unusual and strange.
- Epileptic manifestations. More often these are small convulsive seizures. Individual muscle groups contract involuntarily without threat to life.
White matter gliosis can manifest itself in children as a congenital pathology. The lesions cause dysfunction of the central nervous system: reflex activity is disrupted, vision and hearing deteriorate. Children develop slowly: they get on their feet late and begin to speak.
Causes
Damaged areas in the white matter are caused by the following diseases and conditions:
- Group of vascular diseases: atherosclerosis, amyloid angiopathy, diabetic microangiopathy, hyperhomocysteinemia.
- Inflammatory diseases: meningitis, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's disease.
- Infections: Lyme disease, AIDS and HIV, multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
- Poisoning by substances and heavy metals: carbon monoxide, lead, mercury.
- Vitamin deficiency, especially B vitamins.
- Traumatic brain injuries: bruise, concussion.
- Acute and chronic radiation sickness.
- Congenital pathologies of the central nervous system.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident: ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral infarction.
At-risk groups
Risk groups include people exposed to the following factors:
- Arterial hypertension. They are at increased risk of developing vascular lesions in the white matter.
- Poor nutrition. People who overeat, excessively consume extra carbohydrates. Their metabolism is disrupted, as a result of which fatty plaques are deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels.
- Foci of demyelination in the white matter appear in older people.
- Smoking and alcohol.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Genetic predisposition to vascular diseases and tumors.
- Constant hard physical labor.
- Lack of intellectual work.
- Living in conditions of air pollution.
Treatment and diagnosis
The main way to find multiple lesions is to visualize the medulla on magnetic resonance imaging. On layer by layer
Spots and pinpoint changes in tissue are observed in the images. MRI shows not only lesions. This method also reveals the cause of the lesion:
- A single lesion in the right frontal lobe. The change indicates chronic hypertension or a previous hypertensive crisis.
- Diffuse foci throughout the cortex appear when the blood supply is disrupted due to atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels or.
- Foci of demyelination of the parietal lobes. It speaks of a disruption in the flow of blood through the vertebral arteries.
- Massive focal changes in the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres. This picture appears due to atrophy of the cortex, which forms in old age, from Alzheimer's disease or Pick's disease.
- Hyperintense lesions in the white matter of the brain appear due to acute disruption of the blood supply.
- Small foci of gliosis are observed in epilepsy.
- In the white matter of the frontal lobes, single subcortical foci are predominantly formed after a heart attack and softening of the brain tissue.
- A single focus of gliosis in the right frontal lobe most often appears as a sign of brain aging in older people.
Magnetic resonance imaging is also performed on the spinal cord, in particular on the cervical and thoracic regions.
Related research methods:
Visual and auditory evoked potentials. The ability of the occipital and temporal regions to generate electrical signals is tested.
Lumbar puncture. Changes in the cerebrospinal fluid are examined. Deviation from the norm indicates organic changes or inflammatory processes in the cerebrospinal fluid ducts.
A consultation with a neurologist and psychiatrist is indicated. The first studies the functioning of tendon reflexes, coordination, eye movements, muscle strength and synchrony of extensor and flexor muscles. The psychiatrist examines the patient’s mental sphere: perception, cognitive abilities.
Foci in the white matter are treated with several branches: etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy.
Etiotropic therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. For example, if vasogenic lesions of the white matter of the brain are caused by arterial hypertension, the patient is prescribed antihypertensive therapy: a set of drugs aimed at lowering blood pressure. For example, diuretics, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers.
Pathogenetic therapy is aimed at restoring normal processes in the brain and eliminating pathological phenomena. Drugs are prescribed that improve blood supply to the brain, improve the rheological properties of blood, and reduce the need for oxygen in brain tissue. Vitamins are used. To restore the functioning of the nervous system, it is necessary to take B vitamins.
Symptomatic treatment eliminates symptoms. For example, for seizures, antiepileptic drugs are prescribed to eliminate foci of excitation. In case of low mood and lack of motivation, the patient is given antidepressants.
If lesions in the white matter are accompanied by an anxiety disorder, the patient is prescribed anxiolytics and sedatives.
If cognitive abilities deteriorate, a course of nootropic drugs is indicated - substances that improve the metabolism of neurons.
Didn't find a suitable answer? Find a doctor and ask him a question!
Source: https://sortmozg.com/zabolevaniya/ochagi-v-belom-veshhestve-golovnogo-mozga
Symptoms of focal lesions
Focal brain lesions are caused by damage to blood vessels, which lose elasticity with age. For some, this manifests itself minimally, while for others, the disorders develop into a pathological form. Can appear:
- High blood pressure caused by a lack of oxygen due to the degenerative state of the cerebral vessels.
- Epileptic seizures, during which a person should not put metal objects in his mouth, pour water on him, hit him on the cheeks, etc.
- Mental disorders, memory impairment, distorted perception of reality, atypical behavior.
- Stroke or pre-stroke condition, which can be detected on CT or MRI.
- Increasing throbbing headache in the back of the head, eye sockets, superciliary areas, radiating across the surface of the entire skull.
- Uncontrolled muscle contractions, tremors of the limbs, chin, eyes, neck.
- Ear noise, ringing, congestion leading to nervousness.
- Regular attacks of dizziness leading to nausea and vomiting.
- Photophobia, decreased hearing acuity, blurred vision, double vision, noticeable blurred vision.
- Constant fatigue, apathy.
- Slurred speech.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Muscle paresis, pathological reflex reaction of the limbs.
Many people ask what diseases are caused by focal brain damage, what it is, and why it occurs. It is known that the causes of this disorder may lie in:
- Vascular disorders associated with natural aging, cholesterol accumulations in the walls of blood vessels.
- Osteochondrosis of the neck.
- Oxygen starvation.
- Neoplasms.
- Injuries, open and closed head injuries (age is not important here).
The main signs indicating the presence of vascular origin:
- arrhythmia - a pronounced disturbance of the pulse even at rest (jumps from 60 to 90 beats/min);
- spontaneous episodes of increased or regular high blood pressure;
- unmotivated weakness in the limbs;
- cephalalgia of various types, dizziness;
- impairment of speech, memory, vision or attention, depends on the nature of the impairment;
- increased fatigue.
Based on pain sensations, it is easy to distinguish between general and focal signs, which means a more accurate diagnosis.
Any type or type of brain damage, as well as functional disorders of its structure and activity or the functioning of body systems closely related to it, are sure to affect a person’s daily activities, behavior, and functions. Also, the very location of the lesion can very noticeably affect the functioning of the body’s organ systems, as well as the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal and muscular systems.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with cerebral infarction and cerebral edema
In addition to pathologies that were caused by vascular origin, other types of diagnoses may occur, including single focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature. This kind of pathology can most often occur when there is insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen to the brain tissue.
The reasons for this phenomenon:
- Oncological type tissue damage;
- Insufficient blood supply to a certain area of tissue;
- Injury to the head and brain tissue;
- Acute stage of cervical osteochondrosis.
When, due to vascular origin, a person experiences small focal changes in the brain, the following symptoms are usually observed:
- Significant decrease in brain activity;
- Pain in the head;
- Dementia;
- Frequent dizziness;
- Paresis of muscle tissue, weakening;
- Local, partial paralysis of some muscle groups.
In addition, changes in the blood circulation around the brain substance of a dystrophic nature can lead to a disorder of the human psyche. Due to vascular dystrophy, blood pressure may increase, a stroke may occur, as well as hyperintense brain phenomena. But it may also happen that subcortical lesions may not manifest symptoms.
Clinically, focal brain damage can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- high blood pressure;
- epilepsy attacks;
- mental disorders;
- dizziness;
- congestion in the vascular bed of the fundus;
- frequent headaches;
- sudden muscle contractions;
- paralysis.
The main stages in the progression of cerebral vascular disorders can be identified:
- At the initial stage, the person and the people around him practically do not notice any deviations. Only attacks of headaches are possible, which are usually associated with overload and fatigue. Some patients develop apathy. At this time, the lesions are just emerging, without leading to serious problems of nervous regulation.
- At the second stage, deviations in the psyche and movements become more and more noticeable, and pain becomes more frequent. People around you may notice outbursts of emotion in the patient.
- The third stage is characterized by massive death of neurons, loss of control of the nervous system over movements. Such pathologies are already irreversible; they greatly change the patient’s lifestyle and personality. Treatment can no longer restore lost functions.
There are often situations when changes in the blood vessels of the brain are detected completely by chance, during a diagnosis prescribed for another reason. Some areas of tissue die asymptomatically, without significant disruptions in nervous regulation.
Focal changes in the brain substance of a discirculatory nature
The human body is not eternal and with age various pathological processes develop in it. The most dangerous among them are focal changes in the brain substance of a discirculatory nature. They arise due to disruption of cerebral blood flow.
This pathological process is manifested by a number of neurological symptoms and is characterized by a progressive course. It is no longer possible to bring lost nerve cells back to life, but you can slow down the course of the disease or completely prevent its development.
Causes and signs of pathology
The doctor should tell you what to do if there is a focal change in the substance of the brain, but the patient himself can suspect the presence of pathology. The disease often has a post-ischemic origin.
It is characterized by a violation of blood flow in one of the areas of the hemisphere (hemisphere).
It is difficult for some people to understand what this is, so for convenience, the development of changes in brain matter has been divided into 3 stages:
- First stage. At this stage, signs of focal lesions in the brain matter do not appear. The patient may only feel slight weakness, dizziness and apathy. Occasionally, sleep is disturbed and headaches occur. Foci of vascular origin are just emerging and there are minor disruptions in blood flow;
- Second phase. As the pathology develops, the course of the disease worsens. This manifests itself in the form of migraines, decreased mental abilities, ringing in the ears, outbursts of emotions and loss of coordination of movements;
- Third stage. If the disease has reached this stage, then focal changes in the white matter of the brain have irreversible consequences. Most neurons die and the patient's muscle tone rapidly decreases. Over time, symptoms of dementia (dementia) appear, the senses cease to perform their functions and the person completely loses control over his movements.
Subcortical lesions in the white matter, localized under the cerebral cortex, may not appear at all for a long time. Such failures are diagnosed mainly by chance.
Changes in the white matter of the frontal lobes manifest themselves noticeably more actively and mainly in the form of a decrease in mental abilities.
Dystrophic nature of the damage
In addition to damage caused by vascular origin, there are other types of disease, for example, single focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature. This type of pathology occurs due to lack of nutrition. The reasons for this phenomenon are as follows:
- Weakened blood supply;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in the acute stage;
- Oncological diseases;
- Head injuries.
Damage to the brain substance of a dystrophic nature usually manifests itself due to a lack of nutrition of brain tissue. The patient experiences symptoms:
- Decreased brain activity;
- Dementia;
- Headache;
- Weakening of muscle tissue (paresis);
- Paralysis of certain muscle groups;
- Dizziness.
Diagnostics
Most people with age develop focal changes in the substance that arise due to tissue degeneration or as a result of disruptions in blood flow. You can see them using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
- Changes in the cerebral cortex. Such a lesion occurs mainly due to blockage or compression of the vertebral artery. This is usually associated with congenital anomalies or the development of atherosclerosis. In rare cases, along with the appearance of a lesion in the cerebral cortex, a vertebral hernia occurs;
- Multiple focal changes. Their presence usually indicates a pre-stroke condition. In some cases, they can prevent dementia, epilepsy and other pathological processes associated with vascular atrophy. If such changes are detected, a course of therapy should be started immediately to prevent irreversible consequences;
- Microfocal changes. Such damage is found in virtually every person after 50-55 years. They can be seen with the use of a contrast agent only if they are of a pathological nature. Fine-focal changes are not particularly noticeable, but as they develop they can cause a stroke;
- Changes in the white matter of the frontal and parietal lobes subcortically and periventricularly. This type of damage occurs due to persistently elevated blood pressure, especially if the person has had a hypertensive crisis. Sometimes small single lesions are congenital. The danger arises from the proliferation of lesions in the white matter of the frontal and parietal lobes subcortically. In such a situation, symptoms gradually progress.
If a person is at risk, then an MRI of the brain (brain) should be performed once a year. Otherwise, it is advisable to do such an examination once every 2-3 years for prevention. If an MRI shows a high echogenicity of a lesion of disculatory origin, this may indicate the presence of an oncological disease in the brain.
Methods of combating pathology
Gradually affecting the human brain tissue, the disease can cause irreversible consequences.
To prevent vascular changes in the white matter of the brain, it will be necessary to stop the symptoms that arise and improve blood flow with the help of medications and physical therapy.
Treatment must be comprehensive, which means you will have to change your lifestyle. To do this you will have to follow these rules:
- Active lifestyle. The patient should move more and play sports. After eating, it is advisable to go for a walk, and it doesn’t hurt to do the same before bed. Water procedures, skiing and running have a good effect. Treatment with an active lifestyle improves general condition and also strengthens the cardiovascular system;
- Properly formulated diet. For successful treatment, you will have to give up alcoholic beverages and reduce your consumption of sweets, preserves, as well as smoked and fried foods. You can replace them with boiled or steamed food. Instead of store-bought sweets, you can make homemade pie or eat fruit;
- Avoiding stress. Constant mental stress is one of the causes of many diseases, so it is advisable to relax more and not overwork;
- Healthy sleep. A person should sleep at least 6-8 hours a day. In the presence of pathology, it is advisable to increase sleep time by 1-2 hours;
- Annual examination. If a change in the white matter of the brain is diagnosed, the patient should undergo an MRI twice a year. It is imperative to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and take the necessary tests on time.
Treatment of focal changes usually involves changing lifestyle and eliminating the cause of their development. It is advisable to detect the problem immediately in order to be able to slow down its progression. To do this, you should undergo a full examination annually.
Source: https://NashiNervy.ru/tsentralnaya-nervnaya-sistema/ochagovye-izmeneniya-v-belom-veshhestve-golovnogo-mozga.html
Stages of development
In comparison with other types of pathologies, focal transformations of the discircular type spread in several stages. Each has its own distinctive features. Therefore, specialists must first understand at what stage this disorder is in order to determine the optimal therapeutic technique.
In the initial stages, it is difficult to determine the presence of the disease, since the process of circulatory disorders in the head is poorly developed. In such a situation, the specific signs of the disorder are still not expressed, so diagnosis will be difficult. Patients also do not describe specific complaints.
The second stage is characterized by deterioration of the tissue in the brain, which gradually dies. Such processes are caused by problems with cerebral circulation. At the last stage, half of the brain matter dies, the functioning of the organ is disrupted, and recovery cannot be expected. In each patient, symptoms manifest themselves depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
There are three stages of this pathology:
- Initially, discirculatory changes are characterized by a slight disturbance in the movement of blood in certain brain areas. Because of this, the patient quickly gets tired and often experiences bouts of dizziness and headaches.
- When the disease develops and moves into the second stage, the damage worsens. Memory deteriorates, intellectual abilities decrease. The person becomes extremely irritable and emotional. Coordination of movements worsens, and tinnitus appears.
- At the third stage, a significant part of the neurons die. In this case, the muscles noticeably suffer, obvious signs of dementia appear, and the organs of touch and senses may fail.
How the functionality of organs sensitive to such disorders changes depends on where focal diffuse changes of a vascular nature are localized in the brain and spinal cord.
Preventive measures
In most cases, prevention is an excellent assistant in the fight against problems of vascular origin. Regular activities make it possible to get rid of not only a steadily progressing disease, but often even eliminate the symptoms of an incurable pathology.
Table of recommended activities.
| Measures | Algorithm of actions |
| Lifestyle correction | Provide yourself with a calm environment, avoid stressful situations, and regulate physical activity. Eliminate bad habits |
| Selection of diet plan | The patient is recommended a diet menu with low cholesterol, fatty and spicy foods |
| Correction of daily routine | 8 hours of sleep and meals are required, which are planned at the same time |
| Monitoring indicators | It is necessary to monitor weight, measure blood pressure, lipid balance, coagulogram |
| Treatment of concomitant diseases | Compliance with drug therapy prescribed by a doctor |
| Consultation with the attending doctor | Regular visits to the doctor for preventive purposes |
| Sport | It is useful to regularly do gymnastics, yoga, swimming, walking, etc. |
| For transient disorders | Bed rest is recommended until neuralgic symptoms (vomiting, nausea) disappear |
We suggest you read: The right arm is numb from the shoulder to the fingers: reasons, what to do
Visits: 9,326
Modern methods of therapy
Therapeutic measures are necessary to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease that provokes brain disorder. You will have to use medications that inhibit the development of pathology.
Vascular medications such as pentoxifylline, vinpocetine, cinnarizine, and dihydroergocriptine are required. They have a beneficial effect on the blood supply to brain tissue, stabilize the functioning of capillaries, increase the plasticity of red blood cells, and make the blood liquid. The drugs help eliminate vascular spasm and increase the resistance of arteries and veins to hypoxia.
Cytoflavin and piracetam are used as antioxidant and antihypoxic drugs. Treatment with vestibulotropic drugs stops dizziness, eliminates unsteadiness during movement, and improves the quality of life of patients. At high blood pressure levels, constant monitoring of pressure numbers and contraction frequency is required, stabilizing them according to indications.
To restore memory, attention, and performance, donepezil is used - a drug that normalizes the exchange of neurotransmitters, restores the speed and quality of transmission of nerve impulses as intended. Restores daily activity of patients, corrects apathy, thoughtless obsessive actions, eliminates hallucinations.
Useful to know: Dropsy (hydrocephalus) of the brain in children and adults, symptoms and treatment
Galantamine normalizes neuromuscular transmission, stimulates the production of digestive enzymes, sweat gland secretion, and lowers intraocular pressure. The drug is used for dementia, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, and glaucoma.
Rivastigmine is an effective remedy. But its use is limited by the presence of gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, conduction disorders, arrhythmia, bronchial asthma, urinary tract obstruction, and epilepsy.
For severe psycho-emotional disorders, antidepressants are used. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors have proven themselves to be effective in this pathology. These drugs include venlafaxine, milnacipran, duloxetine, sertraline. Drugs in this group are sold in pharmacies only by prescription.