According to literature data, among all forms of germ cell tumors of the central nervous system, the term accounts for from 36 to 65%.
In our series of observations, germinomas accounted for about 60%.
In the vast majority of cases, germinomas occurred in male patients - 48:3.
The peak occurrence of the term is noted in the second decade of life. The distribution of patients by age is presented in Fig. 105.
Fig. 105. Distribution of patients with germinomas of the pineal region by age.
Functional significance of the gland
The significance of the pineal gland is not fully understood; it is too small and deeply located. But the hormones that it produces have been identified: melatonin, serotonin, pinealin, adrenoglomerulotropin, dimethyltryptamine.
Serotonin is a precursor to melatonin and is involved in the regulation of circadian rhythms (sleep and wakefulness). 80% of melatonin is produced in the pineal gland. Melatonin inhibits the development of the gonads in children, affecting the gonadotropic hormone. To produce it, absolute darkness is needed, otherwise its synthesis immediately stops. Therefore, the formation of melatonin occurs during night sleep. With the end of puberty, production decreases.
The pineal gland in children affects the functioning of the entire endocrine system: the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pituitary gland. It not only participates in the regulation of sexual development, but is also a connecting element between the tissues of the cerebral cortex. In addition, the pineal gland reduces the production of growth hormone, inhibits sexual behavior, the development of tumors, and is responsible for orientation in space and time; regulates the exchange of Ca, P, K, magnesium; regulates seasonal rhythms; has antioxidant properties, exhibits antitumor protection, and delays aging.
Serotonin is not only a precursor to melatonin, but is also considered the hormone of happiness, creates a good mood and improves emotional background. Adrenoglomerulotropin - regulates the production of adrenal hormones, stimulates the production of aldosterone, thus participating in electrolyte metabolism.
Pinealin lowers blood sugar. Little studied.
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is responsible for dreams and clairvoyance, near-death experiences.
For centuries, the pineal gland was considered the seat of the soul, in esotericism - the third eye, determining the ability to clairvoyance and transmit information at a distance - telepathy.
Apparently, this is due to the fact that the pineal gland itself can perform rotational movements, reminiscent of the movements of the eyeball.
In addition, the structure of the gland contains rudimentary elements like a lens and some receptors reminiscent of the eyeball, but they are underdeveloped.
The pineal gland in children actively grows, but already from adolescence its growth gradually decreases. With age, it begins to involute and its activity decreases.
Symptoms
Due to the fact that brain germinoma develops near the third ventricle and is predisposed to grow along the cerebrospinal fluid tract, as it grows it contributes to the disruption of cerebrospinal fluid outflow, as a result of which the symptoms of hydrocephalus quite often come to the fore in its clinical picture. Such patients often complain of intense, bursting headaches, a feeling of pressure in the eyes, nausea not associated with food intake, and even vomiting.
Due to the fact that the neoplasm is located next to the chiasm of the optic nerves, this pathology often causes visual disturbances, manifested by decreased visual acuity, double vision, and visual field defects. Sometimes germinoma of the brain is accompanied by psycho-emotional disorders and memory disorders.
Brain germinoma is localized in the region of the third ventricle and further grows along the cerebrospinal fluid ducts, thereby disrupting the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, her clinical picture is characterized by symptoms of hydrocephalus. Patients complain of a severe, bursting headache, a feeling of pressure in the eyes, as well as nausea and vomiting not associated with food intake.
Located near the chiasm of the optic nerves, germinoma can often manifest itself as visual disturbances (decreased visual acuity, double vision, visual field defects). Brain germinoma may be accompanied by memory impairment and psycho-emotional disorders. Tumors located in the pituitary gland can disrupt the functions of the hypothalamic-pituitary system and lead to the development of neuroendocrine syndromes: diabetes insipidus, menstrual irregularities, anovulation and amenorrhea in women.
Pineal gland diseases

As in any other organ, developmental anomalies, inflammation, damage by parasites, trauma, neoplasms, cysts, etc. are possible here. Pineal cysts are rare - they account for only 2% of brain pathologies. But some researchers believe that the figure is greatly underestimated. There are many more cases, but it is difficult to identify them due to the lack of symptoms.
Types of germinoma
Oncologists distinguish several types of germinoma.
- Seminoma is a malignant testicular tumor of germ cells. It is quite common, characterized by aggressive growth and actively metastasizes. In most cases, it is accompanied by a clear enlargement of the testicle and severe pain in the scrotum. It is treated like most types of cancer - chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery.
- Dysgerminoma is a malignant neoplasm in women that develops from primary indifferent cells of the gonads. The cause is hypoplasia of the genital organs. Symptoms: pain, difficulty urinating and constant weakness.
- Teratoma is in most cases a benign neoplasm. Localized in the ovaries, testicles or in the pineal area. May consist of muscle or bone tissue, hair. Effective treatment methods are radiation and chemotherapy, as well as surgery.
- Teratocarcinoma is a malignant tumor of the ovary, which is formed from immature and mature tissues, affecting the internal genital organs of men and women.
Causes of cysts
What is a pineal cyst? A cyst is a cavity filled with a liquid substance and bounded by a membrane.
A true cyst is an exclusively benign formation and does not degenerate into oncology. But neurosurgeons often encounter a parasitic cyst filled with echinococci.
Most often, such a cyst in the pineal region of the pineal gland is formed as a result of echinococci and other parasites entering the brain through the bloodstream. The larva infects the pineal gland and forms its own capsule, where the products of its vital activity accumulate.
Such a cyst is extremely toxic and dangerous. The difficulty is that this capsule is completely protected from the immune system. A cyst of this origin tends to grow.
- Other reasons for the appearance of a pineal gland cyst include: narrowing or blockage of the gland's outlet canal, in which melatonin begins to accumulate inside, gradually forming a cavity. Such changes are possible after inflammatory processes or embolism.
- Congenital anomalies of the brain in embryogenesis.
- TBI, which can lead to dystrophy and degeneration of brain tissue.
- A stroke, when a hematoma appears as a result of hemorrhage, turning into a cyst.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Untreated infections.
A cyst in the pineal region in children is often congenital in nature (due to brain hypoxia, birth injuries to the head), or occurs after infections that occur immediately after birth.
Clinic and diagnostics
The clinical manifestation of the term varies depending on the location of the primary lesion and/or the presence of metastases.
As noted above, in addition to the pineal region, germinomas are often localized in the chiasmal-sellar region (mainly in women). Departing somewhat from the main topic, let us characterize this localization with the term. For suprasellar the term is characterized by the duration of the anamnesis. In typical situations, children have symptoms of pituitary-hypothalamic insufficiency (diabetes insipidus, growth retardation, secondary hypopituitarism, etc.), for which they undergo hormone therapy for a long time. At the initial stages of the disease, x-ray examinations may not detect a tumor.
Because suprasellar germinomas can cause panhypopituitarism, children with this syndrome should undergo periodic magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI)
.
As for the term pineal region, it should be noted that in the clinical picture, symptoms of increased intracranial pressure and impaired oculomotor function come to the fore. Moreover, as we noted earlier, with germinomas, compared with other tumors of the pineal region, oculomotor disorders are most pronounced.
The main clinical symptoms characteristic of patients with germinomas are presented in Fig. 107.
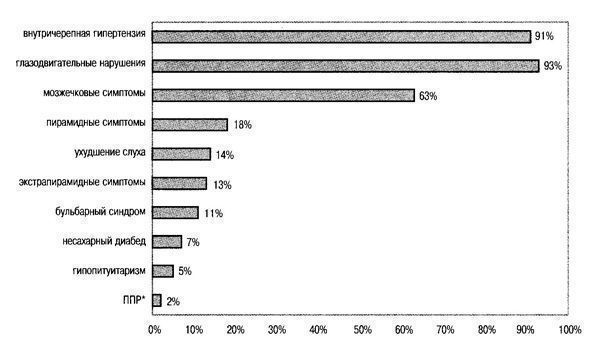
Fig. 107. Main clinical symptoms for germinomas of the pineal region. *PPD—premature sexual development.
Tumor markers - alpha fetoprotein and human chorionic gonadotropin - are absent in germinomas both in the cerebrospinal fluid and in the blood.
With computed tomography (CT)
In the vast majority of cases, the term pineal region is characterized by the presence of a focus of homogeneous increase in density. Less commonly, germinomas have the same density as the medulla. The introduction of radiocontrast agents usually increases tumor density. Often, cysts of different sizes can be detected in the tumor. Petrification is often found in its thickness - a calcified pineal body (Fig. 108). The petrificate is usually located along the midline. According to SRGanti, in germinomas, petrification is detected in 63% of cases.
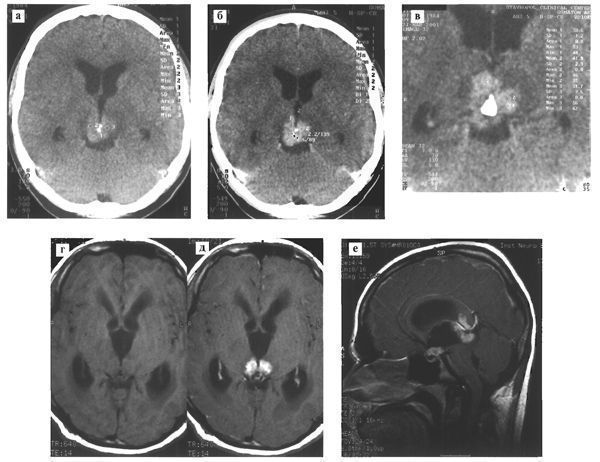
Fig. 108. Germinoma of the pineal region. Various patients.
CT reveals a moderately hyperdense tumor with infiltration of the visual tuberosities, slight expansion of the lateral ventricles (a); after intravenous administration of a contrast agent, its accumulation in the tumor stroma is noted (b); in the thickness of the tumor, along the midline, there is a large petrification (c). MRI in T1 mode before (d) and after (e) intravenous administration of a contrast agent determines tumor infiltration of the visual tuberosities. The signal from the tumor is isointense with the white matter of the brain (d); on the sagittal section (e), in addition to the main focus in the pineal region, a tumor node is identified in the infundibular part of the third ventricle.
On T1-weighted MRI, germinoma is characterized by an iso- or hypointense signal zone; In T2-weighted tomograms, the signal from the tumor is also generally iso- or hypointense. The neoplasm often has a heterogeneous structure, due to the presence of small cysts and petrification in the tumor stroma. Sometimes cysts can reach large sizes. Rarely can traces of hemorrhage be found in germinomas (Fig. 109).
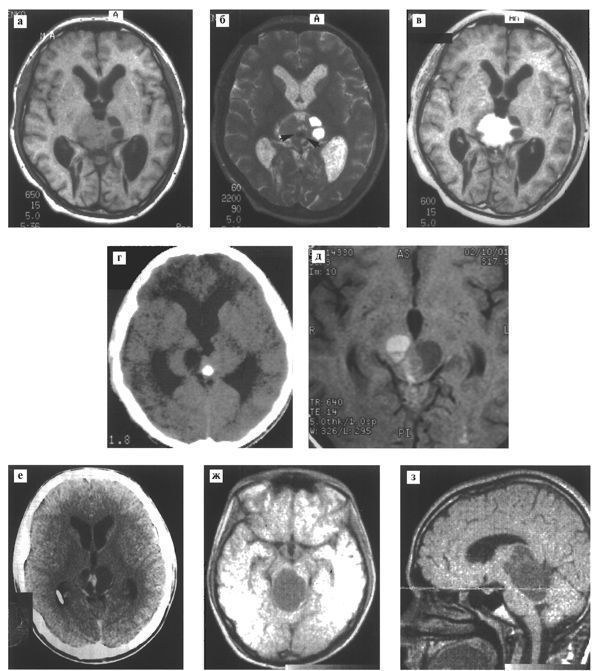
Fig. 109. Radiological variants of the term pineal region. Various patients.
# MRI in Tl, T2 modes in the pineal region reveals a tumor of isohypointense signal, infiltrating the visual tuberosities and having small cysts (a, b); in addition, petrification is detected in T2 mode (b, arrow); When contrasted, the tumor intensively accumulates contrast agent (c).
# CT (d) and MRI in T1 mode (e) of a patient with germinoma of the pineal region. A significant cystic component with traces of hemorrhage is detected in the thickness of the tumor.
# CT (f) and MRI in T1 mode (g, h) determine the tumor, the main volume of which is a cyst.
The boundary between the germinoma and the surrounding medulla in all scanning modes (except in very rare cases) is unclear. Around the tumor in T2 mode a zone of increased signal is detected, caused by swelling of the medulla as a reaction to tumor invasion. Petrifications, which are well visualized on CT, are poorly detected on MRI due to the low signal.
Intravenous administration of a paramagnetic contrast agent usually results in intense contrast enhancement of the tumor. The border of the tumor with the medulla is almost always defined more clearly and cysts in its stroma are better identified.
Germinomas spread and infiltrate surrounding structures in all directions (Fig. 110), often penetrating into the cavity of the third ventricle or invading the lamina tetracoloma.
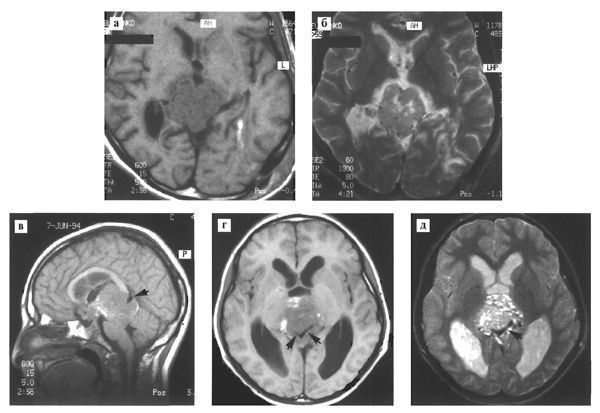
Fig. 110. Germinoma of the pineal region. Various patients.
# MRI in T1 (a) and T2 (b) modes reveals a tumor with pronounced peritumoral edema;
# MRI in T1 (c, d) and T2 (e) modes in sagittal and axial projections reveals a large tumor of the pineal region with spread to the chiasmatic-sellar region. The tumor contains foci of hemorrhage (d) and multiple small cysts (e). Tumor infiltration of adjacent brain structures is detected; The infiltration zone includes large venous collectors of the pineal region - the vein of Galen, internal veins (arrows).
The second most common location of germinoma is the chiasmal-sellar region, sometimes in combination with a tumor node in the pineal region (Fig. 111).
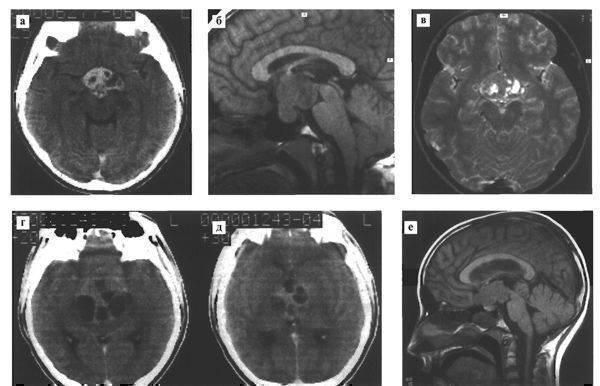
Fig. 111. Germinoma of the chiasmal-sellar region. Various patients.
# On contrast-enhanced CT (a) the tumor is hyperdense with small cystic inclusions; with MRI in T1 mode (b), the signal from the formation is isointense with the medulla. The tumor occupies the infundibular part of the third ventricle, the interpeduncular cistern and invades the sella turcica; in T2 mode (c) small cysts are clearly visualized in the tumor structure
# A contrast-enhanced CT scan (d,e) reveals a large germinoma of the chiasmal-sellar region with cysts.
# MRI (e) of a patient with two germinoma nodes in the chiasmal-sellar and pineal regions.
In extremely rare cases, the primary focus of germinoma can occur in the subcortical ganglia, lateral ventricle, brain stem, and spinal cord (Fig. 112).
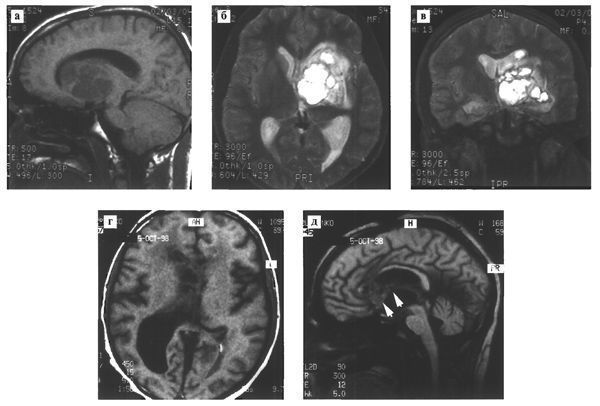
Fig. 112. Rare localization of intracranial term. Various patients.
# With MRI and T1 (a) and T2 (b,c) mode, a heterogeneous structure of a large germinoma with cysts is determined in the subcortical nodes on the left;
# MRI in T1 mode (d) visualizes a volumetric formation with a reduced signal, which is localized in the right lateral ventricle, spreading along the transparent septum and fornix (arrows).
Germinomas are prone to metastasis throughout the subarachnoid space, including the spinal cord. MTJenings found such metastasis in 11% of patients (Fig. 113).
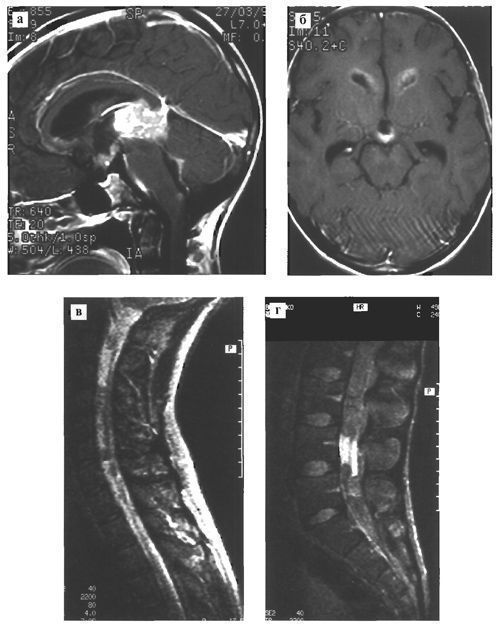
Fig. 113. Germinoma of the pineal region, metastasizing through the ependyma of the ventricles and the subarachnoid space of the brain (a, b) and spinal cord (c, d).
Germinoma of the pineal region: is there a pathognomonic CT and MRI sign of this tumor?
Despite significant advances in X-ray diagnostics, the problem of differential diagnosis of tumors of the pineal region has not yet been completely resolved. According to the literature, there are no specific CT or MRI signs that could determine the histological identity of tumors in a given location, with the exception of teratomas. But even for teratomas there is a limitation - it is not always possible to distinguish between malignant and benign forms of this tumor.
We carried out a thorough analysis of CT and MRI data in 55 patients with germ cell tumors of the pineal region, half of which (27 cases) were germinomas.
In 40% of cases (11 cases), we found the so-called “butterfly” symptom. The characteristic picture of a “butterfly with spread wings” is caused by symmetrical tumor infiltration of the visual tuberosities and an enlarged petrified pineal body located in the midline on the dorsal surface of the tumor or in its thickness (Fig. 114). This symptom can be considered specific to the term, since we were unable to detect it in any of the cases of tumors of the pineal region of a different histological structure.
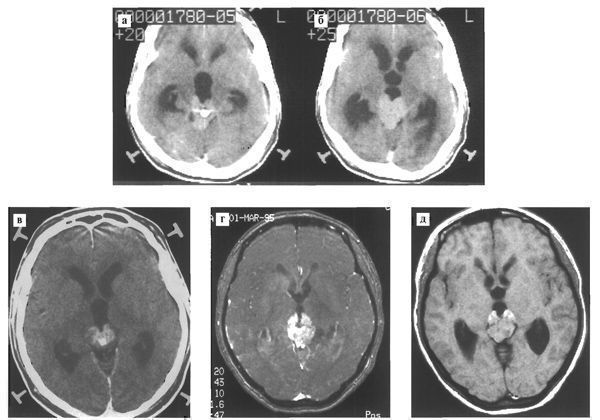
Fig. 114. Germinoma of the pineal region with a characteristic radiographic “butterfly” symptom. Various patients.
# CT scan (a, b) reveals a hyperdense zone of homogeneous structure in the pineal region, in the thickness of which large petrification is detected; the tumor grows into the visual tuberosities and spreads anteriorly along the walls of the third ventricle
# CT (c) and MRI (d,e) reveal a relatively homogeneous structure of a space-occupying formation in the pineal region with a psoriasis inside; the tumor roughly infiltrates the visual tuberosities and grows anteriorly along the walls of the third ventricle, which resembles a butterfly with open wings.
In all patients with tumors of the pineal region in whom this radiological sign was detected, radiation therapy led to complete disappearance of the tumor. This reaction to radiation therapy is typical for the term.
The above facts suggest that the “butterfly” symptom occurs exclusively in patients with germinomas. We believe that in cases where this characteristic picture is revealed, there is no need to clarify the diagnosis using stereotactic biopsy. Radiation therapy may be recommended for such patients.
Kinds
There are 5 types of cysts:
- arachnoid (the most common and most dangerous);
- colloidal;
- pineal;
- dermoid;
- epidermoid.
An arachnoid cyst of the pineal region or cerebrospinal fluid is localized in the arachnoid membranes of the brain, filled with CSF. More often diagnosed in men, it develops after inflammation and infections. Gives symptoms in case of increased ICP and compression of an area of the cerebral cortex with its increased growth.
Colloidal cysts are usually congenital and do not manifest themselves for a long time. If there are disturbances in liquorodynamics, they can cause the development of intracerebral hernias and hydrocephalus with a fatal outcome.
Dermoid and epidermoid cysts manifest themselves during embryogenesis. The contents of such cysts include fat, hair, etc.
They tend to grow rapidly, which indicates the need for urgent removal after the birth of the child.
Pineal cysts are neoplasms of the body of the gland; they are always very small and harmless.
Common types of brain cysts:
- retrocerebellar (occurs directly in the brain, namely in places where gray matter cells die);
- arachnoid (forms between the layers of the membranes of the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid);
- subarachnoid (most often a congenital pathology, accompanied by pulsation in the cranium and painful muscle contraction);
- pineal (appears in the pineal gland and in the area where the hemispheres connect; has a direct effect on the endocrine system);
- pineal (diagnosed in the pineal gland, leads to impaired coordination of movement, vision, and metabolic processes).
There are cysts of the choroid plexuses of the brain, the pineal gland, located between the meninges, in the subcortical ganglia, cerebellum and even the visual thalamus.
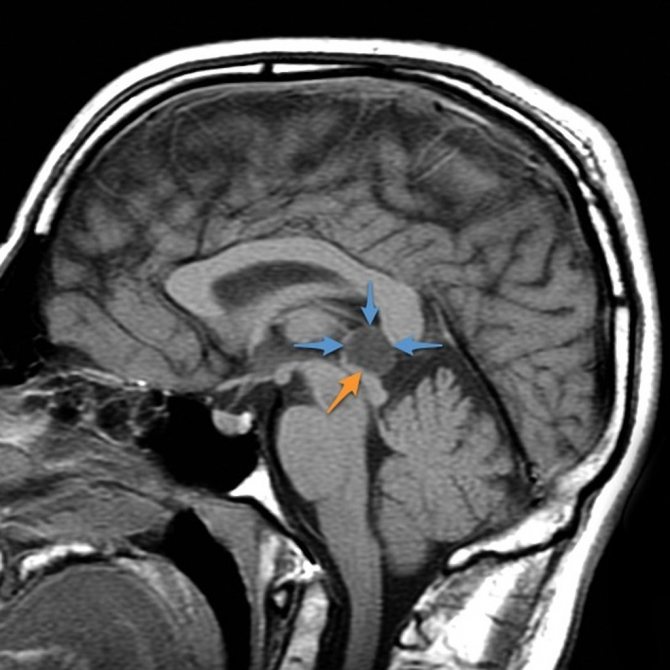
The pineal region is a complex anatomical zone, which includes the pineal gland, adjacent brain structures, cerebrospinal fluid spaces and blood vessels. The pineal gland is located posterior to the third ventricle of the brain, anterior and inferior to it is the posterior commissure of the brain, anterior and superior is the comissura habenularum, below is the lamina quadruple and the cerebral aqueduct, and just above and posterior is the splenium of the corpus callosum. Immediately behind the gland is the quadrigeminal cistern. Spreading anteriorly, this tank forms the velum interpositum, which lies above the pineal gland and extends anteriorly under the fornix. The internal cerebral veins and the great cerebral vein are in close proximity to the pineal gland.
Clinic for pathology of the pineal region
- Intracranial hypertension (compression of the aqueduct, as a result of hydrocephalus)
- Parinaud syndrome (midbrain lesion)
- Cerebellar disorders
- Endocrine disorders
Pathology of the pineal region
Cystic non-neoplastic formations
- Pineal cysts
- Cavity (cyst) of the intermediate sail (lat. Cavum veli interpositi)
- Arachnoid cyst
Tumors originating from the pineal gland parenchyma
In adults, tumors of the pineal region account for 0.5-1%, and in children 3-8% of all intracranial neoplasms.
- Pineocytoma
- Pineoblastoma
- Mixed pineal tumors
- Papillary tumor of the pineal gland
Germ cell tumors
- Germinoma
- Teratoma
- Choriocarcinoma
- Teratoma
- Fetal carcinoma
- Yolk sac carcinoma
- Mixed germ cell tumors
Other pineal tumors
- Astrocytoma
- Meningioma (near the pineal gland)
- Metastasis of the pineal gland
Vascular pathology
- Malformation of the vein of Galen
- Thrombosis of the internal cerebral vein
Signs of a cyst
If the size of the cyst in the pineal region is no more than 1 cm, it does not manifest itself in any way and is not detected. Their diagnosis is most often random during studies for other reasons related to brain pathology and MRI.
The greatest danger is posed by growing cysts of the pineal region, which can cause circulatory problems in the surrounding tissues and lead to hydrocephalus.
Causes
Germinoma is a dysontogenetic tumor: it develops due to genetic defects and defects in fetal development in the womb.
When an embryo develops, its tissues and organ rudiments migrate throughout the body: one tissue develops into another, and a whole organ is formed from one rudiment. Due to developmental defects, the processes of tissue migration and differentiation are disrupted - a tumor appears.
The embryo is most sensitive to negative influences in the first trimester of pregnancy. This is the period when most organs are just beginning to form and grow. Any harmful effect can cause abnormal cell growth or tissue development.
Factors provoking dysontogenesis:
- bad habits of the mother: smoking, alcohol, drugs;
- irradiation;
- intoxication with heavy metals, food poisoning, acute intoxication due to viral diseases;
- living in a poor ecological environment;
- prolonged contact with carcinogens: a diet with predominantly overcooked foods, consumption of processed fruits, vegetables and berries.
Treatment of epiphysis cyst
In most cases, treatment of pineal cysts does not require the use of drugs. The use of drugs is possible only for echinococcosis, at its earliest stage. Symptomatic treatment to eliminate the manifestations of the disease is prescribed only when they appear. And this happens when the blood vessels of the brain or its tissues are compressed by a growing cyst. Or surgical treatment is used - most often. Due to the complexity of access, operations are difficult and there is a high percentage of complications - 60-70%.
Indications for surgery:
- severe symptoms;
- parasitic nature of the cyst;
- cyst growth;
- hydrocephalus;
- influence on the cardiovascular system.
If pathology is identified, further treatment of a cyst in the pineal region of the brain is aimed at reducing the risk of its growth.
Specifics of diagnosis and treatment of germinoma at different stages
Brain germinomas have a high degree of malignancy and are characterized by widespread growth, so a thorough examination is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. After it has been completed, cancer treatment abroad should begin as early as possible.
At any stage of the tumor, diagnosis begins with studying the clinical picture. Patients then undergo neurological diagnostics, which is necessary to identify symptoms of cerebral hydrocele and disorders of the medial structures.
Echoencephalography can detect increased intracranial pressure. If the tumor is large, then during the examination a displacement of the middle brain structures is detected.
An informative way to diagnose germinoma of any stage is tomography (computer, magnetic resonance). Based on the results of such an examination, the location of the tumor, its size and the nature of its development are determined. In later stages, CT and MRI can diagnose metastatic foci in the lateral ventricles and infundibular region of the 3rd ventricle.
Laboratory blood testing is one of the main points of the diagnostic program. The blood is tested for the presence of cancer markers.
A biopsy is performed to make a definitive diagnosis. But this study also requires additional confirmation, since germinoma is characterized by heterogeneity. To clarify the results of the biopsy, morphological studies of certain areas of the brain are performed after tumor resection. Treatment of brain cancer abroad begins only after specialists have no doubt about the diagnosis.
In the case of germinoma, differential diagnosis is necessary, during which the tumor is distinguished from glioma, ganglioneuroma, astrocytoma, and glomus neoplasm.
Diagnosis of germinoma in Israeli clinics includes advanced techniques:
- tomographic scanning;
- cerebroangiography;
- EEG;
- ventriculography;
- diagnostic spinal puncture, after which the cerebrospinal fluid is sent for examination;
- modern laboratory tests (tumor markers, chorionic gonadotropin, fetoprotein, placental phosphaase, etc. are identified)

Treatment tactics are selected taking into account the location of the tumor and the extent of its spread. At an early stage, when the tumor is small, surgical removal is possible. To carry out minimally invasive treatment, radiosurgical treatment is performed using a modern CyberKnife or Gamma Knife installation (stereotactic radiosurgery techniques). The same technique is used if the patient requires treatment for lung cancer abroad due to metastatic damage to the organ.
A large tumor located in a hard-to-reach place cannot be removed by radiosurgery. In such cases, a stereotactic biopsy is prescribed and high-precision radiation therapy of the tumor is performed using the progressive IMRT method. A combination of radiation therapy and rational chemotherapy provides a high therapeutic result.
In case of extensive tumor process in pediatric patients, which is typical for late stages of the tumor, systemic chemotherapy is prescribed.
The most successful treatment for such a serious tumor as germinoma is carried out abroad. Israeli clinics provide therapy in special neurosurgical departments. The main treatment method is low-traumatic removal of the tumor in combination with shunt surgery. All interventions are performed using neuronavigation computer systems. If we talk about prices for cancer treatment abroad, Israeli cancer centers offer the most favorable cost of therapy.
Radical treatment methods

Shunting - a drainage is installed, with the help of which the cyst is emptied, after which its walls fall off and become overgrown. But surgery can often have negative consequences for the body due to the complexity of the brain structure.
Endoscopy – the cyst is removed through a puncture in the skull. This method does not cause complications, but there are contraindications in the form of visual impairment.
Craniotomy is an effective operation where a specific area of the skull is removed to gain access to the brain. Has a high risk of brain damage.
Germinoma of the brain: symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention
All neoplasms affecting the brain are dangerous not only to the patient’s health, but also to life. This is due to the fact that they affect vital parts and cause severe consequences. One such disease is germinoma.
General information
Germinoma is a rare disease that belongs to a type of brain tumor. The neoplasm is formed at the stage of embryonic development. Germinoma can arise from one type of tissue or consist of several types.
Experts have conducted a number of studies, based on which it was found that boys are mainly susceptible to developing the disease.
The tumor is located in the deep parts of the brain, which causes the development of certain consequences and complications. Often, surgical removal of the formation is impossible, due to the location of the germinoma.
Education develops gradually, along with the brain. In certain cases, it is completely inert and appears only when the child reaches 10-11 years of age.
But the tumor may not show signs for up to 20 years. Such a course is considered benign. But in more than half of the cases (about 75%) it is malignant, which is due to the speed of its growth.
Causes of germinoma
The exact reasons for the formation of brain germinoma could not be established. Many experts believe that the main factor in the occurrence of a tumor is a disruption in the development of the fetus. This hypothesis is confirmed by the fact that the pathology is established at a young age.
The following factors can provoke disruption of embryonic development:
- Exposure to radiation.
- Regular or prolonged contact of a pregnant woman with toxic or radioactive substances.
- Intoxication with drugs and various substances.
- The influence of carcinogenic substances.
- Infectious lesions during pregnancy. These include severe forms of influenza, measles, herpes, and chlamydia.
Germinoma is an embryonic formation, since it begins to form from embryonic rudiments until the final development of the fetus.
Treatment methods
When germinoma is diagnosed, treatment is carried out only through surgery. Today, several techniques are used, each of which has its own characteristics, indications and contraindications.
Radiation therapy
Germinoma is characterized by increased sensitivity to both radioactive and chemical radiation. That is why the main method is radiation therapy.
But it is not always possible to use it. This is due to the early age of the patients, since the tumor is detected when the child reaches 10 years of age or earlier.
Radiation therapy is contraindicated in children due to the negative effects of rays on an unformed organism. Treatment with radiation therapy is prescribed to patients over the age of 18 years.
Polychemotherapy
When treating neoplasms in children, specialists more often use polychemotherapy.
The technique involves influencing the tumor with the help of drugs. In this case, the doctor prescribes not one drug, as with chemotherapy, but a complex. When taken together, they can reduce the prevalence of formation or slow down its development.
Polychemotherapy is not able to completely cure the disease, but it allows you to gain time until chemotherapy is contraindicated.
Surgical removal
Surgical removal of a tumor formed in the brain is the most difficult task in neurosurgery. This is due to difficult access to areas of the cerebral cortex where the tumor is most often located.
But despite all the difficulties, the operation can be carried out. Surgical removal of germinoma is prescribed only when other methods do not bring results or there are contraindications for their implementation.
When prescribing surgical removal, the choice of access to the tumor is determined by the doctor after carefully studying the research results, the size and location of the tumor.
Often the procedure is performed using bypass surgery. Contraindications for surgical removal include unclear and rapid growth of the tumor and its location in an area where access is impossible.
A complex approach
In certain cases, the specialist prescribes complex treatment, which uses polychemotherapy and radiation therapy as an addition to surgery.
But an integrated approach to treating patients under the age of 18 is used in rare cases. This is due to severe intoxication of the body. But if each method separately is ineffective, complex therapy is prescribed.
The choice of treatment method for brain germinoma is made by the attending physician after studying the diagnostic results, its location and size.
Particular attention is paid when treating young children, since their bodies are still weak and may respond differently to chemotherapy.
Complications
Germinoma or dysgerminoma of the brain grows as the child grows. It begins to form even at the stages of embryonic development, and may not manifest itself for a long time. This is precisely the danger of the disease.
The first signs appear after 10-12 years and are often pronounced. Moreover, the neoplasm is already significant in size. The only treatment method is removal of the tumor. To do this, several methods or an integrated approach are used.
But in the absence of therapy, various complications may arise in the form of infertility for women. Children experience growth retardation, underweight, and delayed mental and mental development.
Experts also note a disorder of the nervous system, which is expressed in excessive irritability and frequent mood swings.
As germinoma grows, it puts pressure on neighboring parts of the brain, which causes memory impairment, the functioning of the visual apparatus and many body systems.
That is why, when the presence of a neoplasm is established, therapy should be started immediately.
Forecast
The patient's life expectancy is determined by the characteristics of the germinoma. The prognosis is influenced by the degree of malignancy, size, and growth pattern.
According to research results, the average survival rate of patients over five years is 85%.
The life prognosis also depends on when the treatment was carried out and what method was used to remove it.
Prevention measures
In order to protect the child and reduce the risk of developing a neoplasm, a woman should be attentive to her health. First of all, the influence of various factors on the body should be excluded.
A woman should follow a number of the following rules:
- Regularly visit a gynecologist who is managing your pregnancy. It is necessary to follow all his recommendations.
- Eliminate the influence of toxic, chemical and radioactive substances.
- properly . The diet should include fruits and vegetables, as they contain many vitamins and minerals that are beneficial not only for the woman, but also for the child. Products that contain carcinogens, dyes and flavors in large quantities are also harmful.
- Do not take medications without a doctor's prescription. They can cause intoxication of the body.
- Eliminate the development of infectious diseases. To do this, you should not be in crowded places, especially during periods of high morbidity, and take vitamin complexes to maintain immunity. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.
Compliance with preventive measures will help significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease in your baby.
Germinoma of the brain is diagnosed mainly in children aged 10-12 years. But in certain cases it may appear only by the age of 20. The only effective treatment is removal of the tumor.
Surgical excision is not always possible due to the location of the tumor. In this case, other removal methods are used.
To date, experts have not been able to establish the exact reasons for the formation of education. That is why prevention consists of following general rules during pregnancy and being attentive to your health.
Symptoms of cysts in children
They are common to adults, but the development of pineal cysts in a child at an early age has its own characteristics. The child may complain of a headache, may experience vomiting and nausea, impaired motor skills, and poor coordination; complaints of blurred vision and blurred vision.
With pathology of the pineal gland, growth hormone will increase, which will lead to accelerated growth rates. Such children are superior to their peers in weight and height; puberty can also be advanced or, conversely, delayed. Perversions of sexual desire may develop in a child. What you really should be afraid of when you discover a cyst in the pineal region of the brain in a child is hydrocephalus of the brain, when CSF accumulates in its ventricles.
Hydrocephalus leads to mental retardation.
Since the fontanelles of the skull in young children are not yet overgrown and the skull bones are soft, hydrocephalus is manifested not by tissue compression, but by expansion of the subarachnoid space due to divergence of the skull bones and an increase in brain volume.
The head takes on a characteristic shape with an expansion in the frontal region, which in medicine is called the alien symptom.
This is popularly called dropsy of the brain.
Measures to prevent germinoma
The prerequisites for the development of brain germinoma arise during embryonic development, so a pregnant woman should carefully take care of her health in order to minimize the risks of developing germinoma. The first thing to do is to protect yourself from the influence of provoking factors.
Basic preventive measures:
- Regular visits to the gynecologist managing the pregnancy. Mandatory implementation of his recommendations.
- The body should not be allowed to be exposed to radioactive, chemical and toxic substances.
- Provide proper nutrition, consisting of vegetables and fruits. This way the body will receive vitamins and minerals that are necessary for the health of the pregnant woman and the fetus. It is unacceptable to consume harmful products containing dyes, carcinogens, and flavorings in excess quantities.
- Avoid taking medications without a medical prescription to prevent intoxication of the body.
- Prevent the development of infectious diseases. To avoid getting sick, a pregnant woman should avoid visiting places where many people gather. To maintain immune functions, you should take vitamin complexes. But first you need to consult your doctor.
By following preventive measures, a pregnant woman can significantly reduce the risk of germinoma in her child.
Treatment
Dictate the symptoms and treatment of pineal cysts of the brain. Any surgical intervention is always risky, so surgery in children is performed only when the benefit outweighs the risk.
Monitoring a cyst means undergoing MRI diagnostics once every six months. For echinococcosis, treatment with anthelmintic drugs is used.
For hydrocephalus, a puncture of the subarachnoid space is performed with fluid suction.
If hydrocephalus recurs, a cerebro-abdominal shunt operation is performed. Its essence is that a catheter is inserted into the abdominal cavity from the skull and the liquid constantly flows there without lingering in the brain. And since fluid constantly circulates in the stomach, cerebrospinal fluid is quickly absorbed there.
Treatment and therapy

There are three main methods that guide the treatment or elimination of germinoma. The main method is surgery with surgical removal of the tumor. A complementary measure to the main technique is irradiation of nearby cells. Sometimes, as a complex technique, surgery is combined not only with radiation therapy, but also with polychemotherapy.
Surgical intervention is possible only in a small proportion of cases of germinoma detection. When deciding on the possibility of excision, doctors are guided by the following principles:
- The location of the germinoma and the ability to access it.
- Number of tumor formations.
- Size of the tumor.
If, due to the location of the tumor, its surgical removal is not possible, then targeted radiation therapy or polychemotherapy is used. The choice between specific techniques is often made based on the patient’s age. If the patient has not reached adolescence, then there is no possibility of using radiation exposure for germinoma. This is due to the fact that radiation therapy unduly affects the processes of brain development.
A specific type of tumor disease, such as germinoma, responds quite well to treatment with radiation and chemical therapy. Accordingly, this has a positive effect on general medical statistics and survival rates - 95% of those who have undergone chemotherapy and radiation therapy live for at least another 5 years. And 88% of people with inoperable germinomas live about 10 years after undergoing the procedure.
Naturally, in order to avoid recurrent manifestations, it is necessary to conduct preventive visits to oncology specialists.
Preventive measures
Even if the reliable causes of a particular disease, that is, brain germinoma, are unclear, they mostly boil down to the fact that a pregnant woman needs to adhere to all the basics of a healthy lifestyle. Only in this way can one somehow protect the unborn child from the occurrence of such neoplasms as germinoma. Quitting smoking, consuming preservatives, alcohol, drugs, and GMO products can protect the child from many other diseases - lymphangiomas, hemangiomas and others.