RU2100037C1 – Method for treating neuritis of the facial nerve – Google Patents
The invention relates to medicine, namely to neurology, and can be used in the treatment of dysfunction of facial muscles due to damage to the facial nerve.
In all cases, the cause of the disorder of the facial muscles is a violation of the conductivity of the facial nerve, resulting from its diseases or damage.
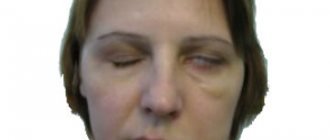
This is accompanied by peripheral paralysis of the facial muscles, which is expressed by a sharp asymmetry of the face, a mask-like expression with a wide open palpebral fissure filled with tears, and a drooping corner of the mouth on the side of the disease. Speech impairment is also noted.
Facial nerve paresis can be infectious or traumatic.
The main methods of their treatment are conservative and surgical. Conservative ones, in turn, are divided into medications, acupuncture and physiotherapeutic.
The invention relates to physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, among which UHF, electrophoresis, ultrasound, electrical stimulation or combinations thereof are currently used.
Electrotherapy is prescribed, as a rule, 3-4 days after the onset of the disease, and first UHF, after a week ultrasound can be used, and after 2-3 weeks, in the subacute period, electrophoresis.
In severe and persistent cases, electrical stimulation is used in combination with drug treatment, and electrical stimulation is recommended no earlier than 10-12 days from the onset of the disease, from 10-15 procedures per course of treatment up to 1-3 months, and in severe cases up to 6 months .
The effectiveness and timing of electrotherapy largely depend on both the duration and severity of the lesion, and on the choice of treatment tactics. Treatment periods range from 15 days to 6 months and, nevertheless, do not always provide a positive therapeutic effect.
If conservative treatment fails, the question of surgical intervention is raised, and operations are performed either on nerves or muscles.
The neurosurgical method involves suturing the peripheral end of the facial nerve of the affected side to the proximal end of one of the adjacent accessory, hypoglossal, phrenic or cervical plexus nerves.
It is believed that the best initial time frame for neuroplasty for traumatic paralysis of the facial muscles is the first 2-3 months from the moment of injury, and for neuritis of infectious etiology, neuroplasty can be switched to after unsuccessful systematic conservative treatment for 3-6 months.
Myoplastic operations consist of either using the preserved neighboring muscles innervated by the trigeminal nerve, and part of their fibers are transplanted with the expectation of replacing the function of dead facial muscles, or the affected muscles are sutured with neighboring healthy ones with the expectation of new “neurotization”, based on the expected possibility of germination nerve fibers from healthy muscle to denervated muscle. To reduce the sharp distortion of the face, they also resort to crossing the corresponding facial muscles of the healthy side.
It should be noted that timely started and persistently carried out complex treatment of facial nerve paresis in each specific case gives a fairly high percentage of recovery. According to summary data, from 73 to 91% of patients recover completely. Treatment periods can reach 1 year or more.
A special case of paresis of the facial nerve consists of those with an initial violation of its anatomical integrity as a result of partial proliferation of the trunk of the facial nerve, compression of the facial nerve in the bone canal due to trauma to the bone wall of the fallopian canal, as a result of surgical treatment of pathology of the middle ear or a fracture of the base of the skull, leading to intraoperative damage to the facial nerve. nerve, etc.
The largest volume of operations differs in patients who lack a fragment of the facial nerve and have a pronounced diastasis of its ends. In the case of diastasis up to 0.2-0.3 cm, it is possible to bring the ends of the nerve closer together and sew them together.
With more pronounced diastasis, sometimes it is also possible to sew the facial nerve end to end, but in such cases a fascial sleeve must be placed over the suture area and covered with a non-free end or a muscle flap.
The problem of replacing nerve defects using grafts is the most difficult and least studied problem.
And yet, at the Research Institute of ENT, it was possible to use transplantation of the posterior cutaneous femoral nerve in two patients with good results, while the central and peripheral fragments of the nerve were sutured to the end, and the graft was placed in the bone bed of the fallopian canal and covered with a fascial flap.
Also known is “A method for restoring the functions of facial muscles in case of violation of the anatomical integrity of the facial nerve” (ed. St. N 1500317).
The method consists in applying an anastomosis between the facial and other motor nerves with the introduction of electrodes into the facial nerve first distal to the site of its damage, and after applying the anastomosis proximal and distal to it and through these electrodes, ES is performed for 2-3 weeks before surgery and for at least 3 weeks after daily 4-5 times a day for 5-10 minutes with rectangular biphasic pulses with a duration of 0.1 to 0.5 ms, a repetition rate of 5 to 50 Hz and an amplitude of 5 to 50 μA. The treatment period is 1.5-2 months.
The invention relates to the treatment of paresis of the facial nerve, including when its integrity is violated. However, since its basis and difference from all known ones is physiotherapeutic effects, a method of treating facial neuritis using a magnetic field was chosen as a prototype.
The technical result of the invention is a reduction in treatment time with results achieved immediately after the course of treatment.
This result is achieved by the fact that in case of paresis of the facial nerve, including after surgery for violation of its integrity, magnetic therapy is carried out using high-intensity pulsed magnetic fields, the induction of which in the first 2 days is more than 1 Tesla, in the next 2 Tesla with a repetition rate pulses of 0.4-0.5 Hz and a duration of 150-160 μs, and this effect is carried out in the first days on the peritragus area of the face, in subsequent days additionally on the superciliary, infraorbital, mandibular regions and 1-2 points of the most affected branch of the facial nerve, and Such exposure is carried out daily for 8-10 days, 60-70 s per point, repeating, if necessary, exposure in the same modes after 1-1.5 months.
The use of high-intensity pulsed magnetic fields, which are known to cause excitation of peripheral nerve fibers, leads to increased local blood flow and thereby to a reduction in edema and removal of cell autolysis products from the site of inflammation.
This in turn stimulates the processes of reparative regeneration of damaged tissues and significantly improves their trophism. Since the penetrating ability of the pulsed magnetic field is 4-5 cm, its stimulating effect covers not only superficial, but also deeply located structures.
This is manifested in achieving a positive therapeutic effect in a fairly short time (8-10 procedures).
The proposed modes of magnetic stimulation, found experimentally in the treatment of patients with facial nerve paresis of various etiologies, provide the highest therapeutic effectiveness, expressed in a decrease or complete disappearance of facial asymmetry.
Exposure in the first days to a magnetic field, the induction of which does not exceed 1 Tesla, and only to the peritragus area of the face, i.e. at the level of the “Ting-Gong” and “Ting-Hui” points, prepares the damaged nerve to perceive the eddy electric currents supplied to it, eliminating its excessive load.
In subsequent days, when swelling decreases, an increase in induction to 2 Tesla and the number of points along all branches of the facial nerve that are affected does not raise concerns about an overdose of stimulation and has a beneficial effect on regenerative processes along the entire length of the facial nerve.
Both in the case of paresis of an inflammatory nature, and after surgery for a violation of its integrity, 8-10 procedures are sufficient to significantly reduce, and in some cases completely eliminate, asymmetry.
If there are residual effects of the course of treatment, after 1-1.5 months it is possible to conduct a second course of magnetic therapy in the same modes.
Of the 11 patients treated with paresis of the facial nerve, including 6 with a violation of its anatomical integrity, 5 patients no longer required re-treatment, in 6 cases a repeat course of magnetic therapy was carried out and further improvement in the function of facial muscles was obtained.
Example 1. Patient P. born in 1955. and I.b. N 801 was admitted to the clinic of the Research Institute of ENT with a diagnosis of facial nerve paresis of post-influenza etiology. Paresis developed 2.5 months ago. During this time, the patient received drug treatment, acupuncture, and physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis). However, all this did not give positive results.
On November 24, 1995, the patient was hospitalized in the 1st clinical department of the ENT Research Institute.
Source: //patents.google.com/patent/RU2100037C1/ru
Physiological basis of electrical stimulation
Muscle contraction in the body is initiated by action on the corresponding motor nerve. Special protein structures – myosin and actin – are responsible for this process in the body.
Actin filaments are connected to myosin filaments through cross bridges - myosin heads. During muscle contraction, these heads temporarily attach to actin filaments and pull them up with a rowing motion. Next, actin and myosin detach from each other and fasten again for the next movement. In the body, all this happens at tremendous speed; it is precisely such movements that ensure muscle contraction. When the muscles relax, the actin and myosin filaments are not connected and take their original position relative to each other.
If we talk about physiotherapeutic procedures carried out in a hospital and affecting the neuromuscular system, then the closest thing to physiological is the use of Lapik current - exponential current. However, any stimulating effect must be balanced by pauses, since prolonged muscle contraction is not physiological - it leads to the accumulation of large amounts of lactic acid in the muscles, and can also provoke trophic disorders.
"Ormed"
Any pain syndrome has a depressing effect on a person, brings suffering and limits physical capabilities.
It is not surprising that cases where pain occurs in the facial area are comparable to disaster.
Moreover, the treatment of the trigeminal nerve (this is the name of the disease) is a complex and slow process, requiring from doctors not only special knowledge and skills, but also responsibility.
Finding specialists who are not afraid to entrust your health is a completely solvable task. As numerous reviews show, treatment of the trigeminal nerve in the Medical Center in the vast majority of cases leads to a complete recovery.
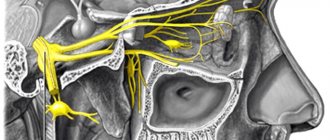
Functions of the trigeminal nerve
A person’s face is a kind of intermediary between the inner “I” and the outside world. Eye movements, facial expressions, speech are not only an opportunity for communication and self-expression. Sensitivity and expressiveness of the face are integral components of determining a person’s personality.
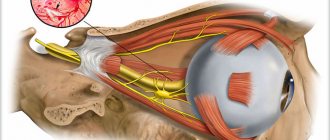
And this possibility depends entirely on the functionality of the cranial nerves located in the soft facial tissues. Among the twelve cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve is considered the largest and most functional. Three branches emerging from its base are responsible for sensitivity and mobility:
- upper and lower eyelids;
- lacrimal gland and membrane of the eyeball;
- temporal and parietal areas;
- nostrils and nasal mucosa;
- cheeks and lips;
- organs and tissues of the oral cavity.
Therefore, if inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs, symptoms and treatment can affect the entire surface of the face - from the forehead to the chin.
What is the essence of the disease
A characteristic manifestation of inflammation is attacks of severe pain on one side of the face, affecting the eyes, lips, cheeks or lower jaw. the appearance of pain can be triggered by ordinary movements - touching the face, brushing teeth, chewing and even talking.
In medical practice, there are often cases when, instead of treating trigeminal neuralgia, patients turned to a dentist for help, mistakenly believing that they had toothache.
medical definitions of inflammation of nerve fibers are neuralgia and neuritis. the difference between these concepts lies in the nature and severity of pathological changes. with neuralgia, neither motor disturbances characteristic of neuritis nor structural changes in nerve tissue are observed.
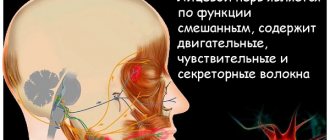
however, with the development of inflammatory processes in the facial nerves, it is appropriate to use any of the terms, since the trigeminal nerve is responsible for both the motor capabilities of the facial muscles and the sensitivity of soft tissues.
whereas the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve involves exposure to those areas of the face where the affected nerve fibers are located.
causes and mechanism of development of neuralgia
The exact causes of the development of inflammatory processes in the fibers of the trigeminal nerve have not yet been established by medicine. However, it has been noted that most often the pathology occurs against the background of provoking factors - injuries, viral infections, inflammation, tumors, hypothermia, nervous shock or migraine attacks.
The appearance of neuralgia is preceded by a pathological change in the blood vessels supplying the nerve. Under pressure from deformed veins and arteries, the myelin sheath of the nerve loses its integrity, impairing its functionality.
The following symptoms indicate that treatment for damage to the trigeminal nerve is necessary:
- a feeling of itching, numbness or tingling in various parts of the face is a signal of an impending exacerbation;
- attacks of severe shooting pain, localized along the line of the nerve fiber - the eyes, the inner point of the eyebrows, temples, the area near the auricle, the back of the neck, teeth and gums;
- distortion of facial expressions;
- twitching of facial muscles.
Constantly waiting for an attack of pain makes a person live in tension and not only disrupts the usual way of life, but also often affects the state of his psyche.
Whereas timely contact with neurologists and adequate treatment of trigeminal neuritis allows you to correct the situation - relieve pain and feelings of physical inferiority, as well as restore mental and emotional balance.
Treatment methods for neuralgia
Traditionally, to eliminate the symptoms of neuralgia of the craniofacial nerves, doctors prescribe drug therapy based on the effects of antiepileptic, antiviral, analgesic drugs, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoids.
The use of medications is justified during painful attacks, since it allows you to quickly relieve pain and relieve a person from suffering.
However, according to experienced neurologists, drug treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve does not eliminate the main cause of the disease and brings only temporary relief.
In addition, taking most prescribed medications is often accompanied by side effects - dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, impaired liver function, and changes in blood composition. And the effectiveness of repeated courses of drug therapy is noticeably reduced.
Some doctors believe that treatment of trigeminal nerve diseases can only be effective through surgery. However, the use of even the most advanced surgical methods does not guarantee the functionality of the facial muscles.
In most cases, surgery is destructive and involves either removal or destruction of the nerve. Among the main side effects of such operations is a change in facial expression.
But there is a way out! Neurologists are confident that effective treatment of the trigeminal nerve should and can be painless, and in practice they confirm that they are right.
How to get rid of facial pain - simple and effective
Medical, located in Belgorod, specializes in the treatment of neurological diseases. And this is its advantage. Because the clinic staff deal with dozens of pathological cases every day, and each time they emerge victorious in the fight against the disease.
The successful use of the interstitial electrical stimulation method for the treatment of trigeminal neuropathy is the result of the vast practical experience of ORMED specialists. Moreover, the leading neurologists of the Center believe that the full therapeutic potential of interstitial effects has not been fully revealed, and the area of its application promises great prospects.
The main secret of the success of the clinic’s specialists is simple, like everything ingenious - eliminating the main cause of the disease, combined with an individual approach to the patient. At the same time, a personal treatment program for each patient is developed in such a way that the effects of interstitial stimulation ensure complete restoration of the functions of the trigeminal nerve.
One of the main advantages of interstitial electrical stimulation, as well as other techniques used in this field, is the lack of invasiveness. All procedures for the treatment of damage to the trigeminal nerve are not only painless, but also bring real relaxation and pleasant sensations.
Interstitial electrical stimulation - a choice for health
Interstitial electrical stimulation is an effective method of therapeutic action directly on the area where the source of pain is located.
During the procedure, disposable needles are inserted under the skin over the affected area, through which current is passed into the internal tissues. The characteristics of therapeutic electrical impulses correspond to the indicators of the biological current of the human body.
Recovery is inevitable. Advantages of the method
Thanks to the interstitial effect of electrical impulses, the redistribution of ionic particles of cell membranes occurs, and thus natural physiological processes are launched - the production of biologically valuable substances, metabolism, and the absorption of nutrients.
But the main thing is that all processes triggered by interstitial electrical stimulation occur against the background of restoration of blood flow. Since electrical impulses are well conducted by a liquid medium, the circulatory and lymphatic systems are the first to receive therapeutic support.
Each electrical stimulation procedure helps restore previously deformed blood vessels. As the tissues of the arteries and veins regenerate, the intensity of blood flow normalizes, muscle spasms go away, pressure on the trigeminal nerve disappears and the process of its revival begins.
The result of using the interstitial stimulation method:
- lasting therapeutic results after just two sessions;
- targeting the source of the disease rather than its symptoms;
- no adverse reactions.
In this case, hospitalization of the patient is not required. Attacks of pain go away even after the first sessions of interstitial electrical stimulation. But for a complete recovery, it is necessary to undergo a course of medical procedures under the constant supervision of neurologists at the Center.
Mechanism of therapeutic effect
Currents used for therapeutic purposes, in addition to provoking muscle excitation and contraction, also produce the following effects:
- Reflexively increase local blood circulation and metabolism.
- Improve lymphatic drainage and prevent venous stagnation.
- Stimulates recovery processes.
- They enhance the activity of the peripheral and central nervous systems, causing a response in them.
- They inhibit atrophic changes and sclerotic processes in the muscle even with a complete interruption of the conduction of impulses along the motor nerve.
- Improves the condition of the motor nerve.
This is the basis of the mechanism of the therapeutic effect of electrical stimulation in medical practice.
Contraindications
Electrical stimulation is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Individual intolerance – the occurrence of pain when the current parameters are normal or when rashes appear on the skin in the area where the electrodes are applied.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- The presence of an acute purulent process in the body.
- Increased body temperature.
- Status epilepticus.
- Muscle contractures.
- Gallstones or urolithiasis.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Pregnancy.
Childhood is not a contraindication; it is possible to prescribe this procedure to a child. During pregnancy, the decision to prescribe this type of physiotherapy is made by the doctor on an individual basis.
Prevention
A set of measures aimed at reducing the occurrence of both the primary disease and its relapses. Necessary:
- Strengthening general immunity.
- Avoid hypothermia and drafts.
- Do not overload the nervous system with overwork, short sleep and stress.
- Do not injure yourself; fractures of the upper jaw and temporal bone are especially dangerous.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the ear, teeth and ENT organs.
It is important to prevent the development of contracture of facial muscles and synkinesis. These are complications when “tightening” sensations appear, involuntary muscle contractions on the healthy side in response to voluntary ones.
Areas of application of electrical stimulation
Various types of electrical stimulation are used in medicine. This procedure is prescribed in the following situations:
- Carrying out diagnostics before therapeutic electrical stimulation. Allows you to determine the nature and level of the lesion, as well as draw up a plan for the necessary treatment.
- Treatment of diseases of the digestive tract such as intestinal paresis, constipation, as well as other pathologies that lead to disruption of smooth muscle organs.
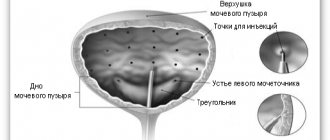
- Treatment of a disease of the urinary system such as bladder paresis (helps to normalize the functioning of the sphincters).
- Conducting electroanesthesia and electroanalgesia. It is carried out by the direct influence of electric current pulses on the structures of the brain. As an independent method of pain relief, it can be used in women in preparation for childbirth and during delivery. In other cases, most often it is combined with the administration of medications.
- Restoring the functions of the musculoskeletal system after injuries (hip, tibia fractures, spinal pathologies), as well as joint diseases (arthrosis).
- Treatment of eye and hearing diseases (for example, stimulation of the auditory nerve for sensorineural deafness).
- Stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve, which may be required for arterial hypertension and angina pectoris when other methods do not have the required effect.
- Stimulation of breathing in case of various lesions of the respiratory center in the brain, as well as in cases of disorders at the level of the respiratory muscles (for example, as a result of injuries or surgical interventions).
- Osteostimulation for speedy recovery after bone fractures and various injuries.
- Impact on biologically active points (for example, electrical stimulation of facial muscles for neuritis of the facial nerve).
- Treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is used in patients in late stages of the disease and in those who require surgical intervention. Carrying out the so-called electrical stimulation of deep brain structures helps to increase functional activity and reduce the severity of motor disorders in more than half of the patients.
Stages of electrical stimulation
Before performing electrical stimulation itself, electrodiagnostics are carried out and specific optimal current parameters for the procedures are determined.
Physiotherapy procedures are carried out in courses, and between several courses of electrical stimulation, the doctor must carry out control diagnostics in order to understand whether it is necessary to continue treatment and, if so, at what current parameters.
In order to select parameters, you need to make sure that time has passed. Thus, electrodiagnostics should be carried out only when at least 2 weeks have already passed since the damage to the neuromuscular system, otherwise incorrect data will be obtained.
Electrical stimulation has its own varieties, which can also be stages of the procedure algorithm.
- Passive electrical stimulation. Doctors use it when voluntary contractions are impossible in the affected muscle, and the muscle is often completely denervated. To perform the procedure using this method, a current with the parameters that were determined earlier during electrodiagnostics is used. After 5-10 procedures, a control study is carried out, during which the body’s response and new optimal current parameters are determined.
- Active electrical stimulation is the second stage. During this procedure, the patient tries in every possible way to contract the affected muscle voluntarily. It turns out that the muscle is stimulated not only by the current supplied to its surface through the electrodes, but also by the impulses that the damaged nerve is capable of producing.
Side effects and complications
Side effects from electrical stimulation may include:
- Excessive stretching or, rarely, rupture of the muscle undergoing electrical stimulation. Occurs only when using an excessive amount of pulse current. The danger of this complication is present when the patient has completely lost sensitivity and the patient cannot report pain during the session.
- Fatigue of the stimulated muscle. As fatigue develops, the amplitude of muscle contraction drops sharply, and so the doctor can understand that excess lactic acid has accumulated in the muscle cells and the procedure must be stopped. Fatigue occurs the faster, the more pronounced the disturbances in nerve conduction are.
- The occurrence of conjugal muscle contractions is when all muscle groups begin to contract together or those located symmetrically.
- The occurrence of contractures of the facial muscles - may appear during the treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve and the provoking influence of electric current. In such cases, they resort to other methods of physiotherapy: heat, microwave, UHF inductothermy, and after 2-3 weeks of the process - ultrasound therapy, hydrocortisone ultraphonophoresis, moderate exercise therapy. You can try a light, short-term massage procedure and an adhesive bandage that prevents overstretching of paretic muscles.
- A sharp increase in electrical excitability, pronounced involuntary muscle contractions. Such effects can be congenital or acquired (cerebral palsy, consequences of poliomyelitis, encephalitis), or occur as manifestations of complications of rheumatism (chorea minor), epilepsy, meningitis. In these cases, along with symptomatic treatment, physiotherapy is carried out aimed at reducing hyperkinesis, contractures, and stimulating weakened muscles.
Thus, the electrical stimulation procedure is widely used in medical practice. This method of physiotherapy allows for effective diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of diseases. With the help of electrodiagnostics and other physiotherapeutic techniques, it is possible to make the approach to the treatment of diseases comprehensive, reduce the use of medications, and speed up the recovery time after injuries and illnesses.
Doctors already have many devices for electrical stimulation in their service, and more and more new ones with improved characteristics continue to be developed. The widespread use of physiotherapeutic treatment methods can help in some cases to partially abandon the prescription of medications in their traditional sense, which is especially important for people with some type of drug intolerance, as well as a high risk of adverse reactions to medications.