Brain cancer is a fairly rare disease. Of all cases of cancer, it accounts for only 1.5%. However, it still affects a huge number of people around the world, and each of them wants to know whether brain cancer is curable. No matter how much we would like to answer this question unambiguously, there is simply no such answer. It all depends on many factors. Where is the tumor located? What shape and size is it? What is the stage of the disease? Are there metastases? What is the general condition of the patient? Are there other diseases? All these and many other questions require answers, and the final verdict on whether brain cancer can be treated in this particular case depends on them.
If your doctor diagnoses you with brain cancer, treatment should begin immediately because every minute truly counts. This disease is treated with the same methods as all other oncology - surgical removal of the tumor and metastasis, chemotherapy, radiation and radiotherapy. Surgical removal is currently the main method used in the treatment of brain cancer. However, it is associated with many difficulties. The experience of the neurosurgeon, as well as the location of the tumor, are of great importance. Sometimes they form in areas where surgical intervention is simply impossible. Today, brain cancer is treated with surgery much more successfully than before. This is due to the development of science and technology. For operations, high-power microscopes, lasers, and endoscopes are used - all of this is successfully used for operations when diagnosed with brain cancer. Treatment in most cases has a more favorable outcome. Of course, even in such cases we rarely talk about removing the entire tumor. The surgeon removes only part of it, the part that affects the most important centers. Otherwise, brain cancer is treated with radiation and chemotherapy. We must not forget about the high risk of complications associated with brain surgery, as well as the fact that some changes, especially when it comes to advanced disease, will remain irreversible.
Any treatment cannot do without drugs, and oncology is no exception. When a person is diagnosed with brain cancer, treatment must include chemotherapy. It is not always possible to completely remove a tumor, as we have already said, but it is completely impossible to remove all cancer cells from the blood. You can only kill them with chemotherapy. These drugs treat brain cancer effectively, but the side effects are very serious and severe. Postponing a course of chemotherapy is an incredibly difficult test for both the patient’s body and his psyche. Once diagnosed with brain cancer, chemotherapy may be given orally or intravenously. Some drugs are injected into the spinal cord. Today, a new practice has emerged that involves administering drugs directly during surgery. For a disease such as brain cancer, treatment with chemotherapy drugs is necessary, but the severity of the side effects will affect the functioning of all body systems for a long time. Constant nausea, vomiting, weakness, unwillingness to live and fight - all cancer patients go through this.
Another way to help defeat brain cancer is radiation therapy. Radiation helps kill cancer cells that cannot be removed with surgery. Also, this method is sometimes the only available means to combat the disease. For example, when the tumor cannot be removed surgically.
Based on all of the above, the question of whether brain cancer can be treated can be answered: “Yes, it can be treated,” but with many reservations. Treatment is long, difficult, expensive, and no one can give a 100% guarantee of success. Of course, this disease, like all others, is easier and better to prevent than to treat. Today, cancer prevention has become more effective than ever thanks to the advent of Transfer Factor. This is an immunomodulator, not an anti-cancer agent, so it does not kill cancer cells and does not affect tumors, but it gives the immune system information and the immunity itself, having received the necessary information, activates killer cells by 480%. At the same time, it acts more subtly and more correctly. Many years of research in the field of immunology have confirmed that immune cells can cope with any aggressor that harms the human body if they have the necessary information about what the aggressor looks like, how to distinguish it, and how to deal with it. Cancer cells are also aggressors, and it is not difficult for a well-informed immune system to destroy them at an early stage. To receive the necessary information, the body needs transfer factors - peptide compounds that accumulate immune information and are able to train new cells of the immune system. Transfer factor is good not only for prevention. It plays an extremely important role in restoring a person’s immunity and health after radiation and chemotherapy. Therefore, today most advanced oncologists prescribe Transfer Factor to their patients. This drug affects only the IQ of immunity, and therefore can be prescribed to any person. It is harmless, does not cause side effects and does not enter into chemical reactions with other substances, which means it can be taken together with any other drugs. Experience in treating cancer with Transfer Factor suggests that this drug significantly increases the patient’s chances of recovery.
Etiology
The development of a brain tumor can be triggered by factors of various natures, from internal inflammatory processes to harmful environmental conditions. And although the causes of brain cancer are not 100% understood, most often they consist of the following phenomena:
- Genetic predisposition. In this case, the patient may have Recklinghausen, Gorlin, Turco, and Li-Fraumeni syndromes. All of them imply deviations in the structure of certain genes, which significantly increases the risk of developing cancer;
- Age. In most cases, brain cancer occurs in people over 40-45 years of age. The exception is medulloblastoma, which is most often diagnosed in children;
- Chemical substances. Human contact with harmful substances, pesticides, carcinogens, heavy metals for a long period, for example in working conditions, can cause the development of cancer. But this fact is more confirmed by real cases than by scientific evidence;
- Irradiation. The radiation dose that a person receives during an X-ray or when using electronic devices is negligible, but there are cases of force majeure, such as accidents at nuclear power plants;
- Weakened immunity. Persons suffering from AIDS, HIV, the Epstein-Barr virus, who have recently undergone organ transplant operations, experience a greater burden on the immune system, and therefore it is not always able to resist the incipient process of cancer cell division;
- Floor. In most cases, men are affected by the disease. The exception is meningiomas.
Secondary brain cancer occurs as a consequence of an oncological process already existing in the body. This occurs due to the fact that metastases from a certain organ move to the brain through the circulatory system.
Types of malignant brain tumors
Brain tumors can be benign or malignant. In the second case, it may be glioblastoma or medullastoma.
Glioblastoma occurs quite often and usually affects people aged 40-55 years. The resulting metastases are localized only within the brain and can be accompanied by the appearance of cysts, hemorrhage and the process of necrosis.
Medullastoma most often forms in the cerebellum and is characterized by a genetic factor. In this regard, it can be found in children and adolescents.
Brain tumors are also usually divided into primary and secondary, depending on whether they were preceded by other oncological inflammation or not.
Memory loss is one of the symptoms of brain cancer
Nutritional Features
Preference should be given to natural products rich in vitamins and microelements necessary for the rapid restoration of healthy tissues. Drinking a sufficient amount of fluid (2.5 -3 liters during the day) will reduce the symptoms of intoxication and speed up the rehabilitation process.
Meningioma
Meningioma is considered the most common benign tumor among all known. It occurs in twenty percent of all cases of diseases of this type. The process of its formation involves the tissue that makes up the spinal cord and the dura mater of the brain.
Pituitary tumor
Pituitary tumor. It is a rare disease during which the production of pituitary hormones occurs. Statistics say that out of a thousand people, one person can get it. This is about fifteen percent of all cases of diseases of this type.
Hemangioblastoma
Hemangioblastoma is considered a benign tumor that is formed from vascular tissue. It has a cyst-like shape. Epithelial cells are the basis for the formation of dermoid and epidermoid cysts. These are quite rare brain tumors, which many experts do not consider as types of benign tumors, but their effect in the process of formation on the brain and its functions has similar manifestations.
How does brain cancer manifest?
Symptoms of brain cancer do not appear immediately and become more pronounced gradually with each new stage. However, they can be divided into several types:
- General cerebral. As the tumor grows, it begins to provoke intracranial pressure, which becomes the cause of these symptoms;
- Focal. They are expressed due to the fact that the formation begins to put pressure on the brain tissue.
It is impossible to say exactly how brain cancer will manifest itself in each individual case, since the symptoms of malignant oncology may not show themselves at all for a long time, and sometimes secondary symptoms appear before the primary ones.
Focal symptoms
These signs of brain cancer directly depend on the location of the tumor. During the course of the disease, the following phenomena may occur:
- Impaired hearing, vision, speech. It becomes difficult for the patient to count or write, and later even to construct sentences. He can confuse not only words, but also sounds. Changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, double vision, drooping upper eyelid, taste disturbance, facial distortion may also be noted;
- Impairments in movement and coordination. The patient may experience difficulty in moving, for example, only the fingers or the entire limb. Moreover, it is difficult for him to maintain balance, and therefore changes in gait are observed;
- Cognitive disorders. The patient's memory deteriorates significantly, he experiences difficulty in demonstrating logic or abstract thinking;
- Sensory disturbances. It can either decrease or worsen. Often patients experience a feeling of goosebumps;
- Convulsions and epileptic seizures;
- Hallucinations. They can be of a different nature: sounds, visions, smells;
- Autonomic disorders. Manifest in the form of abnormal pulse rates, body temperature, heart rate;
- Hormonal disorders. These can be a variety of signs, from a sharp increase in body weight to a broken cycle and impotence.
The patient may exhibit several of the listed symptoms at once, depending on the affected area. If it is detected in the early stages, the patient has a significantly increased chance of returning to normal activities without complications.
Recurrent nausea is a common symptom of brain cancer.
Diagnostics
During the initial diagnosis, the neurologist, during a conversation with the patient, is based on the patient’s complaints. He conducts preliminary examinations: assesses eye movements, hearing, memory, muscle strength, coordination of movements, smell, coordination of movements and mental state. Prescribes histology and cytology.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of basic tests are carried out. They are usually carried out in three stages:
- Tumor detection
Since in the early stages the tumor practically does not bother the patient, in most cases a visit to the doctor occurs only in the second or third stage. According to indications, the doctor either hospitalizes the patient or prescribes outpatient treatment. In most cases, the patient is prescribed a computed tomography scan. It allows you to determine:
- localization of the tumor and its type,
- the presence of cerebral edema or other symptoms,
- tumor recurrences, possible treatment.
If a CT scan does not confirm the presence of a tumor, other types of examination are prescribed.
- Differential diagnosis
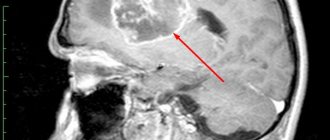
After a series of additional examinations, the doctor makes a preliminary and clinical diagnosis. Stability in the Romberg position, coordination of movements, tactile and pain sensitivity, and activity of tendon reflexes are tested. The patient is sent for a contrast-enhanced MRI - this is the most informative study. Determination of a large tumor is an indication for urgent hospitalization.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) clearly determines the size of the tumor, displays the brain from different angles and allows you to build a three-dimensional image of the tumor. It can be used to accurately map complex brain structures and identify cancer diseases.
Additional methods include:
- Positron emission tomography (PET). Gives an idea of brain activity. The method complements MRI and improves accuracy during radiosurgery,
- Single photon emission computed tomography (SPCT) is performed after CT or MRI to determine the degree of malignancy,
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG) – evaluates the functioning of various areas of the brain,
- Angiography. Blood flow is assessed
- Spinal (lumbar) puncture. It is carried out to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid and study for the presence of abnormal cells using tumor markers,
- Biopsy. Obtaining a sample of tumor tissue to further determine the type of cancer cells. May be performed as part of surgery to remove a tumor or as a diagnostic method.
- Diagnosis confirmation
Having the results of all the studies, specialists additionally prescribe a CT or MRI of the brain. When prescribing surgical intervention, a histological examination of a tumor sample is performed or a stereotactic biopsy is performed, the results of which will allow you to select the correct treatment method.
Manifestation of general cerebral symptoms
General cerebral symptoms can occur quite early. For example, headache in a third of cases manifests itself already at the first stage of the disease.
In addition to pain in the head, which is oppressive in nature, you can also identify:
- Nausea. It is not accompanied by pain or discomfort in the abdomen. Occurs periodically and without any obvious warning signs;
- Vomiting. Often accompanied by increased sweating, heart rhythm disturbances and even loss of consciousness;
- Dizziness. Occurs due to increased intracranial pressure;
- Mental disorders. They can be either focal or cerebral in nature. The patient experiences difficulty expressing his thoughts, memory, and concentration.
Another important symptom may be an epileptic seizure. If the patient encounters it for the first time, and there are no direct reasons for this, you should definitely consult a doctor. This may be a clear sign of a brain tumor.
Stages of brain cancer
Everyone knows of cases where cancer was detected at the last stage. This is explained by the fact that sometimes the process is almost asymptomatic, and the transition from one stage to another can occur in a very short time, depending on the intensity of the disease. For this reason, you should listen carefully to your body and carry out preventive medical examinations.
There are 4 stages of brain cancer:
- Stage 1 brain cancer. During this period, the patient may experience general symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and drowsiness. If a tumor is detected at this time, the probability of its cure is almost 100%, since the number of affected cells is very small;
- Stage 2 brain cancer. Since the growing tumor may begin to compress some brain centers, the patient may experience digestive problems, vomiting, and even epileptic convulsions;
- Stage 3 brain cancer. Already at this stage, the tumor may be inoperable, since its removal can significantly disrupt brain activity. Symptoms during this period are pronounced: convulsions, poor coordination, impaired vision, speech and hearing, as well as memory loss, distracted attention and difficulty concentrating;
- Stage 4 brain cancer. This is the most dangerous stage, which cannot be treated surgically, as the risk of death is very high. All that doctors can do during this period is to provide drug support to the body, conduct radiation therapy and chemotherapy in order to suppress the growth of pathological cells and provide an analgesic effect.
The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the patient’s chances of, if not curing it completely, then at least securing a few more years of life.
MRI of the brain
What happens during radiation therapy?
Before starting radiation therapy, the patient is consulted by a radiation oncologist. During the consultation, the doctor evaluates the medical history and conducts an examination. In addition, consultations are carried out with other specialists who are part of the group of treating personnel.
Once the most suitable treatment method has been selected, the radiotherapy planning phase begins. At this stage, a radiation oncologist who specializes in radiation therapy for malignant tumors conducts treatment simulation. This uses standard radiography or CT, and in some cases MRI. The results of the examination are important for choosing the type and direction of the beam of rays.
It is important to remain still during simulated radiotherapy, although no radiation treatment is given during this period. A fixation mask is used to hold the patient's head in a certain position. As a rule, radiation therapy begins 1-2 days after drawing up a treatment plan.
During each radiation therapy session, the patient lies motionless on the treatment table while the radiologist or technician administers the treatment according to parameters prescribed by the oncologist. A radiotherapy session takes only a few minutes and is completely painless.
During stereotactic radiosurgery, a rigid head frame is used to immobilize the patient. In addition, during the procedure, regular scans (CT or MRI) are performed, which allows you to accurately monitor the position of the tumor and adjust the radiation dose if necessary.
Treatment planning and the first radiotherapy sessions take 1 or 2 hours. After this, each session lasts only a few minutes, and the patient's total stay in the radiology department does not exceed minutes. As a rule, radiotherapy is carried out 1-2 times a day, 5 days a week, for 5-7 weeks.
Diagnostic procedures
Quite often, a suspicion of brain cancer is discovered by chance during medical examinations. But, as a rule, this happens when the tumor is already large. The process of diagnosing this pathology is complicated by the fact that cancer cells are located inside the skull and in the early stages they may not be sufficiently visualized.
If a suspicion of a brain tumor does arise, the patient must undergo several procedures at once:
- Tests for tumor markers;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Biopsy if possible.
The results of the analysis are studied by an oncologist, neurologist and neurosurgeon. After which an accurate diagnosis is established.
MRI results are reviewed by an oncologist
Rehabilitation
It is very important to be constantly vigilant after treatment for a brain tumor in order to detect a possible relapse of the disease in time.
Purpose of rehabilitation
The most important thing is to achieve the maximum possible restoration of lost functions in the patient and return him to everyday and work life independent of others. Even if a complete restoration of functions is not possible, the primary goal is to adapt the patient to the limitations that have arisen in order to significantly make his life easier.
The rehabilitation process should begin as early as possible to prevent a person from becoming disabled.
Recovery is carried out by a multidisciplinary team, which includes a surgeon, chemotherapy, radiologist, psychologist, exercise therapy doctor, physiotherapist, exercise therapy instructor, speech therapist, nurses and junior medical staff. Only a multidisciplinary approach will ensure a comprehensive, high-quality rehabilitation process.
Recovery takes on average 3-4 months.
- adaptation to the consequences of the operation and to a new lifestyle;
- restoration of lost functions;
- training in certain skills.
A rehabilitation program is drawn up for each patient and short-term and long-term goals are established. Short-term goals are tasks that can be accomplished in a short period of time, for example, learning to sit up in bed independently. Once this goal is achieved, a new one is set. Setting short-term goals divides the long process of rehabilitation into certain stages, allowing the patient and doctors to assess the dynamics of the condition.
It must be remembered that the disease is a difficult period for the patient and his relatives, because treating tumors is a difficult process that requires a lot of physical and mental strength. That is why the role of a psychologist (neuropsychologist) in this pathology should not be underestimated, and his professional help is usually needed not only by the patient, but also by relatives.
Brain cancer treatment
Treatment of brain cancer is determined individually in each case. The nature of therapy will depend on many factors: the stage and nature of the disease, the location of the tumor and the characteristics of the patient’s body. A surgical solution to the problem is not always possible.
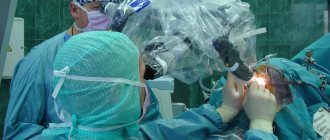
Surgery
Most often, treatment for brain cancer comes down to surgery to remove it. It can be carried out both through craniotomy and using an endoscopic apparatus. The second option is possible in rare cases, only with a certain localization of the outbreak.
The complexity of the operation lies in the fact that when removing a tumor, the surgeon can injure the brain centers, which can not only affect their functioning, but also lead to the death of the patient.
Surgery is the main treatment for brain cancer
Radiation therapy
The use of radiation beams in the fight against cancer is a method that has been used in medicine for a very long time. Depending on the extent of tumor spread, the doctor individually selects the radiation dose.
This therapy is used in the following cases:
- The tumor cannot be removed surgically. The reason for this may be its inaccessibility to the surgeon or a high risk of death;
- Postoperative prevention of relapse of cancer cell growth.
The procedure can be carried out in two ways. Most often this is external irradiation, but the method of introducing radioactive grain into the hearth itself can also be used.
Chemotherapy
It involves taking potent drugs. The treatment is carried out in courses and is more effective when combined with radiation therapy. Chemotherapy rarely involves taking one medication; as a rule, it is a whole course, prescribed according to a specific scheme.
The disadvantage of this treatment is that these drugs have a detrimental effect not only on abnormal cells, but also on healthy ones.
Chemotherapy for brain cancer is carried out in several courses
Cryosurgery
This method involves literally freezing cancer cells, which leads to their destruction. Special equipment allows liquid nitrogen to heat up to -198 degrees and inject it into the thickness of the tumor. Concomitant damage to nearby blood vessels helps prevent further growth and division of malignant cells.
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery involves the use of special high-tech devices. Using a gamma ray or cyber beam, the surgeon targets the tumor site. Usually this involves several procedures.
This method has many advantages. Besides the fact that it is non-invasive in nature, the patient does not even require hospitalization. But this method can only be used for small tumors.
The last notes
There are two types of complications of radiation therapy: local and general.
The effect of rays on cancer cells is obvious. But the only disadvantage is the reflection of such therapy on healthy tissues. This may include lesions of the skin on the head. After the first sessions, skin redness, pigment spots, and burning or itching are observed in the area affected by radiation rays.
There is a disruption in the activity of the vascular system, which affects the receipt of nutrition by tissues, impaired blood flow and the formation of a trophic ulcer. Hair loss is observed. But after some time, hair growth may resume, changing the color and structure of the hair.
Having received a significant dose of radiation, healthy brain tissue is destroyed and eventually dies. This process causes swelling of the brain substance. Symptoms manifest as a general cerebral and focal sign. The patient suffers from headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and mental disorders. If the prescription of steroid drugs does not give the desired effect, then removal of brain tissue necrosis is carried out surgically.
Treatment of tumors in children is prescribed taking into account the effect of radiation therapy on the child’s body. This is done in order to control the growth and development of the child’s body, to prevent the development of new formations, which may make it impossible for the child to learn or lead a normal lifestyle. There is a possibility that a stroke may occur in the future.
The consequences of radiation therapy of the brain of the general group after an irradiation session are blood poisoning with the decay products of cancer cells. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, insomnia, decreased performance, and baldness.
After completing the full course of treatment, which involves the use of radiation therapy for several months, the general symptoms decrease over time and, as a result, disappear. Being irradiated sounds scary, but if you take into account the effectiveness of such a procedure, the consequences fade into the background and the priority is treatment and the complete elimination of the causes and factors that influence education and contribute to its development and progress.
Author of the article: Neurologist Konstantin Olegovich Makheev.
Among the side effects observed immediately after a session of radiation therapy for a brain tumor using modern gentle methods, the most common is a transient feeling of fatigue. Sometimes slight hyperemia (redness) of the facial skin may occur, and in rare cases, easily removable swelling. The occurrence of burns and scars is extremely rare.
In the long term, hair loss may occur in a small area in the area where the rays are projected; over time, the hair will grow back. The nature and percentage of likelihood of long-term consequences depend on the location of the tumor.
Using modern technologies, radical treatment of brain cancer using radiosurgery or undergoing a course of radiation therapy after traditional surgery does not cause problems, and in the vast majority of cases does not require a stay in a medical institution during the rehabilitation period. Recovery takes from several days to several weeks.
Brain tumor is a broad concept that includes various formations localized in the skull. These include benign and malignant degeneration of tissues that arise as a result of abnormal division of brain cells, blood or lymph vessels, meninges, nerves and glands. In this regard, rehabilitation after tumor removal will include a complex of various effects.
Tumors in the brain occur much less frequently than in other organs.
For brain tumors, periodic examination by an oncologist is extremely important. In addition to a standard physical and neurological examination, your doctor may order MRI, MR spectroscopy, perfusion or diffusion MRI, CT scan, PET scan, blood tests, or endoscopic procedures.
Such observation helps the doctor:
- Look for any signs of tumor recurrence
- Monitor the state of the brain
- Detect and treat side effects of radiotherapy or chemotherapy
- Diagnose the appearance of other types of cancer at the earliest stages
In addition, oncologists recommend home care, physical therapy and rehabilitation measures aimed at restoring working capacity, adequate pain relief, and participation in support groups for patients with cancer.
Radiation therapy is the effect of radioactive radiation on tumor cells, as a result of which they stop dividing and lose the ability to form metastases.
This is a rather aggressive, albeit bloodless and non-surgical treatment, which is sometimes the patient’s only chance.
Radiation therapy, the consequences of which in a large percentage of cases are quite pronounced in intensity, has its side effects.
http://vseprorak. ru/luchevaya-terapiya-posledstviya. html
http://rakanet. ru/opuhol-golovnogo-mozga/luchevaya-terapiya-opuholej-golovnogo-mozga/
Decrease in intelligence (progressive). Risk factors for the development of this complication include early age, large area of radiation therapy (whole brain), high doses of ionizing radiation, specific tumor location, concomitant methotrexate therapy, the presence of vasculopathy or leukoencephalopathy, and postoperative complications.
After radiation therapy, the following endocrine disorders are possible.
— Somatotropin deficiency: observed in 80% of children receiving radiation therapy to the entire brain area; can also occur when only the posterior cranial fossa region is irradiated if the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus is affected.
Disturbance of spinal growth after spinal radiation therapy, especially in young children.
Primary (decrease in thyroxine level, increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone level) due to radiation damage to the thyroid gland during craniospinal radiation therapy.
Secondary (decreased levels of thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone): observed less frequently, usually with radiation therapy to the pituitary gland (decreased synthesis of thyroid-stimulating hormone).
Spinal radiotherapy: may cause ovarian dysfunction.
Cyclophosphamide may cause gonadal dysfunction in men.
— They can develop both after low- and high-dose radiation therapy.
— The development of meningiomas and highly differentiated astrocytomas is possible.
— The course is usually aggressive.
- May develop after chemotherapy in the absence of radiation therapy (using etoposide, cyclophosphamide or cisplatin). The development of acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome is likely.
http://dommedika. com/nevrologia/luchevaia terapia u detei. html
Might be interesting:
- Non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma of the floor of the mouth
- Problems on stomach ulcers with answers
- How to check heart vessels for plaque
- Is focal scleroderma contagious or not?
- What are metastases in pancreatic cancer?
- There are three types of papillary patterns
How long do people live with brain cancer?
Unfortunately, life expectancy after an oncological disease in the brain area is significantly reduced. And even a successfully performed operation does not guarantee that the patient will be able to live for several decades, since the disease has a strong impact on the entire body as a whole.
Statistics show that survival rate over the next 5 years after surgical removal of the tumor and treatment reaches 35% if it is benign and about 5% if it is malignant.