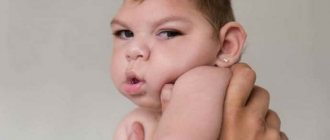
Brain abnormalities often form while a person is in the womb. In this case, the problem can affect both individual cerebral areas and the brain as a whole. Clinical symptoms are uncharacteristic. Most often, there is a delay in development, both psychological and mental, and an epileptic syndrome is formed. How severe the manifestations will be depends entirely on the severity of the lesion. Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound before birth. Afterwards EEG, MRI of the brain and neurosonography are used. Treatment is symptomatic, since it is impossible to completely get rid of brain abnormalities.
Of all congenital diseases, problems with the brain occur in 1/3 of cases. Often this problem leads to the death of the fetus. Only a quarter of all children survive. Also, in newborns it is not always possible to detect an anomaly immediately after birth, so the complications are quite sad.
Description of the problem
What is it - a malformation of the brain in children? This is a disease in which the anatomical structure of cerebral structures is disrupted. How noticeable the symptoms will be depends in all cases on the degree of damage. In up to 75% of all cases, antenatal fetal death occurs. The timing of manifestation is always different. As a rule, symptoms of abnormalities appear in the first months after birth. But due to the fact that the brain is formed before the age of eight, most of the defects become active only after a year. There are often situations when anomalies occur with problems of other organs, for example, fusion of the kidneys, esophageal atresia, and so on. Today, medicine strives to diagnose the problem before the birth of the child in 100% of cases. This is done by gynecologists and obstetricians. Treatment usually involves pediatricians, neurologists, neurosurgeons and neonatologists.
brain development in the womb
Does the unborn baby have a soul? When does she appear? These questions have long been of interest not only to parents, but also to philosophers and theologians. Science presents new knowledge about the first phases of a baby’s life, its development in the womb. Much earlier than expected, the baby’s sensations and skills develop, and the finest brain structures are formed.
We have only recently learned many things about the life of an unborn person. Scientists, armed with electron microscopes, ultrasound equipment and endoscopy (direct observation of the baby in the womb through a special tube), have made stunning discoveries. This seems incredible, but when the size of the human embryo does not yet reach 2 mm, its brain is already functioning, controlling its further development. And at a size of 3.5 mm, that is, at the age of 25 days, the human embryo has all the most important organs: heart, skin, central nervous system, liver, lungs, intestines and sex. These amazing discoveries completely change our understanding of the baby under the mother's heart. Previously, we had no idea how early subtle structures were already visible in such an unimaginably small brain, how early an unborn human being began to react to external stimuli. As if to “respond” with movements, and as in these early abilities, which, by the way, we have only just learned about, reveal the first manifestations of the soul. Now we can reasonably assert that already in the first months or even in the first weeks after conception, a spiritual connection is born between the mother and the baby maturing in her womb. Life before birth begins at the moment when a male reproductive cell unites with a mature female egg. From this moment the development of the organism begins, ending only with death. No stage of this process begins without preparation and does not proceed without consequences. Birth is just a transition to a new state. Already in the first days, the young embryo formed after repeated cell division, the so-called blastula, grows into the tissue of the uterus and is directly included in the mother’s metabolism. Through nutrition, the first relationship between mother and child is established - they largely determine the future development of the body. The embryo participates in everything that happens to the mother. Everything she experiences - joy, excitement, fear or concern - affects the rhythm of the mother’s heart, blood circulation and metabolism. For example, the blood distributes hormones throughout the body that correspond to the situation being experienced, and the fetus also experiences this. Today it is already known that the body reacts to spiritual experiences. When we get scared, our heart starts beating faster. When we experience horror or fear, we sweat. These reactions are caused by hormones produced by the body and carried by the blood during strong anxiety. The small body of the fetus, of course, not yet consciously, receives signals from the mother’s body about her feelings and experiences
Brain Formation
In order to have an idea of what brain structures the defect affects in a newborn, you need to understand exactly how this human organ is formed.
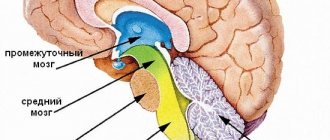
The construction of the nervous system begins already in the first week of pregnancy. The neural tube is finally formed by the 23rd day of gestation. If its fusion does not occur completely, then cerebral anomalies occur. The anterior brain vesicle, divided into two lateral ones, forms the basis of the cerebral hemispheres. Formed by the 28th day of pregnancy. After this, the cortex, convolutions, basal structures of the brain, and so on are formed.
The division of nerve cells during the embryonic stage forms the gray matter, as well as glial cells, which make up the human brain. Gray matter is responsible for the functioning of the nervous system. Glial cells make up the white matter. It is responsible for the connection of all cerebral structures. If a child is born at term, then by the time of birth he has the same number of neurons as an adult. Over the next three months, the brain develops intensively.
Formation of the fetal brain - stages
The fetal nervous system is formed 13 days after fertilization; on the 28th day, the formation of the brain and spinal cord begins; if the closure of the neural tube does not occur at this stage, the child is born with anencephaly. To avoid pathology, doctors recommend taking folic acid (vitamin B9) even during pregnancy planning; the vitamin reduces the development of the defect by 70%.
Intensive brain growth begins from the 7th week of pregnancy; iodine will provide additional support for its healthy development. The iodine content in the mother's body depends on the production of thyroid hormones; its deficiency leads to impaired mental abilities of the child. The recommended amount of iodine in the diet of a pregnant woman is 150-200 mcg per day.
Some medications, chemicals and infectious diseases negatively affect the development of gray matter.
At week 17, the formation of cells responsible for recognizing external stimuli, such as taste, light, smell, sound or touch, begins; electrical impulses are transmitted faster than before. At approximately 26 weeks of pregnancy, important nerve pathways appear that transmit impulses from the eyes, ears, muscles and skin to the “main center” of the body; the first grooves are observed on its surface. Reaction to light and sound is determined at 25-28 weeks. The ability to sense body temperature and control breathing develops in the third trimester.
Causes of anomalies
The causes of brain developmental defects can be different. Failure can occur at any stage of organ formation. If it takes place in the first six months of pregnancy, then the child experiences hypoplasia of parts of the brain, and the number of neurons produced is reduced. Even if the cerebral substance is already fully formed, it can die due to a malfunction. Most often, the cause of this problem is considered to be the influence on the pregnant woman and, accordingly, the fetus of harmful substances that have a teratogenic effect. In other cases, fetal brain malformation occurs in 1% of cases.
Another influential reason is exogenous. Many chemical compounds have a teratogenic effect. It is caused by both radioactive contamination and some biological factors. Problematic ecology can have a detrimental effect, causing harmful substances to enter the body of a pregnant woman. Smoking, alcoholism and drug addiction can also lead to the formation of abnormalities. Diabetes mellitus and hyperthyroidism lead to the same effect. Some medications also have teratogenic effects. Doctors do not prescribe such drugs to pregnant women, but there are cases when at an early stage nothing is known about the existence of the fetus. Only one dose is enough for a defect to form. Infections suffered by a pregnant woman can lead to abnormalities. Rubella, cytomegaly and others are considered especially dangerous.
How to help fetal brain development.
Every mother wants to give her child the best start in life. But sometimes it can be difficult to know what to do, especially with so much advice in books, magazines and on the Internet. Just listen to your doctors and follow their advice. They will likely offer simple tips to help keep both you and your baby healthy.
Nourish your body.
When you eat healthy foods, drink plenty of water, and take prenatal vitamins, you give your baby's developing brain the nutrition it needs for optimal growth.
Do more exercise.
If you haven't exercised before pregnancy, you should talk to your doctor before starting any exercise regimen. Generally, walking, water aerobics, and prenatal yoga classes are safe options for physical activity during pregnancy. Just make sure you don't overdo it. It's not worth the risk of injuring yourself or your developing baby.
Avoid toxins.
Toxins are harmful to everyone, including the pregnant mother and her unborn baby. Fortunately, avoiding environmental toxins is fairly easy unless you work for a dry cleaning company, farm, or factory, in which case you can ask to be transferred to a less toxic area of production.
In general, you should avoid long-term exposure to cleaning products, pay attention to air quality warnings, and avoid pollutants from heavy traffic.
Manage your stress.
There are many studies that link high levels of stress during pregnancy to adverse fetal brain development. Do everything you can to reduce stress in your life. Lighten your workload and learn to relax. One way to reduce stress is to focus on various relaxation techniques, such as breathing exercises, journaling and meditation.
Talk to your baby.
Research shows that when you talk to your baby in the womb, you lay the foundation for their social and emotional development. These one-way conversations will also improve language and memory skills in the future. So, make sure you talk to your child on a regular basis.
Turn on the music.
There's a lot of controversy over whether playing Mozart to your unborn baby will boost IQ, but playing music is generally good for both of you. Not only can music, especially classical music, be relaxing, but it can also help your unborn baby learn new sounds and tones.
Stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
Don't smoke or drink during pregnancy!
For example, drinking alcohol can interfere with the development of cognitive brain cells in the fetus. Drinking alcohol during pregnancy often leads to lower IQ, poor cognitive skills, attention deficit, impulsive behavior and even poor coordination. Nicotine reduces your baby's blood flow and nutrition because it constricts your blood vessels. It also affects cognitive brain cells.
Conclusion.
When it comes to fetal brain development, the best thing you can do to support your baby's brain development and growth is to live a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating right, exercising, getting plenty of sleep, and reducing stress levels. If you are concerned about your diet or stress levels, consult your doctor. There are things you can do today to get on the right track to ensure your child's brain grows and develops as it should.
Types of anomalies
Unfortunately, congenital malformations of the brain have a large number of varieties. Let's look briefly at each of them:
- Anencephaly. Represents the absence of the brain and skull bones. Instead of an important organ, the child has many connective growths and cysts. There are times when the “brain” is exposed or covered with skin. This pathology is considered fatal in any case.
- Heterotopia. During neural migration, some neurons may be delayed and not reach the cortex. Such clusters can be single or multiple. The form can be tape or nodular. It differs from tuberous sclerosis in that the contrast does not accumulate. A similar malformation of the brain in children is manifested by oligophrenia. The severity of symptoms depends on the size and number of heterotopions. If the accumulation is single, then the first manifestations may appear after 10 years.
- Encephalocele. The pathology affects the bones of the skull; they do not connect in some places. In this case, deformation of cerebral tissues and membranes is observed. The disease develops along the midline. Some children have an asymmetrical problem. Sometimes the disease can mimic cephalohematoma. In such cases, x-rays are used to make an accurate diagnosis. The prognosis depends entirely on the size and contents of the encephalocele. If the protrusion is small and there is nervous tissue in the cavity, then surgery can be used.
- Focal cortical dysplasia, or FCD. This malformation of the brain is accompanied by the presence of huge neurons and abnormal astrocytes in the organ. As a rule, they are localized in the frontal and temporal parts of the skull. In the first time after the development of the disease, the child may experience demonstrative motor phenomena. They take the form of gestures. An example is marking time and so on.
- Microcephaly. The problem is characterized by a decrease in brain volume and mass. This happens due to the underdevelopment of the organ. Occurs once every 5 thousand newborns. In this case, the child’s head circumference is reduced, and the skull has disturbed proportions. Oligophrenia occurs in 11% of all patients with microcephaly. Sometimes idiocy develops. In addition, the child is lagging behind in physical development.
- Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. Most often accompanied by the development of Aicardi syndrome. Girls are at risk. Ophthalmic defects, dystrophic foci and other problems may occur. This malformation of the brain can be detected by ophthalmoscopy.
- Macrocephaly. Characterized by an increase in brain volume. Microcephaly is less common. Manifests itself as mental retardation. Some patients experience seizures. There is partial macrocephaly, when the volume and weight of only one of the brain hemispheres is increased. The brain section of the skull is asymmetrical.
- Micropolygyria. There are a large number of small convolutions on the surface of the cortex. Normally there should be 6 layers of the cortex, in patients there should be no more than four. It can be local or diffuse. The latter is manifested by epilepsy, which develops after a year, mental retardation, problems with the pharyngeal and masticatory muscles.
- Cystic cerebral dysplasia. This malformation of the brain is accompanied by the formation of cystic cavities in the organ. They connect to the ventricular system. Cysts can be of completely different sizes. In some cases, they develop only on one hemisphere. The appearance of cysts can manifest as epilepsy, which is not treatable with anticonvulsant therapy. If the cysts are single, then over time they resolve.
- Pachygyria. The main convolutions are strengthened, but the tertiary and secondary ones are completely absent. The furrows shorten and begin to straighten.
- Holoprosencephaly. The hemispheres are not separated, being a single hemisphere. The lateral ventricles are also considered one unit. The shape of the skull is noticeably disturbed, and there may be somatic defects. As a rule, such children are either stillborn or die within the first 24 hours.
- Agiriya. Absence of convolutions or their underdevelopment. In addition, the architecture of the cortex is disrupted. The child has a disorder of mental and motor development, as well as seizures. As a rule, such children die in the first year of life.
How a child’s brain develops: myths and reality
At the next meeting of the “Club for Parents” (18+) of the newspaper “Strana Kaliningrad” we talked with a neurophysiologist, associate professor at the Institute of Living Systems of the IKBFU. I. Kanta Irina Vakolyuk about how a child’s brain develops. Parents learned what and at what age their child can learn, whether the baby will have “injuries” received before birth for the rest of his life, and what music lessons he can take. “Hear” color and “see” sounds
There are a lot of myths about how the brain works.
For example, what if you don’t impart basic skills to your child before the age of three, then it will be too late. And by the age of ten, the brain is formed almost like that of an adult. And that we do not use our thinking apparatus to its fullest, but only to some 10%. To distinguish truth from fiction, you need to understand physiology. And here a lot of interesting things open up. When we are literally two weeks from the moment of conception, a person’s brain is already formed. First it is the neural tube, on which three brain vesicles appear on the 25th day. Everything will grow from them later. The first to develop are sensory areas necessary, for example, for vision or hearing. Then it's time for the language skills and cognitive function areas. – Babies are synesthetes: they “hear” colors and “see” sounds because they have connections between the auditory and visual cortex, as well as between the retina and the part of the thalamus (the brain structure in which all signals are processed and integrated), in which receives information about sounds. This feature remains in some adults, but if for children this is the norm, then at an older age it is already a deviation, explains the neurophysiologist. Each period has its own.
At different ages, completely different areas of the brain are actively working.
In children, the brain stem plays a major role. It controls heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature. Responsible for awakening and sleep, feeling of appetite and satiety. In adults, the most important areas are the limbic system and the cerebral cortex. The limbic system controls sexual behavior, emotions and movements. The cerebral cortex is responsible for thinking and meaningful behavior, planning. – New connections are formed in babies at an amazing speed, it reaches its maximum by the age of six. Newborns develop automatic and motor functions and five senses. Unconscious memory allows you to recognize your mother and other family members. Between the ages of one and three years, conscious memory develops and abilities for learning, social interaction, and emotional response are established. The period from four to ten years is characterized by high brain activity (more than that of an adult). Logical abilities are being formed,” says the expert. Use it or lose it
An important period begins at 6–7 years: at this age, the process of pruning begins - cleaning, thinning connections in the nervous system.
Unnecessary - what is no longer used is cut off. And this period is just as important for brain development as the period of growth. Once upon a time it was important for you to learn to walk - in order to cope with the task, a huge number of new connections appeared. But you have completed everything - and they are no longer needed. Connections are cut to make room for new skills and knowledge. – During adolescence, the brain loses 1% of its gray matter each year. And this is his development. The “use it or lose it” principle applies: if you don’t use something, it goes away,” explains Vakolyuk. But by the age of 18, we have already formed a certain personality base - the biological basis of mental processes. – The process of brain formation will continue until the age of 30. But if, for example, a teenager is used to methodically doing some small work, then he can do whatever he wants, but the tendency to do this will remain, the expert explains. - However, even after thirty is not the end. Further, new brain cells will also appear: neurogenesis continues throughout life. The brain will still be capable of learning, but will become less plastic. So it will cope well with complex functions, but it will begin to adapt less well to changes or unforeseen circumstances. The embryo remembers everything
To further understand the development of a child’s brain, it is important to understand what parts of the brain such as the hippocampus and amygdala are responsible for and how they work.
The amygdala is formed before birth and is responsible for emotions. In adolescents, it grows before all other structures, so emotions such as joy and sadness are off the charts at this age. The hippocampus is the structure by which we “remember.” Until the age of 2.5–3 years, it matures, and our memory is poorly formed: this is why there are no and cannot be memories of ourselves before this age. – There really are no memories. However, according to recent research, it turns out that psychological trauma is recorded in neural networks at the level of the amygdala. That is, in the full sense of the word, you really won’t remember how your mother shouted at you at 6 months of age or left you alone for a long time. But this can affect behavior already in adulthood and come out in critical situations, says the neurophysiologist. – The development of the hippocampus, according to the latest data, strongly depends on the contact of the mother with the child before birth and immediately after it. Depending on the state of calm or stress, the hormonal system functions differently, and it changes the functioning of the brain. Scientists observed three groups of children - ordinary kids from intact families; children who, although they were far from their biological parents, still received attention and love from other adults (foster families, orphanages, etc.); and abandoned children who may have had relatives, but they showed no interest in them. Using fMRI, it was revealed that the size of their hippocampus was different. In those who were cared for, it grew much faster than in the second and, even more so, the third group. Then these children were better socialized, studied more successfully, etc. Another discovery in recent years is prenatal psychological trauma. It would seem that the baby is still in the tummy, how could the embryo have problems? – Research shows that they can, and there is a physiological basis for this. If a pregnant expectant mother has difficulties, she is worried and nervous, then the child may also experience psychological trauma. The fact is that in this condition, a woman’s levels of cortisol and corticosteroids increase. This also changes the child’s hormonal background. Later, such “little things” manifest themselves in distrust of the world, anxiety and difficulties in forming attachments,” the expert comments. Age and development Newborns:
- Automatic functions and motor functions develop;
– 5 senses are formed;
– the brain grows in volume; – unconscious memory allows you to recognize the mother and family members. From 1 year to 3 years:
- The brain grows and conscious memory develops.
- Abilities for learning, social
- interaction and emotional response.
From 4 to 10 years:
- High brain activity (more than that of an adult).
- Formation of logical abilities.
From 11 years and older:
- The process of maturation of neural connections.
Is it true that: 1. There is right-hemisphere drawing.
Any decision of the brain, and therefore your action, does not occur in only one part of the brain. The signal really comes from a specific point in the cortex, but you see a drawing, a brush, paper - and the occipital lobe of the cerebral cortex is involved. Once you become aware of the process, the prefrontal cortex turns on. With the help of the hippocampus, you remember what to do and how to do it. Through the amygdala, the emotion associated with drawing arises, and so on. So when drawing, both sides of the brain are used.
2. Music lessons develop gray matter.
In order for us to take actions and do them consciously, we need the left and right halves of the brain to be “friends” with each other. For this you need a well-developed corpus callosum (it connects them). A large study has shown that music promotes growth. Moreover, it also depends on the instrument. Those who play the piano have a 25% stronger corpus callosum than those who choose wind instruments or violin. Well, much larger than those who do not play music at all.
3. The brain is lazy and does not want to learn.
This is wrong. The brain is always ready to learn because it cannot exist otherwise. This is his physiological need. The only question is what: to talk, distinguish colors and temperatures, speak foreign languages, etc.
4. Hugs are important.
Indeed, with tactile contact (hugs, stroking), those brain structures where nitric oxide is released are excited. It works as a calming signal. So all social animals have a written program according to which, if they see or hear the suffering of a fellow animal, they begin to lick, stroke, and warm him. This happens unconsciously.
Important at different stages
- New connections are formed in babies at an amazing rate, peaking at age six.
- After 6–7 years, the process of pruning begins - thinning and removing unnecessary connections in the nervous system. It is as important for brain development as the growth period.
- A teenager's brain between the ages of 13 and 18 loses 1% of its gray matter each year, but this is development.
- The basic formation of the brain is completed by the age of 30, but new cells appear in it throughout life and the ability to learn is preserved.
Hot spots of activity
- In children – brain stem and midbrain: control of the heart, blood vessels, lungs, stomach, pressure and body temperature; awakening/sleep, appetite, spatial orientation,
- In adults - the limbic system and cerebral cortex: emotions, motor activity, sex, control of actions, thinking, planning.
What hinders and what helps
- Physical activity stimulates the brain.
- Boredom “slows down” the brain (it does not pay attention to boring things).
- To better understand and remember information, it is necessary to use several senses of perception.
- Good sleep improves thinking.
- Chronic stress suppresses the brain's ability to learn.
Neurophysiologist Irina Vakolyuk convincingly debunked common myths about the development of the human nervous system
At the meeting, readers of our newspaper learned from a specialist about what they need to pay attention to at a particular age of the child.
Between the ages of 4 and 10 years, the brain is very active - more than in adults.
During this period, the formation of logical abilities takes place. Our project “Club for Parents”
This is an opportunity for readers of the newspaper “Strana Kaliningrad” to meet with experts and ask them their questions. Psychologists, doctors, teachers and other specialists give open lectures and discuss with participants on the newspaper site. The next meeting will take place in 2020, follow the announcements in our newspaper and sign up - participation in the “Club for Parents” (18+) is free!
quote ,
: , :Until 2.5–3 years of age, memory is poorly formed: this is why there are no and cannot be memories of oneself before this age. However, all psychological traumas are recorded in our neural networks
share Facebook
OK
tags club for parents brain child neurophysiologist Irina Vakolyuk Kaliningrad
Additional views
In addition, there are phylontogenetically determined malformations of the human brain. They are characterized by the absence of separation of the hemispheres. In some cases, the forebrain is not at all or partially divided into hemispheres. Another type of disease is the correct development of the skull, but the absence of the cerebral hemispheres.
There is such a thing as phylogenetically determined malformations of the human brain. In short, these are anomalies that no longer occur in modern conditions, but were inherent in our ancestors. There are three types of such defects. The first is associated with underdevelopment of organs. If we talk only about the brain, then this is the absence of convolutions, the cortex, and the non-separation of the hemispheres. Sometimes a small number of thickened convolutions are found. The second type is associated with the preservation of embryonic structures that were previously characteristic of ancestors. The third type is characterized by atavistic defects, due to which the organs are not in the place where they should be, but where they were previously located in normal conditions among their ancestors.
Diagnostic methods
If we are talking about severe malformations of the brain, then an external examination will be sufficient for diagnosis. In other cases, you need to pay attention to the condition of the child in the first year of life. Cramps and muscle hypotonia may occur. To exclude the hypoxic or traumatic nature of the lesion, it is necessary to consider the anamnesis. As a rule, if there was no asphyxia in the child at birth, fetal hypoxia or trauma during childbirth, then most likely the pathology is congenital. During pregnancy, diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound. Already in the first trimester, using this method it is possible to prevent the birth of a child who has a severe cerebral anomaly.
How is it diagnosed?
The immaturity of the cerebral cortex in a child, and possible functional disorders, are examined using various techniques. In newborns, the first diagnostic test is a total assessment (from o to 10 points) of the condition in the first minutes of life - the Apgar scale.
A low score (5 or less) suggests more careful monitoring of the child and additional diagnostic methods.
Immaturity of the brain and damage to the central nervous system can manifest itself at a later age; for children aged 3 years and older, indications for diagnosis are various developmental disorders (speech, mental, physical).
Diagnostic methods
- EEG – records the activity of brain structures and allows you to analyze the degree of maturity of neurons, taking into account age-related characteristics. For children under 1 year of age, this method allows you to evaluate all areas of the brain and identify pathology (through the large fontanelle);
- MRI – allows you to assess the general condition of tissues, functional disorders and localization of pathology;
- Neurosonography - ultrasound waves allow you to visualize brain structures and the vascular network. It is possible to identify pathology at an early stage and congenital anomalies.
Identifying brain dysfunction at an early stage allows for timely implementation of the necessary therapy and avoiding serious consequences.
Additional diagnostic methods
Another type of diagnostics is neurosonography. It is carried out through the fontanel. After birth, an MRI of the brain can be done. It will allow you to study the problem 100%, understand what the nature of the disease is, where the anomaly is located, whether there are cysts, what size they are, and so on. If there is a convulsive syndrome, then the selection of therapy is carried out after an EEG. If we are talking about familial cases of cerebral anomalies, then before and during pregnancy you need to be observed by a geneticist. In this case, DNA analysis and genealogical examination are done. In order to identify problems with other organs, an ultrasound, x-ray, and so on are done.
Treatment
Therapy is mainly aimed at reducing symptoms. In case of congenital malformation of the brain (code Q04 is assigned according to ICD-10), the child should be observed by a pediatrician, neonatologist, neurologist and epileptologist. If there is a convulsive syndrome, then it is necessary to prescribe anticonvulsant therapy. Most brain abnormalities are accompanied by the development of epilepsy. It is not treatable with anticonvulsant monotherapy. Therefore, two drugs are used at once, for example, Levetiracetam and Lamotrigine. If hydrocephalus occurs, the doctor carries out dehydration therapy. If necessary, bypass surgery is performed. To improve the body’s metabolism, as well as return brain tissue to normal functionality, it is necessary to take B vitamins, glycine, and so on. Nootropic drugs are allowed only if there is no episyndrome.
Forecast
The prognosis is usually unfavorable, but also depends on the degree of the defect. If epilepsy develops at a young age, which does not respond to standard therapy, then doctors consider this symptom to be unfavorable. A brain defect together with somatic problems also does not provide a high chance of long-term survival. Therefore, it is important to understand even before the birth of a child that he has problems with brain development.
Factors influencing fetal brain development.
There are many factors that can affect fetal brain development, but most healthy women do not need to make drastic changes to their lives to promote healthy brain development in their baby.
The most important factor for optimal brain growth is a healthy lifestyle, which includes a healthy diet and exercise. It is also very important to avoid alcohol and cigarettes because these substances can impair the formation of fetal brain cells.
Infections.
In general, infections pose the greatest risk to a growing and developing child. But most mothers are immune to the most dangerous of them, which include chickenpox and measles. However, toxoplasmosis, some sexually transmitted diseases, and cytomegalovirus are also concerns and should be discussed with your doctor.
Stress.
So what about other factors in your life, such as stress? Do they affect fetal brain development? Some researchers believe that stress can affect a child's brain growth and development. One study found that a mother's stress during pregnancy alters neural connections in her unborn baby's brain.
The cerebellum is most vulnerable to the effects of early life stress.
Choline.
Choline, an essential nutrient found in eggs, beef, and liver, may help prevent problems with fetal brain development, even when pregnant moms are suffering from an illness such as the flu.
Additionally, the researchers found that at one year of age, children whose mothers had the infection and had lower choline levels had children with a sharply reduced ability to pay attention, play quietly, and cuddle with their parents. None of these effects were seen when mom had higher levels of choline in her body.
Interestingly, prenatal vitamins typically do not contain choline. As a result, the researchers concluded that supplements recommended for pregnant women may help expectant mothers achieve the high levels of choline their babies need. As with any supplements, their use should be discussed with your doctor.
Results
As a conclusion, it must be emphasized that the described problem cannot be cured. Any therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms. Most sick children die within the first 3 years of life. Moreover, a small percentage of those affected survive until this period. Most often, children are either stillborn or die in the first day or first year.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to identify all the causes of malfunctions in the body that lead to brain defects. But it should be noted that a pregnant woman needs to monitor her health as carefully as possible and get rid of all bad habits. There is no guarantee that seemingly ordinary smoking will not cause a malfunction in the formation of the fetal brain.
Those children who are born and live to at least 10 years old take pills all their lives. It is difficult for them to walk, do some things on their own, and speak. Of course, it all depends on the degree of brain damage. There are those children who have a slight deviation. The important task of a parent is to spend all the time with the child and develop him. A small percentage of children are able to integrate well into society and exist quietly on their own. The chance is small, but it is there.
Possible violations and causes
Neurophysiological immaturity, often observed in premature infants, ultrasound examination reveals underdevelopment of brain structures. Impairments and developmental delays depend on the degree of prematurity and the individual compensatory capabilities of the body.
Congenital brain abnormalities are not associated with age and lead to mental retardation, or impairment of the child’s intellectual capabilities.
Causes of dysfunction:
- Pathological pregnancy - infectious diseases during gestation affect brain cells, causing encephalitis, which leads to delayed mental development and mental retardation;
- Chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia or acute, due to difficult labor, leads to functional brain disorders and neurological disorders. Prolonged lack of oxygen is dangerous due to the appearance of foci of necrosis in brain structures;
- Skull injuries during childbirth - tissue damage leads to hemorrhage, disturbances in brain activity depend on the severity of the injury.
Morphofunctional immaturity of the cortex is inherent in all newborns, as a result of which increased excitability and muscle tone are observed. In the absence of pathologies, excitability by the second month of life becomes like that of an adult.