What is the substantia nigra and where is it located?
The substance is one of the oldest parts in the structure of the brain, located in its core - the quadrigeminal midbrain. Historically, it was responsible for the movements of our ancestors, then, when they became more complex, the structure also changed. The substantia nigra grew overgrown with nerve connections, forming a more complex structure.
The black substance received its name due to the action of the pigment - neuromelanin, which colors cells dark. The substantia nigra of the midbrain is heterogeneous; it is divided into two halves: right and left. In addition, the substance has two layers: ventral and compact. The ventral one is closer to the front of the head, and the compact one is closer to the back. The first ensures the synthesis of the neurotransmitter dopamine, the second processes incoming information and transmits it to other structures.
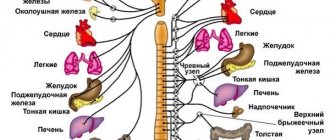
Ultrasound of the substantia nigra of the brain shows that it is connected with all parts, but most closely with the basal ganglia and visual thalamus.
An abundant blood supply indicates the high role of the structure in the functioning of the body. The functions of the substantia nigra include:
- carrying out basic movements: swallowing, chewing, breathing, eye movements and others;
- regulation of small and precise movements of the limbs;
- assistance in expressing emotions;
- participation in emotional processes;
- provoking certain mental disorders.
How does the midbrain develop?
Children in their mother's womb must go through many stages of development. During the embryonic stage, the midbrain grows from a small vesicle and remains intact throughout life. Throughout development, more and more new cells appear in this part, they compress the cerebral aqueduct. If there are disturbances at this stage, problems with the cerebral aqueduct may develop - partial or complete blockage. One of the most dangerous consequences is such a dangerous disease as hydrocephalus.
Helpful information.
Every time a person remembers information, neural connections are formed. This means that the structures of various parts, including the midbrain, are constantly changing; it does not freeze in a certain state.
The role of the substance in the development of pathologies
The role of the substance in the development of mental illness is great. It contains neurons, the processes of which diverge throughout the brain, affecting the cerebral peduncles and the internal capsule.
Their endings, containing terminal microvesicles that produce dopamine, are located in the neostriatum. Any damage to this structure leads to disturbances in motor functions and psycho-emotional ones.
The mechanism of development of schizophrenia has been studied for many years, but researchers have not come to a consensus. Various theories of the formation of this disease have been put forward, one of which connects schizophrenia with disturbances in the functioning of the substantia nigra, the nucleus of which is located in the midbrain. This is the so-called dopamine hypothesis.
Studies show that patients with schizophrenia exhibit deviations in the synthesis and perception of dopamine.
So, they manifest:
- increased hormone production;
- an increase in the concentration of dopamine in synapses;
- increased production of serotonin;
- greater volume of dopamine released when exposed to amphetamines.
Such hypersensitivity contributes to excessive stimulation of brain neurons and its overexcitation. The patient is unable to control the stream of consciousness, and his perception of the surrounding reality changes. Similar conditions arise when taking psychotropic substances, which cause hallucinations and other abnormalities in healthy people, but have a much stronger effect on patients.
According to statistics, the development of schizophrenia affects more men than women. In the former, it usually develops earlier and is more severe. Women typically experience symptoms between the ages of 25 and 30.
Transcranial Dopplerography of the substantia nigra made it possible to examine its structure and discover that in schizophrenia, changes in the dopamine system affect the associative striatum rather than the limbic one.
Moreover, deviations in the synthesis of dopamine by neurons in the direction of increasing its production are observed even before the development of the disease. But the higher these deviations, the greater the likelihood of developing schizophrenia.
Scientists cite several reasons for their appearance:
- disturbances in the system that controls the influence of the hippocampus on the dopamine pathway;
- changes occurring in the structure of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter;
- malfunctions in the functioning of cortical structures affecting dopamine systems;
- influence of other neurotransmitter systems.
Organ structure
It is known that the average human brain has different parts, each of which performs its own role. Quadrigeminal - the structure consists of paired hills. The upper ones are visual and the lower ones are auditory.
The legs contain a black substance. Thanks to it, a person not only lies, but can make precise movements with his hands and eat food. At a certain point, the middle region processes information about when to bring a spoon to the mouth, how to chew food, and what function will allow it to be swallowed.
Useful to know: Brain: functions, structure
The ocular motor nerve originates between the crura and exits from there. It is responsible for the constriction of the pupil and some motor functions of the eyeball. To understand the structure of the midbrain, you need to know where it is located. It is composed of the intermediate and cerebral hemispheres of the cerebrum, its structure is simple and has only two sections. Quadrigemole on nearby two paired colliculi, which form the upper wall. They resemble a plate in appearance. Legs - conductive channels are located there, going to the hemispheres of the anterior section and connecting it with the lower parts of the nervous system.
What is dance therapy?
Patients with Parkinson's disease often experience difficulty initiating movement, freezing, and gradual deterioration of the condition. Tremo represents another reason for the patient's possible isolation, depression and reluctance to go outside, which leads to a significant deterioration in quality of life. Dancing for Parkinson's patients is one of those methods that can be used for the purpose of rehabilitation, restoration and support of general health. Dancing helps patients with Parkinson's disease feel better.
- Musical accompaniment has a positive effect on brain activity.
- The need to coordinate your own movements to music stimulates work processes in the brain centers.
- Movement itself improves blood circulation processes.
- Regular exercise improves the patient's coordination, mobility and balance.
It is also worth noting that dancing for Parkinson’s patients can distract them from the disease itself. It is a known fact that when a patient thinks about his illness often and predominantly in a negative context, his condition worsens much more rapidly than those patients who approach life with love and positivity. The surge of positive emotions experienced during dance classes is also reflected in the internal state of patients with Parkinson's disease.
Dance is movement, and Movement is LIFE!
Classes must be taught by instructors with medical education. Before starting classes, consultation with a specialist is required.
Age characteristics and prevention
The brain is a complex structure. It operates with close interaction between all segments. The center that controls the middle section is the cerebral cortex. With age, connections become weaker, and reflex activity weakens. Since the area is responsible for motor function, even minor disruptions in this tiny segment lead to the loss of this important ability. It is more difficult for a person to move, and serious disorders lead to diseases of the nervous system and complete paralysis. How to prevent disorders in the functioning of the brain in order to remain healthy until old age?
First of all, you should avoid hitting your head. If this happens, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately after the injury. It is possible to preserve the functions of the midbrain and the entire organ until old age if you train it with regular exercises:
- The lifestyle a person leads is important for physical and mental health. Drinking alcohol and smoking destroy neurons, which gradually leads to a decrease in mental and reflex activity. Therefore, you should give up bad habits, and the sooner you do this, the better.
- Moderate physical activity and walks in nature supply the brain with oxygen, which has a beneficial effect on its activity.
- You shouldn’t give up reading, solving charades and puzzles: intellectual activity keeps the brain active.
- An important aspect of the functioning of brain structures is nutrition: fiber, protein, and greens must be present in the diet. The midbrain responds positively to intake of antioxidants and vitamin C.
- It is necessary to control blood pressure: the health of the vascular system affects the general condition of a person.
The brain is a flexible system that can be successfully developed. Therefore, by constantly improving your mind and body, you can maintain clarity of thoughts and motor activity until old age.
The midbrain, its structure and functions are determined by the location of the structure, providing movement, auditory and visual reactions. If you have difficulty maintaining balance or lethargy, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination to find the cause of the disturbances and eliminate the problem.
A person is a complex and subtle substance responsible for the regulation of the entire organism.
The structure and features of the functioning of this organ are still not fully understood; scientists are discovering new features every day that allow the brain to work. But such a part as the substantia nigra of the brain or substantia nigra has been known for a long time.
Functions
All areas of the brain work interconnectedly, together creating a unique system for supporting human life. The main functions of the midbrain are designed to perform the following role:
- Sensory functions. The load for sensory sensations is carried by the neurons of the quadrigeminal nuclei. Signals from the organs of vision and hearing, the cerebral cortex, the thalamus and other brain structures arrive to them along pathways. They provide accommodation of vision to the degree of illumination by changing the size of the pupil; his movement and turns of his head towards the irritating factor.
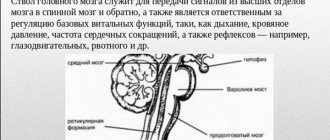
- Conductor. The midbrain plays the role of a conductor. The base of the legs, nuclei and substantia nigra are mainly responsible for this function. Their nerve fibers are connected to the cortex and underlying brain regions.
- Integrative and motor. Receiving commands from sensory systems, the nuclei convert the signals into active actions. Motor commands are given by the stem generator. They enter the spinal cord, making possible not only muscle contraction, but also the formation of body posture. A person is able to maintain balance in various positions. Reflexive movements are also made when moving the body in space, helping to adapt so as not to lose orientation.
In the midbrain there is a center that regulates the degree of pain. Receiving a signal from the cerebral cortex and nerve fibers, the gray matter begins to produce endogenous opiates, which determine the pain threshold, increasing or decreasing it.
Reflex functions
The midbrain carries out its functions through reflexes. With the help of the medulla oblongata, complex movements of the eyes, head, torso, and fingers are performed. Reflexes are divided into:
- visual;
- auditory;
- sentinel (indicative, answering the question “what is it?”).
They also ensure redistribution of skeletal muscle tone. The following types of reactions are distinguished:
- Static ones include two groups - postural reflexes, which are responsible for maintaining a person’s posture, and rectifying ones, which help to return to the normal position if it has been disturbed. This type of reflexes regulates the medulla oblongata and spinal cord, reading data from the vestibular apparatus, with tension in the neck muscles, organs of vision, and skin receptors.
- Statokinetic. Their goal is to maintain balance and orientation in space while moving. A striking example: a cat falling from a height will in any case land on its paws.
The statokinetic group of reflexes is also divided into types.
- With linear acceleration, a lift reflex appears. When a person quickly rises up, the flexor muscles tense; when lowered, the tone of the extensor muscles increases.
- During angular acceleration, for example, during rotation, to maintain visual orientation, nystagmus of the eyes and head occurs: they are turned in the opposite direction.
All reflexes of the midbrain are classified as innate, that is, unconditioned types. An important role in integration processes is assigned to the red core. Its nerve cells activate the skeletal muscles, help maintain the usual body position and take a pose to perform any manipulations.
The substantia nigra is involved in controlling muscle tone and restoring normal posture. The structure is responsible for the sequence of acts of chewing and swallowing; the work of fine motor skills of the hands and eye movements depend on it. The substance is involved in the work of the autonomic system: it regulates the tone of blood vessels, heart rate, and breathing.
Defeats
There are a large number of syndromes associated with damage to the red nuclei, their tracts and nearby structures. But this is not a medical article, so we will focus only on a few especially interesting ones.
If the rostral part of the red nucleus is damaged, the patient experiences severe tremor and the sensitivity of the contralateral half of the body decreases.
If the same tremor occurs in combination with a “frozen hand,” then we can talk about rubrothalamic syndrome.
Often, along with the red nucleus, the oculomotor system also suffers. In such cases, muscle weakness or tremors and divergent strabismus, drooping eyelids and other symptoms associated with the eyes are simultaneously observed.
Control questions:
- where is the red nucleus located and why is it called that?
- what is its main role?
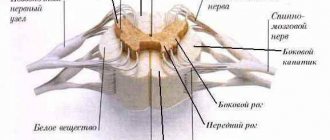
The red nucleus of the midbrain functions in interaction with the corticospinal tract, having close connections with the motor cortex (cortical-red nuclear fibers), cerebellum, reticular formation, olives (Fig. 14-3B)
. Axons extend from the giant cells of the red nucleus to form the red nuclear spinal tract (rubrospinal tract). The fibers of this pathway terminate predominantly on the interneurons of the intermediate zone of the gray matter of the spinal cord, but some of the axons contact directly with the motor neurons of the spinal cord.
In the giant cell part of the red nucleus (as in the motor cortex) all the muscles of the body are represented; by stimulating this section, single and group muscle contractions can be obtained. The corticorubrospinal
tract
serves as an additional route for transmitting relatively discrete signals from the motor cortex to the spinal cord.
If the corticospinal fibers are destroyed and the corticorubrospinal tracts are preserved, discrete movements are partially preserved, but fine movements of the fingers and hand are significantly impaired. Thus, blockade of the corticorubrospinal tract disrupts the motor activity of the muscles in the wrist area. The corticospinal and rubrospinal tracts are located in the lateral columns of the spinal cord, control the more distal muscles of the limbs, and together constitute the lateral motor system of the spinal cord
.
The vestibuloreticulospinal system lies medially in the spinal cord and is called the medial motor system of the spinal cord
.