Prefrontal cortex training
20.03.2019
The prefrontal cortex is the part of the brain that makes a person psychologically and socially human. Higher complex behavioral functions and the ability to think are provided by this particular area of the cerebral hemispheres. We can say that a person can think thanks to the prefrontal cortex.
Prefrontal cortex
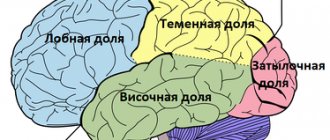
Anatomically, the prefrontal cortex is located in the frontal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres. The area includes 3 zones:
- posterolateral;
- median;
- orbitofrontal.
Relationships
It has the greatest number of connections with other parts of the brain. The frontal region has especially many connections with the diencephalon: the thalamus, hypothalamus. The anterior cortex also communicates with the structures of the brainstem and other areas of the cortex: the occipital, parietal and temporal.
The posterior region of the cortex is predominantly associated with areas responsible for attention, thought processes and motor acts. The inner side of the prefrontal cortex communicates with the limbic system, which is responsible for the lower and higher emotions of a person.
The anterior cortex has communications with the brain stem structures. Most of all - with the reticular formation (the structure responsible for energy balance and activation of the cortex). Therefore, the prefrontal region depends on the state of the brainstem, which regulates the activation and inhibition of the cerebral cortex.
Functions
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for higher cognitive functions in humans. This area of the brain belongs to the third functional block according to Luria, and is called “programming, regulation and control.” The cortex is responsible for the course of a person’s conscious life, for the course of mental processes.
It involves the formation of behavior patterns, adaptation to the situation and the selection of behavioral patterns to it. For example, during the course of a person’s life he gains experience—models of behavior in a certain situation.
If he finds himself in an unfamiliar environment or circumstances, the prefrontal cortex begins to “search” for previous patterns that are suitable for the situation, or forms completely new ones that are suitable for unfamiliar conditions.
Specific functions:
- Empathy is a complex emotion accessible only to humans. Empathy is formed due to a complex of externally received signals from another person. This complex includes: facial expressions, gestures, tone of voice, speed, circumstances. The prefrontal cortex synthesizes this information into a single image and forms empathy for another person.
- Emotional control and balance. Emotions are generated by subcortical structures in the diencephalon. The prefrontal cortex allows us to make sense of these emotions and control affect—something that animals cannot. This area acts as a filter and regulator of feelings.
- Reaction to a stimulus: the interval between the action of a stimulus and the response to it is the latent period, during which information about the source is “comprehended.”
- Self-awareness and the ability to be aware of past and present experiences. Planning the future, setting goals and building motivation. In addition, the prefrontal cortex not only stores experience, but also connects various links between the past, present and future. Here is an autobiography about myself.
- Intuition is the ability to penetrate into the essence of a situation through insight (sudden insight). Intuition has a physiological basis, since it is a previous experience stored in the subcortex. And due to large connections between the prefrontal cortex and subcortical structures, intuition can be realized as part of planning behavior or goals.
- Morality. Daniel Siegel, a professor of psychiatry at Los Angeles Medical School, says that the prefrontal cortex is responsible for issues related to morality and moral values.
- Volitional control of behavior.
- Forecasting future events and consequences of one's actions.
Brodmann's areas 9, 10, 11, 12, 46 and 47 are located in the prefrontal cortex.
Field 9 is responsible for:
- Short-term memory and assessment of how long ago events were, that is, a person can sensually imagine and form a mental image of how long ago it was. For example, we can imagine the time difference between yesterday's events and events ten years ago.
- Auditory perception of words.
- Identifying other people, determining their intentions and predicting behavior.
- Spatial thinking. When we imagine multidimensional figures in our minds, the 9th field is activated.
Field 10 is responsible for:
- Decision making and behavior planning.
- Establishing a logical chain of events between theories, hypotheses and assumptions.
- RAM. This phenomenon can be compared to the computer's RAM, which is responsible for performing several tasks simultaneously and storing information about them in parallel.
The 11th field is responsible for understanding the sense of smell and giving it meaning. This zone allows you to smell a certain smell and remember an event in your life. Thanks to the 11th field, emotions are associated with smells.
Field 12 helps the frontal cortex control subcortical structures.
Fields 46 and 47 are responsible for the combination of simultaneous turning of the eyes and head to the side, for singing and modulation of the movements of the speech apparatus, which allows one to clearly pronounce speech sounds.
How can you train your prefrontal cortex?
Training the prefrontal cortex involves reading, counting and writing. There is a technique, the points of which must be followed every day. On average, executing the entire algorithm does not take more than 5 minutes a day:
- Remembering yesterday's events. To do this, within a few minutes you need to remember yesterday’s activities: who the conversation was with, how the interlocutor was dressed, what the weather was like, what they read and what words were spoken. In general, the task is to remember as much as possible from yesterday.
- Reading aloud. You can read any small, simple article that catches your eye. The bottom line: after reading the column, you need to write down the time spent reading, after which you need to comprehend the information and retell it out loud to yourself. After just a month of daily training, memory properties improve by up to 20%.
- Writing words. You need to write not on the keyboard, but with a pen. On paper, you can write down your thoughts, an article you read, or outline your plans for the next week.
The prefrontal cortex naturally atrophies as people age. This fact is associated with senile dementia or dementia, which can develop into Alzheimer's disease. Medical fact: people whose lifestyle is associated with intellectual pursuits are less susceptible to involutional changes in the cerebral cortex.
As atrophy progresses, memory deteriorates. It is more difficult for a person to remember events from life, the speed of thinking decreases, and the consolidation of associations slows down.
This cortex also performs the function of forgetting. This is a natural process of freeing the hippocampus from “garbage” - one of the protective mechanisms of the human psyche.
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
This region, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, or posterolateral region, is the organic substrate of working or short-term memory. A 1936 study showed that in great apes in which this part of the brain was destroyed, short-term memory deteriorated.
The dorsolateral zone is involved in the formation of voluntary attention (the ability to concentrate, stability and switchability). This is where irrelevant thoughts and feelings are filtered out.
Everyone is familiar with the concept when you try to concentrate on one thing, but the wrong thoughts “climb” into your head - this is an incompleteness of the dorsolateral region.
However, when this area is activated, a person retains the ability to work on one idea or thought for a long time, without being distracted by extraneous stimuli.
This area forms a person’s sense of justice. This site made it possible for the human species to develop the concept of justice, the feeling of guilt and blaming other people, and the imposition of a sentence for assistance in wrongful actions.
Didn't find a suitable answer? Find a doctor and ask him a question!
Source: https://sortmozg.com/structure/prefrontalnaya-kora
General information
The prefrontal cortex is one of the parts of the frontal lobes of the brain, with the help of which any action performed by a person is controlled, controlled and focused. In addition, this area allows the individual to effectively distribute his time, and also influences the social behavioral line in society.
PC includes 6 (9, 10, 11, 12, 46, 47) Broadmon fields. It is located directly behind the frontal bone and is the anterior third of the cerebral cortex.
Psychiatrist Thomas Galtieri characterized this zone as a tool that allows a person to set a goal, develop a plan for its implementation and achieve it even in the presence of obstacles, by making timely changes to the developed line of behavior. He believed that the presence of a well-developed and normally functioning PC is the main factor in the effectiveness of an individual.
The role of the prefrontal cortex in mnestic processes
The prefrontal cortex is one of the parts of the frontal lobes of the brain, with the help of which any action performed by a person is controlled, controlled and focused. In addition, this area allows the individual to effectively distribute his time, and also influences the social behavioral line in society.
PC includes 6 (9, 10, 11, 12, 46, 47) Broadmon fields. It is located directly behind the frontal bone and is the anterior third of the cerebral cortex.
Psychiatrist Thomas Galtieri characterized this zone as a tool that allows a person to set a goal, develop a plan for its implementation and achieve it even in the presence of obstacles, by making timely changes to the developed line of behavior. He believed that the presence of a well-developed and normally functioning PC is the main factor in the effectiveness of an individual.
PC structure
The structure is based on three areas of the frontal lobe - dorsolateral, medial and orbitofrontal.
The dorsolateral region controls the expression of emotions in a specific situation through its connection with the limbic system. In addition, this area of the cerebral cortex influences a person’s attention.
The medial region is responsible for recording information into short-term memory and allows you to compare data received by the senses and stored in the brain. Also, this part of the cortex allows you to transfer information from short-term memory to its permanent storage location.
The orbitofrontal region helps to use accumulated experience when making decisions.
Clinical significance
Over the past few decades, brain imaging systems have been used to determine the volume of brain regions and neural connections. Several studies have shown that volume reduction and connectivity of the frontal lobe with other brain regions is observed in patients diagnosed with mental disorders and prescribed powerful antipsychotic medications;
those who are exposed to repeated stressors; those who consume explicit materials excessively; suicides; persons deprived of liberty; criminals; psychopaths; people affected by lead poisoning; and daily male cannabis users (only 13 were tested). It is believed that at least some of the human abilities to feel guilt or remorse, and to interpret reality, depend on a well-functioning prefrontal cortex.
It is also widely believed that the size and number of connections in the prefrontal cortex relates directly to conscious sensation, as the prefrontal cortex in humans occupies a significantly larger percentage of the brain than in any other animal. And he suggested that, as the brain has tripled in size over five million years of human evolution, the prefrontal cortex has increased in size sixfold.
A review on executive functions in healthy exercisers noted that the left and right portions of the prefrontal cortex, which is divided at the medial longitudinal fissure, appear to become increasingly interconnected in response to consistent aerobic exercise. Two peer-reviewed structural neuroimaging studies show that marked improvements in prefrontal and hippocampal gray matter volume occur in healthy adults who participate in moderate-intensity exercise over several months.
A functional neuroimaging review of practice-based meditation suggested that practicing mindfulness increases prefrontal activation, which has been noted to correlate with increased well-being and decreased anxiety; However, the review noted the need for cohort studies in future studies to better establish this.
Treatments with anticancer drugs are often toxic to brain cells, leading to memory loss and cognitive dysfunction that may persist long after the period of exposure. This condition is called chemo brain. To determine the underlying cause of this condition, mice were treated with the chemotherapy drug mitomycin C.
Chronic alcohol consumption results in permanent changes in brain function, including altered decision-making ability. The prefrontal cortex of chronic alcoholics has been shown to be vulnerable to oxidative DNA damage and neuronal cell death.
Symptoms of dysfunction
Disruption in this area is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Absent-mindedness, in which a person cannot concentrate on obtaining the necessary information. This happens due to the fact that incoming data is not stored in short-term memory due to it being overwritten by newly arrived data.
- Incorrect or incomplete assessment of the situation. In this case, the information is either distorted or received incompletely, since multiple signals arrive from the sensory area at the same time, which overlap each other, as a result of which the PC either perceives the strongest data, or they are all missed.
- Impulsivity, in which a person does actions without first thinking and analyzing their consequences.
- Lack of critical thinking. This symptom is manifested by the fact that a person takes any information on faith and does not double-check it.
- Performing any action without planning. In this case, a person goes towards his intended goal with a large number of unexpected difficulties that could have been avoided.
- Making the same mistakes when a decision is made without reference to accumulated experience, but only on desires.
- A complete or partial lack of emotionality, due to the fact that the prefrontal cortex is unable to process and display received signals from the limbic system.
- Hyperactivity, which manifests itself in the inability to concentrate on a specific task and violent expression of emotions.
If at least one of the above symptoms occurs, a person needs to see a doctor for a brain examination. The functioning of the cortex is tested using the SPECT technique, which is based on comparing the activity of a given area of the brain in a state of rest and stimulation. In case of pathologies in the stimulated mode, activity will either remain in place or decline.
Some of the main reasons for the appearance of pathologies in the brain are hemorrhage in the brain due to a head injury or extensive stroke and intoxication of the body with harmful substances (alcohol, poisons, toxins, etc.).
There are also frequent cases of PC deviation due to genetic and viral diseases that affect the central nervous system (CNS). In addition, the performance of PC functions can be affected by prolonged stress and lack of sleep.
We should not forget the fact that the cortex ceases to perform its functions partially or completely as a person ages. This is caused by a severe reduction in neurons in this area of the brain.
story
he became irritable, short-tempered, and impatient—characteristics he previously did not display—so that friends described him as “no longer a Gage”; and, while he had previously been a capable and efficient worker, thereafter he was unable to complete tasks.
However, careful analysis of the primary data shows that descriptions of Gage's psychological changes tend to be exaggerated when they are carried out with the description given by Dr. Gage, the most striking feature being that the changes described in the years following Gage's death are much more dramatic than anything reported while he was alive,
Subsequent studies of patients with prefrontal injuries showed that patients verbalized what the most appropriate social responses would be under certain circumstances. However, when actually performing, they instead pursued behavior aimed at immediate gratification, despite knowing long-term results would be self-defeating.
Interpretation of these data indicates that not only are the skills of comparison and understanding of possible outcomes fueled in the prefrontal cortex, but the prefrontal cortex (when functioning correctly) controls the mental ability to delay immediate gratification for a better and more rewarding long-term gratifying outcome. This ability to anticipate rewards is one of the key elements that determines optimal executive function in the human brain.
There is much current research devoted to understanding the role of the prefrontal cortex in neurological disorders. Many diseases, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and ADHD, have been associated with dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex, and thus this region of the brain holds potential for new treatments for these conditions.
Clinical trials have begun on several drugs that have been shown to improve prefrontal cortex function, including Guanfacine, which acts through the alpha-adrenergic 2A receptor. The downstream target of this drug, the HCN channel, is one of the most recent intelligence areas in the prefrontal cortex of pharmacology.
Etymology
The term "prefrontal" as a description of a part of the brain appears to have been coined by Richard Owen in 1868. For him, the prefrontal region was limited to the anterior—most part of the frontal lobe (roughly corresponding to the frontal pole). It has been suggested that his choice of term was based on the prefrontal bone present in most amphibians and reptiles.
Preventing problems
There are a number of measures that can not only prevent disorders of the prefrontal cortex, but also enhance its performance. For this purpose, specialized medications are used that activate the work of the central nervous system and brain (glycine, undevit, aminalon, bilobil, Brain Rush, etc.).
In addition, the good condition of the body as a whole has a positive effect on the functioning of this zone.
To maintain it, it is necessary to: limit or completely abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages, follow a fruit and vegetable diet, and also engage in physical exercise daily.
It is also recommended to use meditative practices that help relax the central nervous system and help activate the prefrontal cortex.
If the cause of problems is stress, age or sleep, then a visit to psychologists may be prescribed to undergo specialized training that is aimed at developing the functions performed by the prefrontal cortex.
An example would be exercises that help you plan your day wisely, set and step-by-step fulfill life goals, and control your behavior in stressful situations.
Additional images
- Animation of the prefrontal cortex of the left hemisphere (shown in red)
- Foreground
- side view
- Medial perspective
external reference
Source: https://zdorov4ik.ru/rol-prefrontalnoy-kory-mnesticheskikh-protsessakh/
Pump up your brains. Four Science-Backed Ways to Get Smarter
2020-02-16T08:00+0300
2020-02-16T08:07+0300
https://ria.ru/20200216/1564798980.html
Pump up your brains. Four Science-Backed Ways to Get Smarter
https://cdn21.img.ria.ru/images/152451/99/1524519902_0:3:1036:586_1036x0_80_0_0_e6c3e0afd9dc3a5c44ef47eea39485d7.jpg
RIA News
https://cdn22.img.ria.ru/i/export/ria/logo.png
RIA News
https://cdn22.img.ria.ru/i/export/ria/logo.png
MOSCOW, February 16 - RIA Novosti, Alfiya Enikeeva. Aerobics strengthens memory and improves cognitive function at any age, researchers from Columbia University (USA) recently said. And the older a person is, the more beneficial sports are for the brain.
Scientists have previously shown that neurogenesis—increasing the number of neurons and improving the functioning of synapses—is promoted not only by physical exercise. Potentially beneficial benefits include yoga and even properly selected foods.
How else can you improve brain function - in the material of RIA Novosti.
You run a lot, you think better
Experiments on laboratory animals a few years ago showed that regular physical activity improves mental abilities. Thus, in rats that were forced to run daily for seven weeks, the number of neurons in the hippocampus, an area of the brain that is also responsible for learning and memory, increased.
Moreover, the length of distances run by rodents directly correlated with the number of new nerve cells in their brain. But exercises with weights, although they contributed to an increase in the muscle mass of animals, did not have such an effect on the hippocampus.
According to American and Lebanese scientists (they also forced mice to run), during training, more brain-derived neurotrophic factor BDNF is released in the animals’ bodies. This protein is responsible for neurogenesis and plays an important role in the formation of long-term memory. It is this that probably contributes to the emergence of new neurons in the brains of animals.
Indirect evidence indicates that physical activity also increases the plasticity of the human brain - the ability of its cells to change connections with other neurons and remember new information.
In addition, aerobic exercise makes the hippocampus more elastic - blood supply improves and there are practically no inflammatory processes, which has a beneficial effect on mental abilities. Testing memory, concentration and goal setting in 132 volunteers, conducted by scientists at Columbia University, confirmed this.
After six months of regular training, all participants in the experiment showed cognitive improvements. Moreover, the older the volunteers were, the greater the effect the sport had on their brain state. However, you should not overdo it with physical exercise, French neuroscientists warn. Long hours of grueling training, on the contrary, negatively affects brain function and causes people to make rash decisions.
Yoga for the brain
According to the work of American scientists, yoga affects the brain in a similar way - it strengthens its structures associated with memory and emotion management. The results of 11 studies showed that meditation and special breathing exercises increased the volume of the hippocampus.
In addition, people who regularly practice yoga have more developed prefrontal and cingulate cortices, as well as the amygdala, compared to others. These areas are associated with planning and decision making, attention, memory, learning, and emotional regulation.
A study of the brains of 42 elderly women, some of whom had been practicing yoga regularly for 15 years, confirmed that adherents of these practices had increased thickness of the left prefrontal cortex. Moreover, compared to those who had never meditated or performed breathing exercises, the difference was significant.
According to the authors of the study, thanks to this, lovers of Eastern practices have a better chance of maintaining a clear mind in old age. In addition, meditation helps stop the degradation of gray matter and a decrease in the number of nerve connections in people suffering from constant pain.
Experienced yogis also show a significant increase in the number of neurons in the insular cortex, an area of the brain that plays an important role in pain tolerance.
Drawing improves memory
In 2014, British and Belgian researchers found that professional artists had an increased number of neurons in areas of the brain responsible for fine motor skills and visualization. Scientists have suggested that this feature may be congenital, although they did not rule out the influence of external factors, including upbringing and regular drawing lessons.
According to German neuroscientists, it is constant artistic practice that leads to an increase in the number of nerve cells and improves neural connections. They asked 28 volunteers, whose average age was about 64, to take a ten-day painting course or visit several art galleries. Before the experiment and immediately after it, all volunteers underwent an MRI scan.
It turned out that participants from the first group increased the functional density of neural connections in the prefrontal and parietal cortex - areas associated with decision making and planning complex cognitive behavior. In other words, nerve cells in these areas of the brain began to communicate better with each other.
According to scientists from Drexel University (USA), drawing improves blood flow in the brain and activates the pleasure center in the prefrontal cortex. Moreover, it does not matter at all what and how professionally a person portrays. In addition, drawing can significantly improve memory.
At least, the students who drew geometric shapes and simple patterns during the experiments (they were given lectures at this time) demonstrated better memorization of the material told.
Food for brain
According to several studies, foods containing natural antioxidants, flavonoids, can affect brain function. First of all, we are talking about coffee and dark chocolate. Thus, in an experiment by Australian scientists, participants who ate chocolate at least once a week were better able to cope with various memory and attention tasks. In the case of coffee, flavonoids protect the brain from premature aging and the accumulation of proteins in its structures, which can lead to Alzheimer's disease. And caffeine, in turn, improves memory.
Source: https://ria.ru/20200216/1564798980.html
Prefrontal cortex: functions. Prefrontal cortex dysfunction
The prefrontal cortex is a region of the brain that is responsible for a colossal number of functions. A person’s mental abilities, behavior, and emotionality depend on the degree of its activity.
Location
The prefrontal cortex is located just behind the frontal bone, in front of the hemispheres, and is supplied with blood through the anterior and middle arteries. That is, in fact, it is part of the frontal lobe of the brain, which can be divided into three sections:
- dorsolateral;
- medial;
- orbitofrontal.
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex has most of its functions, as it controls emotions and cognitive functions. It is called the “slate” of consciousness, on which we can place the image or information we need at a given moment in time.
But in order to understand the significance of this part of the brain, it is necessary to consider all aspects of its work, as well as the functions for which it is responsible.
Empathy
Empathy is a term that is often mistakenly interpreted as the ability to sympathize and empathize, but in fact this feeling has a more important meaning. It allows you to see and feel how others treat you.
In the modern civilized world, empathy has only a sociocultural aspect, but for primitive man, the ability to quickly recognize an enemy or friend was the key to preserving his life. Therefore, we can safely say that the prefrontal cortex of the brain has a protective function.
Emotionality
It is human nature to experience emotions - from intense joy to deep sadness or anger. But how appropriately he expresses his feelings depends on how others perceive him as a mentally healthy person.
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is responsible for both a person's ability to experience emotions and the ability to evaluate a situation before expressing them nonverbally.
The emotion itself is directly formed by the limbic system, then through neural connections it enters the prefrontal cortex, which evaluates whether and how to express the emotion.
That is, in this way a certain protective function of the brain works, capable of reducing the degree of intensity of human emotions.
However, it is important to understand that the powers of the prefrontal cortex are not as strong as they seem: if the limbic system is overstimulated, the cortex will not be able to suppress the emotion, and it is more likely to burst out.
For example, if a person is moderately angry, he may pull himself together and express his offense in silence, but if the degree of his anger is strong, he may well shout at the offender, cry, or even use physical force.
And this will not indicate that there are functional disorders or organic lesions in the prefrontal cortex of the brain: it is simply physiologically capable of coping with only moderate emotions.
Planning
In order to make plans, a person must not only imagine a hypothetical picture of the future with its possibilities, difficulties, nuances, but also turn to his experience and compare situations. Thus, the prefrontal cortex allows for effective forecasting, which is necessary in any area of the life of a capable person.
Implementation of the plan
In order to obtain a specific result, it is not enough for a person to simply evaluate the initial data and see an image of what he wants to receive. He needs to have a plan for achieving the goal, step-by-step instructions compiled for him by his brain. At the same time, we are not necessarily talking about solving important and complex problems.
For example, having experienced a feeling of hunger, a person may realize that a bowl of hot soup is a good solution to the problem that has arisen. But if he is not able to create an algorithm of actions for himself: go to the kitchen, open the refrigerator, cook food, then his ability to know what he needs is absolutely useless.
Criticality
One of the most important diagnostic factors used by psychiatrists is a person’s ability to be critical. At the same time, it is important to evaluate with an adequate level of criticality both the events occurring around you, the actions of other people, and your own actions.
As a rule, people who have mental illness or whose development of the prefrontal cortex is impaired are not capable of self-criticism and evaluate their behavior as consistent with the norm, even in the most crazy actions.
Cognitive functions
The most important properties of the brain are the perception of information, its processing, memorization and restoration from memory if necessary. The prefrontal cortex of the brain is responsible for all these processes. That is, the ability to learn, remember, and analyze depends on how correctly the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain functions.
Self-control
The concept of self-control is very closely related to emotions, the level of criticality and planning of actions. For example, if a person suddenly wants to sing a song loudly in the middle of the street, his prefrontal cortex will most likely prevent him from doing this, slowing down the impulse, which would be perceived by others as the act of an out-of-control individual.
But when a person has an addiction, that is, a strong dependence on a habit, the control of the prefrontal cortex may weaken. For example, a heavy smoker may light a cigarette indoors, despite the ban, because the core of the brain demands to get its dose of pleasure.
Prefrontal cortex disorders
Problems with the activity of the prefrontal cortex can be easily recognized by the signs listed below. But it is important to understand that these signs are not specific, that is, they can be caused by defects of the prefrontal cortex or other diseases.
- Problems with attention - a person cannot concentrate on a problem, task, conversation, it is difficult for him to concentrate on any subject for a long time, even if we are talking about watching a movie.
- Errors in the interpretation of events happening around, that is, a person may incorrectly perceive the attitude of other people towards him, not understand the danger of close contact with them, or, on the contrary, harbor resentment, suspecting that behind every word or deed of another person there is an intention to harm him.
- Repeating the same mistakes - a person's ability to learn from experience is one of the most important tools of evolution. Having put his hand into the fire and realizing that it is painful and dangerous, a person enters this information into his consciousness and in the future is careful not to allow direct contact of the flame with the skin. With pathologies of the prefrontal cortex, a person may repeat the same mistakes over and over again, causing physical or emotional harm to himself.
- Disorganization - we can talk about the inability to plan your day and complete all tasks on time. The popular psychological term “procrastination,” which refers to the pathological desire to put things off until later, may also be a consequence of disruption of the prefrontal cortex.
- Impulsivity, or more precisely, the inability to suppress one’s impulses. This may be expressed in the inability to control one’s emotions or in the inability to deny oneself pleasure: eating foods prohibited for medical reasons, drinking alcohol, and so on.
Function restoration
Prefrontal cortex weakness can occur for a variety of reasons. In particular, it appears with age, under the influence of severe stress and for other reasons. If a person, comparing the signs of dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex, has noted some signs in himself, the recommendations listed below may help him:
- It is necessary to avoid any spontaneous decisions, especially in difficult emotional situations. In case of conflict, you should gently withdraw from the conversation and carefully think about what is happening. To make it easier to get out of the conflict, you can come up with a reason in advance that you can use if necessary.
- Effective organization requires making plans and writing lists. A simple daily planner can make life much more convenient and easier for a person with a weakened prefrontal cortex.
- In order to develop cognitive functions, you need to look for new ways to absorb information. For example, speaking out loud, drawing a diagram, writing on paper - one of the methods will certainly be effective, and a person will be able to perceive and remember information much easier.
- It is important to learn reflection - to analyze your actions, clearly understand why such a step was taken in a given situation, what it led to and whether this should be done in the future. In this way, a person independently develops the habit of applying accumulated experience to solve any problems, if, due to organic disorders, the brain does not resort to such an algorithm on its own.
So, the prefrontal cortex, the development of which made it possible to avoid committing rash acts, can be developed by a person provided that he has the will and the ability to control his limbic system and emotions.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/315140/prefrontalnaya-kora-funktsii-narusheniya-funktsiy-prefrontalnoy-koryi
PC structure
The structure is based on three areas of the frontal lobe - dorsolateral, medial and orbitofrontal.
The dorsolateral region controls the expression of emotions in a specific situation through its connection with the limbic system. In addition, this area of the cerebral cortex influences a person’s attention.
The medial region is responsible for recording information into short-term memory and allows you to compare data received by the senses and stored in the brain. Also, this part of the cortex allows you to transfer information from short-term memory to its permanent storage location.
The orbitofrontal region helps to use accumulated experience when making decisions.
Location
The prefrontal cortex is located just behind the frontal bone, in front of the hemispheres, and is supplied with blood through the anterior and middle arteries. That is, in fact, it is part of the frontal lobe of the brain, which can be divided into three sections:
- dorsolateral;
- medial;
- orbitofrontal.
But in order to understand the significance of this part of the brain, it is necessary to consider all aspects of its work, as well as the functions for which it is responsible.
Preventing problems
There are a number of measures that can not only prevent disorders of the prefrontal cortex, but also enhance its performance. For this purpose, specialized medications are used that activate the work of the central nervous system and brain (glycine, undevit, aminalon, bilobil, Brain Rush, etc.).
In addition, the good condition of the body as a whole has a positive effect on the functioning of this zone. To maintain it, it is necessary to: limit or completely abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages, follow a fruit and vegetable diet, and also engage in physical exercise daily. It is also recommended to use meditative practices that help relax the central nervous system and help activate the prefrontal cortex.
An example would be exercises that help you plan your day wisely, set and step-by-step fulfill life goals, and control your behavior in stressful situations.
The prefrontal cortex is a region of the brain that is responsible for a colossal number of functions. A person’s mental abilities, behavior, and emotionality depend on the degree of its activity.
Text for benefit: how writing practices train the brain
Don’t be upset if, after asking questions, you find yourself thinking like “my cortex is not developed at all!”
Like the muscles of the body, the prefrontal cortex can be developed and “trained” every day - from childhood to old age (although some researchers claim that the cortex can only be trained until the age of forty, but this is not certain)).
There are many exercises for training the cortex and developing concentration, attentiveness, easily achieving all your goals, and achieving psychological and emotional balance. The most effective of them:
1. Solving mathematical problems
When you solve simple timed problems, both hemispheres are actively working: the anterior parts of the frontal lobes of both hemispheres (prefrontal cortex), the angular gyrus, speech area, visual area and temporal gyrus are working. It is extremely important to train regularly.
Just like going to the gym, brain exercises work best in the morning. At this time the brain is more active.
One of the simplest and most effective exercises is a notebook for developing memory and intelligence.
Just buy a workbook, divide it into 60 days and write out simple math examples for addition, subtraction, division and multiplication (20 examples per day). The goal is to solve problems every day as quickly as possible.
At first, solving examples may take about 10 minutes, then with regular training you will cope with similar problems in 5 minutes, after two or three months - in 2-3 minutes. Don't forget to set a timer and record the results. Examples of interesting examples and tasks can be found here: //psyfactor.org/lib/razvitiye-mozga.htm.
2. Reading, especially out loud
The skill of reading aloud activates not only the prefrontal cortex, but also the auditory perception of information. Aerobatics is reading aloud what was written in your personal diary. By the way, an interesting fact is that most people who keep their diaries do not re-read them, mostly ashamed of their own experiences. An excellent opportunity to work with the prefrontal cortex, acceptance of yourself and your feelings and self-esteem.
3. Meditation
Often there are too many parallel commands in our heads. When we multitask, we don't know what to do and that's why we feel anxious and stressed. In order to return to normal, you need to concentrate and collect your thoughts. If you feel that your thoughts are confused and your attention is scattered, try to retire and do meditation. Set a timer for 10-15 minutes, sit with your back straight and just concentrate on your breathing. Observe how the air fills your lungs; you can mentally record your inhalations and exhalations. It is important not to control your breathing, but simply to observe it. You can read about meditation and engage in it together with the “Live Mindfully” community: //www.instagram.com/zhitvnimatelno.
4. Breathing practices
Breathing actively fills cells with oxygen, which is why it is so important to breathe correctly. The cells of the prefrontal cortex, which are filled with air, help it work clearly and correctly. For beginners, yoga practices are great - Bhastrika breathing and/or Kapalbhati . By doing these exercises for 5-10 minutes every morning, you will notice how your mind clears, trains and calms. Igor Budnikov, founder of the “Welcome back home” Academy, talks and shows in detail about breathing practices (with him you can also take a free course on proper breathing and meditation): //welcomebackhome.ru/breath.
5. Writing practices
When you think about a phrase you hear, the prefrontal cortex of the left hemisphere, which is responsible for speech, and the lower part of the temporal lobe of the left hemisphere, which is responsible for recognizing meaning, work.
If you write down a phrase, both hemispheres of the brain begin to work simultaneously. The prefrontal cortex of both hemispheres works, as well as the temporal lobe and parietal lobe of both hemispheres. It turns out that when you write, your brain works twice as active.
How the brain and body work during writing practices:
First, we see signs and symbols with our eyes. At this moment, the occipital lobe of both hemispheres, with the help of which we see, works, as well as several areas of the prefrontal cortex of the left hemisphere. All learned signs are “stored” in the posterior lower part of the temporal lobe of the left hemisphere (memory training). Secondly, we write the same sign many times. At this moment, many areas of the brain work. The posterior part of the prefrontal cortex of both hemispheres is especially active (training attentiveness, focus, concentration). Thirdly, in addition to the prefrontal cortex, the body works - through the hand, handwriting, we relax and maintain emotional balance.
Our Glagolitic text school specializes in writing and writing practices.
With us you can work on text in three formats:
1) Get creative and try texts in the company of like-minded people at free writers' breakfasts #bunswithtext. More information about breakfast: //.com/bulochkistekstom.
2) Take up writing, get to know yourself, learn about mindfulness practices, become more attentive and feel the therapeutic effect of text at the #textsummer marathon.
More details about the marathon: //glagolica-school.ru/textoleto.3) Take up text therapy. Text therapy is an online course of written practices to work through limiting attitudes and increase awareness. The program was developed by three authors: a psychologist, a psychotherapist and the founder of the school of text. During the course you will see attitudes (patterns of thinking and behavior) that interfere with your daily life, you will receive tools for working with them and our support. As a result of the course, you will become more attentive to yourself and other people, you will begin to think and act differently.
More details about the course: //glagolica-school.ru/textoterapiya.
Source: //glagolica-school.ru/healthytexts